POST消息体传输方式
直接发送消息体
最长见的就是直接在POST请求头里设置了Content-Length属性,也就是所谓的定长,只要接收端根据这个去读定长的字节就行,这个方便是方便,但是如果一个比较大的数据,可能要消耗比较大的内存。
块传输
还有一种是Transfer-Encoding: chunked,然后消息体可以分成好几次传,有一定的格式规范,这个其实就可以降低接收端的内存消耗,特别是一些不定长的数据。比如要从数据库里源源不断的读消息传出去,你可能不知道总共有多大,只有读了才知道。
Netty有关Http的编解码器
HttpRequestDecoder请求解码器
继承HttpObjectDecoder,是一个通用的HTTP解码器,也是继承以前讲过的ByteToMessageDecoder,主要的方法在HttpObjectDecoder都实现了。
//根据请求行创建HttpMessage 版本,方法,URI
@Override protected HttpMessage createMessage(String[] initialLine) throws Exception { return new DefaultHttpRequest( HttpVersion.valueOf(initialLine[2]), HttpMethod.valueOf(initialLine[0]), initialLine[1], validateHeaders); } //无效请求 @Override protected HttpMessage createInvalidMessage() { return new DefaultFullHttpRequest(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_0, HttpMethod.GET, "/bad-request", validateHeaders); } //是否是请求解码 @Override protected boolean isDecodingRequest() { return true; }
HttpObjectDecoder
基本属性
因为要解析HTTP协议格式,所以需要有换行符解析器,请求头解析器,还要看是否是用content-length传输还是用transfer-encoding块传输。还定义了一些状态,用来执行不同的逻辑。
private static final String EMPTY_VALUE = ""; private static final Pattern COMMA_PATTERN = Pattern.compile(","); private final int maxChunkSize;//块的最大长度 private final boolean chunkedSupported;//是否支持分块chunk发送 protected final boolean validateHeaders;//是否验证头名字合法性 private final boolean allowDuplicateContentLengths; private final HeaderParser headerParser;//请求头解析器 private final LineParser lineParser;//换行符解析器 private HttpMessage message;//请求的消息,包括请求行和请求头 private long chunkSize;//保存下一次要读的消息体长度 private long contentLength = Long.MIN_VALUE;//消息体长度 private volatile boolean resetRequested;//重置请求 // These will be updated by splitHeader(...) private CharSequence name;//头名字 private CharSequence value;//头的值 private LastHttpContent trailer;//请求体结尾 /** * The internal state of {@link HttpObjectDecoder}. * <em>Internal use only</em>. */ private enum State { SKIP_CONTROL_CHARS,//检查控制字符 READ_INITIAL,//开始读取 READ_HEADER,//读取头 READ_VARIABLE_LENGTH_CONTENT,//读取可变长内容,用于chunk传输 READ_FIXED_LENGTH_CONTENT,//读取固定长内容 用于Content-Length READ_CHUNK_SIZE,//chunk传输的每个chunk尺寸 READ_CHUNKED_CONTENT,//每个chunk内容 READ_CHUNK_DELIMITER,//chunk分割 READ_CHUNK_FOOTER,//最后一个chunk BAD_MESSAGE,//无效消息 UPGRADED//协议切换 } private State currentState = State.SKIP_CONTROL_CHARS;//当前状态
构造函数
构造函数,参数对应一行最大长度,请求头的最大长度,请求体或者某个块的最大长度,是否支持chunk块传输。
/** * Creates a new instance with the default * {@code maxInitialLineLength (4096}}, {@code maxHeaderSize (8192)}, and * {@code maxChunkSize (8192)}. */ protected HttpObjectDecoder() { this(DEFAULT_MAX_INITIAL_LINE_LENGTH, DEFAULT_MAX_HEADER_SIZE, DEFAULT_MAX_CHUNK_SIZE, DEFAULT_CHUNKED_SUPPORTED); } /** * Creates a new instance with the specified parameters. */ protected HttpObjectDecoder( int maxInitialLineLength, int maxHeaderSize, int maxChunkSize, boolean chunkedSupported) { this(maxInitialLineLength, maxHeaderSize, maxChunkSize, chunkedSupported, DEFAULT_VALIDATE_HEADERS); } /** * Creates a new instance with the specified parameters. */ protected HttpObjectDecoder( int maxInitialLineLength, int maxHeaderSize, int maxChunkSize, boolean chunkedSupported, boolean validateHeaders) { this(maxInitialLineLength, maxHeaderSize, maxChunkSize, chunkedSupported, validateHeaders, DEFAULT_INITIAL_BUFFER_SIZE); } /** * Creates a new instance with the specified parameters. */ protected HttpObjectDecoder( int maxInitialLineLength, int maxHeaderSize, int maxChunkSize, boolean chunkedSupported, boolean validateHeaders, int initialBufferSize) { this(maxInitialLineLength, maxHeaderSize, maxChunkSize, chunkedSupported, validateHeaders, initialBufferSize, DEFAULT_ALLOW_DUPLICATE_CONTENT_LENGTHS); } protected HttpObjectDecoder( int maxInitialLineLength, int maxHeaderSize, int maxChunkSize, boolean chunkedSupported, boolean validateHeaders, int initialBufferSize, boolean allowDuplicateContentLengths) { checkPositive(maxInitialLineLength, "maxInitialLineLength"); checkPositive(maxHeaderSize, "maxHeaderSize"); checkPositive(maxChunkSize, "maxChunkSize"); AppendableCharSequence seq = new AppendableCharSequence(initialBufferSize); lineParser = new LineParser(seq, maxInitialLineLength); headerParser = new HeaderParser(seq, maxHeaderSize); this.maxChunkSize = maxChunkSize; this.chunkedSupported = chunkedSupported; this.validateHeaders = validateHeaders; this.allowDuplicateContentLengths = allowDuplicateContentLengths; }
AppendableCharSequence 可添加的字符序列
这个底层是一个字符数组,可以动态添加到最后。
