1.继承中类型的转换
源代码:
class Mammal{}
class Dog extends Mammal {}
class Cat extends Mammal{}
public class TestCast
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Mammal m;
Dog d=new Dog();
Cat c=new Cat();
m=d;
d=m;
d=(Dog)m;
d=c;
c=(Cat)m;
}
}
这个程序不能正常运行,因为在主函数里d=m;这句话不符合Java的规则,
在继承中,基类不能对子类的对象赋值,而子类可以对基类的对象赋值,
而且,非继承关系的两个类再赋值是也应该先进行强制转化,比如:d=c;,
强制转化也不是每次都可以成功的。可以使用instanceof运算符判断一个对
象是否可以转换为指定的类型,如果可以,则继续进行。
2.继承中方法的覆盖
源代码:ass Parent2{
public void Print()
{
System.out.println("今天是个好日子!!");
}
}
class Child2 extends Parent2{
public void Print()
{
//super.Print();
System.out.println("今天不是个好日子!!");
}
}
public class super1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Child2 a=new Child2();
a.Print();
}
}
运行结果截图:
今天不是个好日子!!
原因分析:在子类中重新声明一个与父类同名同参数的函数,会使父类的函数被子类的覆盖,从而不会被输出出来,
若想调用父类的函数,则必须使用Super来调用。
提示:
(1)覆盖方法的允许访问范围不能小于原方法。
(2)覆盖方法所抛出的异常不能比原方法更多。
(3)声明为final方法不允许覆盖。
例如,Object的getClass()方法不能覆盖。
(4)不能覆盖静态方法。
3.继承条件下的构造方法调用:
源代码:
class Grandparent
{
public Grandparent()
{
System.out.println("GrandParent Created.");
}
public Grandparent(String string)
{
System.out.println("GrandParent Created.String:" + string);
}
}
class Parent1 extends Grandparent
{
public Parent1()
{
super("Hello.Grandparent.");
System.out.println("Parent Created");
// super("Hello.Grandparent.");
}
}
class Child1 extends Parent1
{
public Child1()
{
System.out.println("Child Created");
}
}
public class TestInherits
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Child1 c = new Child1();
}
}
运行结果截图;
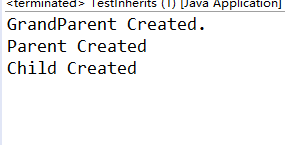
程序结果分析:在类的继承过程中,父类的构造函数也会被子类所继承,当子类创建对象时,会首先调用父类构造函数,
随后在调用自身的构造函数当在子类中显示的调用父类的另一个构造函数,应该用Super调用,
通过 super 调用基类构造方法,必须是子类构造方法中的第一个语句。子类的对象在创建时会先调用父类的构造函数,
在调用自身的构造函数,反过来则不行,因为构造函数是用来给类的对象进行初始化的,父类的定义的public和protected函数和变量都会自动被继承到子类中,
如果父类不初始化,这些定义在父类的函数和变量不能在子类中使用。
4.java中的多态
源代码:
public class ParentChildTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parent parent=new Parent();
parent.printValue();
Child child=new Child();
child.printValue();
parent=child;
parent.printValue();
parent.myValue++;
parent.printValue();
((Child)parent).myValue++;
parent.printValue();
}
}
class Parent{
public int myValue=100;
public void printValue() {
System.out.println("Parent.printValue(),myValue="+myValue);
}
}
class Child extends Parent{
public int myValue=200;
public void printValue() {
System.out.println("Child.printValue(),myValue="+myValue);
}
}
运行结果截图;

程序原因分析:当子类与父类拥有一样的方法,并且让一个父类变量引用一个子类对象时,到底调用哪个方法,由对象自己的“真实”类型所决定,这就是说:对象是子类型的,它就调用子类型的方法,是父类型的,它就调用父类型的方法。
提示:
重写“的概念只针对方法,如果在子类中”重写“了父类中的变量,那么在编译时会报错