Spark中的任务管理是很重要的内容,可以说想要理解Spark的计算流程,就必须对它的任务的切分有一定的了解。不然你就看不懂Spark UI,看不懂Spark UI就无法去做优化...因此本篇就从源码的角度说说其中的一部分,Stage的切分——DAG图的创建
先说说概念
在Spark中有几个维度的概念:
- 应用Application,你的代码就是一个应用
- Job,Job是以action为边界的。
- Stage,是按照宽窄依赖来界定的
- Task,最终落实到各个工作节点上的任务,是真正意义上的任务
光说上面的概念,可能还不是很了解它的原理,说的通俗点:
Spark的代码都会运行在一个叫做driver的东西上,然后driver回去解析代码,遇到action操作,就提交一个job;然后从最后一个rdd反向解析这个job的rdd,碰到宽依赖就创建一个stage;最后以stage为单位,创建一个任务集,提交给各个机器去执行。
举个例子,在程序员的世界里,有那么几种角色:产品经理(负责提需求)、项目经理(负责管理研发)、程序员(负责写程序)。当产品经理有什么需求时,会找一下项目经理,给它一份需求文档。项目经理根据需求文档,按照业务拆分成不同的模块,然后以模块为单位分配给程序员。比如电商项目背景里,有的程序员专门负责支付,有的专门负责客服,有的专门负责商品。
这样,对应到Spark中:
- 产品经理,就是client,负责提出一些有目的性的需求
- 项目经理,就是driver程序,负责解析这些需求,把任务按照一定的规则拆分(stage)
- 程序员,就是excutor,负责最终的执行。
那么在Spark中的任务拆分,具体的流程可以参考下面的图:
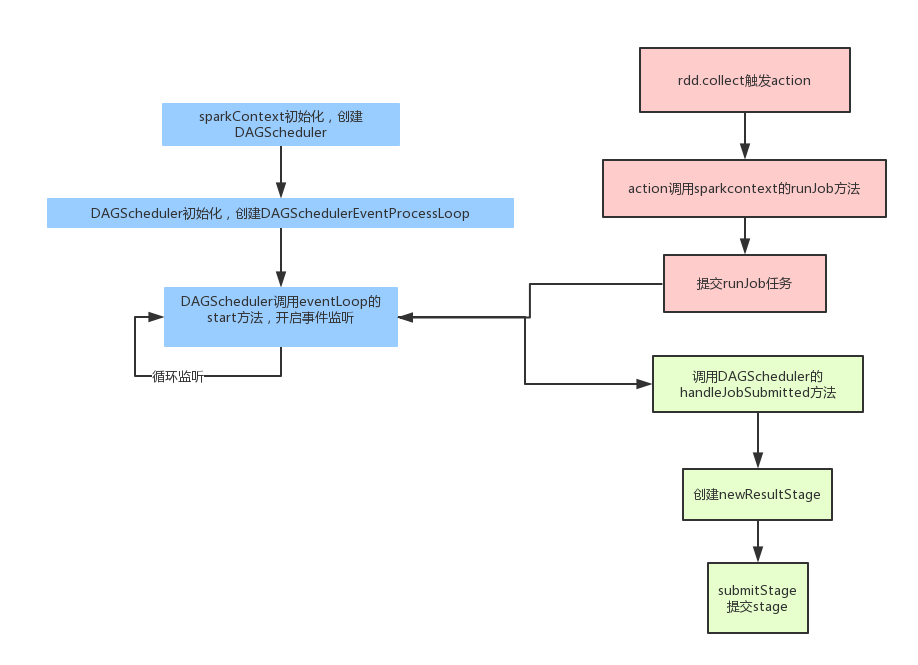
- 首先在SparkContext初始化的时候会创建DAGScheduler,这个DAGScheduelr每个应用只有一个。然后DAGScheduler创建的时候,会初始化一个事件捕获对象,并且开启监听。之后我们的任务都会发给这个事件监听器,它会按照任务的类型创建不同的任务。
- 再从客户端程序方面说,当我们调用action操作的时候,就会触发runjob,它内部其实就是向前面的那个事件监听器提交一个任务。
- 最后事件监听器调用DAGScheduler的handleJobSubmitted真正的处理
- 处理的时候,会先创建一个resultStage,每个job只有一个resultstage,其余的都是shufflestage.然后根据rdd的依赖关系,按照广度优先的思想遍历rdd,遇到shufflerdd就创建一个新的stage。
- 形成DAG图后,遍历等待执行的stage列表,如果这个stage所依赖的父stage执行完了,它就可以执行了;否则还需要继续等待。
- 最终stage会以taskset的形式,提交给TaskScheduler,然后最后提交给excutor。
任务的接收
SparkContext初始化创建DagScheduler
_dagScheduler = new DAGScheduler(this)
DAGScheduler
private[scheduler] val waitingStages = new HashSet[Stage]
private[scheduler] val runningStages = new HashSet[Stage]
private[scheduler] val failedStages = new HashSet[Stage]
private[scheduler] val activeJobs = new HashSet[ActiveJob]
private[scheduler] val eventProcessLoop = new DAGSchedulerEventProcessLoop(this)
// 启动事件监听
eventProcessLoop.start()
EventLoop#run
private val eventThread = new Thread(name) {
setDaemon(true)
override def run(): Unit = {
try {
while (!stopped.get) {
val event = eventQueue.take()
try {
onReceive(event)
} catch {
...