HeaderParser头解析器
其实就是检查字节缓冲区,获取一行头信息,ByteProcessor 这个就是处理是否遇到某个字节,就是process方法。这边处理的就是如果发现是回车,就不添加任何字符,返回true,继续解析,遇到换行就返回false,不解析了,否则将字符添加到字符序列中,返回true,继续解析。
private static class HeaderParser implements ByteProcessor { private final AppendableCharSequence seq;//可添加的字符序列 private final int maxLength;//最大长度 private int size;//索引 HeaderParser(AppendableCharSequence seq, int maxLength) { this.seq = seq; this.maxLength = maxLength; } //解析缓冲区 public AppendableCharSequence parse(ByteBuf buffer) { final int oldSize = size; seq.reset(); int i = buffer.forEachByte(this); if (i == -1) {//没读到换行,或者报异常了 size = oldSize; return null; } buffer.readerIndex(i + 1); return seq; } //读到的字符个数清零 public void reset() { size = 0; } //处理数据,遇到换行了就结束 @Override public boolean process(byte value) throws Exception { char nextByte = (char) (value & 0xFF); if (nextByte == HttpConstants.LF) {//遇到换行符 int len = seq.length();//可添加字符序列长度 // Drop CR if we had a CRLF pair if (len >= 1 && seq.charAtUnsafe(len - 1) == HttpConstants.CR) {//字符序列长度大于1,且以回车符结尾 -- size; seq.setLength(len - 1);去掉回车符 } return false;//结束 } increaseCount();//溢出了 seq.append(nextByte);//添加 return true; } protected final void increaseCount() { if (++ size > maxLength) { // TODO: Respond with Bad Request and discard the traffic // or close the connection. // No need to notify the upstream handlers - just log. // If decoding a response, just throw an exception. throw newException(maxLength); } } //头过大 protected TooLongFrameException newException(int maxLength) { return new TooLongFrameException("HTTP header is larger than " + maxLength + " bytes."); } }
process哪里用到呢
其实是在parse方法的buffer.forEachByte(this)里。
forEachByte
这个方法就是传一个字节处理器,然后字节缓冲区挨个处理字节,返回索引。
public int forEachByte(ByteProcessor processor) { ensureAccessible(); try { return forEachByteAsc0(readerIndex, writerIndex, processor); } catch (Exception e) { PlatformDependent.throwException(e); return -1; } }
forEachByteAsc0
这个就是具体的方法啦,里面调用了processor的process方法,从头到位把每个字节传进去处理,如果有遇到换行符,会返回相应索引,否则就是-1。
int forEachByteAsc0(int start, int end, ByteProcessor processor) throws Exception { for (; start < end; ++start) { if (!processor.process(_getByte(start))) { return start; } } return -1; }
LineParser行解析器
继承了头解析器,只是解析的时候要reset一下,就是把读到的个数清0,因为是一行行读,每次读完一行就得清理个数。虽然字符串序列可以不处理,可以复用。
private final class LineParser extends HeaderParser { LineParser(AppendableCharSequence seq, int maxLength) { super(seq, maxLength); } @Override public AppendableCharSequence parse(ByteBuf buffer) { // Suppress a warning because HeaderParser.reset() is supposed to be called reset(); // lgtm[java/subtle-inherited-call] return super.parse(buffer); } @Override public boolean process(byte value) throws Exception { if (currentState == State.SKIP_CONTROL_CHARS) { char c = (char) (value & 0xFF); if (Character.isISOControl(c) || Character.isWhitespace(c)) { increaseCount(); return true; } currentState = State.READ_INITIAL; } return super.process(value); } @Override protected TooLongFrameException newException(int maxLength) { return new TooLongFrameException("An HTTP line is larger than " + maxLength + " bytes."); } }
decode解码
这个是最核心的方法,包括了解析请求行,请求头,请求体,但是会将请求行和请求头整合起来形成一个请求DefaultHttpRequest传递到后面,把请求体再封装成消息体传递到后面,因为请求体可能很大,所以也可能会有多次封装,那后面处理器就可能收到多次消息体。如果是GET的话是没有消息体的,首先收到一个DefaultHttpRequest,然后是一个空的LastHttpContent。如果是POST的话,先收到DefaultHttpRequest,然后可能多个内容DefaultHttpContent和一个DefaultLastHttpContent。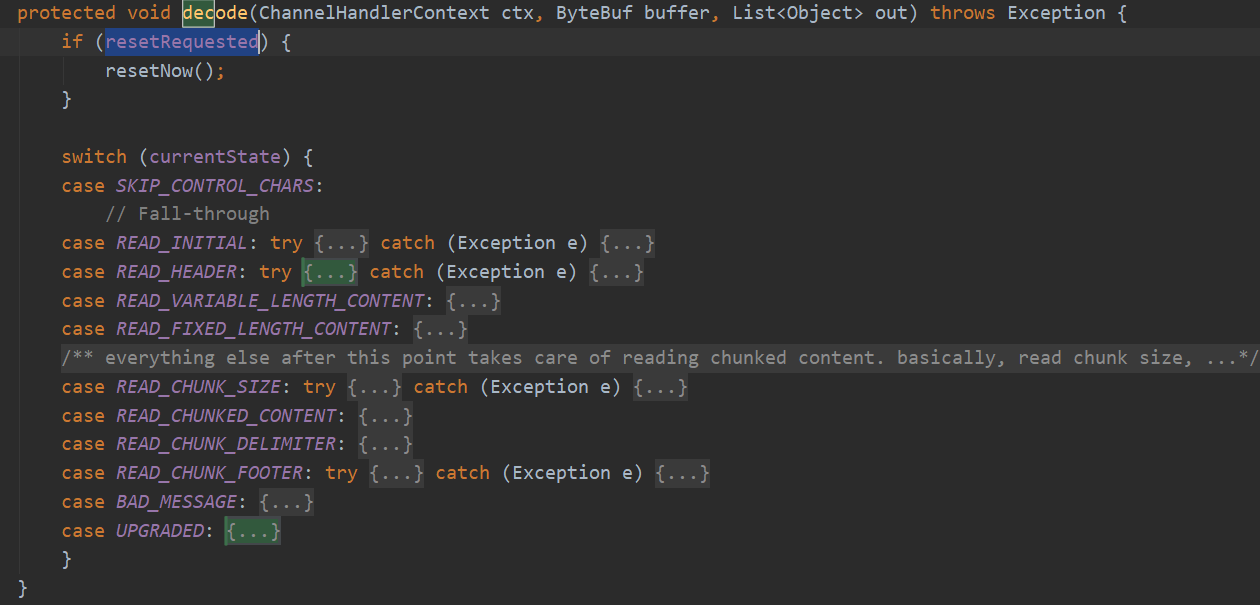
根据状态来说明
开始读取READ_INITIAL
会开始读取一行,如果没有读到换行符,可能是因为数据还没收全,那就什么都不做,返回。
否则就开始分割,分割出方法,URI,协议,当然如果请求头无效,就不管了,重新返回到SKIP_CONTROL_CHARS状态。如果是有效的,就封装成请求消息HttpMessage包括请求行和请求头信息,讲状态切换到READ_HEADER读头信息。
case READ_INITIAL: try { AppendableCharSequence line = lineParser.parse(buffer);//解析一行数据 if (line == null) {//没解析到换行符 return; } String[] initialLine = splitInitialLine(line);//行分割后的数组 if (initialLine.length < 3) {//小于3个就说明格式(方法 URI 版本)不对,直接忽略 // Invalid initial line - ignore. currentState = State.SKIP_CONTROL_CHARS; return; } message = createMessage(initialLine);//创建请求消息 currentState = State.READ_HEADER;//状态修改为读头部 // fall-through } catch (Exception e) { out.add(invalidMessage(buffer, e)); return; }
splitInitialLine分割请求行
可以看到其实执行了3次检测,刚好把请求行给分割出来,最后用字符串切割出来封装成数组返回。
