概要
上一章,我们学习了Collection的架构。这一章开始,我们对Collection的具体实现类进行讲解;首先,讲解List,而List中ArrayList又最为常用。因此,本章我们讲解ArrayList。先对ArrayList有个整体认识,再学习它的源码,最后再通过例子来学习如何使用它。内容包括:
第1部分 ArrayList简介
第2部分 ArrayList数据结构
第3部分 ArrayList源码解析(基于JDK1.8)
第4部分 ArrayList遍历方式
第1部分 ArrayList介绍
ArrayList简介
ArrayList 是一个数组队列,相当于 动态数组。与Java中的数组相比,它的容量能动态增长。它继承于AbstractList,实现了List, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable这些接口。
ArrayList 继承了AbstractList,实现了List。它是一个数组队列,提供了相关的添加、删除、修改、遍历等功能。
ArrayList 实现了RandmoAccess接口,即提供了随机访问功能。RandmoAccess是java中用来被List实现,为List提供快速访问功能的。在ArrayList中,我们即可以通过元素的序号快速获取元素对象;这就是快速随机访问。稍后,我们会比较List的“快速随机访问”和“通过Iterator迭代器访问”的效率。
ArrayList 实现了Cloneable接口,即覆盖了函数clone(),能被克隆。
ArrayList 实现java.io.Serializable接口,这意味着ArrayList支持序列化,能通过序列化去传输。
和Vector不同,ArrayList中的操作不是线程安全的!所以,建议在单线程中才使用ArrayList,而在多线程中可以选择Vector或者CopyOnWriteArrayList。
ArrayList构造函数
/** * 当指明初始化数组的大小时,直接将数组初始化为指定容量的数组。 */ public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) { if (initialCapacity > 0) { this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; } else if (initialCapacity == 0) { this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } else { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ initialCapacity); } } /** * 当没有指明数组容量时,初始化为空数组。当第一次添加元素时,会扩容为DEFAULT_CAPACITY,也就是容量为10. */ public ArrayList() { this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; }
第2部分 ArrayList数据结构
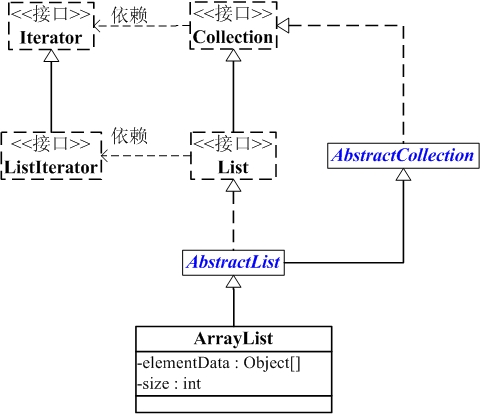
ArrayList的继承关系
java.lang.Object
↳ java.util.AbstractCollection<E>
↳ java.util.AbstractList<E>
↳ java.util.ArrayList<E>
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {}
ArrayList与Collection关系如下图:
ArrayList包含了两个重要的对象:elementData 和 size。
(01) elementData 是"Object[]类型的数组",它保存了添加到ArrayList中的元素。实际上,elementData是个动态数组,我们能通过构造函数 ArrayList(int initialCapacity)来执行它的初始容量为initialCapacity;如果通过不含参数的构造函数ArrayList()来创建ArrayList,则elementData会初始化为空数组(上面构造函数源码),当第一次添加元素时,会扩容至默认容量10。
(02) size 则是动态数组的实际大小。
第3部分 ArrayList源码解析(基于JDK1.8)
为了更了解ArrayList的原理,下面对ArrayList源码代码作出分析。ArrayList是通过数组实现的,源码比较容易理解。

public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L; /** * Default initial capacity. */ private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; /** * Shared empty array instance used for empty instances. */ private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; /** * 数组用来存储元素。当new ArrayList时没有指明大小,那么就会使用默认的空数组。 * 当第一次add元素的时候,会将数组容量设为默认值DEFAULT_CAPACITY 10. */ transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access /** * 数组所包含的元素个数,注意和elementData.length区别开。 *size<=length * @serial */ private int size; /** * 当指明初始化数组的大小时,直接将数组初始化为指定容量的数组。 */ public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) { if (initialCapacity > 0) { this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; } else if (initialCapacity == 0) { this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } else { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ initialCapacity); } } /** * 当没有指明数组容量时,初始化为空数组。当第一次添加元素时,会扩容为DEFAULT_CAPACITY,也就是容量为10. */ public ArrayList() { this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) { elementData = c.toArray(); if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) { // c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652) if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class) elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class); } else { // replace with empty array. this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } } /** * 将当前数组截成size大小的数组,也就是有元素部分留下,剩下的长度不要了。 */ public void trimToSize() { modCount++; if (size < elementData.length) { elementData = (size == 0) ? EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA : Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); } } /** * 调整容量。首先判断,如果有必要,则将容量扩大至至少能放下minCapacity个元素。 */ public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) { /** * 这里主要确保:如果数组为空,则至少需要扩容到DEFAULT_CAPACITY。 * 如果不为空,扩大至至少能放下minCapacity个元素。 */ int minExpand = (elementData != DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) ? 0 : DEFAULT_CAPACITY; if (minCapacity > minExpand) { ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity); } } private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) { /** * 如果数组为空,则要扩大至Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity) */ if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); } ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity); } private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) { modCount++; // 当前要求的个数比当前数组的length要大,则扩容。 if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) grow(minCapacity); } /** * The maximum size of array to allocate. * Some VMs reserve some header words in an array. * Attempts to allocate larger arrays may result in * OutOfMemoryError: Requested array size exceeds VM limit */ private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8; /** * 扩容,保证最少可以存放minCapacity个元素。