先上问题吧,我们统计了14天的气象数据(指标包括outlook,temperature,humidity,windy),并已知这些天气是否打球(play)。如果给出新一天的气象指标数据:sunny,cool,high,TRUE,判断一下会不会去打球。
table 1
| outlook | temperature | humidity | windy | play |
| sunny | hot | high | FALSE | no |
| sunny | hot | high | TRUE | no |
| overcast | hot | high | FALSE | yes |
| rainy | mild | high | FALSE | yes |
| rainy | cool | normal | FALSE | yes |
| rainy | cool | normal | TRUE | no |
| overcast | cool | normal | TRUE | yes |
| sunny | mild | high | FALSE | no |
| sunny | cool | normal | FALSE | yes |
| rainy | mild | normal | FALSE | yes |
| sunny | mild | normal | TRUE | yes |
| overcast | mild | high | TRUE | yes |
| overcast | hot | normal | FALSE | yes |
| rainy | mild | high | TRUE | no |
这个问题当然可以用朴素贝叶斯法求解,分别计算在给定天气条件下打球和不打球的概率,选概率大者作为推测结果。
现在我们使用ID3归纳决策树的方法来求解该问题。
预备知识:信息熵
熵是无序性(或不确定性)的度量指标。假如事件A的全概率划分是(A1,A2,...,An),每部分发生的概率是(p1,p2,...,pn),那信息熵定义为:

通常以2为底数,所以信息熵的单位是bit。
补充两个对数去处公式:

ID3算法
构造树的基本想法是随着树深度的增加,节点的熵迅速地降低。熵降低的速度越快越好,这样我们有望得到一棵高度最矮的决策树。
在没有给定任何天气信息时,根据历史数据,我们只知道新的一天打球的概率是9/14,不打的概率是5/14。此时的熵为:

属性有4个:outlook,temperature,humidity,windy。我们首先要决定哪个属性作树的根节点。
对每项指标分别统计:在不同的取值下打球和不打球的次数。
table 2
| outlook | temperature | humidity | windy | play | |||||||||
| yes | no | yes | no | yes | no | yes | no | yes | no | ||||
| sunny | 2 | 3 | hot | 2 | 2 | high | 3 | 4 | FALSE | 6 | 2 | 9 | 5 |
| overcast | 4 | 0 | mild | 4 | 2 | normal | 6 | 1 | TRUR | 3 | 3 | ||
| rainy | 3 | 2 | cool | 3 | 1 | |
|||||||
下面我们计算当已知变量outlook的值时,信息熵为多少。
outlook=sunny时,2/5的概率打球,3/5的概率不打球。entropy=0.971
outlook=overcast时,entropy=0
outlook=rainy时,entropy=0.971
而根据历史统计数据,outlook取值为sunny、overcast、rainy的概率分别是5/14、4/14、5/14,所以当已知变量outlook的值时,信息熵为:5/14 × 0.971 + 4/14 × 0 + 5/14 × 0.971 = 0.693
这样的话系统熵就从0.940下降到了0.693,信息增溢gain(outlook)为0.940-0.693=0.247
同样可以计算出gain(temperature)=0.029,gain(humidity)=0.152,gain(windy)=0.048。
gain(outlook)最大(即outlook在第一步使系统的信息熵下降得最快),所以决策树的根节点就取outlook。

接下来要确定N1取temperature、humidity还是windy?在已知outlook=sunny的情况,根据历史数据,我们作出类似table 2的一张表,分别计算gain(temperature)、gain(humidity)和gain(windy),选最大者为N1。
依此类推,构造决策树。当系统的信息熵降为0时,就没有必要再往下构造决策树了,此时叶子节点都是纯的--这是理想情况。最坏的情况下,决策树的高度为属性(决策变量)的个数,叶子节点不纯(这意味着我们要以一定的概率来作出决策)。
Java实现
最终的决策树保存在了XML中,使用了Dom4J,注意如果要让Dom4J支持按XPath选择节点,还得引入包jaxen.jar。程序代码要求输入文件满足ARFF格式,并且属性都是标称变量。
实验用的数据文件:
@relation weather.symbolic@attribute outlook {sunny, overcast, rainy}@attribute temperature {hot, mild, cool}@attribute humidity {high, normal}@attribute windy {TRUE, FALSE}@attribute play {yes, no}@datasunny,hot,high,FALSE,nosunny,hot,high,TRUE,noovercast,hot,high,FALSE,yesrainy,mild,high,FALSE,yesrainy,cool,normal,FALSE,yesrainy,cool,normal,TRUE,noovercast,cool,normal,TRUE,yessunny,mild,high,FALSE,nosunny,cool,normal,FALSE,yesrainy,mild,normal,FALSE,yessunny,mild,normal,TRUE,yesovercast,mild,high,TRUE,yesovercast,hot,normal,FALSE,yesrainy,mild,high,TRUE,no |
程序代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
|