private static String[] splitInitialLine(AppendableCharSequence sb) { int aStart; int aEnd; int bStart; int bEnd; int cStart; int cEnd; aStart = findNonSPLenient(sb, 0);//找出不是空格的第一个索引 aEnd = findSPLenient(sb, aStart);//找出空格索引 bStart = findNonSPLenient(sb, aEnd); bEnd = findSPLenient(sb, bStart); cStart = findNonSPLenient(sb, bEnd); cEnd = findEndOfString(sb); return new String[] { sb.subStringUnsafe(aStart, aEnd), sb.subStringUnsafe(bStart, bEnd), cStart < cEnd? sb.subStringUnsafe(cStart, cEnd) : "" }; }
HttpRequestDecoder#createMessage创建请求消息
创建一个DefaultHttpRequest,就是一个HttpRequest接口的默认实现,封装请求行和请求头信息。
protected HttpMessage createMessage(String[] initialLine) throws Exception { return new DefaultHttpRequest( HttpVersion.valueOf(initialLine[2]),//协议版本 HttpMethod.valueOf(initialLine[0]), initialLine[1], validateHeaders);//方法和URI }
invalidMessage无效消息
创建一个无效消息,状态直接为BAD_MESSAGE无效,把缓冲区内的数据直接都略过,如果请求消息没创建好,就创建一个,然后设置失败结果并带上异常信息返回。
private HttpMessage invalidMessage(ByteBuf in, Exception cause) { currentState = State.BAD_MESSAGE;//设置无效数据,这样后面同一个消息的数据都会被略过 // Advance the readerIndex so that ByteToMessageDecoder does not complain // when we produced an invalid message without consuming anything. in.skipBytes(in.readableBytes());//直接不可读,略过可读数据 if (message == null) { message = createInvalidMessage(); } message.setDecoderResult(DecoderResult.failure(cause));//设置失败 HttpMessage ret = message; message = null; return ret; }
createInvalidMessage创建完整的请求
直接返回完整的请求消息,参数设置成有问题的就可以了。
protected HttpMessage createInvalidMessage() { return new DefaultFullHttpRequest(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_0, HttpMethod.GET, "/bad-request", validateHeaders); }
READ_HEADER读取头
首先会先解析请求头,然后看里面有没有transfer-encoding或者content-length,来进行后续的消息体读取。
case READ_HEADER: try {//读取请求头 State nextState = readHeaders(buffer); if (nextState == null) { return; } currentState = nextState; switch (nextState) { case SKIP_CONTROL_CHARS://没有内容,直接传递两个消息 // fast-path // No content is expected. out.add(message); out.add(LastHttpContent.EMPTY_LAST_CONTENT);//空内容 resetNow(); return; case READ_CHUNK_SIZE: //块协议传递 if (!chunkedSupported) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Chunked messages not supported"); } // Chunked encoding - generate HttpMessage first. HttpChunks will follow. out.add(message); return; default: //没有transfer-encoding或者content-length头 表示没消息体,比如GET请求 /** * <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7230#section-3.3.3">RFC 7230, 3.3.3</a> states that if a * request does not have either a transfer-encoding or a content-length header then the message body * length is 0. However for a response the body length is the number of octets received prior to the * server closing the connection. So we treat this as variable length chunked encoding. */ long contentLength = contentLength(); if (contentLength == 0 || contentLength == -1 && isDecodingRequest()) {//没消息体,直接就补一个空消息体 out.add(message);//消息行和消息头 out.add(LastHttpContent.EMPTY_LAST_CONTENT);//空消息体 resetNow();//重置属性 return; } assert nextState == State.READ_FIXED_LENGTH_CONTENT || nextState == State.READ_VARIABLE_LENGTH_CONTENT; out.add(message);//有消息体,就先放入行和头信息,下一次解码再进行消息体的读取 if (nextState == State.READ_FIXED_LENGTH_CONTENT) { // chunkSize will be decreased as the READ_FIXED_LENGTH_CONTENT state reads data chunk by chunk. chunkSize = contentLength;//如果是固定长度的消息体,要保存下一次要读的消息体长度 } // We return here, this forces decode to be called again where we will decode the content return; } } catch (Exception e) { out.add(invalidMessage(buffer, e)); return; }
readHeaders解析头
主要就是按行解析头消息,然后进行头信息分割,然后放入headers ,最后根据content-length来决定后面的状态,是读取固定长READ_FIXED_LENGTH_CONTENT还是可变长READ_VARIABLE_LENGTH_CONTENT,还是是读取块大小READ_CHUNK_SIZE。
private State readHeaders(ByteBuf buffer) { final HttpMessage message = this.message; final HttpHeaders headers = message.headers();//获得请求头 AppendableCharSequence line = headerParser.parse(buffer);//解析请求头 if (line == null) { return null; } if (line.length() > 0) { do { char firstChar = line.charAtUnsafe(0); if (name != null && (firstChar == ' ' || firstChar == ' ')) { //please do not make one line from below code //as it breaks +XX:OptimizeStringConcat optimization String trimmedLine = line.toString().trim(); String valueStr = String.valueOf(value); value = valueStr + ' ' + trimmedLine; } else { if (name != null) { headers.add(name, value);//如果名字解析出来表示值也出来了,就添加进去 } splitHeader(line);//分割请求头 } line = headerParser.parse(buffer);//继续解析头 if (line == null) { return null; } } while (line.length() > 0); } // Add the last header. if (name != null) {//添加最后一个 headers.add(name, value); } // reset name and value fields name = null; value = null; List<String> contentLengthFields = headers.getAll(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_LENGTH); if (!contentLengthFields.isEmpty()) {//长度头的值集合非空 // Guard against multiple Content-Length headers as stated in // https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7230#section-3.3.2: // // If a message is received that has multiple Content-Length header // fields with field-values consisting of the same decimal value, or a // single Content-Length header field with a field value containing a // list of identical decimal values (e.g., "Content-Length: 42, 42"), // indicating that duplicate Content-Length header fields have been // generated or combined by an upstream message processor, then the // recipient MUST either reject the message as invalid or replace the // duplicated field-values with a single valid Content-Length field // containing that decimal value prior to determining the message body // length or forwarding the message. boolean multipleContentLengths = contentLengthFields.size() > 1 || contentLengthFields.get(0).indexOf(COMMA) >= 0; if (multipleContentLengths && message.protocolVersion() == HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1) { if (allowDuplicateContentLengths) {//是否允许重复的长度头值,其实只允许一个值, // Find and enforce that all Content-Length values are the same String firstValue = null; for (String field : contentLengthFields) { String[] tokens = COMMA_PATTERN.split(field, -1); for (String token : tokens) { String trimmed = token.trim(); if (firstValue == null) { firstValue = trimmed; } else if (!trimmed.equals(firstValue)) {//存在多个值,且不一样,报错 throw new IllegalArgumentException( "Multiple Content-Length values found: " + contentLengthFields); } } } // Replace the duplicated field-values with a single valid Content-Length field headers.set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_LENGTH, firstValue); contentLength = Long.parseLong(firstValue); } else { // Reject the message as invalid throw new IllegalArgumentException( "Multiple Content-Length values found: " + contentLengthFields); } } else { contentLength = Long.parseLong(contentLengthFields.get(0));//获取消息体长 } } if (isContentAlwaysEmpty(message)) {//空内容 HttpUtil.setTransferEncodingChunked(message, false);//不开启块传输 return State.SKIP_CONTROL_CHARS; } else if (HttpUtil.isTransferEncodingChunked(message)) { if (!contentLengthFields.isEmpty() && message.protocolVersion() == HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1) {//HTTP_1_1如果开启了快协议,就不能设置Content-Length了 handleTransferEncodingChunkedWithContentLength(message); } return State.READ_CHUNK_SIZE;//块传输,要获取大小 } else if (contentLength() >= 0) { return State.READ_FIXED_LENGTH_CONTENT;//可以固定长度解析消息体 } else { return State.READ_VARIABLE_LENGTH_CONTENT;//可变长度解析,或者没有Content-Length,http1.0以及之前或者1.1 非keep alive,Content-Length可有可无 } }
如果是HTTP1.1一个头只能对应一个值,即使多个值,也必须时一样的值。而且Content-Length和Transfer-Encoding不能同时存在。http1.0以及之前或者http1.1没设置keepalive的话Content-Length可有可无。
Header的结构
外部看上去很像是跟MAP一样添加头信息,其实内部还是使用了数组和单链表和双向循环链表,好比是HashMap的加强版。使用了hash算法定位数组的索引,然后有冲突的时候用单链表头插进去,而且头信息顺序按照双向循环链表连起来了,方便前后定位。

READ_VARIABLE_LENGTH_CONTENT读取可变长内容
直接读取可读的字节,然后封装成DefaultHttpContent内容传递。
case READ_VARIABLE_LENGTH_CONTENT: { // Keep reading data as a chunk until the end of connection is reached. int toRead = Math.min(buffer.readableBytes(), maxChunkSize); if (toRead > 0) { ByteBuf content = buffer.readRetainedSlice(toRead); out.add(new DefaultHttpContent(content)); } return; }
READ_FIXED_LENGTH_CONTENT读取固定长内容
固定长度就是有contentLength,读取长度,如果等于记录的长度chunkSize ,就表示读完了,直接传递最后内容DefaultLastHttpContent。否则说明没读完,就传递内容DefaultHttpContent。
case READ_FIXED_LENGTH_CONTENT: {//有固定长消息体 int readLimit = buffer.readableBytes(); // Check if the buffer is readable first as we use the readable byte count // to create the HttpChunk. This is needed as otherwise we may end up with // create an HttpChunk instance that contains an empty buffer and so is // handled like it is the last HttpChunk. // // See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/433 if (readLimit == 0) { return; } int toRead = Math.min(readLimit, maxChunkSize);//读取的个数 if (toRead > chunkSize) {//如果大于块长度chunkSize,就读chunkSize个 toRead = (int) chunkSize; } ByteBuf content = buffer.readRetainedSlice(toRead); chunkSize -= toRead; if (chunkSize == 0) {//块全部读完了 // Read all content. out.add(new DefaultLastHttpContent(content, validateHeaders));//创建最后一个内容体,返回 resetNow();//重置参数 } else { out.add(new DefaultHttpContent(content));//还没读完,就创建一个消息体 } return; }