基本原则是扩容至数组长度的1.5倍 */ private void grow(int minCapacity) { // overflow-conscious code //当前数组长度(容量) int oldCapacity = elementData.length; //新容量是当前数组容量的1.5倍。 int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); //如果1.5倍的新容量都比minCapacity小,那么新容量就为minCapacity if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) newCapacity = minCapacity; /** * 新容量比最大数组容量还要大的时候,就要重新赋值新容量了。不能超过最大值。 */ if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); // minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win: elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); } private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) { if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow throw new OutOfMemoryError(); return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; } public int size() { return size; } public boolean isEmpty() { return size == 0; } public boolean contains(Object o) { return indexOf(o) >= 0; } /** * 找出元素的位置,可以看出ArrayList可以存放null */ public int indexOf(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) if (elementData[i]==null) return i; } else { for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) if (o.equals(elementData[i])) return i; } return -1; } public int lastIndexOf(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--) if (elementData[i]==null) return i; } else { for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--) if (o.equals(elementData[i])) return i; } return -1; } /** * 克隆的时候,数组得单独克隆 */ public Object clone() { try { ArrayList<?> v = (ArrayList<?>) super.clone(); v.elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); v.modCount = 0; return v; } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { // this shouldn't happen, since we are Cloneable throw new InternalError(e); } } public Object[] toArray() { return Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) { if (a.length < size) // Make a new array of a's runtime type, but my contents: return (T[]) Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, a.getClass()); System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, a, 0, size); if (a.length > size) a[size] = null; return a; } // Positional Access Operations @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E elementData(int index) { return (E) elementData[index]; } /** * 按索引得到元素只要判断索引没有越界,就直接返回数组对应元素 */ public E get(int index) { rangeCheck(index); return elementData(index); } /** * 将指定位置的元素换成新元素 */ public E set(int index, E element) { rangeCheck(index); E oldValue = elementData(index); elementData[index] = element; return oldValue; } /** * 添加元素,如果是第一次添加,就会扩容到DEFAULT_CAPACITY大小; * 不是第一次添加也会判断是否需要扩容,基本规则是扩容到当前数组容量的1.5倍。 * modCount会增加 */ public boolean add(E e) { ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! elementData[size++] = e; return true; } /** *每次添加都要判断是否需要扩容 * 先将index后的元素后移一个,再插入 * modCount++ */ public void add(int index, E element) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, size - index); elementData[index] = element; size++; } /** * 删除元素,modCount++ * 将index后的元素往前移,并将最后一个元素置为Null */ public E remove(int index) { rangeCheck(index); modCount++; E oldValue = elementData(index); int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work return oldValue; } /** * 删除指定的元素。该元素可以为null。 */ public boolean remove(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (elementData[index] == null) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } else { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } return false; } /* * Private remove method that skips bounds checking and does not * return the value removed. */ private void fastRemove(int index) { modCount++; int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work } /** * 将所有元素置为Null */ public void clear() { modCount++; // clear to let GC do its work for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) elementData[i] = null; size = 0; } /** * Appends all of the elements in the specified collection to the end of * this list, in the order that they are returned by the * specified collection's Iterator. The behavior of this operation is * undefined if the specified collection is modified while the operation * is in progress. (This implies that the behavior of this call is * undefined if the specified collection is this list, and this * list is nonempty.) * * @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list * @return <tt>true</tt> if this list changed as a result of the call * @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null */ public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew); size += numNew; return numNew != 0; } /** * Inserts all of the elements in the specified collection into this * list, starting at the