一、缓存模块
MyBatis作为一个强大的持久层框架,缓存是其必不可少的功能之一,Mybatis中的缓存分为一级缓存和二级缓存。但本质上是一样的,都是使用Cache接口实现的。缓存位于 org.apache.ibatis.cache包下。
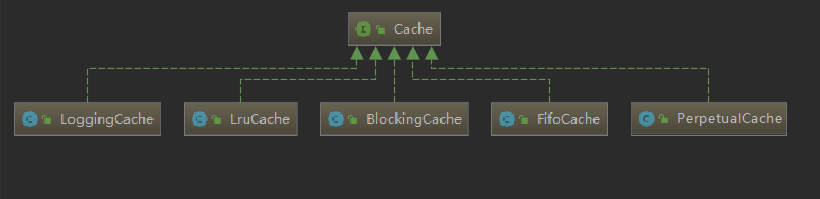
通过结构能够发现Cache其实使用到了装饰器模式来实现缓存的处理。先来看看Cache中的基础类的API;Cache接口的实现类很多,但是大部分都是装饰器,只有PerpetualCache提供了Cache接口的基本实现。
1.1 Cache接口
Cache接口是缓存模块中最核心的接口,它定义了所有缓存的基本行为,Cache接口的定义如下:
public interface Cache { /** * 缓存对象的 ID * @return The identifier of this cache */ String getId(); /** * 向缓存中添加数据,一般情况下 key是CacheKey value是查询结果 * @param key Can be any object but usually it is a {@link CacheKey} * @param value The result of a select. */ void putObject(Object key, Object value); /** * 根据指定的key,在缓存中查找对应的结果对象 * @param key The key * @return The object stored in the cache. */ Object getObject(Object key); /** * As of 3.3.0 this method is only called during a rollback * for any previous value that was missing in the cache. * This lets any blocking cache to release the lock that * may have previously put on the key. * A blocking cache puts a lock when a value is null * and releases it when the value is back again. * This way other threads will wait for the value to be * available instead of hitting the database. * 删除key对应的缓存数据 * * @param key The key * @return Not used */ Object removeObject(Object key); /** * Clears this cache instance. * 清空缓存 */ void clear(); /** * Optional. This method is not called by the core. * 缓存的个数。 * @return The number of elements stored in the cache (not its capacity). */ int getSize(); /** * Optional. As of 3.2.6 this method is no longer called by the core. * <p> * Any locking needed by the cache must be provided internally by the cache provider. * 获取读写锁 * @return A ReadWriteLock */ default ReadWriteLock getReadWriteLock() { return null; } }
1.2 PerpetualCache
PerpetualCache在缓存模块中扮演了ConcreteComponent的角色,其实现比较简单,底层使用HashMap记录缓存项,具体的实现如下
/** * 在装饰器模式用 用来被装饰的对象 * 缓存中的 基本缓存处理的实现 * 其实就是一个 HashMap 的基本操作 * @author Clinton Begin */ public class PerpetualCache implements Cache { private final String id; // Cache 对象的唯一标识 // 用于记录缓存的Map对象 private final Map<Object, Object> cache = new HashMap<>(); public PerpetualCache(String id) { this.id = id; } @Override public String getId() { return id; } @Override public int getSize() { return cache.size(); } @Override public void putObject(Object key, Object value) { cache.put(key, value); } @Override public Object getObject(Object key) { return cache.get(key); } @Override public Object removeObject(Object key) { return cache.remove(key); } @Override public void clear() { cache.clear(); } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (getId() == null) { throw new CacheException("Cache instances require an ID."); } if (this == o) { return true; } if (!(o instanceof Cache)) { return false; } Cache otherCache = (Cache) o; // 只关心ID return getId().equals(otherCache.getId()); } @Override public int hashCode() { if (getId() == null) { throw new CacheException("Cache instances require an ID."); } // 只关心ID return getId().hashCode(); } }
