代码地址:https://gitee.com/xiexiandong/abc_bigdata.git
一、窗口函数
- 在定义了窗口分配器之后,我们需要为每一个窗口明确的指定计算逻辑,这个就是窗口函数要做的事情,当系统决定一个窗口已经准备好执行之后,这个窗口函数将被用 来处理窗口中的每一个元素(可能是分组的)。
1.ReduceFunction
- 含义:ReduceFunction定义了如何把两个输入的元素进行合并来生成相同类型的输出元素的过程, Flink使用ReduceFunction来对窗口中的元素进行增量聚合

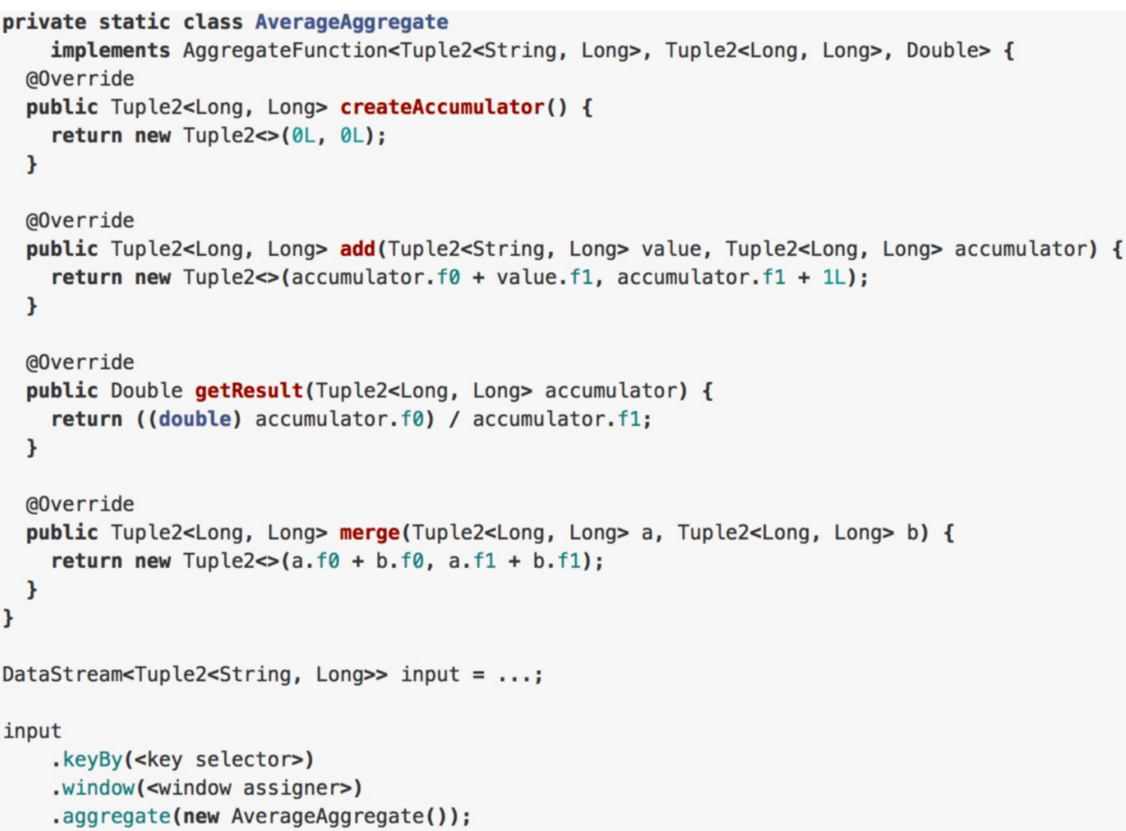
2.AggregateFunction
- AggregateFunction是ReduceFunction的 普适版本,它需要指定三个类型:输入类 型(IN)、累加器类型(ACC)和输出类型 (OUT)。输入类型是输入流中的元素类型, AggregateFunction有一个方法可以将一个输入元素添加到一个累加器中。该接口还具有创建初始累加器、将两个累加 器合并到一个累加器以及从累加器中提 取输出(类 型为OUT)的方法。
3、FoldFunction
- 含义:FoldFunction指定了一个输入元素如何与一个指定输出类型的元素合并的过程,这个FoldFunction 会被每一个加入到窗口中的元素和当前的输出值增量地调用,第一个元 组合(混搭)

4、WindowFunction/AllWindowFunction
- 含义:一个WindowFunction将获得一个包含了window中的所有元素迭代(Iterable),并且提供灵活性。这些带来了性能的成本和资源的消耗,因为window中的元素无法 进行增量迭代,而是缓存起来直到window被认为是可以处理时为止
- 可以跟ReduceFunction /AggregateFunction/FoldFunction结合使用

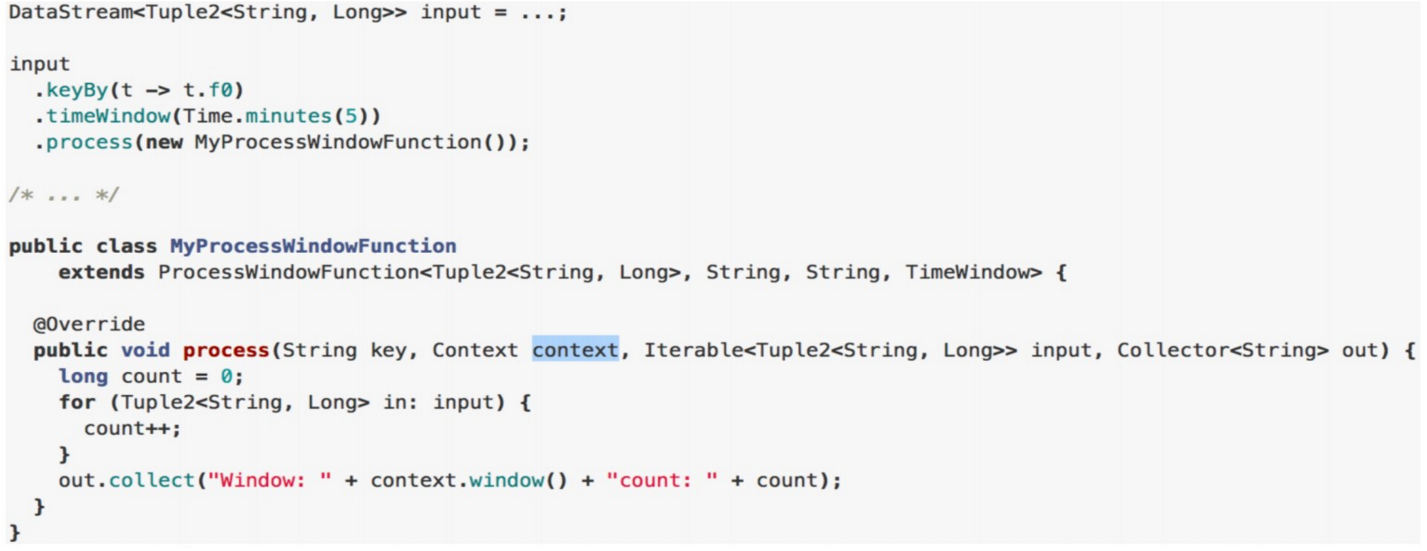
5、ProcessWindowFunction/ProcessAllWindowFunction
- 含义:ProcessWindowFunction获得一个包含窗口所有元素的可迭代器,以及一个具有时间和状态信息访问权的上下文对象,这使得它比其他窗口函数提供更大的灵活 性。这是以性能和资源消耗为代价的,因为元素不能增量地聚合,而是需要在内部缓冲,直到认为窗口可以处理为止。
- WindowFunctionde的升级版,可以跟ReduceFunction / AggregateFunction/FoldFunction结合使用。
二、windows的operator demo
1、Windows的基础使用
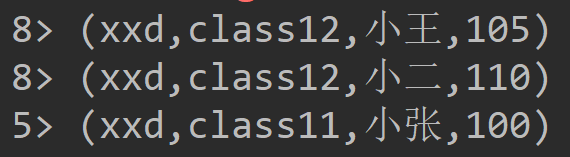
import org.apache.flink.configuration.{ConfigConstants, Configuration} import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala.{DataStream, StreamExecutionEnvironment} object ReduceFunctionOnCountWindow { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { import org.apache.flink.api.scala._ //生成配置对象 val config = new Configuration() //开启spark-webui config.setBoolean(ConfigConstants.LOCAL_START_WEBSERVER, true) //配置webui的日志文件,否则打印日志到控制台 config.setString("web.log.path", "/tmp/logs/flink_log") //配置taskManager的日志文件,否则打印日志到控制台 config.setString(ConfigConstants.TASK_MANAGER_LOG_PATH_KEY, "/tmp/logs/flink_log") //配置tm有多少个slot config.setString("taskmanager.numberOfTaskSlots", "8") // 获取运行环境 val env: StreamExecutionEnvironment = StreamExecutionEnvironment.createLocalEnvironmentWithWebUI(config) val tuple = List( ("xxd", "class12", "小王", 50), ("xxd", "class12", "小李", 55), ("xxd", "class12", "小二", 55), ("xxd", "class12", "小三", 55), ("xxd", "class11", "小张", 50), ("xxd", "class11", "小孙", 50)) // 定义socket数据源,使用集合生成 val input = env.fromCollection(tuple) //先分组,然后数据按分组进行不同的窗口,当窗口数据量达到两条时,启动reduce计算两条记录的分组合 val windows: DataStream[(String, String, String, Int)] = input.keyBy(1).countWindow(2).reduce((a, b) => (a._1, a._2, a._3, a._4 + b._4)) windows.print() env.execute() } }
结果:
import org.apache.flink.configuration.{ConfigConstants, Configuration} import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala.{DataStream, StreamExecutionEnvironment} object ReduceFunctionOnCountWindowAll { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { import org.apache.flink.api.scala._ //生成配置对象 val config = new Configuration() //开启spark-webui config.setBoolean(ConfigConstants.LOCAL_START_WEBSERVER, true) //配置webui的日志文件,否则打印日志到控制台 config.setString("web.log.path", "/tmp/logs/flink_log") //配置taskManager的日志文件,否则打印日志到控制台 config.setString(ConfigConstants.TASK_MANAGER_LOG_PATH_KEY, "/tmp/logs/flink_log") //配置tm有多少个slot config.setString("taskmanager.numberOfTaskSlots", "8") // 获取运行环境 val env: StreamExecutionEnvironment = StreamExecutionEnvironment.createLocalEnvironmentWithWebUI(config) val tuple = List( ("xxd", "class12", "小王", 50), ("xxd", "class11", "小李", 55), ("xxd", "class12", "小张", 50), ("xxd", "class11", "小孙", 45), ("xxd", "class11", "小强", 45)) // 定义socket数据源,使用集合生成 val input = env.fromCollection(tuple) //先分组,然后数据按分组进行不同的窗口,当窗口数据量达到两条时,启动reduce计算两条记录的分组合 //WindowAll与Windows的区别是一个windows里的数据只能在一个task中进行运行 val windows: DataStream[(String, String, String, Int)] = input.keyBy(1).countWindowAll(2).reduce((a, b) => (a._1 + " " + b._1, a._2 + " " + b._2, a._3 + " " + b._3, a._4 + b._4)) windows.print() env.execute() } }
2、Windows的Aggregate窗口自定义聚合函数
import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.AggregateFunction import org.apache.flink.configuration.{ConfigConstants, Configuration} import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala.StreamExecutionEnvironment object AggFunctionOnCountWindow { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { import org.apache.flink.api.scala._ //生成配置对象 val config = new Configuration() //开启spark-webui config.setBoolean(ConfigConstants.LOCAL_START_WEBSERVER, true) //配置webui的日志文件,否则打印日志到控制台 config.setString("web.log.path", "/tmp/logs/flink_log") //配置taskManager的日志文件,否则打印日志到控制台 config.setString(ConfigConstants.TASK_MANAGER_LOG_PATH_KEY, "/tmp/logs/flink_log") //配置tm有多少个slot config.setString("taskmanager.numberOfTaskSlots", "8") // 获取运行环境 val env: StreamExecutionEnvironment = StreamExecutionEnvironment.createLocalEnvironmentWithWebUI(config) val tuple = List( ("xxd", "class12", "小王", 50), ("xxd", "class11", "小张", 50), ("xxd", "class12", "小李", 55)) // 定义socket数据源,使用集合生成 val input = env.fromCollection(tuple) //先分组,然后数据按分组进行不同的窗口,当窗口数据量达到两条时,启动aggregate计算两条记录的分组合 input .keyBy(1) .countWindow(2) .aggregate(new SumAggregate) .print() env.execute() } } class SumAggregate extends AggregateFunction[(String, String, String, Int), (String, Long), (String, Long)] { /** * 创建累加器来保存中间状态(name和count) */ override