READ_CHUNK_SIZE读取块大小
如果是chunk块传输,根据块传输协议,就应该是获取块大小。
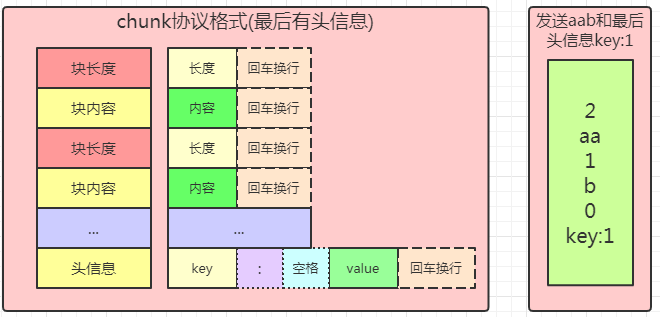
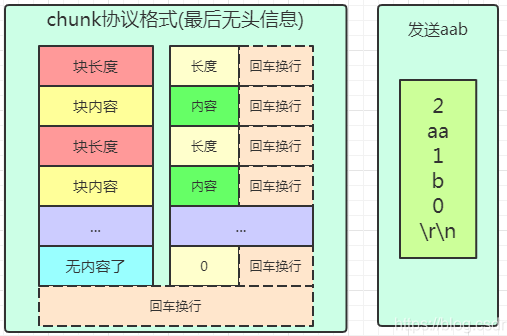
比如要传输aab,使用块协议,第一块长度是2,内容是aa,第二块长度是1,内容是b,第三块长度是0,内容是空(就有回车换行),记得长度内容后面都有回车换行。
case READ_CHUNK_SIZE: try {//读取块尺寸 AppendableCharSequence line = lineParser.parse(buffer); if (line == null) { return; } int chunkSize = getChunkSize(line.toString()); this.chunkSize = chunkSize;//块长度 if (chunkSize == 0) {//读到块结束标记 0 currentState = State.READ_CHUNK_FOOTER; return; } currentState = State.READ_CHUNKED_CONTENT;//继续读内容 // fall-through } catch (Exception e) { out.add(invalidChunk(buffer, e));//无效块 return; }
如果读取的块长度是0了,那说明要到最后一个了,状态就要转到 READ_CHUNK_FOOTER,否则就转到读内容 READ_CHUNKED_CONTENT。
getChunkSize获取块尺寸
;,空格,控制字符都算截止符。
private static int getChunkSize(String hex) { hex = hex.trim(); for (int i = 0; i < hex.length(); i ++) { char c = hex.charAt(i); if (c == ';' || Character.isWhitespace(c) || Character.isISOControl(c)) { hex = hex.substring(0, i); break; } } return Integer.parseInt(hex, 16); }
READ_CHUNKED_CONTENT读取块内容
根据块长度chunkSize读取字节,如果读取长度等于chunkSize,表示读完了,需要读取分隔符,也就是换车换行了,状态转到READ_CHUNK_DELIMITER,否则就将读取的内容,封装成DefaultHttpContent传递下去,然后下一次继续读取内容。
case READ_CHUNKED_CONTENT: {//读取块内容,其实没读取,只是用切片,从切片读,不影响原来的 assert chunkSize <= Integer.MAX_VALUE; int toRead = Math.min((int) chunkSize, maxChunkSize); toRead = Math.min(toRead, buffer.readableBytes()); if (toRead == 0) { return; } HttpContent chunk = new DefaultHttpContent(buffer.readRetainedSlice(toRead));//创建一个块,里面放的是切片 chunkSize -= toRead; out.add(chunk); if (chunkSize != 0) {//当前块还没接受完,就返回 return; } currentState = State.READ_CHUNK_DELIMITER;//接受完,找到块分割符 // fall-through }
READ_CHUNK_DELIMITER读取块分隔符
其实就是回车换行符,找到了就转到READ_CHUNK_SIZE继续去取下一个块长度。
case READ_CHUNK_DELIMITER: {//找到块分隔符 final int wIdx = buffer.writerIndex(); int rIdx = buffer.readerIndex(); while (wIdx > rIdx) { byte next = buffer.getByte(rIdx++); if (next == HttpConstants.LF) {//找到换行符,继续读下一个块的大小 currentState = State.READ_CHUNK_SIZE; break; } } buffer.readerIndex(rIdx); return; }
READ_CHUNK_FOOTER读最后一个块
如果读取的块长度chunkSize=0的话,就说明是最后一个块了,然后要看下是否还有头信息在后面,有头信息的话会封装成DefaultLastHttpContent,如果没有的话头信息就是LastHttpContent.EMPTY_LAST_CONTENT
case READ_CHUNK_FOOTER: try {//读到最后一个了 LastHttpContent trailer = readTrailingHeaders(buffer);//读取最后的内容,可能有头信息,也可能没有 if (trailer == null) {//还没结束的,继续 return; } out.add(trailer);//添加最后内容 resetNow(); return; } catch (Exception e) { out.add(invalidChunk(buffer, e)); return; }
readTrailingHeaders读取最后的头信息
会去读取一行,如果没读出来换行,表示可能没收到数据,也就是没读完,那就返回,继续下一次。
如果读出来发现就只有回车换行,那就说明没有头信息,结束了,就返回一个 LastHttpContent.EMPTY_LAST_CONTENT,否则的话就创建一个DefaultLastHttpContent内容,然后进行头信息的解析,解析出来的头信息就放入内容中,并返回内容。
private LastHttpContent readTrailingHeaders(ByteBuf buffer) { AppendableCharSequence line = headerParser.parse(buffer); if (line == null) {//没有换行,表示没读完呢 return null; } LastHttpContent trailer = this.trailer; if (line.length() == 0 && trailer == null) {//直接读到 即读到空行,表示结束,无头信息,返回空内容 // We have received the empty line which signals the trailer is complete and did not parse any trailers // before. Just return an empty last content to reduce allocations. return LastHttpContent.EMPTY_LAST_CONTENT; } CharSequence lastHeader = null; if (trailer == null) { trailer = this.trailer = new DefaultLastHttpContent(Unpooled.EMPTY_BUFFER, validateHeaders);//空内容 } while (line.length() > 0) {//chunk最后可能还有头信息 key: 1 char firstChar = line.charAtUnsafe(0); if (lastHeader != null && (firstChar == ' ' || firstChar == ' ')) { List<String> current = trailer.trailingHeaders().getAll(lastHeader); if (!current.isEmpty()) { int lastPos = current.size() - 1; //please do not make one line from below code //as it breaks +XX:OptimizeStringConcat optimization String lineTrimmed = line.toString().trim(); String currentLastPos = current.get(lastPos); current.set(lastPos, currentLastPos + lineTrimmed); } } else {//解析头信息 splitHeader(line); CharSequence headerName = name; if (!HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_LENGTH.contentEqualsIgnoreCase(headerName) && !HttpHeaderNames.TRANSFER_ENCODING.contentEqualsIgnoreCase(headerName) && !HttpHeaderNames.TRAILER.contentEqualsIgnoreCase(headerName)) { trailer.trailingHeaders().add(headerName, value); } lastHeader = name; // reset name and value fields name = null; value = null; } line = headerParser.parse(buffer); if (line == null) { return null; } } this.trailer = null; return trailer; }