然后可以来看看cache.decorators包下提供的装饰器。他们都实现了Cache接口。这些装饰器都在PerpetualCache的基础上提供了一些额外的功能,通过多个组合实现一些特殊的需求。
1.3 BlockingCache
这是一个阻塞同步的缓存,它保证只有一个线程到缓存中查找指定的key对应的数据
/** * Simple blocking decorator * 阻塞版的缓存 装饰器 * Simple and inefficient version of EhCache's BlockingCache decorator. * It sets a lock over a cache key when the element is not found in cache. * This way, other threads will wait until this element is filled instead of hitting the database. * * @author Eduardo Macarron * */ public class BlockingCache implements Cache { private long timeout; // 阻塞超时时长 private final Cache delegate; // 被装饰的底层 Cache 对象 // 每个key 都有对象的 ReentrantLock 对象 private final ConcurrentHashMap<Object, ReentrantLock> locks; public BlockingCache(Cache delegate) { // 被装饰的 Cache 对象 this.delegate = delegate; this.locks = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); } @Override public String getId() { return delegate.getId(); } @Override public int getSize() { return delegate.getSize(); } @Override public void putObject(Object key, Object value) { try { // 执行 被装饰的 Cache 中的方法 delegate.putObject(key, value); } finally { // 释放锁 releaseLock(key); } } @Override public Object getObject(Object key) { acquireLock(key); // 获取锁 Object value = delegate.getObject(key); // 获取缓存数据 if (value != null) { // 有数据就释放掉锁,否则继续持有锁 releaseLock(key); } return value; } @Override public Object removeObject(Object key) { // despite of its name, this method is called only to release locks releaseLock(key); return null; } @Override public void clear() { delegate.clear(); } private ReentrantLock getLockForKey(Object key) { return locks.computeIfAbsent(key, k -> new ReentrantLock()); } private void acquireLock(Object key) { Lock lock = getLockForKey(key); if (timeout > 0) { try { boolean acquired = lock.tryLock(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); if (!acquired) { throw new CacheException("Couldn't get a lock in " + timeout + " for the key " + key + " at the cache " + delegate.getId()); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new CacheException("Got interrupted while trying to acquire lock for key " + key, e); } } else { lock.lock(); } } private void releaseLock(Object key) { ReentrantLock lock = locks.get(key); if (lock.isHeldByCurrentThread()) { lock.unlock(); } } public long getTimeout() { return timeout; } public void setTimeout(long timeout) { this.timeout = timeout; } }
通过源码我们能够发现,BlockingCache本质上就是在操作缓存数据的前后通过ReentrantLock对象来实现了加锁和解锁操作。
| 缓存实现类 | 缓存实现类 | 作用 | 装饰条件 |
|
基本缓存 |
缓存基本实现类 |
默认是PerpetualCache,也可以自定义比如RedisCache、EhCache等,具备基本功能的缓存类 | 无 |
| LruCache |
LRU策略的缓存 |
当缓存到达上限时候,删除最近最少使用的缓存(Least Recently Use) |
eviction="LRU"(默认) |
| FifoCache |
FIFO策略的缓存 |
当缓存到达上限时候,删除最先入队的缓存 |
eviction="FIFO" |
| SoftCacheWeakCache |
带清理策略的缓存 |
通过JVM的软引用和弱引用来实现缓存,当JVM内存不足时,会自动清理掉这些缓存,基于SoftReference和WeakReference |
eviction="SOFT"eviction="WEAK" |
| LoggingCache |
带日志功能的缓存 |
比如:输出缓存命中率 | 基本 |
| SynchronizedCache |
同步缓存 |
基于synchronized关键字实现,解决并发问题 |
