一.日志模块
首先日志在我们开发过程中占据了一个非常重要的地位,是开发和运维管理之间的桥梁,在Java中的日志框架也非常多,Log4j,Log4j2,Apache Commons Log,java.util.logging,slf4j等,这些工具对外的接口也都不尽相同,为了统一这些工具,MyBatis定义了一套统一的日志接口供上层使用。如果要看懂首先对于适配器模式要了解下
1.1 Log
Log接口中定义了四种日志级别,相比较其他的日志框架的多种日志级别显得非常的精简,但也能够满足大多数常见的使用了
public interface Log { boolean isDebugEnabled(); boolean isTraceEnabled(); void error(String s, Throwable e); void error(String s); void debug(String s); void trace(String s); void warn(String s); }
1.2 LogFactory
LogFactory工厂类负责创建日志组件适配器,通过这玩意能找到具体的实现
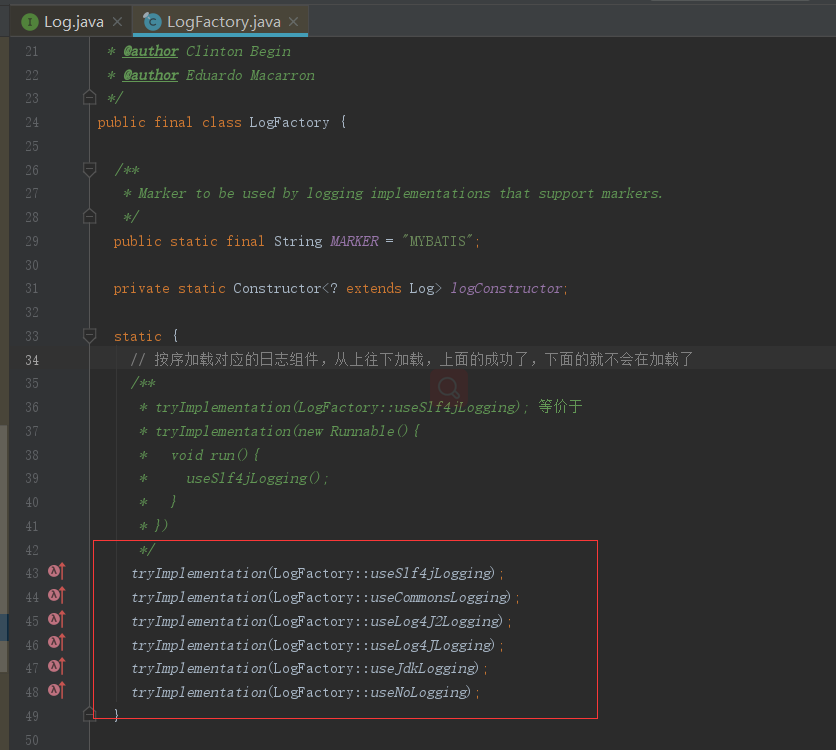
在LogFactory类加载时会执行其静态代码块,其逻辑是按序加载并实例化对应日志组件的适配器,然后使用LogFactory.logConstructor这个静态字段,记录当前使用的第三方日志组件的适配器。具体代码如下
1.3 日志应用
如果想知道在MyBatis系统启动的时候日志框架是如何选择的,那么首先要在全局配置文件中我们可以设置对应的日志类型选择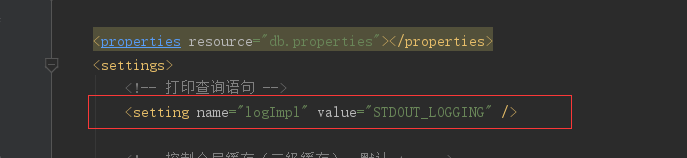
在Configuration的构造方法中其实是设置的各个日志实现的别名的,其中STDOUT_LOGGING这个也可以在里面找到
然后在解析全局配置文件的时候就会处理日志的设置
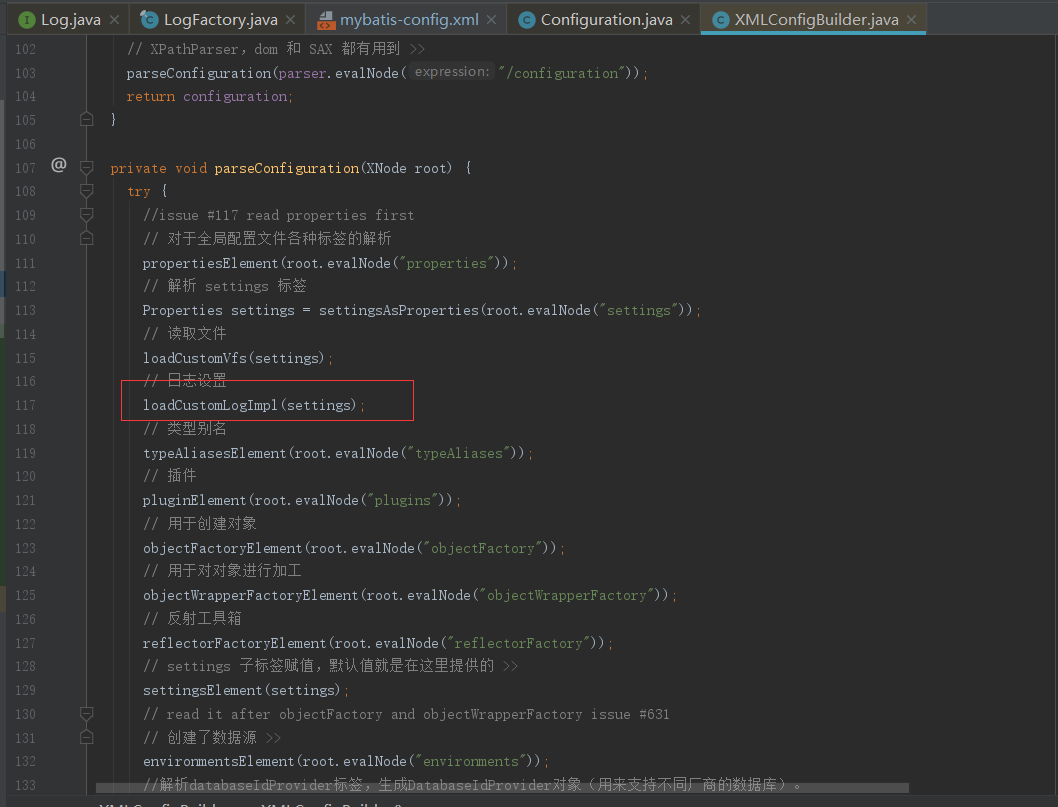
进入方法
private void loadCustomLogImpl(Properties props) { // 获取 logImpl设置的 日志 类型 Class<? extends Log> logImpl = resolveClass(props.getProperty("logImpl")); // 设置日志 configuration.setLogImpl(logImpl); }
进入setLogImpl方法中
public void setLogImpl(Class<? extends Log> logImpl) { if (logImpl != null) { this.logImpl = logImpl; // 记录日志的类型 // 设置 适配选择 LogFactory.useCustomLogging(this.logImpl); } }
再进入useCustomLogging方法
public static synchronized void useCustomLogging(Class<? extends Log> clazz) { setImplementation(clazz); }
