转自:https://blog.csdn.net/haiyan_qi/article/details/77373900
概述
示例 https://github.com/qihaiyan/jwt-boot-auth
用spring-boot开发RESTful API非常的方便,在生产环境中,对发布的API增加授权保护是非常必要的。现在我们来看如何利用JWT技术为API增加授权保护,保证只有获得授权的用户才能够访问API。
开发一个简单的API
spring提供了一个网页可以便捷的生成springboot程序。
如图:在Search for dependencies中选择H2、Web、Security、JPA,这几个依赖在我们的示例工程中会用到。
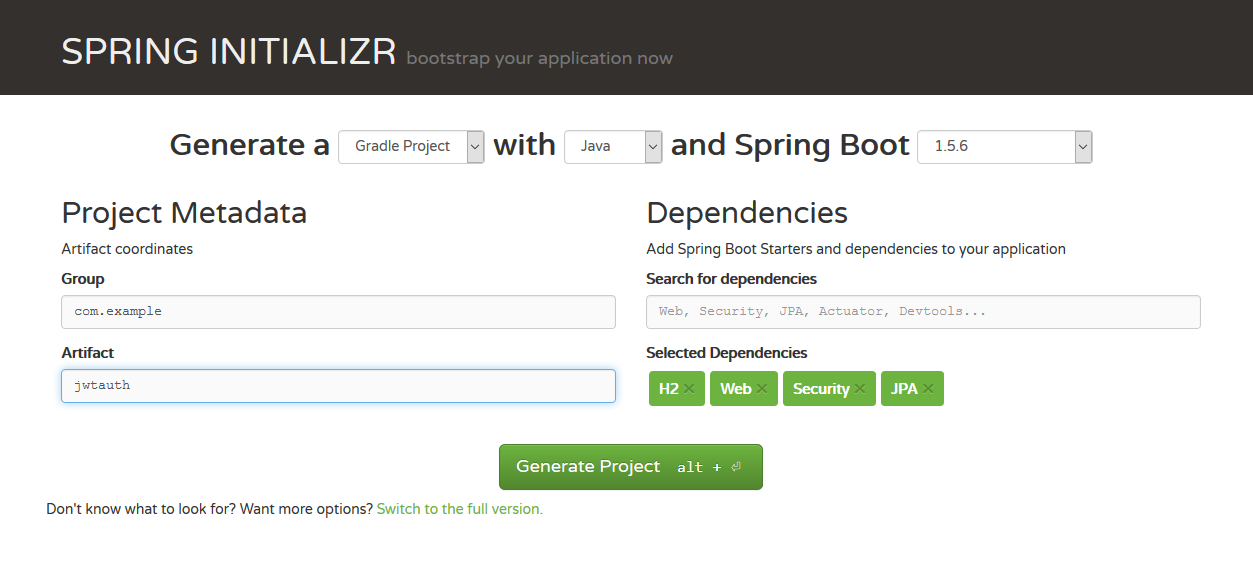
点击Generate Project按钮后,下载文件到本地。
在JwtauthApplication.java中增加一个方法:
@RequestMapping("/hello")
@ResponseBody
public String hello(){
return "hello";
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
这样一个简单的RESTful API就开发好了。
现在我们运行一下程序看看效果,打开命令行工具,执行:
cd jwtauth
gradle bootRun- 1
- 2
等待程序启动完成后,可以简单的通过curl工具进行API的调用:
curl http://localhost:8080/tasks- 1
至此,我们的接口就开发完成了。但是这个接口没有任何授权防护,任何人都可以访问,这样是不安全的,下面我们开始加入授权机制。
增加用户注册功能
首先增加一个实体类MyUser:
package com.example.jwtauth;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
@Entity
public class MyUser {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private long id;
private String username;
private String password;
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
然后增加一个Repository类MyUserRepository,可以读取和保存用户信息:
package com.example.jwtauth;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface MyUserRepository extends JpaRepository<MyUser, Long> {
MyUser findByUsername(String username);
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
得益于SpringDataJpa,只需要定义一个interface,就让我们拥有了数据的CRUD功能。由于我们在build.gradle中引入了H2,所以我们拥有了一个本地数据库,不需要做任何配置,springboot就会使用这个数据库,不得不说springboot确实极大的减轻了开发工作量。
下面增加一个类UserController,实现用户注册的接口:
package com.example.jwtauth;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/users")
public class UserController {
private MyUserRepository applicationUserRepository;
private BCryptPasswordEncoder bCryptPasswordEncoder;
public UserController(MyUserRepository myUserRepository,
BCryptPasswordEncoder bCryptPasswordEncoder) {
this.applicationUserRepository = myUserRepository;
this.bCryptPasswordEncoder = bCryptPasswordEncoder;
}
@PostMapping("/signup")
public void signUp(@RequestBody MyUser user) {
user.setPassword(bCryptPasswordEncoder.encode(user.getPassword()));
applicationUserRepository.save(user);
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
其中的
@PostMapping("/signup")- 1
这个方法定义了用户注册接口,并且指定了url地址是/users/signup。由于类上加了注解 @RequestMapping(“/users”),类中的所有方法的url地址都会有/users前缀,所以在方法上只需指定/signup子路径即可。
密码采用了BCryptPasswordEncoder进行加密,我们在Application中增加BCryptPasswordEncoder实例的定义。
@SpringBootApplication
@RestController
public class JwtauthApplication {
@Bean
public BCryptPasswordEncoder bCryptPasswordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
// ...- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
增加JWT认证功能
用户填入用户名密码后,与数据库里存储的用户信息进行比对,如果通过,则认证成功。传统的方法是在认证通过后,创建sesstion,并给客户端返回cookie。现在我们采用JWT来处理用户名密码的认证。区别在于,认证通过后,服务器生成一个token,将token返回给客户端,客户端以后的所有请求都需要在http头中指定该token。服务器接收的请求后,会对token的合法性进行验证。验证的内容包括:
-
内容是一个正确的JWT格式
-
检查签名
-
检查claims
-
检查权限
处理登录
创建一个类JWTLoginFilter,核心功能是在验证用户名密码正确后,生成一个token,并将token返回给客户端:
package com.example.jwtauth;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import io.jsonwebtoken.Jwts;
import io.jsonwebtoken.SignatureAlgorithm;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationManager;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter;
import javax.servlet.FilterChain;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
public class JWTLoginFilter extends UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter {
private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
public JWTLoginFilter(AuthenticationManager authenticationManager) {
this.authenticationManager = authenticationManager;
}
@Override
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest req,
HttpServletResponse res) throws AuthenticationException {
try {
MyUser user = new ObjectMapper()
.readValue(req.getInputStream(), MyUser.class);
return authenticationManager.authenticate(
new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
user.getUsername(),
user.getPassword(),
new ArrayList<>())
);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Override
protected void successfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest req,
HttpServletResponse res,
FilterChain chain,
Authentication auth) throws IOException, ServletException {
String token = Jwts.builder()
.setSubject(((User) auth.getPrincipal()).getUsername())