基本 |
| BlockingCache |
阻塞缓存 |
通过在get/put方式中加锁,保证只有一个线程操作缓存,基于Java重入锁实现 |
blocking=true |
| SerializedCache |
支持序列化的缓存 |
将对象序列化以后存到缓存中,取出时反序列化 |
readOnly=false(默认) |
| ScheduledCache |
定时调度的缓存 |
在进行get/put/remove/getSize等操作前,判断缓存时间是否超过了设置的最长缓存时间(默认 |
flushInterval不为空 |
| TransactionalCache |
事务缓存 |
在二级缓存中使用,可一次存入多个缓存,移除多个缓存 |
在TransactionalCacheManager中用Map维护对应关系 |
1.4 缓存的应用
1.4.1 缓存对应的初始化
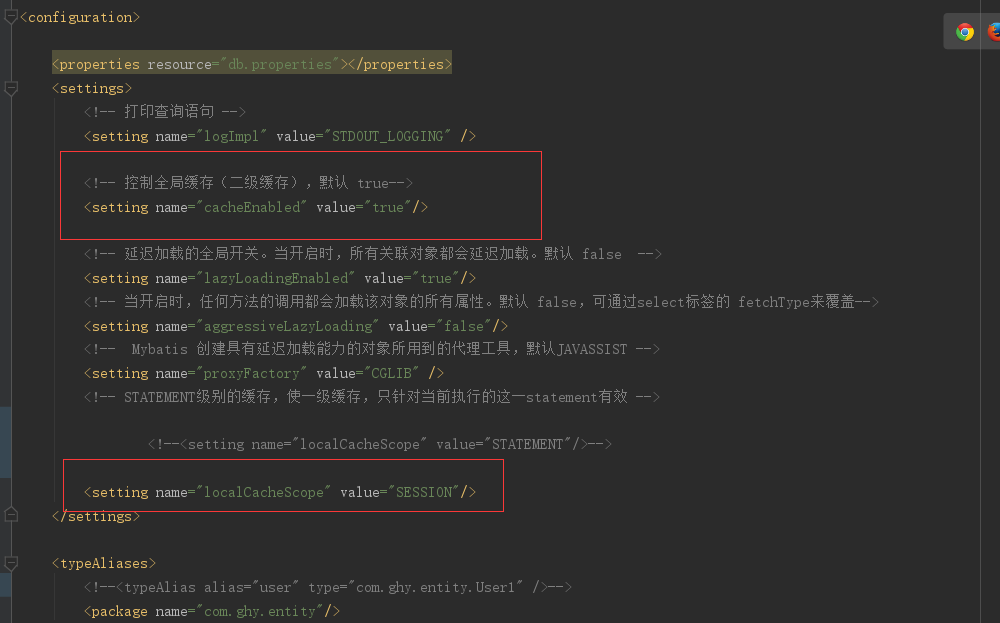
在之前写的代码中断个点看下可能直接点,在断点前说明下要求,如要开启缓存要在配置文件开启一级和二级缓存
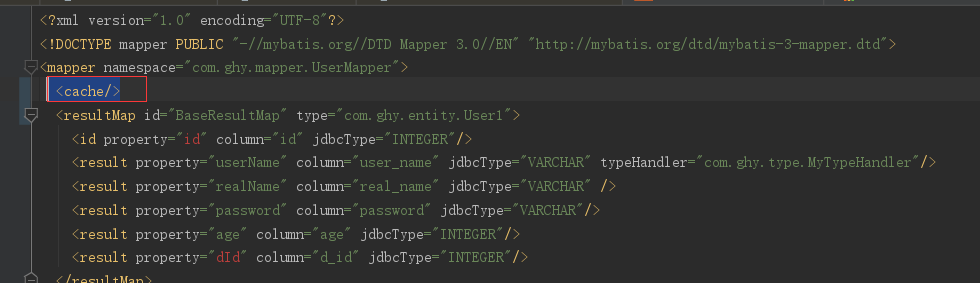
然后呢在mapper.XML文件加入<cache/>标签就可以了
下面来断点看下
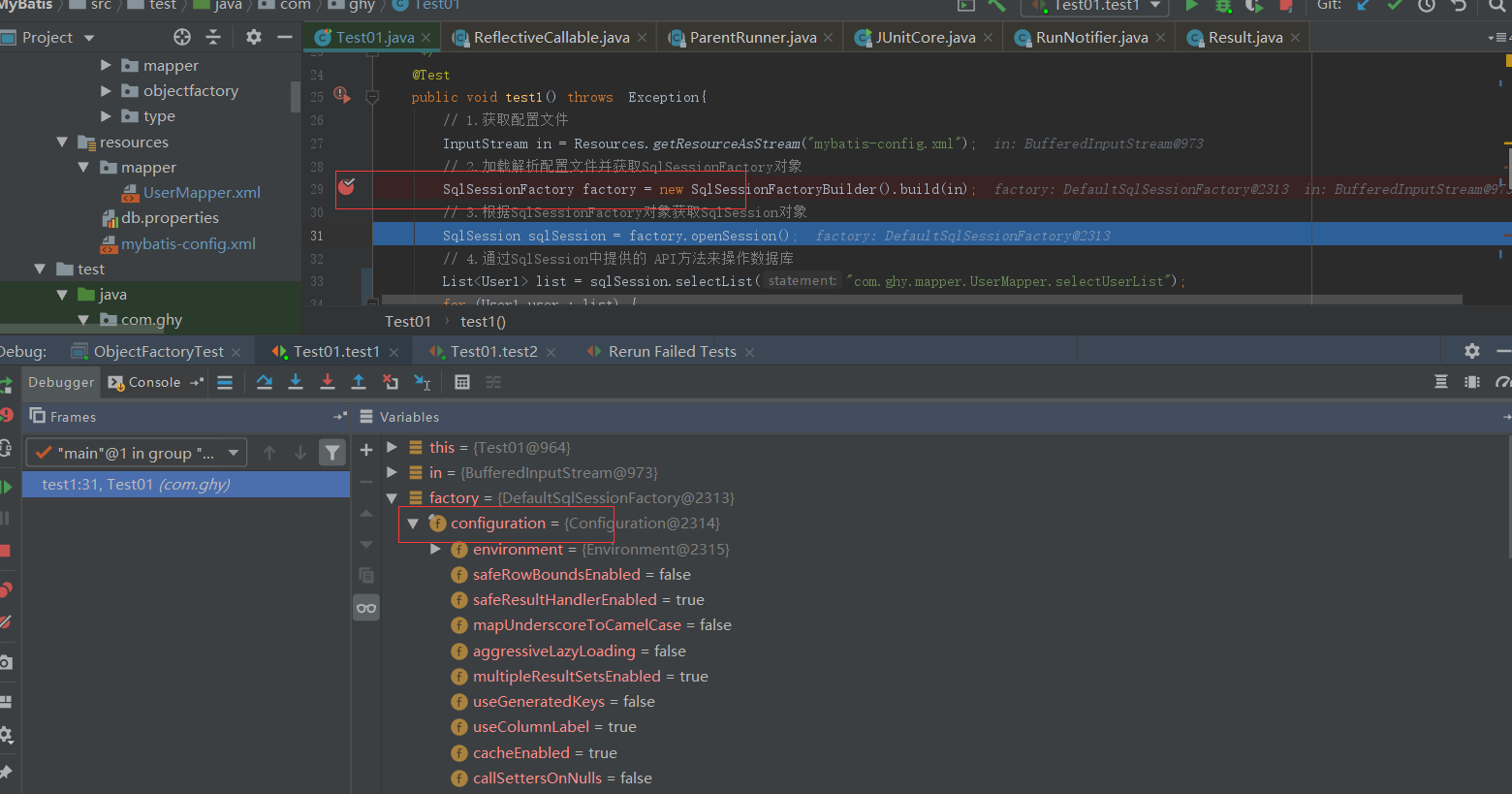
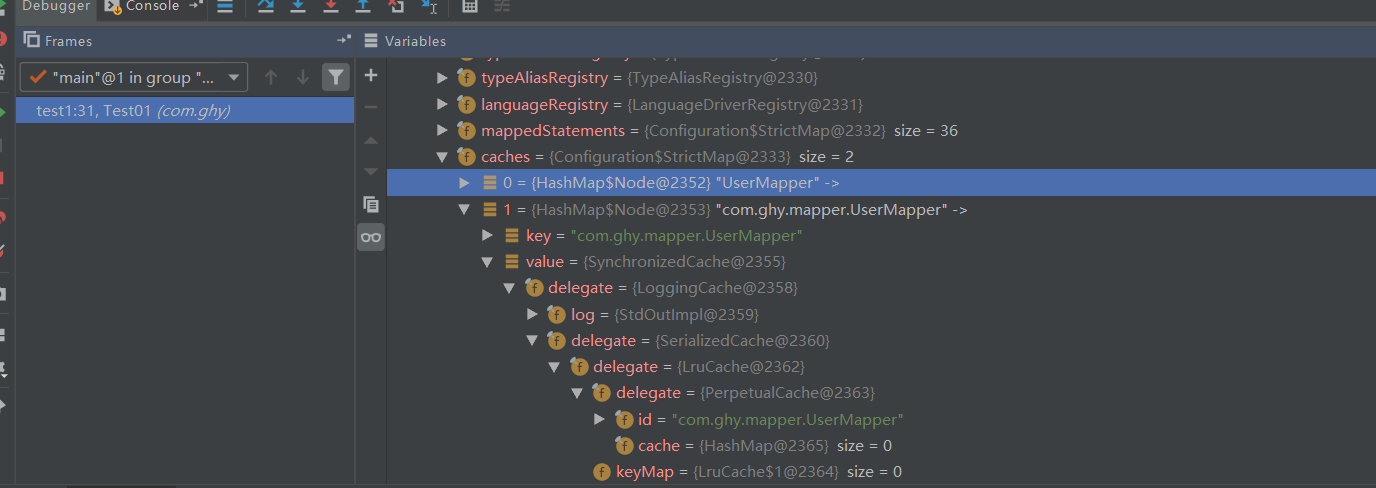
通过上面截图可以很清楚的看到这是一个装饰器过程,接下来看下在Configuration初始化的时候怎么给我们的各种Cache实现注册对应的别名
在解析settings标签的时候,设置的默认值有如下;因为前面源码跟了好多次,这里面我直接进到解析这一段代码了

public Configuration parse() { //检查是否已经解析过了 if (parsed) { throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once."); } parsed = true; // XPathParser,dom 和 SAX 都有用到 >> parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration")); return configuration; }
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) { try { //issue #117 read properties first // 对于全局配置文件各种标签的解析 propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties")); // 解析 settings 标签 Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings")); // 读取文件 loadCustomVfs(settings); // 日志设置 loadCustomLogImpl(settings); // 类型别名 typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases")); // 插件 pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins")); // 用于创建对象 objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory")); // 用于对对象进行加工 objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory")); // 反射工具箱 reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory")); // settings 子标签赋值,默认值就是在这里提供的 >> settingsElement(settings); // read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631 // 创建了数据源 >> environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments")); //解析databaseIdProvider标签,生成DatabaseIdProvider对象(用来支持不同厂商的数据库)。 databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider")); typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers")); // 解析引用的Mapper映射器 mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers")); } catch (Exception e) { throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e); } }
在上面的全局配置文件中在settingsElement(settings);的赋值中会做一些默认的处理,点进去看下
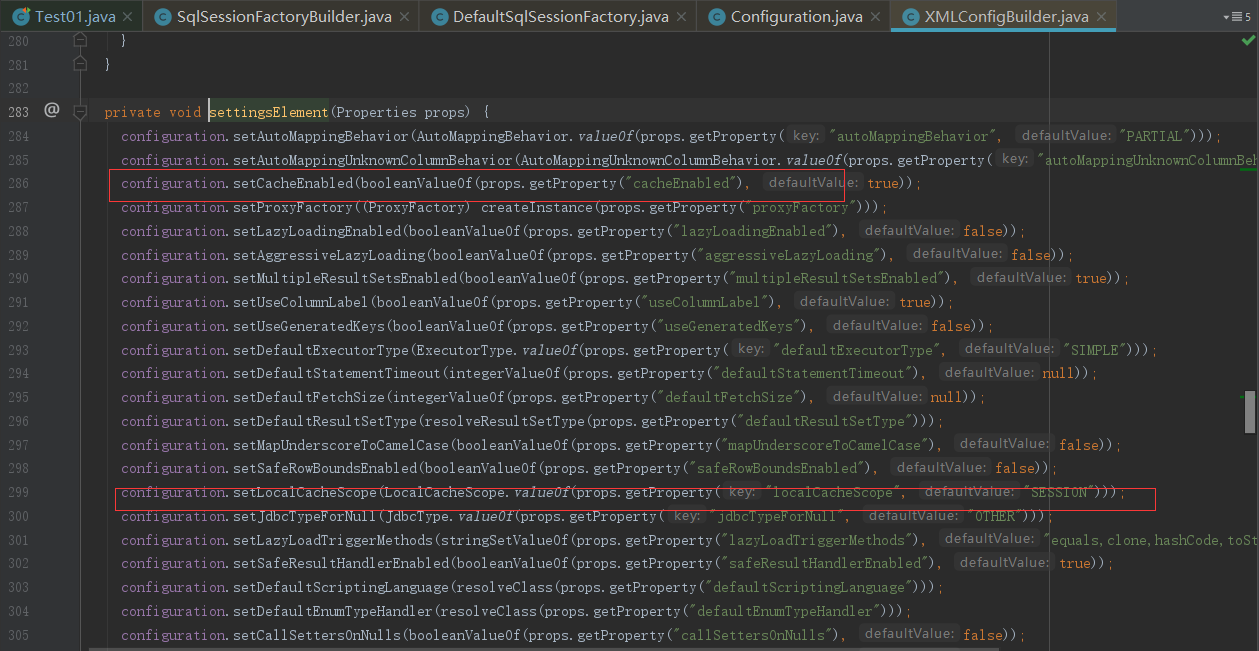
通过上面发现cacheEnabled默认为true,localCacheScope默认为 SESSION,在初始化过程中关键的还是映射文件的解析,点击mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));进去看下