private static void setImplementation(Class<? extends Log> implClass) { try { // 获取指定适配器的构造方法 Constructor<? extends Log> candidate = implClass.getConstructor(String.class); // 实例化适配器 Log log = candidate.newInstance(LogFactory.class.getName()); if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Logging initialized using '" + implClass + "' adapter."); } // 初始化 logConstructor 字段 logConstructor = candidate; } catch (Throwable t) { throw new LogException("Error setting Log implementation. Cause: " + t, t); } }
这就关联上了前面在LogFactory中看到的代码,启动测试方法看到的日志也和源码中的对应上来了,还有就是我们自己设置的会覆盖掉默认的sl4j日志框架的配置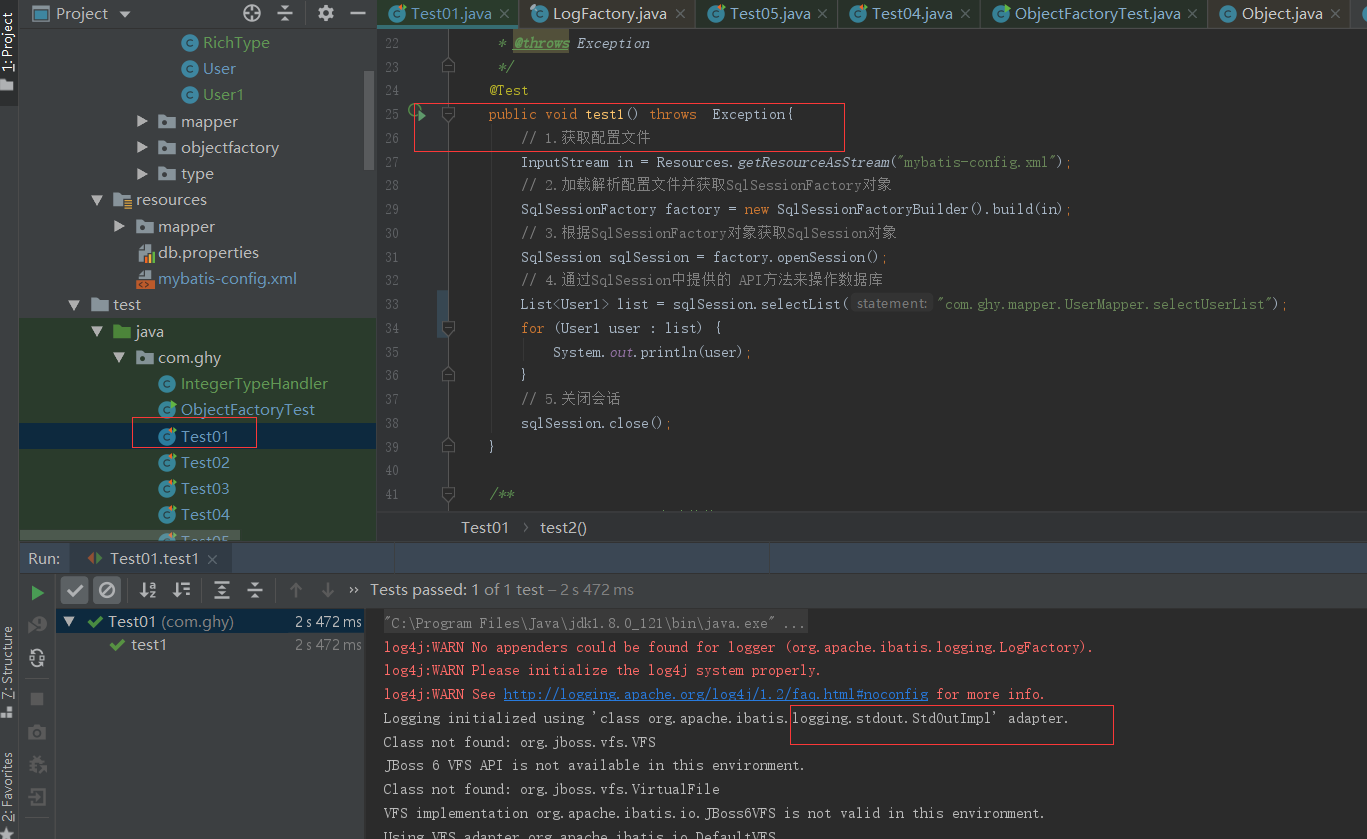
1.4 JDBC 日志
当开启了 STDOUT的日志管理后,当执行SQL操作时会发现在控制台中可以打印出相关的日志信息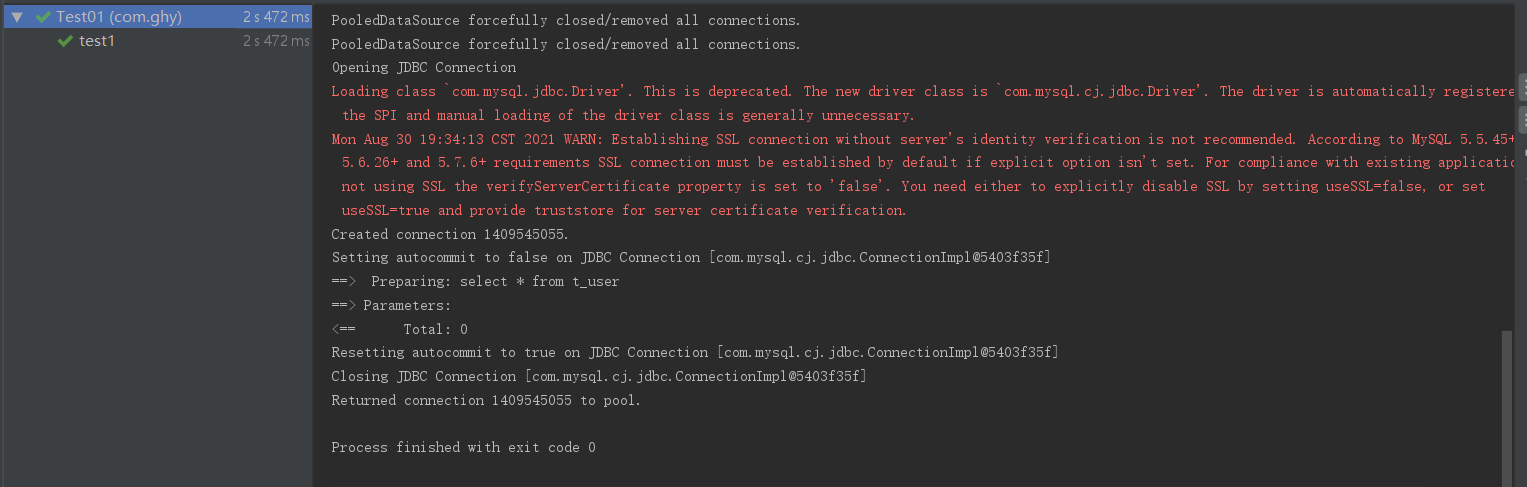
那这些日志信息是怎么打印出来的呢?其实在MyBatis中的日志模块中包含了一个jdbc包,它并不是将日志信息通过jdbc操作保存到数据库中,而是通过JDK动态代理的方式,将JDBC操作通过指定的日志框架打印出来。下面就来看看它是如何实现的。
1.4.1 BaseJdbcLogger
BaseJdbcLogger是一个抽象类,它是jdbc包下其他Logger的父类。继承关系如下
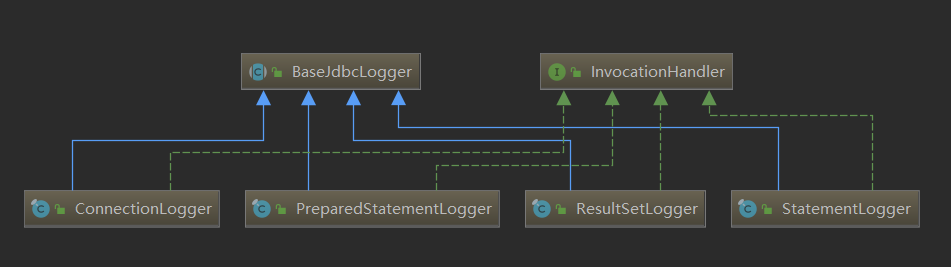
从图中也可以看到4个实现都实现了InvocationHandler接口。属性含义如下
// 记录 PreparedStatement 接口中定义的常用的set*() 方法 protected static final Set<String> SET_METHODS; // 记录了 Statement 接口和 PreparedStatement 接口中与执行SQL语句有关的方法 protected static final Set<String> EXECUTE_METHODS = new HashSet<>(); // 记录了PreparedStatement.set*() 方法设置的键值对 private final Map<Object, Object> columnMap = new HashMap<>(); // 记录了PreparedStatement.set*() 方法设置的键 key private final List<Object> columnNames = new ArrayList<>(); // 记录了PreparedStatement.set*() 方法设置的值 Value private final List<Object> columnValues = new ArrayList<>(); protected final Log statementLog;// 用于日志输出的Log对象 protected final int queryStack; // 记录了SQL的层数,用于格式化输出SQL