.setExpiration(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + 60 * 60 * 24 * 1000))
.signWith(SignatureAlgorithm.HS512, "MyJwtSecret")
.compact();
res.addHeader("Authorization", "Bearer " + token);
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
该类继承自UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter,重写了其中的2个方法:
attemptAuthentication :接收并解析用户凭证。
successfulAuthentication :用户成功登录后,这个方法会被调用,我们在这个方法里生成token。
授权验证
用户一旦登录成功后,会拿到token,后续的请求都会带着这个token,服务端会验证token的合法性。
创建JwtAuthenticationFilter类,我们在这个类中实现token的校验功能。
package com.example.jwtauth;
import io.jsonwebtoken.Jwts;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationManager;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.www.BasicAuthenticationFilter;
import javax.servlet.FilterChain;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class JwtAuthenticationFilter extends BasicAuthenticationFilter {
public JwtAuthenticationFilter(AuthenticationManager authManager) {
super(authManager);
}
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest req,
HttpServletResponse res,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
String header = req.getHeader("Authorization");
if (header == null || !header.startsWith("Bearer ")) {
chain.doFilter(req, res);
return;
}
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication = getAuthentication(req);
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authentication);
chain.doFilter(req, res);
}
private UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken getAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request) {
String token = request.getHeader("Authorization");
if (token != null) {
// parse the token.
String user = Jwts.parser()
.setSigningKey("MyJwtSecret")
.parseClaimsJws(token.replace("Bearer ", ""))
.getBody()
.getSubject();
if (user != null) {
return new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(user, null, new ArrayList<>());
}
return null;
}
return null;
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
该类继承自BasicAuthenticationFilter,在doFilterInternal方法中,从http头的Authorization 项读取token数据,然后用Jwts包提供的方法校验token的合法性。如果校验通过,就认为这是一个取得授权的合法请求。
SpringSecurity配置
通过SpringSecurity的配置,将上面的方法组合在一起。
package com.example.jwtauth;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.SecurityProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
@Configuration
@Order(SecurityProperties.ACCESS_OVERRIDE_ORDER)
public class MyWebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
private UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
private BCryptPasswordEncoder bCryptPasswordEncoder;
public MyWebSecurityConfig(UserDetailsService userDetailsService, BCryptPasswordEncoder bCryptPasswordEncoder) {
this.userDetailsService = userDetailsService;
this.bCryptPasswordEncoder = bCryptPasswordEncoder;
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.cors().and().csrf().disable().authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers(HttpMethod.POST, "/users/signup").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.addFilter(new JWTLoginFilter(authenticationManager()))
.addFilter(new JwtAuthenticationFilter(authenticationManager()));
}
@Override
public void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService).passwordEncoder(bCryptPasswordEncoder);
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
这是标准的SpringSecurity配置内容,就不在详细说明。注意其中的
.addFilter(new JWTLoginFilter(authenticationManager()))
.addFilter(new JwtAuthenticationFilter(authenticationManager()))
这两行,将我们定义的JWT方法加入SpringSecurity的处理流程中。
下面对我们的程序进行简单的验证:
# 请求hello接口,会收到403错误
curl http://localhost:8080/hello
# 注册一个新用户
curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" -X POST -d '{
"username": "admin",
"password": "password"
}' http://localhost:8080/users/signup
# 登录,会返回token,在http header中,Authorization: Bearer 后面的部分就是token
curl -i -H "Content-Type: application/json" -X POST -d '{
"username": "admin",
"password": "password"
}' http://localhost:8080/login
# 用登录成功后拿到的token再次请求hello接口
# 将请求中的XXXXXX替换成拿到的token
# 这次可以成功调用接口了
curl -H "Content-Type: application/json"
-H "Authorization: Bearer XXXXXX"
"http://localhost:8080/hello"
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
总结
至此,给SpringBoot的接口加上JWT认证的功能就实现了,过程并不复杂,主要是开发两个SpringSecurity的filter,来生成和校验JWT token。
JWT作为一个无状态的授权校验技术,非常适合于分布式系统架构,因为服务端不需要保存用户状态,因此就无需采用redis等技术,在各个服务节点之间共享session数据。