}
}
} catch {...}
}
}
DAGSchedulerEventProcessLoop#onReceive
override def onReceive(event: DAGSchedulerEvent): Unit = {
val timerContext = timer.time()
try {
doOnReceive(event)
} finally {
timerContext.stop()
}
}
private def doOnReceive(event: DAGSchedulerEvent): Unit = event match {
// 处理Job提交事件
case JobSubmitted(jobId, rdd, func, partitions, callSite, listener, properties) =>
dagScheduler.handleJobSubmitted(jobId, rdd, func, partitions, callSite, listener, properties)
// 处理Map Stage提交事件
case MapStageSubmitted(jobId, dependency, callSite, listener, properties) =>
dagScheduler.handleMapStageSubmitted(jobId, dependency, callSite, listener, properties)
// 处理Stage取消事件
case StageCancelled(stageId) =>
dagScheduler.handleStageCancellation(stageId)
// 处理Job取消事件
case JobCancelled(jobId) =>
dagScheduler.handleJobCancellation(jobId)
// 处理Job组取消事件
case JobGroupCancelled(groupId) =>
dagScheduler.handleJobGroupCancelled(groupId)
// 处理所以Job取消事件
case AllJobsCancelled =>
dagScheduler.doCancelAllJobs()
// 处理Executor分配事件
case ExecutorAdded(execId, host) =>
dagScheduler.handleExecutorAdded(execId, host)
// 处理Executor丢失事件
case ExecutorLost(execId) =>
dagScheduler.handleExecutorLost(execId, fetchFailed = false)
case BeginEvent(task, taskInfo) =>
dagScheduler.handleBeginEvent(task, taskInfo)
case GettingResultEvent(taskInfo) =>
dagScheduler.handleGetTaskResult(taskInfo)
// 处理完成事件
case completion @ CompletionEvent(task, reason, _, _, taskInfo, taskMetrics) =>
dagScheduler.handleTaskCompletion(completion)
// 处理task集失败事件
case TaskSetFailed(taskSet, reason, exception) =>
dagScheduler.handleTaskSetFailed(taskSet, reason, exception)
// 处理重新提交失败Stage事件
case ResubmitFailedStages =>
dagScheduler.resubmitFailedStages()
}
任务的提交
RDD#collect()
提交任务
def collect(): Array[T] = withScope {
val results = sc.runJob(this, (iter: Iterator[T]) => iter.toArray)
Array.concat(results: _*)
}
SparkContext#runJob
def runJob[T, U: ClassTag](
rdd: RDD[T],
func: (TaskContext, Iterator[T]) => U,
partitions: Seq[Int],
resultHandler: (Int, U) => Unit): Unit = {
...
dagScheduler.runJob(rdd, cleanedFunc, partitions, callSite, resultHandler, localProperties.get)
...
}
DAGScheduler#runJob
def runJob[T, U](
rdd: RDD[T],
func: (TaskContext, Iterator[T]) => U,
partitions: Seq[Int],
callSite: CallSite,
resultHandler: (Int, U) => Unit,
properties: Properties): Unit = {
...
val waiter = submitJob(rdd, func, partitions, callSite, resultHandler, properties)
waiter.awaitResult() match {
case JobSucceeded =>
logInfo("Job %d finished: %s, took %f s".format
(waiter.jobId, callSite.shortForm, (System.nanoTime - start) / 1e9))
case JobFailed(exception: Exception) =>
logInfo("Job %d failed: %s, took %f s".format
(waiter.jobId, callSite.shortForm, (System.nanoTime - start) / 1e9))
// SPARK-8644: Include user stack trace in exceptions coming from DAGScheduler.
val callerStackTrace = Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace.tail
exception.setStackTrace(exception.getStackTrace ++ callerStackTrace)
throw exception
}
}
DAGScheduler#submitJob
def submitJob[T, U](
rdd: RDD[T],
func: (TaskContext, Iterator[T]) => U,
partitions: Seq[Int],
callSite: CallSite,
resultHandler: (Int, U) => Unit,
properties: Properties): JobWaiter[U] = {
...
val waiter = new JobWaiter(this, jobId, partitions.size, resultHandler)
eventProcessLoop.post(JobSubmitted(
jobId, rdd, func2, partitions.toArray, callSite, waiter,
SerializationUtils.clone(properties)))
...
}
job的切分
DAGScheduler#handleJobSubmitted
private[scheduler] def handleJobSubmitted(jobId: Int,
finalRDD: RDD[_],
func: (TaskContext, Iterator[_]) => _,
partitions: Array[Int],
callSite: CallSite,
listener: JobListener,
properties: Properties) {
var finalStage: ResultStage = null
try {
finalStage = newResultStage(finalRDD, func, partitions, jobId, callSite)
} catch {
...