1.4.2 ConnectionLogger
ConnectionLogger的作用是记录数据库连接相关的日志信息,在实现中是创建了一个Connection的代理对象,在每次Connection操作的前后都可以实现日志的操作。
public final class ConnectionLogger extends BaseJdbcLogger implements InvocationHandler { // 真正的Connection对象 private final Connection connection; private ConnectionLogger(Connection conn, Log statementLog, int queryStack) { super(statementLog, queryStack); this.connection = conn; } @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] params) throws Throwable { try { // 如果是调用从Object继承过来的方法,就直接调用 toString,hashCode,equals等 if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) { return method.invoke(this, params); } // 如果调用的是 prepareStatement方法 if ("prepareStatement".equals(method.getName())) { if (isDebugEnabled()) { debug(" Preparing: " + removeBreakingWhitespace((String) params[0]), true); } // 创建 PreparedStatement PreparedStatement stmt = (PreparedStatement) method.invoke(connection, params); // 然后创建 PreparedStatement 的代理对象 增强 stmt = PreparedStatementLogger.newInstance(stmt, statementLog, queryStack); return stmt; // 同上 } else if ("prepareCall".equals(method.getName())) { if (isDebugEnabled()) { debug(" Preparing: " + removeBreakingWhitespace((String) params[0]), true); } PreparedStatement stmt = (PreparedStatement) method.invoke(connection, params); stmt = PreparedStatementLogger.newInstance(stmt, statementLog, queryStack); return stmt; // 同上 } else if ("createStatement".equals(method.getName())) { Statement stmt = (Statement) method.invoke(connection, params); stmt = StatementLogger.newInstance(stmt, statementLog, queryStack); return stmt; } else { return method.invoke(connection, params); } } catch (Throwable t) { throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t); } } /** * Creates a logging version of a connection. * * @param conn - the original connection * @return - the connection with logging */ public static Connection newInstance(Connection conn, Log statementLog, int queryStack) { InvocationHandler handler = new ConnectionLogger(conn, statementLog, queryStack); ClassLoader cl = Connection.class.getClassLoader(); // 创建了 Connection的 代理对象 目的是 增强 Connection对象 给他添加了日志功能 return (Connection) Proxy.newProxyInstance(cl, new Class[]{Connection.class}, handler); } /** * return the wrapped connection. * * @return the connection */ public Connection getConnection() { return connection; } }
其他几个xxxxLogger的实现和ConnectionLogger几乎是一样的就不重复说了,看懂一个就可以看懂所有
1.4.3 应用实现
在实际处理的时候,看下日志模块是如何工作的,在我们要执行SQL语句前需要获取Statement对象,而Statement对象是通过Connection获取的,所以在SimpleExecutor中就可以看到相关的代码
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException { Statement stmt; Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog); // 获取 Statement 对象 stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout()); // 为 Statement 设置参数 handler.parameterize(stmt); return stmt; }
先进入如到getConnection方法中
protected Connection getConnection(Log statementLog) throws SQLException { Connection connection = transaction.getConnection(); if (statementLog.isDebugEnabled()) { // 创建Connection的日志代理对象 return ConnectionLogger.newInstance(connection, statementLog, queryStack); } else { return connection; } }