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception { if (parent != null) { for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) { // 不同的定义方式的扫描,最终都是调用 addMapper()方法(添加到 MapperRegistry)。这个方法和 getMapper() 对应 // package 包 if ("package".equals(child.getName())) { String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name"); configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage); } else { String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource"); String url = child.getStringAttribute("url"); String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class"); if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) { // resource 相对路径 ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource); InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments()); // 解析 Mapper.xml,总体上做了两件事情 >> mapperParser.parse(); } else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) { // url 绝对路径 ErrorContext.instance().resource(url); InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url); XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments()); mapperParser.parse(); } else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) { // class 单个接口 Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass); configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface); } else { throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one."); } } } } }
直接进入他的关键代码mapperParser.parse();,
public void parse() { // 总体上做了两件事情,对于语句的注册和接口的注册 if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) { // 1、具体增删改查标签的解析。 // 一个标签一个MappedStatement。 >> configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper")); configuration.addLoadedResource(resource); // 2、把namespace(接口类型)和工厂类绑定起来,放到一个map。 // 一个namespace 一个 MapperProxyFactory >> bindMapperForNamespace(); } parsePendingResultMaps(); parsePendingCacheRefs(); parsePendingStatements(); }
上面是映射文件的解析操作,可以看他进了标签的解析,进去看下
private void configurationElement(XNode context) { try { String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace"); if (namespace == null || namespace.equals("")) { throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty"); } builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace); // 添加缓存对象 cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref")); // 解析 cache 属性,添加缓存对象 cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache")); // 创建 ParameterMapping 对象 parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap")); // 创建 List<ResultMapping> resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap")); // 解析可以复用的SQL sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql")); // 解析增删改查标签,得到 MappedStatement >> buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete")); } catch (Exception e) { throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. The XML location is '" + resource + "'. Cause: " + e, e); } }
看到这里好像找到了想找的东西,可以看到上面代码我标的两个地方的标签解析,跟进去看下
private void cacheElement(XNode context) { // 只有 cache 标签不为空才解析 if (context != null) { String type = context.getStringAttribute("type", "PERPETUAL"); Class<? extends Cache> typeClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(type); String eviction = context.getStringAttribute("eviction", "LRU"); Class<? extends Cache> evictionClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(eviction); Long flushInterval = context.getLongAttribute("flushInterval"); Integer size = context.getIntAttribute("size"); boolean readWrite = !context.getBooleanAttribute("readOnly", false); boolean blocking = context.getBooleanAttribute("blocking", false); Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties(); builderAssistant.useNewCache(typeClass, evictionClass, flushInterval, size, readWrite, blocking, props); } }