specified position. Shifts the element * currently at that position (if any) and any subsequent elements to * the right (increases their indices). The new elements will appear * in the list in the order that they are returned by the * specified collection's iterator. * * @param index index at which to insert the first element from the * specified collection * @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list * @return <tt>true</tt> if this list changed as a result of the call * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} * @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null */ public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount int numMoved = size - index; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew, numMoved); System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew); size += numNew; return numNew != 0; } /** * Removes from this list all of the elements whose index is between * {@code fromIndex}, inclusive, and {@code toIndex}, exclusive. * Shifts any succeeding elements to the left (reduces their index). * This call shortens the list by {@code (toIndex - fromIndex)} elements. * (If {@code toIndex==fromIndex}, this operation has no effect.) * * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if {@code fromIndex} or * {@code toIndex} is out of range * ({@code fromIndex < 0 || * fromIndex >= size() || * toIndex > size() || * toIndex < fromIndex}) */ protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) { modCount++; int numMoved = size - toIndex; System.arraycopy(elementData, toIndex, elementData, fromIndex, numMoved); // clear to let GC do its work int newSize = size - (toIndex-fromIndex); for (int i = newSize; i < size; i++) { elementData[i] = null; } size = newSize; } /** * Checks if the given index is in range. If not, throws an appropriate * runtime exception. This method does *not* check if the index is * negative: It is always used immediately prior to an array access, * which throws an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if index is negative. */ private void rangeCheck(int index) { if (index >= size) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); } /** * A version of rangeCheck used by add and addAll. */ private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) { if (index > size || index < 0) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); } /** * Constructs an IndexOutOfBoundsException detail message. * Of the many possible refactorings of the error handling code, * this "outlining" performs best with both server and client VMs. */ private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) { return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size; } /** * Removes from this list all of its elements that are contained in the * specified collection. * * @param c collection containing elements to be removed from this list * @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call * @throws ClassCastException if the class of an element of this list * is incompatible with the specified collection * (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>) * @throws NullPointerException if this list contains a null element and the * specified collection does not permit null elements * (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>), * or if the specified collection is null * @see Collection#contains(Object) */ public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) { Objects.requireNonNull(c); return batchRemove(c, false); } /** * Retains only the elements in this list that are contained in the * specified collection. In other words, removes from this list all * of its elements that are not contained in the specified collection. * * @param c collection containing elements to be retained in this list * @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call * @throws ClassCastException if the class of an element of this list * is incompatible with the specified collection * (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>) * @throws NullPointerException if this list contains a null element and the * specified collection does not permit null elements * (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>), * or if the specified collection is null * @see Collection#contains(Object) */ public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) { Objects.requireNonNull(c); return batchRemove(c, true); } private boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement) { final Object[] elementData = this.elementData; int r = 0, w = 0; boolean modified = false; try { for (; r < size; r++) if (c.contains(elementData[r]) == complement) elementData[w++] = elementData[r]; } finally { // Preserve behavioral compatibility with AbstractCollection, // even if