代码示例:
public static boolean acquire(RedissonClient redisson, String lockKey, Long waitTime, Long leaseTime) {
// 实例化锁对象(此时未请求redis) RLock lock = redisson.getLock(lockKey); boolean lockResult; try { lock.lock();
// 加锁 lockResult = lock.tryLock(waitTime, leaseTime, TimeUnit.SECONDS); }catch (Exception e){ lockResult = false; } if (lockResult){ log.info("======lock success <"+lockKey+">======"+Thread.currentThread().getName()); }else { log.error("======lock error <"+lockKey+">======"+Thread.currentThread().getName()); } //加锁成功 return lockResult; }
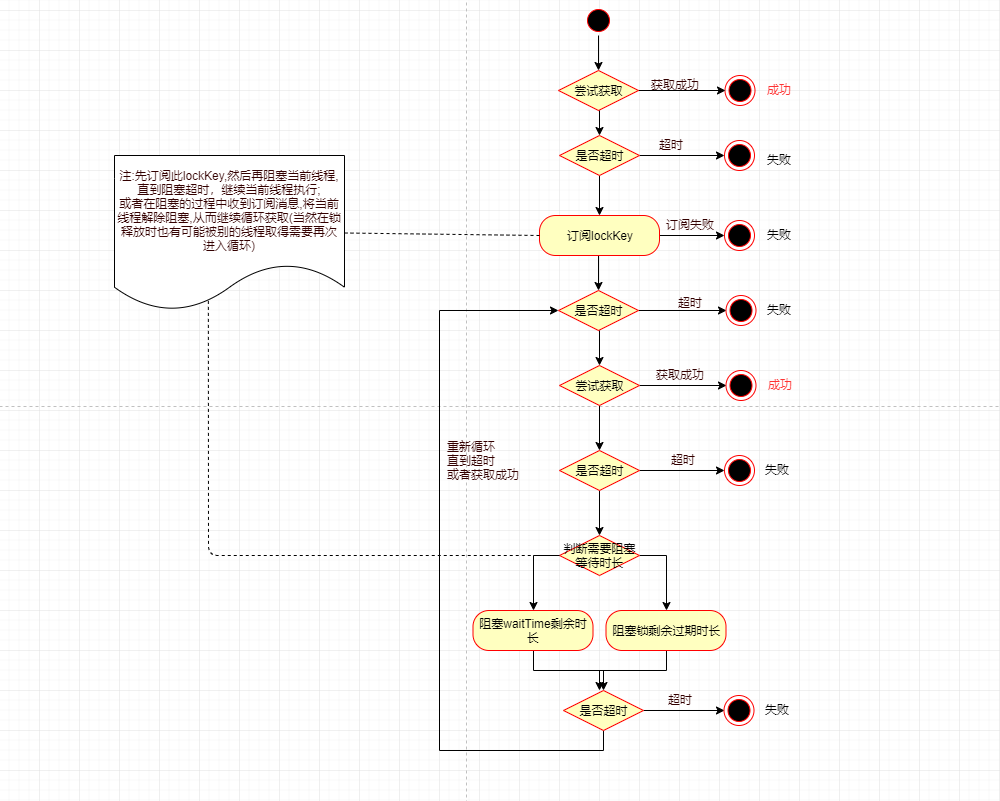
流程图:
源码分析:
Redisson实例化
/************************Redisson************************/ //创建RedissonClient实现类对象 public static RedissonClient create(Config config) { Redisson redisson = new Redisson(config); if (config.isRedissonReferenceEnabled()) { redisson.enableRedissonReferenceSupport(); } return redisson; } //实例化 new Redisson(config); //方法被protected修饰, 只能通过静态方法create(Config config)创建 protected Redisson(Config config) { this.config = config; //配置赋值 Config configCopy = new Config(config); //连接管理器 连接redis有多种模式(集群 托管 单例 主从 哨兵), 所以需要根据配置创建一种连接方式 connectionManager = ConfigSupport.createConnectionManager(configCopy); //执行器 依赖连接管理器 commandExecutor = new CommandSyncService(connectionManager); //回收管理器 evictionScheduler = new EvictionScheduler(commandExecutor); //编解码器 codecProvider = config.getCodecProvider(); //解释器 resolverProvider = config.getResolverProvider(); }
1 锁实例化(只是实例化 未请求redis) RLock lock = redisson.getLock(lockKey)
简述获取锁的过程
/**************************Redisson***********************/ @Override public RLock getLock(String name) { //commandExecutor命令执行器 //id redisson唯一ID(一般一组redis只注入一个redisson) return new RedissonLock(commandExecutor, name, id); } /**************************RedissonLock***********************/ protected RedissonLock(CommandExecutor commandExecutor, String name, UUID id) { super(commandExecutor, name); this.commandExecutor = commandExecutor; this.id = id; } /**************************RedissonExpirable***********************/ RedissonExpirable(CommandAsyncExecutor connectionManager, String name) { super(connectionManager, name); } /**************************RedissonObject***********************/ public RedissonObject(CommandAsyncExecutor commandExecutor, String name) { this(commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCodec(), commandExecutor, name); } public RedissonObject(Codec codec, CommandAsyncExecutor commandExecutor, String name) { this.codec = codec; this.name = name; this.commandExecutor = commandExecutor; }