def createAccumulator(): (String, Long) = { ("", 0L) } /** * 将元素添加到累加器并返回新的累加器value */ override def add(value: (String, String, String, Int), accumulator: (String, Long)): (String, Long) = { (s"${value._3} ${accumulator._1}", accumulator._2 + value._4) } /** * 从累加器提取结果 */ override def getResult(accumulator: (String, Long)): (String, Long) = { accumulator } /** * 合并两个累加器并返回 */ override def merge(a: (String, Long), b: (String, Long)): (String, Long) = { (s"${a._1} ${b._1}", a._2 + b._2) } }
3、Windows的Process窗口自定义聚合函数
import org.apache.flink.configuration.{ConfigConstants, Configuration} import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala.StreamExecutionEnvironment import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala.function.ProcessWindowFunction import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.windows.GlobalWindow import org.apache.flink.util.Collector object ProcessWinFunOnCountWindow { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { import org.apache.flink.api.scala._ //生成配置对象 val config = new Configuration() //开启spark-webui config.setBoolean(ConfigConstants.LOCAL_START_WEBSERVER, true) //配置webui的日志文件,否则打印日志到控制台 config.setString("web.log.path", "/tmp/logs/flink_log") //配置taskManager的日志文件,否则打印日志到控制台 config.setString(ConfigConstants.TASK_MANAGER_LOG_PATH_KEY, "/tmp/logs/flink_log") //配置tm有多少个slot config.setString("taskmanager.numberOfTaskSlots", "8") // 获取运行环境 val env: StreamExecutionEnvironment = StreamExecutionEnvironment.createLocalEnvironmentWithWebUI(config) val tuple = List( ("xxd", "class12", "小王", 50), ("xxd", "class11", "小张", 50), ("xxd", "class12", "小李", 55)) // 定义socket数据源,使用集合生成 val input = env.fromCollection(tuple) //先分组,然后数据按分组进行不同的窗口,当窗口数据量达到两条时,启动process计算两条记录的平均值 input .keyBy(f => f._2) .countWindow(2) .process(new AvgProcessWindowFunction) .print() env.execute() } } class AvgProcessWindowFunction extends ProcessWindowFunction[(String, String, String, Int), String, String, GlobalWindow] { /** * 分组并计算windows里所有数据的平均值 * * @param key 分组key * @param context windows上下文 * @param elements 分组的value * @param out operator的输出结果 */ override def process(key: String, context: Context, elements: Iterable[(String, String, String, Int)], out: Collector[String]): Unit = { var sum = 0 var count = 0 for (in <- elements) { sum += in._4 count += 1 } out.collect(s"Window:${context.window} count:${count} avg:${sum / count}"); } }
4、windows join
- cogroup
- 侧重于group,是对同一个key上的两组集合进行操作
- CoGroup的作用和join基本相同,但有一点不一样的是,如果未能找到新到来的数据与另一个流在window中存在的匹配数据,仍会可将其输出
- 只能在window中用