c.contains() throws. if (r != size) { System.arraycopy(elementData, r, elementData, w, size - r); w += size - r; } if (w != size) { // clear to let GC do its work for (int i = w; i < size; i++) elementData[i] = null; modCount += size - w; size = w; modified = true; } } return modified; } /** * Save the state of the <tt>ArrayList</tt> instance to a stream (that * is, serialize it). * * @serialData The length of the array backing the <tt>ArrayList</tt> * instance is emitted (int), followed by all of its elements * (each an <tt>Object</tt>) in the proper order. */ private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s) throws java.io.IOException{ // Write out element count, and any hidden stuff int expectedModCount = modCount; s.defaultWriteObject(); // Write out size as capacity for behavioural compatibility with clone() s.writeInt(size); // Write out all elements in the proper order. for (int i=0; i<size; i++) { s.writeObject(elementData[i]); } if (modCount != expectedModCount) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } /** * Reconstitute the <tt>ArrayList</tt> instance from a stream (that is, * deserialize it). */ private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s) throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException { elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; // Read in size, and any hidden stuff s.defaultReadObject(); // Read in capacity s.readInt(); // ignored if (size > 0) { // be like clone(), allocate array based upon size not capacity ensureCapacityInternal(size); Object[] a = elementData; // Read in all elements in the proper order. for (int i=0; i<size; i++) { a[i] = s.readObject(); } } } /** * Returns a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper * sequence), starting at the specified position in the list. * The specified index indicates the first element that would be * returned by an initial call to {@link ListIterator#next next}. * An initial call to {@link ListIterator#previous previous} would * return the element with the specified index minus one. * * <p>The returned list iterator is <a href="#fail-fast"><i>fail-fast</i></a>. * * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) { if (index < 0 || index > size) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index); return new ListItr(index); } /** * Returns a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper * sequence). * * <p>The returned list iterator is <a href="#fail-fast"><i>fail-fast</i></a>. * * @see #listIterator(int) */ public ListIterator<E> listIterator() { return new ListItr(0); } /** * Returns an iterator over the elements in this list in proper sequence. * * <p>The returned iterator is <a href="#fail-fast"><i>fail-fast</i></a>. * * @return an iterator over the elements in this list in proper sequence */ public Iterator<E> iterator() { return new Itr(); } /** * 迭代器中有expectedModCount */ private class Itr implements Iterator<E> { int cursor; // 下一个返回元素的下标,默认是0 int lastRet = -1; // 上一个返回元素的下标。-1表示还没有返回 int expectedModCount = modCount; public boolean hasNext() { return cursor != size; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public E next() { /** * 检查expectedModCount与modCount是否相等,不相等表示已经被修改过,抛出异常 */ checkForComodification(); int i = cursor; if (i >= size) throw new NoSuchElementException(); Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; if (i >= elementData.length) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); cursor = i + 1; return (E) elementData[lastRet = i]; }
总结:
(01) ArrayList 实际上是通过一个数组去保存数据的。当我们构造ArrayList时;若使用默认构造函数,会先分配一个空数组,当第一次添加时,则扩容为默认容量大小10。
(02) 当ArrayList容量不足以容纳全部元素时,ArrayList会重新设置容量:newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1)。也就是为原数组容量的1.5倍。(如果超过最大容量,就设为最大容量)
(03) ArrayList的克隆函数,即是将全部元素克隆到一个数组中。
(04) ArrayList实现java.io.Serializable的方式。当写入到输出流时,先写入“容量”,再依次写入“每一个元素”;当读出输入流时,先读取“容量”,再依次读取“每一个元素”。
(05)源码中有个modCount变量,每做一次修改,都会增加一个。在迭代器中有expectedModCount变量,变量时会判断这两个变量是否相同。如果不相同,表示在遍历过程中,数组被修改过,抛出异常。fail-fast
第4部分 ArrayList遍历方式
ArrayList支持3种遍历方式
(01) 第一种,通过迭代器遍历。即通过Iterator去遍历。
Integer value = null;
Iterator iter = list.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
value = (Integer)iter.next();
}
(02) 第二种,随机访问,通过索引值去遍历。
由于ArrayList实现了RandomAccess接口,它支持通过索引值去随机访问元素。
Integer value = null;
int size = list.size();
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
value = (Integer)list.get(i);
}
(03) 第三种,for循环遍历。如下:
Integer value = null;
for (Integer integ:list) {
value = integ;
}
下面通过一个实例,比较这3种方式的效率,实例代码(ArrayListRandomAccessTest.java)如下:
 View Code
View Code运行结果:
iteratorThroughRandomAccess:3 ms
iteratorThroughIterator:8 ms
iteratorThroughFor2:5 ms
由此可见,遍历ArrayList时,使用随机访问(即,通过索引序号访问)效率最高,而使用迭代器的效率最低!
参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3308556.html,这篇文章是1.6,本文1.8