再进入到handler.prepare方法中
@Override public Statement prepare(Connection connection, Integer transactionTimeout) throws SQLException { ErrorContext.instance().sql(boundSql.getSql()); Statement statement = null; try { statement = instantiateStatement(connection); setStatementTimeout(statement, transactionTimeout); setFetchSize(statement); return statement; } catch (SQLException e) { closeStatement(statement); throw e; } catch (Exception e) { closeStatement(statement); throw new ExecutorException("Error preparing statement. Cause: " + e, e); } }
@Override protected Statement instantiateStatement(Connection connection) throws SQLException { String sql = boundSql.getSql(); if (mappedStatement.getKeyGenerator() instanceof Jdbc3KeyGenerator) { String[] keyColumnNames = mappedStatement.getKeyColumns(); if (keyColumnNames == null) { return connection.prepareStatement(sql, PreparedStatement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS); } else { // 在执行 prepareStatement 方法的时候会进入进入到ConnectionLogger的invoker方法中 return connection.prepareStatement(sql, keyColumnNames); } } else if (mappedStatement.getResultSetType() == ResultSetType.DEFAULT) { return connection.prepareStatement(sql); } else { return connection.prepareStatement(sql, mappedStatement.getResultSetType().getValue(), ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY); } }

在执行sql语句的时候

如果是查询操作,后面的ResultSet结果集操作,其他是也通过ResultSetLogger来处理的