import org.apache.flink.configuration.{ConfigConstants, Configuration} import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala.{DataStream, StreamExecutionEnvironment} import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.assigners.ProcessingTimeSessionWindows import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.time.Time import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.triggers.CountTrigger import org.apache.flink.util.Collector import scala.collection.mutable.ListBuffer object CoGroupOnSessionWindow { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { import org.apache.flink.api.scala._ //生成配置对象 val config = new Configuration() //开启spark-webui config.setBoolean(ConfigConstants.LOCAL_START_WEBSERVER, true) //配置webui的日志文件,否则打印日志到控制台 config.setString("web.log.path", "/tmp/logs/flink_log") //配置taskManager的日志文件,否则打印日志到控制台 config.setString(ConfigConstants.TASK_MANAGER_LOG_PATH_KEY, "/tmp/logs/flink_log") //配置tm有多少个slot config.setString("taskmanager.numberOfTaskSlots", "8") // 获取运行环境 val env: StreamExecutionEnvironment = StreamExecutionEnvironment.createLocalEnvironmentWithWebUI(config) // 定义socket数据源1 val input1 = env.socketTextStream("localhost", 6666, ' ') val map1: DataStream[(String, Int)] = input1.flatMap(_.split(" ")).map((_, 1)) // 定义socket数据源2 val input2 = env.socketTextStream("localhost", 7777, ' ') val map2: DataStream[(String, Int)] = input2.flatMap(_.split(" ")).map((_, 1)) /** * 1、创建两个socket stream。输入的字符串以空格为界分割成Array[String]。然后再取出其中前两个元素组成(String, String)类型的tuple。 * 2、join条件为两个流中的数据((String, String))第一个元素相同。 * 3、为测试方便,这里使用session window。只有两个元素到来时间前后相差不大于10秒之时才会被匹配。 * Session window的特点为,没有固定的开始和结束时间,只要两个元素之间的时间间隔不大于设定值,就会分配到同一个window中,否则后来的元素会进入新的window。 * 4、将window默认的trigger修改为count trigger。这里的含义为每到来一个元素,都会立刻触发计算。 * 5、由于设置的并行度为8,所以有8个task * 6、所以两边相同的key会跑到其中一个task中,这样才能达到join的目的 * 但是由于使用的是cogroup所以两边流跑到一个task中的key无论能不能匹配,都会以执行打印 * 不能匹配的原因可能其中一个流相同的那个key还没有发送过来 * */ map1.coGroup(map2) .where(_._1) .equalTo(_._1) .window(ProcessingTimeSessionWindows.withGap(Time.seconds(10))) .trigger(CountTrigger.of(1)) .apply((a, b, o: Collector[String]) => { val list: ListBuffer[String] = ListBuffer[String]("Data in stream1: ") a.foreach(f => list += s"${f._1}<->${f._2} ") list += "Data in stream2: " b.foreach(f => list += s"${f._1}<->${f._2} ") o.collect(list.reduce(_ + _)) }).print() env.execute() } }
- join
-
而join是对同一个key上的每对元素进行操作
-
类似inner join
-
按照一定条件分别取出两个流中匹配的元素,返回给下游处理
-
Join是cogroup 的特例
-
只能在window中用
-