2 请求rediss获取锁 lock.tryLock(waitTime, leaseTime, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
/************************RedissonLock************************/ public boolean tryLock(long waitTime /*获取锁等待时间*/, long leaseTime /*锁过期时间*/, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException { long time = unit.toMillis(waitTime); long current = System.currentTimeMillis(); //当前线程ID 用户拼接key final long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId(); //尝试获取锁 如果ttl==null则获取到锁 ttl!=null则表示锁已存在,ttl为锁剩余时间(毫秒) //tryAcquire最终实现方法tryAcquireAsync在下面代码 Long ttl = tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit); //获取锁成功 if (ttl == null) { return true; } //time = time-上一次尝试获取锁之后所用时间 time -= (System.currentTimeMillis() - current); //这里有两种情况 //1 若waitTime为负数(不失效缓存), 则返回false //2 若waitTime为正数 经过第一次尝试获取锁之后未获取成功 但已经超过等待时长 返回false if (time <= 0) { return false; } current = System.currentTimeMillis(); //订阅消息 final RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> subscribeFuture = subscribe(threadId); //阻塞等待一段时间(time) 等待订阅结果 if (!await(subscribeFuture, time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) { if (!subscribeFuture.cancel(false)) { subscribeFuture.addListener(new FutureListener<RedissonLockEntry>() { @Override public void operationComplete(Future<RedissonLockEntry> future) throws Exception { if (subscribeFuture.isSuccess()) { unsubscribe(subscribeFuture, threadId); } } }); } //尝试获取CountDownLatch锁失败时直接返回失败 return false; } try { time -= (System.currentTimeMillis() - current); //超过waittime返回失败 if (time <= 0) { return false; } //死循环 很简单 就是在等待时长内重复获取锁 直到获取成功或超时 while (true) { long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); //尝试获取锁 tryAcquire最终实现方法tryAcquireAsync在下面代码 ttl = tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit); // 过期时间为null 则获取成功 if (ttl == null) { return true; } time -= (System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime); //依然判断超时 if (time <= 0) { return false; } currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); //等待时间大于过期时间 那么就等已存在的过期之后再获取 if (ttl >= 0 && ttl < time) { //阻塞时长ttl getEntry(threadId).getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } //尝试获取锁 else { //阻塞时长time getEntry(threadId).getLatch().tryAcquire(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } //再次计算time>0 time -= (System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime); //若是小于等于0则为超时 直接返回false 否则进入下一次循环( while (true) ) if (time <= 0) { return false; } } } finally { //最终取消订阅 订阅代码为 final RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> subscribeFuture = subscribe(threadId) unsubscribe(subscribeFuture, threadId); } } //尝试获取锁(同步) private <T> RFuture<Long> tryAcquireAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, final long threadId) { //若过期时间为有限时间(leaseTime==-1为永不过期) if (leaseTime != -1) { return tryLockInnerAsync(leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG); } //以下为永不过期 //设置把永不过期时间改为30秒过期 RFuture<Long> ttlRemainingFuture = tryLockInnerAsync(LOCK_EXPIRATION_INTERVAL_SECONDS, TimeUnit.SECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG); //注册监听器 ttlRemainingFuture.addListener(new FutureListener<Long>() { //获取锁操作结束触发下面操作 @Override public void operationComplete(Future<Long> future) throws Exception { //如果为获取到锁 不做任何事情 if (!future.isSuccess()) { return; } Long ttlRemaining = future.getNow(); // 获取到了锁 if (ttlRemaining == null) { //定期对锁进行延时 达到永不过期目的 scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId); } } }); return ttlRemainingFuture; } //尝试获取锁(同步方式) //看下面代码之前需要先了解Redis的Hash的数据结构, 下面脚本使用的就是Hash //String数据结构为 Map<Key, Value>, 通常根据Key取值 //Hash数据结构为Map<Key, Map<Field, Value>>, Field <T> RFuture<T> tryLockInnerAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command) { //时间转换 internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime); //执行调用redis脚本 return commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command, //为了方便理解对下面数组进行解释 KEYS[1]为Hash:设置的lockKey, ARGV[1]过期时间:leaseTime, ARGV[2]为Hash的Field:当前线程ID和当前redisson拼接 //如果key不存在 则设置当前key(KEYS[1]) field(ARGV[2]) value(1), 设置key(KEYS[1])过期时间ARGV[1] 返回空值(nil) "if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " + "redis.call('hset', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " + "redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " + "return nil; " + "end; " + //如果根据key和field能查询到值, 则value在原来基础上加1 //这里可能会有误解: 上面已经判断key已经存在, 因为这里是独占锁, //若根据此锁不属于当前线程(redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) != 1), 则肯定被其他线程占有,获取锁失败 "if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " + "redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " + "redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " + "return nil; " + "end; " + //返回当前key的剩余时间 "return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);", //关键代码 Collections.<Object>singletonList(getName()) /*KEYS*/, internalLockLeaseTime /*ARGV[1]*/, getLockName(threadId)/*ARGV[2]*/ ); }
额外拓展:
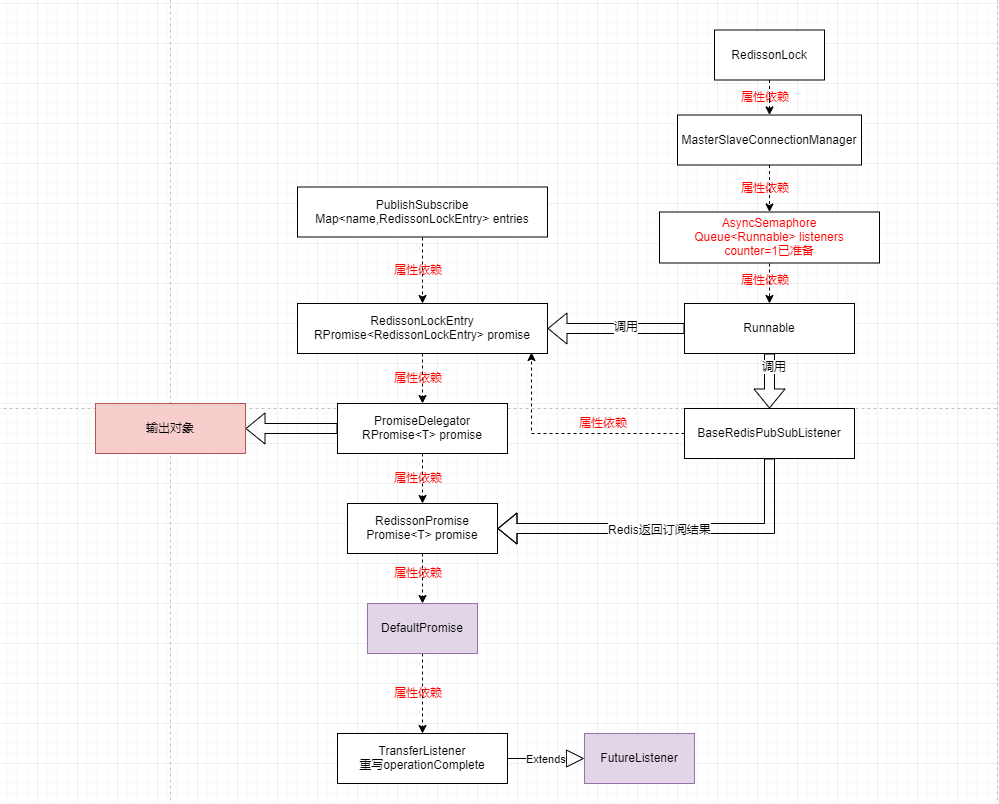
redisson使用大量的异步操作(基于netty),代码比较难读,下面针对订阅lockKey的代码画出大致类结构图 RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> subscribeFuture = subscribe(threadId)