BAD_MESSAGE无效消息
case BAD_MESSAGE: { // Keep discarding until disconnection. buffer.skipBytes(buffer.readableBytes());//坏消息,直接略过,不读 break; }
UPGRADED协议切换
其实就是协议的转换。
case UPGRADED: {//协议切换 int readableBytes = buffer.readableBytes(); if (readableBytes > 0) { // Keep on consuming as otherwise we may trigger an DecoderException, // other handler will replace this codec with the upgraded protocol codec to // take the traffic over at some point then. // See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2173 out.add(buffer.readBytes(readableBytes)); } break; }
resetNow重置属性
每次成功解码操作后都要重新设置属性。
private void resetNow() { HttpMessage message = this.message; this.message = null; name = null; value = null; contentLength = Long.MIN_VALUE; lineParser.reset(); headerParser.reset(); trailer = null; if (!isDecodingRequest()) {//不是请求解码,如果要升级协议 HttpResponse res = (HttpResponse) message; if (res != null && isSwitchingToNonHttp1Protocol(res)) { currentState = State.UPGRADED; return; } } resetRequested = false; currentState = State.SKIP_CONTROL_CHARS; }
至此整个基本完成。
总结
首先会将请求行和请求头解析出来,根据请求头中是否有Content-Length或者Transfer-Encoding: chunked属性来判断是否还需要进行解码,如果需要,还持续进行解码,直到把消息体全部收完为止,而且期间会解码一次传递一次消息,因此自定义的处理器会不断的收到消息,第一次是消息行和消息头,后面就是消息体,直到收到最后一次消息体才会结束。基本上是按这么解码的,每一块都会被向后传递: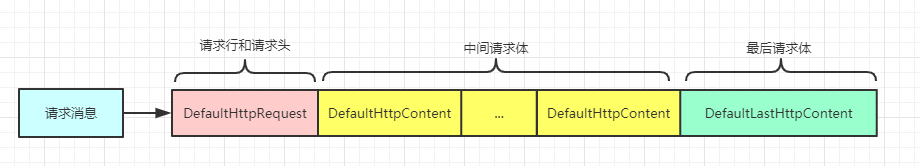
如果是比较大的包,比如文件,可以直接用这个,块传输,边传输边进行其他操作,比如一遍下载一遍看视频,断点续传啊这类。占用内存少,接受一个处理完可以释放内存,或者复用。
HttpObjectAggregator
一个HTTP请求最少也会在HttpRequestDecoder里分成两次往后传递,第一次是消息行和消息头,第二次是消息体,哪怕没有消息体,也会传一个空消息体。如果发送的消息体比较大的话,可能还会分成好几个消息体来处理,往后传递多次,这样使得我们后续的处理器可能要写多个逻辑判断,比较麻烦,那能不能把消息都整合成一个完整的,再往后传递呢,当然可以,用HttpObjectAggregator。
public class HttpObjectAggregator extends MessageAggregator<HttpObject, HttpMessage, HttpContent, FullHttpMessage>
public abstract class MessageAggregator<I, S, C extends ByteBufHolder, O extends ByteBufHolder>
extends MessageToMessageDecoder<I>
他有4个泛型,分别对应是聚合HTTP类型的,HTTP通用消息请求行和请求头的,HTTP消息体,HTTP完整通用消息,包括消息体
属性
HTTP有个头属性Except:100-continue用来优化服务器和客户端数据传输的,在要发送比较大的数据的时候,不会直接发送,而是会先征求下服务器意见是否可以继续发送数据,服务器可以允许也可以不允许,都应该响应一下。
//接受100-continue,响应状态码100
private static final FullHttpResponse CONTINUE = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.CONTINUE, Unpooled.EMPTY_BUFFER);
//不接受,响应状态码417 不支持
private static final FullHttpResponse EXPECTATION_FAILED = new DefaultFullHttpResponse( HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.EXPECTATION_FAILED, Unpooled.EMPTY_BUFFER);
//不接受,响应状态码413 消息体太大而关闭连接
private static final FullHttpResponse TOO_LARGE_CLOSE = new DefaultFullHttpResponse( HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.REQUEST_ENTITY_TOO_LARGE, Unpooled.EMPTY_BUFFER);
//不接受,响应状态码413 消息体太大,没关闭连接
private static final FullHttpResponse TOO_LARGE = new DefaultFullHttpResponse( HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.REQUEST_ENTITY_TOO_LARGE, Unpooled.EMPTY_BUFFER); static {//设定头消息 EXPECTATION_FAILED.headers().set(CONTENT_LENGTH, 0); TOO_LARGE.headers().set(CONTENT_LENGTH, 0); TOO_LARGE_CLOSE.headers().set(CONTENT_LENGTH, 0); TOO_LARGE_CLOSE.headers().set(CONNECTION, HttpHeaderValues.CLOSE); } private final boolean closeOnExpectationFailed;//如果消息过大是否关闭连接,报异常
MessageAggregator
属性
private static final int DEFAULT_MAX_COMPOSITEBUFFER_COMPONENTS = 1024;//最大复合缓冲区组件个数 private final int maxContentLength;//最大消息图长度 private O currentMessage;//当前消息 private boolean handlingOversizedMessage;//是否处理过大消息 private int maxCumulationBufferComponents = DEFAULT_MAX_COMPOSITEBUFFER_COMPONENTS;//累加组件的最大个数 private ChannelHandlerContext ctx;//处理器上下文 private ChannelFutureListener continueResponseWriteListener;// 100-continue响应监听器 private boolean aggregating;//是否正在聚合
acceptInboundMessage判断类型
public boolean acceptInboundMessage(Object msg) throws Exception { // No need to match last and full types because they are subset of first and middle types. if (!super.acceptInboundMessage(msg)) {//是否是泛型I类型,比如HttpObject类型 return false; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") I in = (I) msg; if (isAggregated(in)) {//是否聚合好了 return false; } // NOTE: It's tempting to make this check only if aggregating is false. There are however // side conditions in decode(...) in respect to large messages. if (isStartMessage(in)) {//是否是开始聚合 aggregating = true;//开始聚合 return true; } else if (aggregating && isContentMessage(in)) {//正在内容聚合 return true; } return false; }
decode真正的聚合
如果是开始消息,也就不是请求体,那就开始判断是否有Except:100-continue头信息,有的话根据长度和是否支持来判断是否要返回响应。之后判断如果前面解码失败,就直接整合消息体返回,否则就创建复合缓冲区,如果是消息体的话就添加进去,然后封装成一个完整的消息类型。