package dt;import java.io.BufferedReader;import java.io.File;import java.io.FileReader;import java.io.FileWriter;import java.io.IOException;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Iterator;import java.util.LinkedList;import java.util.List;import java.util.regex.Matcher;import java.util.regex.Pattern;import org.dom4j.Document;import org.dom4j.DocumentHelper;import org.dom4j.Element;import org.dom4j.io.OutputFormat;import org.dom4j.io.XMLWriter;public class ID3 { private ArrayList<String> attribute = new ArrayList<String>(); // 存储属性的名称 private ArrayList<ArrayList<String>> attributevalue = new ArrayList<ArrayList<String>>(); // 存储每个属性的取值 private ArrayList<String[]> data = new ArrayList<String[]>();; // 原始数据 int decatt; // 决策变量在属性集中的索引 public static final String patternString = "@attribute(.*)[{](.*?)[}]"; Document xmldoc; Element root; public ID3() { xmldoc = DocumentHelper.createDocument(); root = xmldoc.addElement("root"); root.addElement("DecisionTree").addAttribute("value", "null"); } public static void main(String[] args) { ID3 inst = new ID3(); inst.readARFF(new File("/home/orisun/test/weather.nominal.arff")); inst.setDec("play"); LinkedList<Integer> ll=new LinkedList<Integer>(); for(int i=0;i<inst.attribute.size();i++){ if(i!=inst.decatt) ll.add(i); } ArrayList<Integer> al=new ArrayList<Integer>(); for(int i=0;i<inst.data.size();i++){ al.add(i); } inst.buildDT("DecisionTree", "null", al, ll); inst.writeXML("/home/orisun/test/dt.xml"); return; } //读取arff文件,给attribute、attributevalue、data赋值 public void readARFF(File file) { try { FileReader fr = new FileReader(file); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr); String line; Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(patternString); while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(line); if (matcher.find()) { attribute.add(matcher.group(1).trim()); String[] values = matcher.group(2).split(","); ArrayList<String> al = new ArrayList<String>(values.length); for (String value : values) { al.add(value.trim()); } attributevalue.add(al); } else if (line.startsWith("@data")) { while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { if(line=="") continue; String[] row = line.split(","); data.add(row); } } else { continue; } } br.close(); } catch (IOException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } } //设置决策变量 public void setDec(int n) { if (n < 0 || n >= attribute.size()) { System.err.println("决策变量指定错误。"); System.exit(2); } decatt = n; } public void setDec(String name) { int n = attribute.indexOf(name); setDec(n); } //给一个样本(数组中是各种情况的计数),计算它的熵 public double getEntropy(int[] arr) { double entropy = 0.0; int sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { entropy -= arr[i] * Math.log(arr[i]+Double.MIN_VALUE)/Math.log(2); sum += arr[i]; } entropy += sum * Math.log(sum+Double.MIN_VALUE)/Math.log(2); entropy /= sum; return entropy; } //给一个样本数组及样本的算术和,计算它的熵 public double getEntropy(int[] arr, int sum) { double entropy = 0.0; for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { entropy -= arr[i] * Math.log(arr[i]+Double.MIN_VALUE)/Math.log(2); } entropy += sum * Math.log(sum+Double.MIN_VALUE)/Math.log(2); entropy /= sum; return entropy; } public boolean