会发现上面开始解析相关的属性信息了,并在最后一步进行了保存,继续跟进去看下
public Cache useNewCache(Class<? extends Cache> typeClass, Class<? extends Cache> evictionClass, Long flushInterval, Integer size, boolean readWrite, boolean blocking, Properties props) { Cache cache = new CacheBuilder(currentNamespace) .implementation(valueOrDefault(typeClass, PerpetualCache.class)) .addDecorator(valueOrDefault(evictionClass, LruCache.class)) .clearInterval(flushInterval) .size(size) .readWrite(readWrite) .blocking(blocking) .properties(props) .build(); configuration.addCache(cache); currentCache = cache; return cache; }
然后可以发现 如果存储 cache 标签,那么对应的 Cache对象会被保存在 currentCache 属性中。
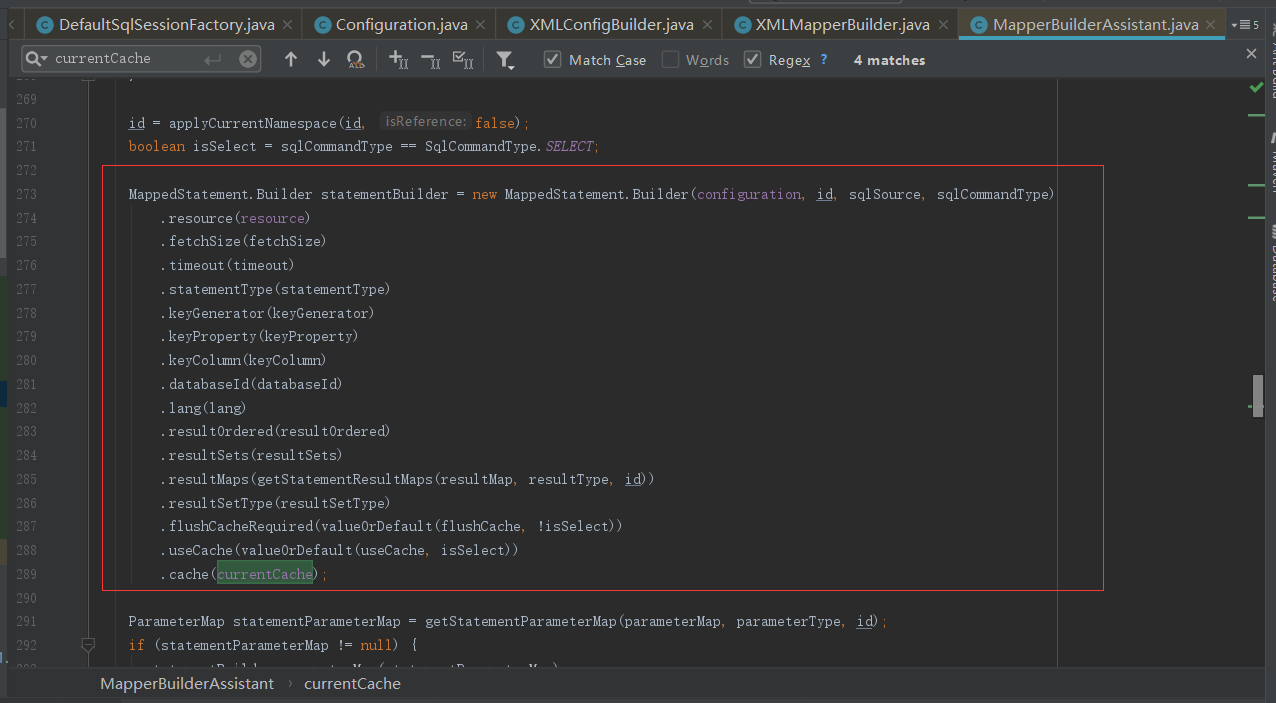
进而在 Cache 对象 保存在了 MapperStatement 对象的 cache 属性中。这就是cache节点创建的整个过程。
1.4.2 一级缓存
一级缓存也叫本地缓存(Local Cache),MyBatis的一级缓存是在会话(SqlSession)层面进行缓存的。MyBatis的一级缓存是默认开启的,不需要任何的配置(如果要关闭,localCacheScope设置为STATEMENT)。在BaseExecutor对象的query方法中有关闭一级缓存的逻辑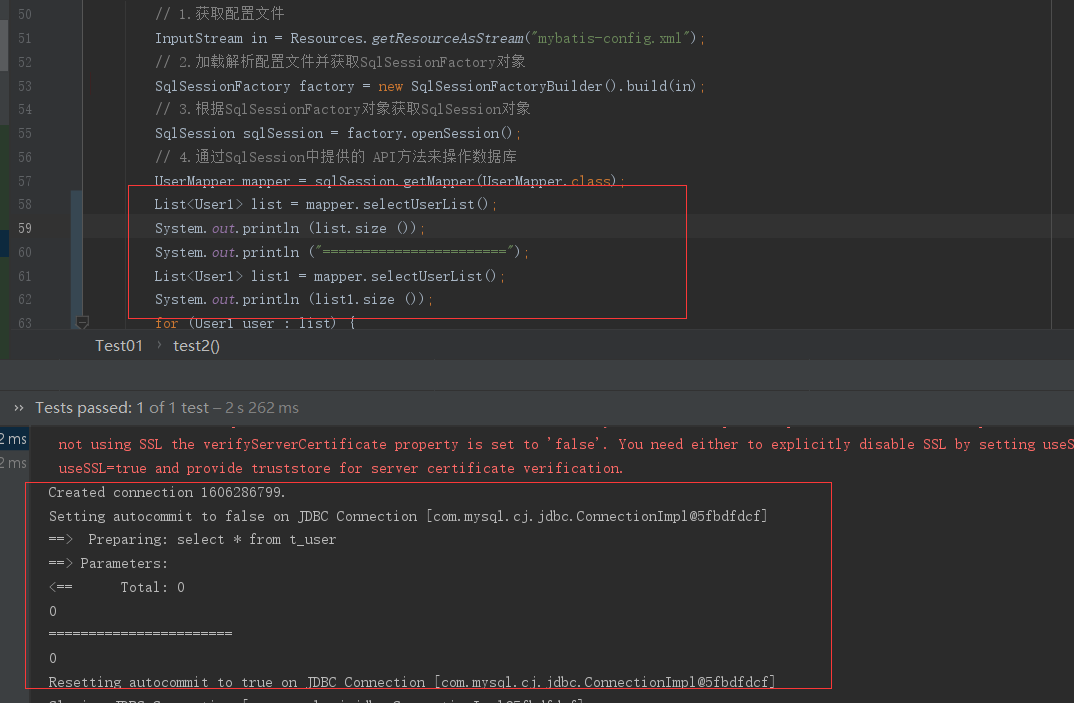
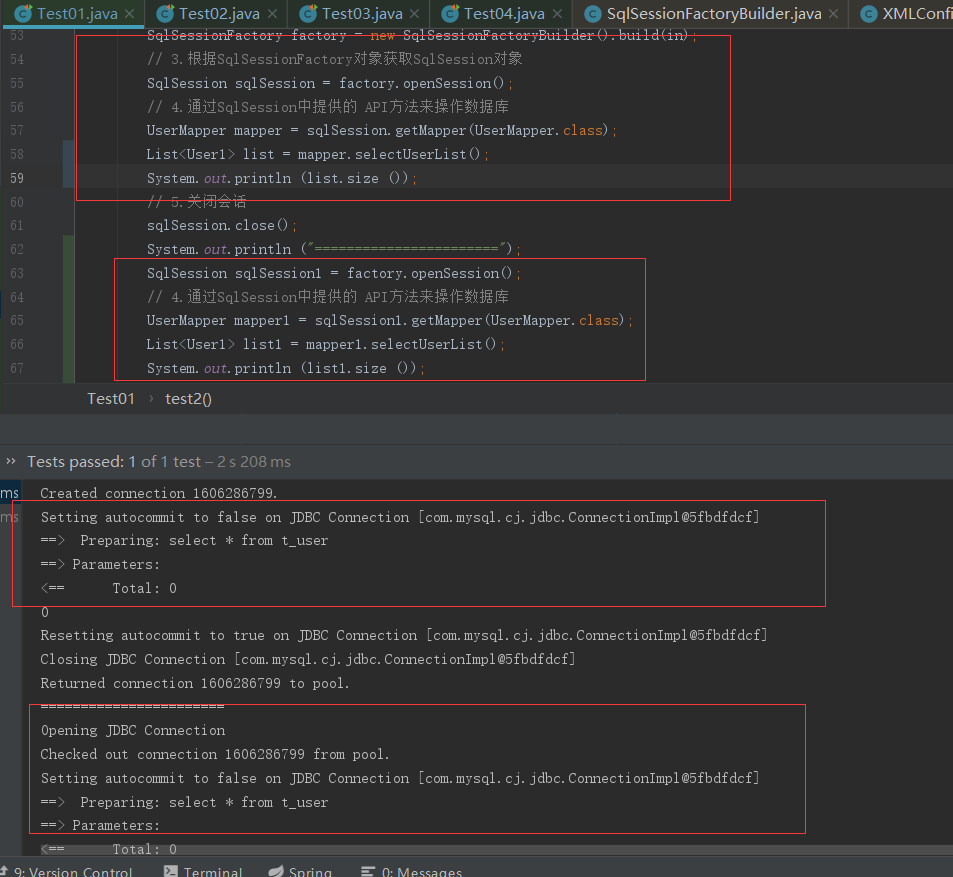
从上面的效果可以很清楚的感受到在一个会话内,第二次查询是直接走缓存的,在不同会话内缓存是不起效的。下面会了解缓存做了啥跟进代码看下。入口从上面演示就可以猜到是从
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();进入的
@Override public SqlSession openSession() { return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false); }
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) { //事务对象 Transaction tx = null; try { final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment(); // 获取事务工厂 final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment); // 创建事务 tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit); // 根据事务工厂和默认的执行器类型,创建执行器 >>执行SQL语句操作 final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType); return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit); } catch (Exception e) { closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close() throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } }
在创建对应的执行器的时候会有缓存的操作
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) { executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType; executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType; Executor executor; if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) { executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction); } else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {//针对Statement做缓存 executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction); } else { // 默认 SimpleExecutor,每一次只是SQL操作都创建一个新的Statement对象 executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction); } // 二级缓存开关,settings 中的 cacheEnabled 默认是 true if (cacheEnabled) { executor = new CachingExecutor(executor); } // 植入插件的逻辑,至此,四大对象已经全部拦截完毕;这里面是一个拦截器链 executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor); return executor; }