如果是消息体了,就加入到复合画冲去里,然后判断是否是最后一个消息体,是的话就进行最后的整合,其实就是设置Content-Length头信息。
protected void decode(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx, I msg, List<Object> out) throws Exception { assert aggregating; if (isStartMessage(msg)) {//是否是开始消息 handlingOversizedMessage = false;//没处理超大信息 if (currentMessage != null) {//上次的消息没释放 currentMessage.release(); currentMessage = null; throw new MessageAggregationException(); } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") S m = (S) msg; // Send the continue response if necessary (e.g. 'Expect: 100-continue' header) // Check before content length. Failing an expectation may result in a different response being sent. Object continueResponse = newContinueResponse(m, maxContentLength, ctx.pipeline()); if (continueResponse != null) {//有 100-continue响应 // Cache the write listener for reuse. ChannelFutureListener listener = continueResponseWriteListener; if (listener == null) {//不存在监听器要创建一个 continueResponseWriteListener = listener = new ChannelFutureListener() { @Override public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception { if (!future.isSuccess()) { ctx.fireExceptionCaught(future.cause()); } } }; } // Make sure to call this before writing, otherwise reference counts may be invalid. boolean closeAfterWrite = closeAfterContinueResponse(continueResponse); handlingOversizedMessage = ignoreContentAfterContinueResponse(continueResponse); //这里会直接刷出去,所以HttpResponseEncoder需要放在这个前面,不然写出去没编码过会报错的 final ChannelFuture future = ctx.writeAndFlush(continueResponse).addListener(listener); if (closeAfterWrite) { future.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE); return; } if (handlingOversizedMessage) { return; } } else if (isContentLengthInvalid(m, maxContentLength)) {//消息体长度是否超过了 // if content length is set, preemptively close if it's too large invokeHandleOversizedMessage(ctx, m); return; } //解码不成功 if (m instanceof DecoderResultProvider && !((DecoderResultProvider) m).decoderResult().isSuccess()) { O aggregated; if (m instanceof ByteBufHolder) { aggregated = beginAggregation(m, ((ByteBufHolder) m).content().retain()); } else { aggregated = beginAggregation(m, EMPTY_BUFFER); } finishAggregation0(aggregated); out.add(aggregated); return; } // A streamed message - initialize the cumulative buffer, and wait for incoming chunks. CompositeByteBuf content = ctx.alloc().compositeBuffer(maxCumulationBufferComponents);//创建复合缓冲区 if (m instanceof ByteBufHolder) {//是内容 appendPartialContent(content, ((ByteBufHolder) m).content()); } currentMessage = beginAggregation(m, content);//开始聚合 } else if (isContentMessage(msg)) {//后面属于消息体聚合 if (currentMessage == null) {//长度超过最大了,直接丢弃了,不处理了 // it is possible that a TooLongFrameException was already thrown but we can still discard data // until the begging of the next request/response. return; } // Merge the received chunk into the content of the current message. CompositeByteBuf content = (CompositeByteBuf) currentMessage.content();//提取内容 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") final C m = (C) msg; // Handle oversized message. if (content.readableBytes() > maxContentLength - m.content().readableBytes()) {// 超过最大长度了,处理过大的消息 // By convention, full message type extends first message type. @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") S s = (S) currentMessage; invokeHandleOversizedMessage(ctx, s); return; } // Append the content of the chunk. appendPartialContent(content, m.content());//添加新的内容到复合缓冲区 // Give the subtypes a chance to merge additional information such as trailing headers. aggregate(currentMessage, m);//整合尾部请求头 final boolean last;//是不是最后一次聚合 if (m instanceof DecoderResultProvider) {//处理解码结果 DecoderResult decoderResult = ((DecoderResultProvider) m).decoderResult(); if (!decoderResult.isSuccess()) {//没解码成功 if (currentMessage instanceof DecoderResultProvider) { ((DecoderResultProvider) currentMessage).setDecoderResult( DecoderResult.failure(decoderResult.cause())); } last = true; } else { last = isLastContentMessage(m);//是否是最后的内容 } } else { last = isLastContentMessage(m); } if (last) {//是最后的 finishAggregation0(currentMessage); // All done out.add(currentMessage); currentMessage = null; } } else { throw new MessageAggregationException(); } }
HttpObjectAggregator的isStartMessage
对HTTP来说其实就是判断是否是通用的消息行和消息头信息。
protected boolean isStartMessage(HttpObject msg) throws Exception { return msg instanceof HttpMessage; }
