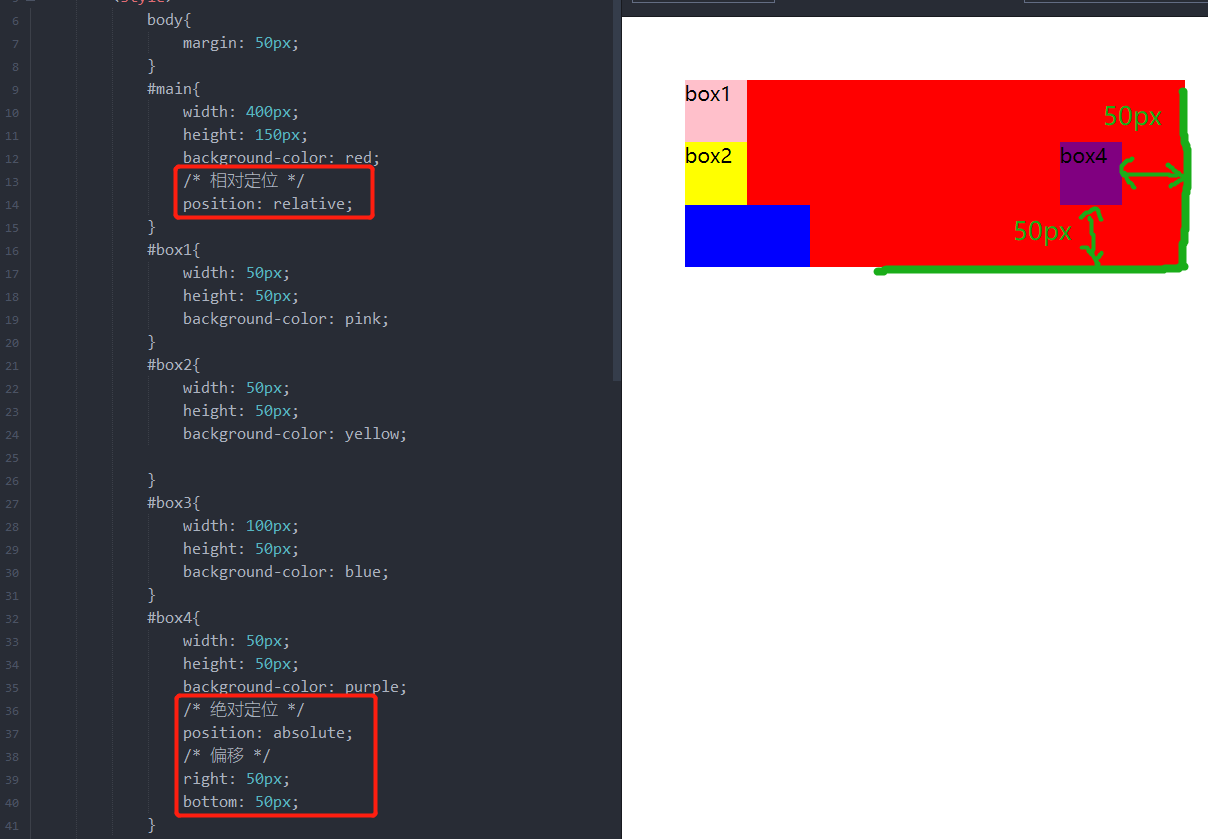
position 的值为 absolute 时,就是开启了绝对定位。
元素设置绝对定位以后,如果不设置偏移量,元素的位置不会发生变化。
绝对定位的元素是相对于距离他最近的祖先元素进行定位,如果所有的祖先元素都没有开启定位,则相对于浏览器窗口进行定位。
绝对定位的元素会完全脱离文档流。
绝对定位会改变元素的性质。内联变块,块的高度和宽度都被内容撑开,并且不独占一行。
绝对定位会使元素提升一个层级。
例子
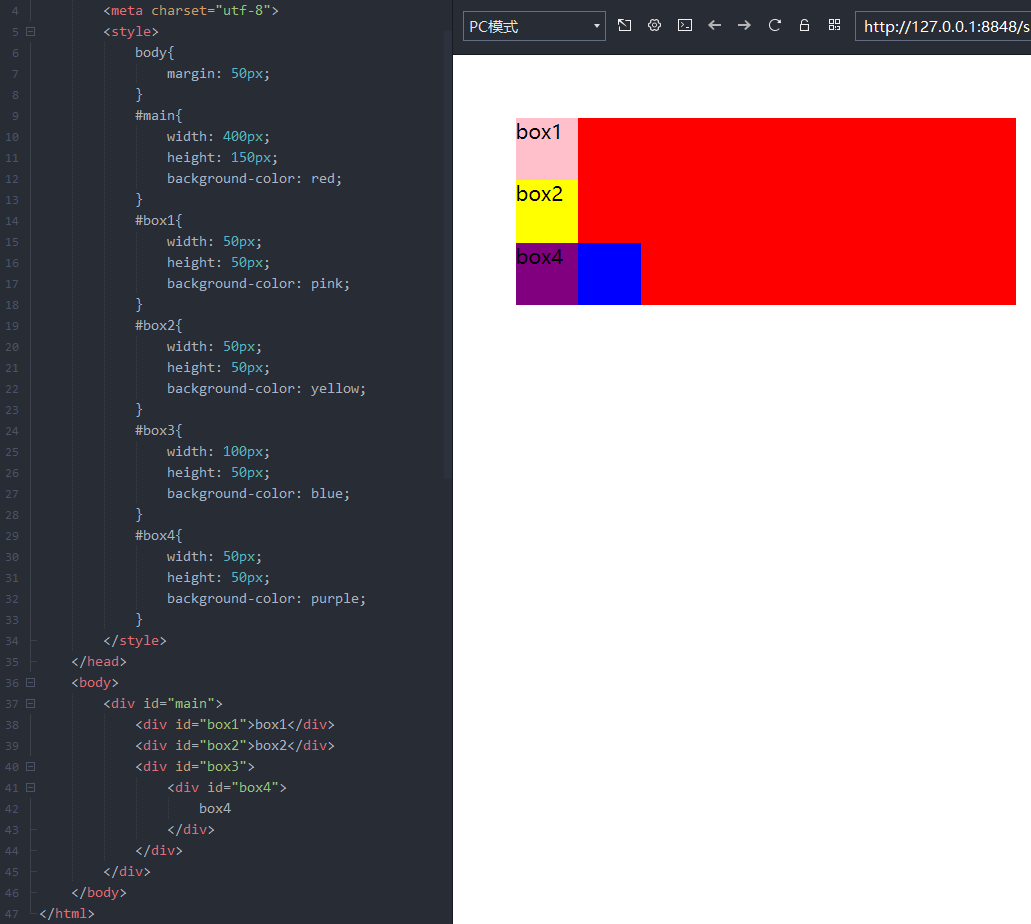
未设置绝对定位时

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <style> body{ margin: 50px; } #main{ width: 400px; height: 150px; background-color: red; } #box1{ width: 50px; height: 50px; background-color: pink; } #box2{ width: 50px; height: 50px; background-color: yellow; } #box3{ width: 100px; height: 50px; background-color: blue; } #box4{ width: 50px; height: 50px; background-color: purple; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="main"> <div id="box1">box1</div> <div id="box2">box2</div> <div id="box3"> <div id="box4"> box4 </div> </div> </div> </body> </html>
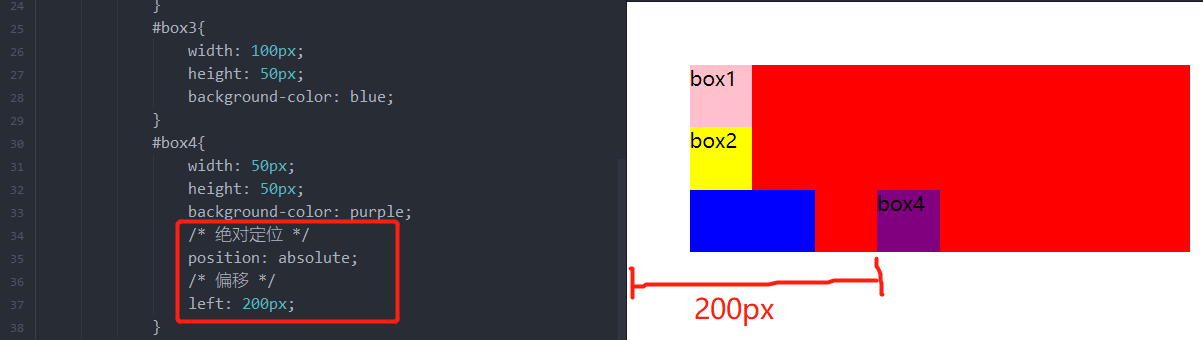
绝对定位的元素是相对于距离他最近的祖先元素进行定位,如果所有的祖先元素都没有开启定位,则相对于浏览器窗口进行定位。
在上面代码的基础上,在样式 box4 上开启绝对定位,设置偏移量为 left: 200px。因为盒子 box4 的所有祖先元素都没有开启定位,所以盒子相对浏览器窗口定位,因为设置了 left: 200px,所以只改变盒子左边边到浏览器的距离,设置之后,浏览器在盒子左边边的左 200px 处。
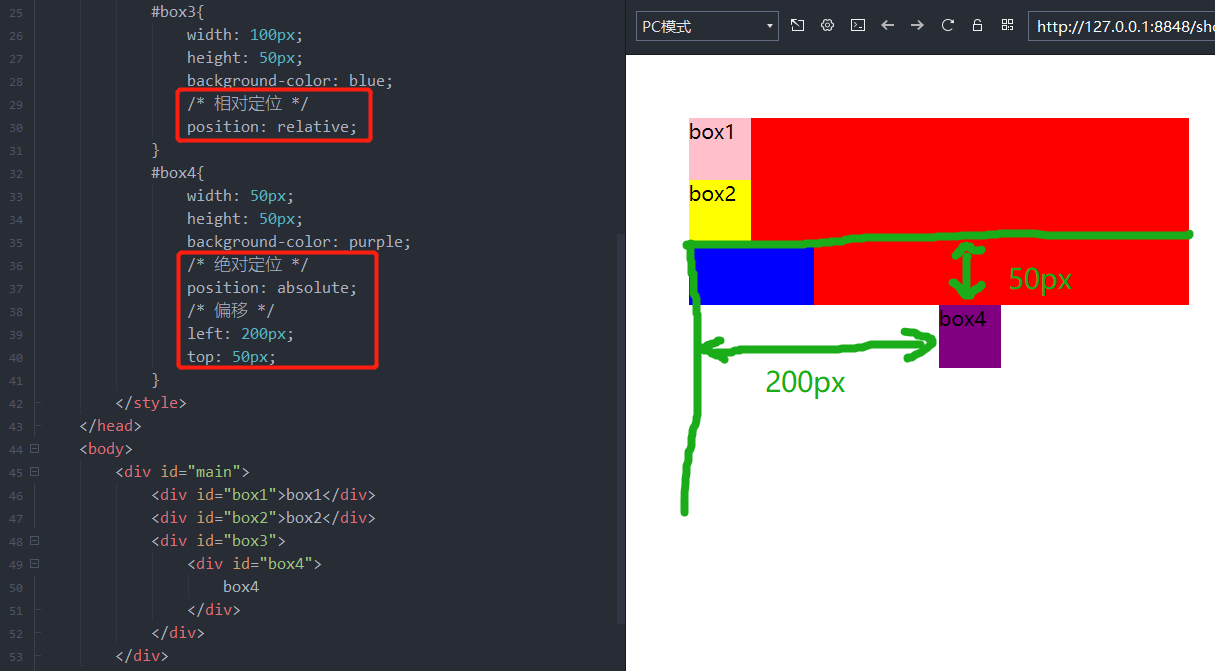
如果祖先元素开启了定位,则相对祖先元素进行定位。下面在盒子 box4 上开启绝对定位,在盒子 box4 的祖先元素之一盒子 box3 上开启相对定位,在盒子 box4 上设置偏移量,则盒子 box4 相对 box3 定位。

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <style> body{ margin: 50px; } #main{ width: 400px; height: 150px; background-color: red; /* 相对定位 */ position: relative; } #box1{ width: 50px; height: 50px; background-color: pink; } #box2{ width: 50px; height: 50px; background-color: yellow; } #box3{ width: 100px; height: 50px; background-color: blue; } #box4{ width: 50px; height: 50px; background-color: purple; /* 绝对定位 */ position: absolute; /* 偏移 */ right: 50px; bottom: 50px; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="main"> <div id="box1">box1</div> <div id="box2">box2</div> <div id="box3"> <div id="box4"> box4 </div> </div> </div> </body> </html>
如果想要相对别的祖先元素定位,就在别的祖先元素上开启定位。这里在 main 盒子上开启相对定位,则盒子 box4 相对盒子 main 定位。