import org.apache.flink.configuration.{ConfigConstants, Configuration} import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala.{DataStream, StreamExecutionEnvironment} import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.assigners.ProcessingTimeSessionWindows import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.time.Time import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.triggers.CountTrigger object JoinOnSessionWindow { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { import org.apache.flink.api.scala._ //生成配置对象 val config = new Configuration() //开启spark-webui config.setBoolean(ConfigConstants.LOCAL_START_WEBSERVER, true) //配置webui的日志文件,否则打印日志到控制台 config.setString("web.log.path", "/tmp/logs/flink_log") //配置taskManager的日志文件,否则打印日志到控制台 config.setString(ConfigConstants.TASK_MANAGER_LOG_PATH_KEY, "/tmp/logs/flink_log") //配置tm有多少个slot config.setString("taskmanager.numberOfTaskSlots", "8") // 获取运行环境 val env: StreamExecutionEnvironment = StreamExecutionEnvironment.createLocalEnvironmentWithWebUI(config) // 定义socket数据源1 val input1 = env.socketTextStream("localhost", 6666, ' ') val map1: DataStream[(String, Int)] = input1.flatMap(_.split(" ")).map((_, 1)) // 定义socket数据源2 val input2 = env.socketTextStream("localhost", 7777, ' ') val map2: DataStream[(String, Int)] = input2.flatMap(_.split(" ")).map((_, 1)) /** * 1、创建两个个socket stream。输入的字符串以空格为界分割成Array[String]。然后再取出其中前两个元素组成(String, String)类型的tuple。 * 2、join条件为两个流中的数据((String, String))第一个元素相同。 * 3、为测试方便,这里使用session window。只有两个元素到来时间前后相差不大于10秒之时才会被匹配。 * Session window的特点为,没有固定的开始和结束时间,只要两个元素之间的时间间隔不大于设定值,就会分配到同一个window中,否则后来的元素会进入新的window。 * 4、将window默认的trigger修改为count trigger。这里的含义为每到来一个元素,都会立刻触发计算。 * 5、处理匹配到的两个数据,例如到来的数据为(1, "xxd")和(1, "xxd"),输出到下游则为"xxd == xxd" * 6、结论: * a、join只返回匹配到的数据对。若在window中没有能够与之匹配的数据,则不会有输出。 * b、join会输出window中所有的匹配数据对。 * c、不在window内的数据不会被匹配到。 **/ map1.join(map2) .where(_._1) .equalTo(_._1) .window(ProcessingTimeSessionWindows.withGap(Time.seconds(10))) .trigger(CountTrigger.of(1)) .apply((a, b) => { s"${a._1} == ${b._1}" }).print() env.execute() } }
- Interval Join
- KeyedStream,KeyedStream → DataStream
- 在给定的时间边界内(默认包含边界),相当于一个窗口,按照指定的key对两个KeyedStream进行join操作,把符合join条件的两个event拉到一起,然后怎么处理由用 户你来定义。
- key1 == key2 && e1.timestamp + lowerBound <= e2.timestamp <= e1.timestamp + upperBound
import org.apache.flink.configuration.{ConfigConstants, Configuration} import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala.{DataStream, KeyedStream, StreamExecutionEnvironment} import org.apache.flink.api.scala._ import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.TimeCharacteristic import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.co.ProcessJoinFunction import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.timestamps.AscendingTimestampExtractor import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.time.Time import org.apache.flink.util.Collector case class MyClass(school: String, classs: String, name: String, time: Long) case class MyResult(name: String, result: Int, time: Long) case class MyJoin(classs: String, name: String, result: Int) object IntervalJoin { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { //生成配置对象 val config = new Configuration() //开启spark-webui config.setBoolean(ConfigConstants.LOCAL_START_WEBSERVER, true) //配置webui的日志文件,否则打印日志到控制台 config.setString("web.log.path", "/tmp/flink_log") //配置taskManager的日志文件,否则打印日志到控制台 config.setString(ConfigConstants.TASK_MANAGER_LOG_PATH_KEY, "/tmp/flink_log") //配置tm有多少个slot config.setString("taskmanager.numberOfTaskSlots", "8") // 获取运行环境 val env: StreamExecutionEnvironment = StreamExecutionEnvironment.createLocalEnvironmentWithWebUI(config) //设置流数据处理的时间为事件时间 env.setStreamTimeCharacteristic(TimeCharacteristic.EventTime) val tuple = List( MyClass("xxd", "class12", "小王", System.currentTimeMillis), MyClass("xxd", "class12", "小李", System.currentTimeMillis), MyClass("xxd", "class11", "小张", System.currentTimeMillis), MyClass("xxd", "class11", "小强", System.currentTimeMillis)) val tuple2 = List( MyResult("小王", 88, System.currentTimeMillis), MyResult("小李", 88, System.currentTimeMillis), MyResult("小张", 88, System.currentTimeMillis), MyResult("小强", 88, System.currentTimeMillis)) val input1: DataStream[MyClass] = env.fromCollection(tuple).assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(new AscendingTimestampExtractor[MyClass] { override def extractAscendingTimestamp(element: MyClass): Long = { element.time } }) val input2: DataStream[MyResult] = env.fromCollection(tuple2).assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(new AscendingTimestampExtractor[MyResult] { override def extractAscendingTimestamp(element: MyResult): Long = { element.time } }) val keyedStream: KeyedStream[MyClass, String] = input1.keyBy(_.name) val otherKeyedStream: KeyedStream[MyResult, String] = input2.keyBy(_.name) //e1.timestamp + lowerBound <= e2.timestamp <= e1.timestamp + upperBound // key1 == key2 && leftTs - 20 <= rightTs <= leftTs + 20 keyedStream.intervalJoin(otherKeyedStream) .between(Time.milliseconds(-20), Time.milliseconds(20)) .upperBoundExclusive() .lowerBoundExclusive() .process(new ProcessJoinFunction[MyClass, MyResult, MyJoin]() { override def processElement(left: MyClass, right: MyResult, ctx: ProcessJoinFunction[MyClass, MyResult, MyJoin]#Context, out: Collector[MyJoin]) = { out.collect(MyJoin(left.classs, left.name, right.result)) } }).print() env.execute("IntervalJoin") } }