从上面代码可以知道如果 cacheEnabled 为 true 就会通过 CachingExecutor 来装饰executor 对象,然后就是在执行SQL操作的时候会涉及到缓存的具体使用。这个就分为一级缓存和二级缓存,通过这个跟踪会发现在创建会话时会创建执行器,而执行器里面跟缓存有关系的是二级缓存,跟我想找的一级缓存没什么关系;那么一级缓存在哪呢,这时候我想一级缓存是跟会话有关,那么他的位置一定在会话内的这段代码里,那我就找下一段代码
// 4.通过SqlSession中提供的 API方法来操作数据库 List<User1> list = sqlSession.selectList("com.ghy.mapper.UserMapper.selectUserList");
进入selectList看下
@Override public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement) { return this.selectList(statement, null); }
@Override public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) { try { MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement); // 如果 cacheEnabled = true(默认),Executor会被 CachingExecutor装饰 return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER); } catch (Exception e) { throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } }
在上面代码中可以看到一个查询操作,那肯定是要进去看下他在查询前有没有缓存判断,如果没有说明selectList代码是不走缓存的;
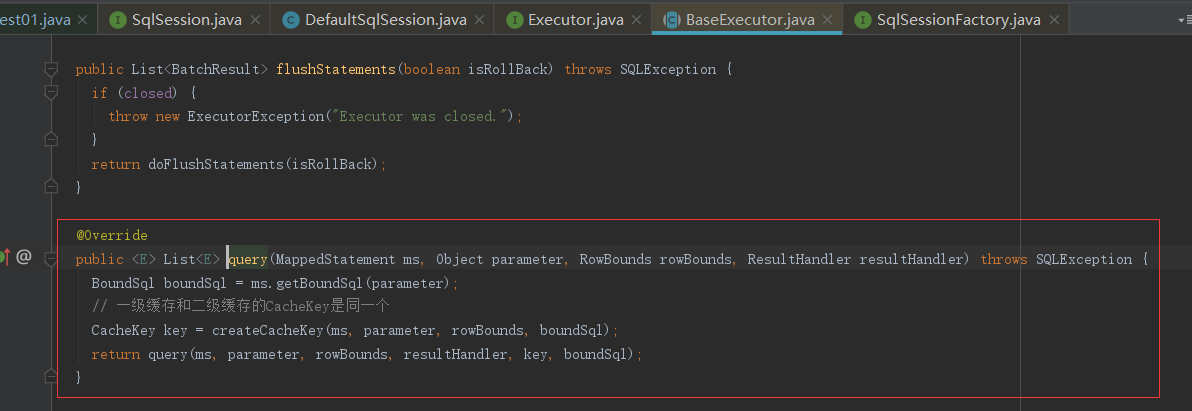
在上面代码中发现了一些跟缓存相关的操作CacheKey
@Override public CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) { if (closed) { throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed."); } CacheKey cacheKey = new CacheKey(); cacheKey.update(ms.getId()); cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getOffset()); // 0 cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getLimit()); // 2147483647 = 2^31-1 cacheKey.update(boundSql.getSql()); List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings(); TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = ms.getConfiguration().getTypeHandlerRegistry(); // mimic DefaultParameterHandler logic for (ParameterMapping parameterMapping : parameterMappings) { if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) { Object value; String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty(); if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) { value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName); } else if (parameterObject == null) { value = null; } else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) { value = parameterObject; } else { MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject); value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName); } cacheKey.update(value); // development } } if (configuration.getEnvironment() != null) { // issue #176 cacheKey.update(configuration.getEnvironment().getId()); } return cacheKey; }
发现上面是一个缓存创建的逻辑,这个东西debugger看一下其实就明白了;其实这写了一堆就是生成一个东西,生成一个缓存的KEY,而且这个KEY是跟我们写的SQL有关;明白了这个key的作用后回退一步跟进query看他拿这个key去做了什么