infoPure(ArrayList<Integer> subset) { String value = data.get(subset.get(0))[decatt]; for (int i = 1; i < subset.size(); i++) { String next=data.get(subset.get(i))[decatt]; //equals表示对象内容相同,==表示两个对象指向的是同一片内存 if (!value.equals(next)) return false; } return true; } // 给定原始数据的子集(subset中存储行号),当以第index个属性为节点时计算它的信息熵 public double calNodeEntropy(ArrayList<Integer> subset, int index) { int sum = subset.size(); double entropy = 0.0; int[][] info = new int[attributevalue.get(index).size()][]; for (int i = 0; i < info.length; i++) info[i] = new int[attributevalue.get(decatt).size()]; int[] count = new int[attributevalue.get(index).size()]; for (int i = 0; i < sum; i++) { int n = subset.get(i); String nodevalue = data.get(n)[index]; int nodeind = attributevalue.get(index).indexOf(nodevalue); count[nodeind]++; String decvalue = data.get(n)[decatt]; int decind = attributevalue.get(decatt).indexOf(decvalue); info[nodeind][decind]++; } for (int i = 0; i < info.length; i++) { entropy += getEntropy(info[i]) * count[i] / sum; } return entropy; } // 构建决策树 public void buildDT(String name, String value, ArrayList<Integer> subset, LinkedList<Integer> selatt) { Element ele = null; @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") List<Element> list = root.selectNodes("//"+name); Iterator<Element> iter=list.iterator(); while(iter.hasNext()){ ele=iter.next(); if(ele.attributeValue("value").equals(value)) break; } if (infoPure(subset)) { ele.setText(data.get(subset.get(0))[decatt]); return; } int minIndex = -1; double minEntropy = Double.MAX_VALUE; for (int i = 0; i < selatt.size(); i++) { if (i == decatt) continue; double entropy = calNodeEntropy(subset, selatt.get(i)); if (entropy < minEntropy) { minIndex = selatt.get(i); minEntropy = entropy; } } String nodeName = attribute.get(minIndex); selatt.remove(new Integer(minIndex)); ArrayList<String> attvalues = attributevalue.get(minIndex); for (String val : attvalues) { ele.addElement(nodeName).addAttribute("value", val); ArrayList<Integer> al = new ArrayList<Integer>(); for (int i = 0; i < subset.size(); i++) { if (data.get(subset.get(i))[minIndex].equals(val)) { al.add(subset.get(i)); } } buildDT(nodeName, val, al, selatt); } } // 把xml写入文件 public void writeXML(String filename) { try { File file = new File(filename); if (!file.exists()) file.createNewFile(); FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(file); OutputFormat format = OutputFormat.createPrettyPrint(); // 美化格式 XMLWriter output = new XMLWriter(fw, format); output.write(xmldoc); output.close(); } catch (IOException e) { System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } }} |
最终生成的文件如下:
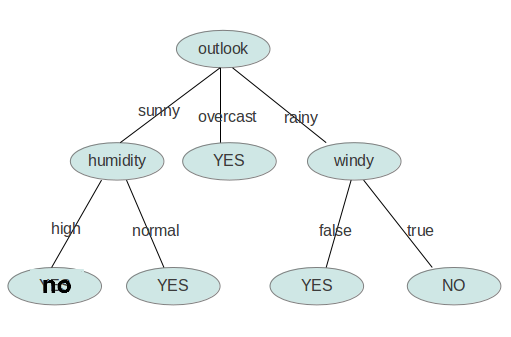
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><root> <DecisionTree value="null"> <outlook value="sunny"> <humidity value="high">no</humidity> <humidity value="normal">yes</humidity> </outlook> <outlook value="overcast">yes</outlook> <outlook value="rainy"> <windy value="TRUE">no</windy> <windy value="FALSE">yes</windy> </outlook> </DecisionTree></root> |
用图形象地表示就是: