定义
- 若左子树非空,则左子树上所有结点关键字值均小于根节点关键字值
- 若右子树非空,则右子树上所有节点关键字值均大于根节点关键字值
- 左,右子树分别是一颗二叉排序树
二叉排序树插入
二查排序树插入定义:若原二叉树为空,则直接插入节点。否则,若关键字K小于根节点关键字,则插入到左子树中。若关键字K大于根节点关键字,则插入到右子树当中。插入的时间复杂度是树高O(H)
public void insert(Node p, int k) { if (p != null) { if (k < p.val) if (p.LChild == null) { p.LChild = new Node(); p.LChild.val = k; } else insert(p.LChild, k); else { if (p.RChild == null) { p.RChild = new Node(); p.RChild.val = k; } else insert(p.RChild, k); } } }
二叉排序树的删除
删除分三种情况:
- 如果被删除的节点是叶子节点,就直接删除
- 如果被删除的节点只有左子树或右子树,则将其左子树或右子树代替该节点
- 如果左右子树都存在,那么则将其右子树中序遍历的第一个节点First替换该节点(值替换),并将First从树中删除
- 删除节点的时间复杂度为O(H)
public void delete(int k) { Node parent = new Node(); parent.LChild = node; Node p = node; Node t = null; // 找出欲删除的节点P while (p != null && p.val != k) { parent = p; if (k < p.val) p = p.LChild; else p = p.RChild; } // 欲删节点的左右孩子都不为空 if (p.LChild != null && p.RChild != null) { // 找出p的后继节点(中序遍历) Node post = inOrderFisrt(p.RChild); // 将后继节点值copy给p p.val = post.val; // 将欲删除的节点修改为post节点 p = post; } // 欲删节点的左孩子或右孩子为空 if (p.LChild == null) t = p.RChild; else if (p.RChild == null) t = p.LChild; if (p == parent.LChild) parent.LChild = t; else parent.RChild = t; }
中序遍历查找第一个节点
private Node inOrderFisrt(Node t) { Node p = null; while (t != null) { p = t; t = t.LChild; } return p; }
二叉排序树构造
在构造二查排序树时,只需要不断调用二叉排序树的插入算法即可。下面的代码是不断从一个数组中取出欲插入的数,然后调用insert方法将其插入到二叉树当中。
private void initBST(Node node, int[] arr) { for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) { insert(node, arr[i]); } }
二叉排序树的查找
查找算法用递归实现,每次查找时都与根节点进行比较,如果小于根节点,则往左子树上走。否则,向右子树上走。
public Node search(Node p, int k) { if (p != null) { if (p.val == k) return p; else { if (k > p.val) return search(p.RChild, k); else return search(p.LChild, k); } } else return null; }
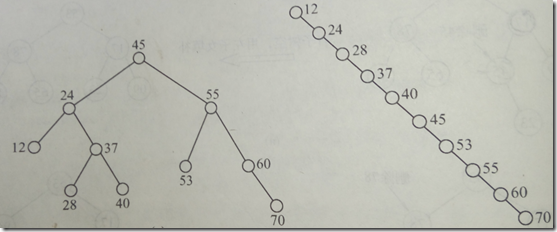
查找效率分析
二叉排序树的查找效率和树的构造有关。如果树的左右子树高度相当,那么查找效率为O(logN),否则效率就很低,最低为O(N)。列如下面两棵树,同样找节点70,则左边的效率明显比右边的高。