@Override public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { // 异常体系之 ErrorContext ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId()); if (closed) { throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed."); } if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) { // flushCache="true"时,即使是查询,也清空一级缓存 clearLocalCache(); } List<E> list; try { // 防止递归查询重复处理缓存 queryStack++; // 查询一级缓存 // ResultHandler 和 ResultSetHandler的区别 list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null; if (list != null) { //缓存中有数据 handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql); } else { // 真正的查询流程 list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); } } finally { queryStack--; } if (queryStack == 0) { for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) { deferredLoad.load(); } // issue #601 deferredLoads.clear(); if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) { // issue #482 clearLocalCache(); } } return list; }
从上面就找到了查找一级缓存的位置了,如果list判断是空说明缓存没数据他会走queryFromDatabase去查询并且把数据缓存起来
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { List<E> list; // 先占位 localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER); try { // 三种 Executor 的区别,看doUpdate // 默认Simple list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); } finally { // 移除占位符 localCache.removeObject(key); } // 写入一级缓存 localCache.putObject(key, list); if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) { localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter); } return list; }

1.4.3 二级缓存
二级缓存是用来解决一级缓存不能跨会话共享的问题的,范围是namespace级别的,可以被多个SqlSession共享(只要是同一个接口里面的相同方法,都可以共享),生命周期和应用同步。二级缓存的设置,首先是settings中的cacheEnabled要设置为true,当然默认的就是为true,这个步骤决定了在创建Executor对象的时候是否通过CachingExecutor来装饰。前面源码中也有说明过;要想看二级缓存效果,</cache>标签要打开
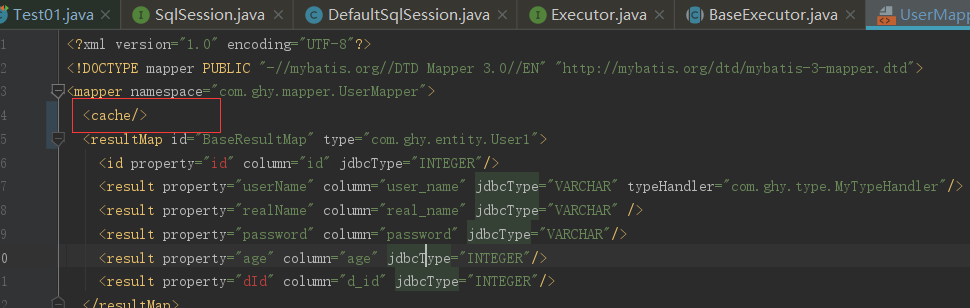
然后把一级缓存配置关闭了,其实由于一级缓存的作用域太小,在实际生产中用的也比较少

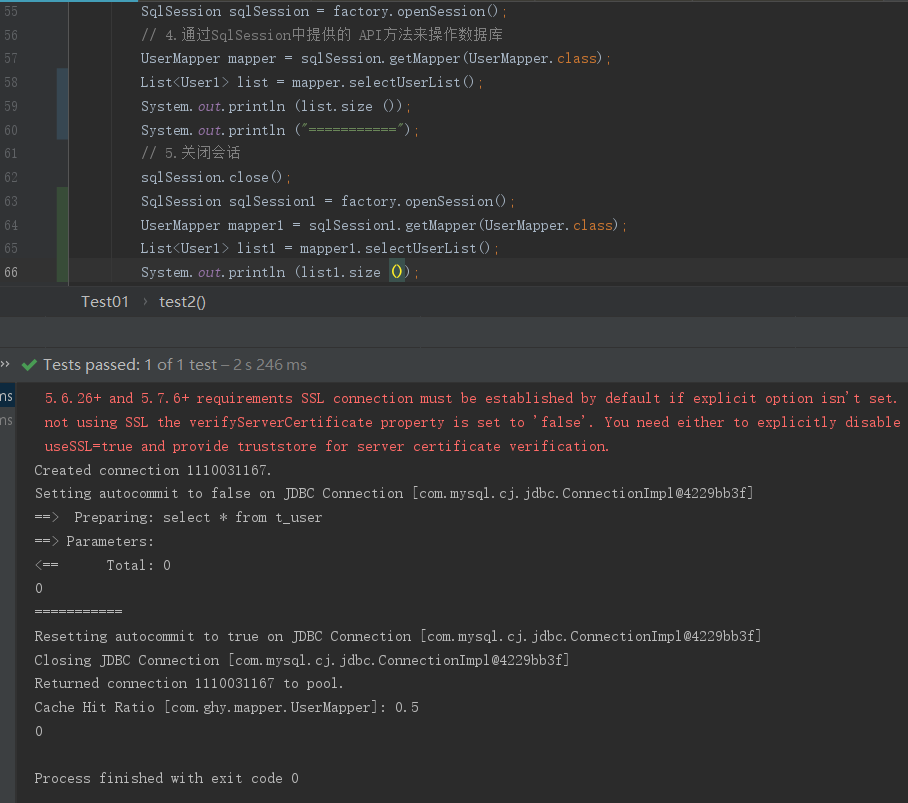
从上面可以发现第二次查询就没走数据库查询,说明二级缓存生效了。接下来看下二级缓存源码,其实在上面已经写出来了,入口是factory.openSession();
@Override public SqlSession openSession() { return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false); }
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) { //事务对象 Transaction tx = null; try { final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment(); // 获取事务工厂 final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment); // 创建事务 tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit); // 根据事务工厂和默认的执行器类型,创建执行器 >>执行SQL语句操作 final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType); return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit); } catch (Exception e) { closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close() throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } }
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) { executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType; executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType; Executor executor; if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) { executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction); } else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {//针对Statement做缓存 executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction); } else { // 默认 SimpleExecutor,每一次只是SQL操作都创建一个新的Statement对象 executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction); } // 二级缓存开关,settings 中的 cacheEnabled 默认是 true if (cacheEnabled) { executor = new CachingExecutor(executor); } // 植入插件的逻辑,至此,四大对象已经全部拦截完毕;这里面是一个拦截器链 executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor); return executor; }