HttpObjectAggregator的isLastContentMessage
是否是最后的内容。
protected boolean isLastContentMessage(HttpContent msg) throws Exception { return msg instanceof LastHttpContent; }
HttpObjectAggregator的isAggregated
是否聚合好了。
protected boolean isAggregated(HttpObject msg) throws Exception { return msg instanceof FullHttpMessage; }
HttpObjectAggregator的newContinueResponse
如果需要100-continue响应的话,要把100-continue头设置去掉,不往后传播了。
protected Object newContinueResponse(HttpMessage start, int maxContentLength, ChannelPipeline pipeline) { Object response = continueResponse(start, maxContentLength, pipeline); // we're going to respond based on the request expectation so there's no // need to propagate the expectation further. if (response != null) { start.headers().remove(EXPECT);//如果有100-continue响应,就不用再传播下去了 } return response; }
HttpObjectAggregator的continueResponse
这个就是上面说的根据是否支持100-continue,是否长度超过限制等进行响应。
private static Object continueResponse(HttpMessage start, int maxContentLength, ChannelPipeline pipeline) { if (HttpUtil.isUnsupportedExpectation(start)) {//不支持Expect头 // if the request contains an unsupported expectation, we return 417 pipeline.fireUserEventTriggered(HttpExpectationFailedEvent.INSTANCE); return EXPECTATION_FAILED.retainedDuplicate(); } else if (HttpUtil.is100ContinueExpected(start)) {//支持100-continue请求 // if the request contains 100-continue but the content-length is too large, we return 413 if (getContentLength(start, -1L) <= maxContentLength) { return CONTINUE.retainedDuplicate();//继续 } pipeline.fireUserEventTriggered(HttpExpectationFailedEvent.INSTANCE); return TOO_LARGE.retainedDuplicate();//消息体太大 } return null; }
HttpObjectAggregator的closeAfterContinueResponse
是否不支持100-continue后把连接断开。
protected boolean closeAfterContinueResponse(Object msg) { return closeOnExpectationFailed && ignoreContentAfterContinueResponse(msg); }
HttpObjectAggregator的ignoreContentAfterContinueResponse
如果直接给他报400的话就要断开了,后面的内容就不忽略了。
protected boolean ignoreContentAfterContinueResponse(Object msg) { if (msg instanceof HttpResponse) { final HttpResponse httpResponse = (HttpResponse) msg; return httpResponse.status().codeClass().equals(HttpStatusClass.CLIENT_ERROR); } return false; }
HttpObjectAggregator的beginAggregation
开始聚合就是创建一个聚合的类,根据不同情况创建请求还是响应的完整类型。
protected FullHttpMessage beginAggregation(HttpMessage start, ByteBuf content) throws Exception { assert !(start instanceof FullHttpMessage); HttpUtil.setTransferEncodingChunked(start, false); AggregatedFullHttpMessage ret; if (start instanceof HttpRequest) { ret = new AggregatedFullHttpRequest((HttpRequest) start, content, null);//聚合请求 } else if (start instanceof HttpResponse) { ret = new AggregatedFullHttpResponse((HttpResponse) start, content, null);//聚合响应 } else { throw new Error(); } return ret; }
appendPartialContent
这个就是将内容添加到复合缓冲区里。
private static void appendPartialContent(CompositeByteBuf content, ByteBuf partialContent) { if (partialContent.isReadable()) {//可读的话就加进去 content.addComponent(true, partialContent.retain()); } }
HttpObjectAggregator#aggregate
这个就是整合尾部的头信息,因为chunk协议可能会有尾部头信息的。
protected void aggregate(FullHttpMessage aggregated, HttpContent content) throws Exception { if (content instanceof LastHttpContent) {//如果是最后的尾部内容就整合尾部头信息 // Merge trailing headers into the message. ((AggregatedFullHttpMessage) aggregated).setTrailingHeaders(((LastHttpContent) content).trailingHeaders()); } }
finishAggregation0
完成聚合,标志位也设置为false了,最后再坚持一遍头信息。
private void finishAggregation0(O aggregated) throws Exception { aggregating = false; finishAggregation(aggregated); } protected void finishAggregation(FullHttpMessage aggregated) throws Exception { // Set the 'Content-Length' header. If one isn't already set. // This is important as HEAD responses will use a 'Content-Length' header which // does not match the actual body, but the number of bytes that would be // transmitted if a GET would have been used. // // See rfc2616 14.13 Content-Length if (!HttpUtil.isContentLengthSet(aggregated)) {//没设置Content-Length头的话要设置 aggregated.headers().set( CONTENT_LENGTH, String.valueOf(aggregated.content().readableBytes())); } }
总的来说,就是把先到的包保存下来,等最后接收完了一起传递给后面的。用的时候,这个放到HttpResponseEncoder后面,否则他出站的错误消息不经过HttpResponseEncoder响应解码器,底层传输是不支持的:
ch.pipeline().addLast(new HttpRequestDecoder()); ch.pipeline().addLast(new HttpResponseEncoder()); ch.pipeline().addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(1024*64));