从这里可以看到如果判断成立,那么会对executor做一个装饰;后面做查询操作时就要从sqlSession.selectList("com.ghy.mapper.UserMapper.selectUserList");跟踪起了
@Override public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) { try { MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement); // 如果 cacheEnabled = true(默认),Executor会被 CachingExecutor装饰 return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER); } catch (Exception e) { throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } }
一样,进入query方法看他是怎么执行的

这里要进的就是CachingExecutor里面了,这里面是二级缓存的东西
@Override public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException { // 获取SQL BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject); // 创建CacheKey:什么样的SQL是同一条SQL? >> CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql); return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); }
这里面创建createCacheKey的过程和一级缓存一样,这里就不想再写一次了;
@Override public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { Cache cache = ms.getCache(); // cache 对象是在哪里创建的? XMLMapperBuilder类 xmlconfigurationElement() // 由 <cache> 标签决定 if (cache != null) { // flushCache="true" 清空一级二级缓存 >> flushCacheIfRequired(ms); if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) { ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql); // 获取二级缓存 // 缓存通过 TransactionalCacheManager、TransactionalCache 管理 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key); if (list == null) { list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); // 写入二级缓存 tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116 } return list; } } // 走到 SimpleExecutor | ReuseExecutor | BatchExecutor return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); }
这就是二级缓存过程;
cache属性详解:
| 属性 | 含义 | 取值 |
| type |
缓存实现类 |
需要实现Cache接口,默认是PerpetualCache,可以使用第三方缓存 |
| size |
最多缓存对象个数 |
默认1024 |
| eviction |
回收策略(缓存淘汰算法) |
LRU – 最近最少使用的:移除最长时间不被使用的对象(默认)。FIFO |
| flushInterval |
定时自动清空缓存间隔 |
自动刷新时间,单位 ms,未配置时只有调用时刷新 |
| readOnly |
是否只读 |
true:只读缓存;会给所有调用者返回缓存对象的相同实例。因此这些 |
| blocking |
启用阻塞缓存 |
通过在get/put方式中加锁,保证只有一个线程操作缓存,基于Java重入锁实现 |
1.4.4 第三方缓存
在实际开发的时候我们一般也很少使用MyBatis自带的二级缓存,这时我们会使用第三方的缓存工具Ehcache获取Redis来实现 https://github.com/mybatis/redis-cache
添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.caches</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-redis</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-beta2</version>
</dependency>
然后加上Cache标签的配置
<cache type="org.mybatis.caches.redis.RedisCache" eviction="FIFO" flushInterval="60000" size="512" readOnly="true"/>
然后添加redis的属性文件
这样缓存就存入redis中了,至于怎么读到redis.properites文件的,这个可以从源码中找下
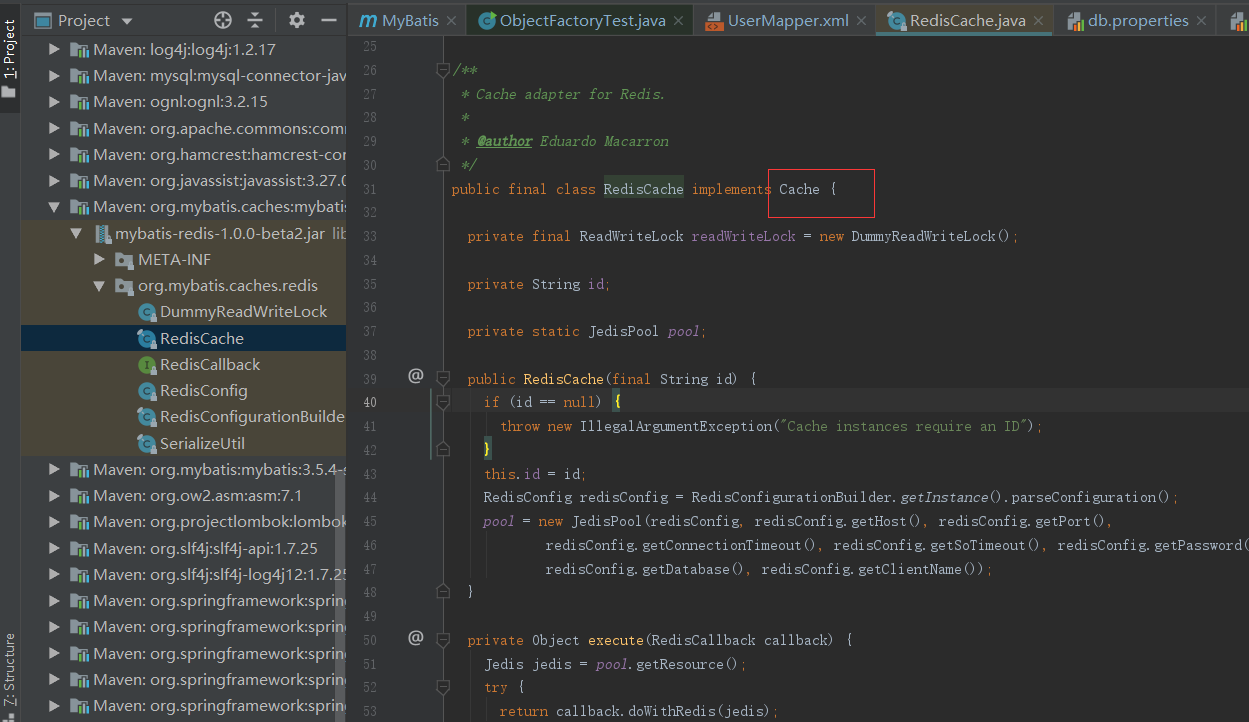
从上面看到在构造方法中会做一些初始的操作,其中的JedisPool是操作连接去操作redis的;
public RedisConfig parseConfiguration() { return parseConfiguration(getClass().getClassLoader()); }
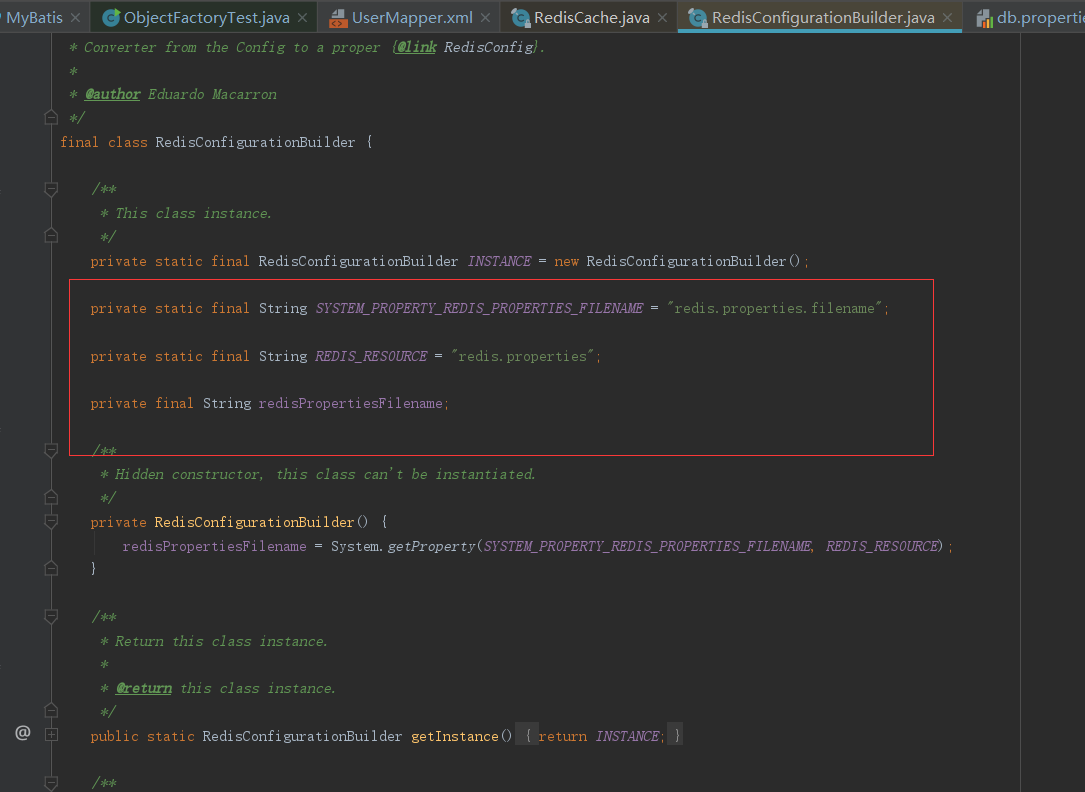
从源码中可以发现他已经做好了redis连接配置文件的默认命名了;