}
//生成 ActiveJob
val job = new ActiveJob(jobId, finalStage, callSite, listener, properties)
clearCacheLocs()
...
submitStage(finalStage)
submitWaitingStages()
}
DAGScheduler#newRessultStage
private def newResultStage(
rdd: RDD[_],
func: (TaskContext, Iterator[_]) => _,
partitions: Array[Int],
jobId: Int,
callSite: CallSite): ResultStage = {
//获得当前stage的父stage
val (parentStages: List[Stage], id: Int) = getParentStagesAndId(rdd, jobId)
val stage = new ResultStage(id, rdd, func, partitions, parentStages, jobId, callSite)
stageIdToStage(id) = stage
updateJobIdStageIdMaps(jobId, stage) // 更新该job中包含的stage
stage
}
DAGScheduler$getParentStagesAndId
private def getParentStagesAndId(rdd: RDD[_], firstJobId: Int): (List[Stage], Int) = {
val parentStages = getParentStages(rdd, firstJobId)
val id = nextStageId.getAndIncrement()
(parentStages, id)
}
DAGScheduler#getParentStages
private def getParentStages(rdd: RDD[_], firstJobId: Int): List[Stage] = {
val parents = new HashSet[Stage] //所有的依赖的stage
val visited = new HashSet[RDD[_]] //存储访问过的stage
// We are manually maintaining a stack here to prevent StackOverflowError
// caused by recursively visiting
val waitingForVisit = new Stack[RDD[_]] //保存未访问过的stage
def visit(r: RDD[_]) {
if (!visited(r)) { //如果没有访问过
visited += r
// Kind of ugly: need to register RDDs with the cache here since
// we can't do it in its constructor because # of partitions is unknown
for (dep <- r.dependencies) { //读取依赖信息
dep match {
case shufDep: ShuffleDependency[_, _, _] =>
parents += getShuffleMapStage(shufDep, firstJobId) //如果是宽依赖,则加入依赖的数组中
case _ =>
waitingForVisit.push(dep.rdd) //如果是窄依赖,则入栈,继续访问
}
}
}
}
waitingForVisit.push(rdd) //入栈
while (waitingForVisit.nonEmpty) {
visit(waitingForVisit.pop())
}
parents.toList
}
DAGScheduler#getShuffleMapStage
private def getShuffleMapStage(
shuffleDep: ShuffleDependency[_, _, _],
firstJobId: Int): ShuffleMapStage = {
shuffleToMapStage.get(shuffleDep.shuffleId) match {
case Some(stage) => stage //如果已经生成过,直接返回
case None => //如果没有生成过,创建新的stage
// We are going to register ancestor shuffle dependencies
// 为所有的shuffle stage生成 ShuffleMapStage
getAncestorShuffleDependencies(shuffleDep.rdd).foreach { dep =>
shuffleToMapStage(dep.shuffleId) = newOrUsedShuffleStage(dep, firstJobId)
}
// Then register current shuffleDep
val stage = newOrUsedShuffleStage(shuffleDep, firstJobId)
shuffleToMapStage(shuffleDep.shuffleId) = stage
stage
}
}
DAGScheduler#newOrUsedShuffleStage
private def newOrUsedShuffleStage(
shuffleDep: ShuffleDependency[_, _, _],
firstJobId: Int): ShuffleMapStage = {
val rdd = shuffleDep.rdd
val numTasks = rdd.partitions.length
val stage = newShuffleMapStage(rdd, numTasks, shuffleDep, firstJobId, rdd.creationSite)
if (mapOutputTracker.containsShuffle(shuffleDep.shuffleId)) {
val serLocs = mapOutputTracker.getSerializedMapOutputStatuses(shuffleDep.shuffleId)
val locs = MapOutputTracker.deserializeMapStatuses(serLocs)
(0 until locs.length).foreach { i =>
if (locs(i) ne null) {
// locs(i) will be null if missing
stage.addOutputLoc(i, locs(i))
}
}
} else {
// Kind of ugly: need to register RDDs with the cache and map output tracker here
// since we can't do it in the RDD constructor because # of partitions is unknown
logInfo("Registering RDD " + rdd.id + " (" + rdd.getCreationSite + ")")
mapOutputTracker.registerShuffle(shuffleDep.shuffleId, rdd.partitions.length)
}
stage
}
DAGScheduler#newShuffleMapStage
private def newShuffleMapStage(
rdd: RDD[_],
numTasks: Int,
shuffleDep: ShuffleDependency[_, _, _],
firstJobId: Int,
callSite: CallSite): ShuffleMapStage = {
//获得当前stage的父stage
val (parentStages: List[Stage], id: Int) = getParentStagesAndId(rdd, firstJobId)
val stage: ShuffleMapStage = new ShuffleMapStage(id, rdd, numTasks, parentStages,
firstJobId, callSite, shuffleDep)
stageIdToStage(id) = stage
updateJobIdStageIdMaps(firstJobId, stage)// 更新该job中包含的stage
stage
}
DAGScheduler#submitStage
private def submitStage(stage: Stage) {
val jobId = activeJobForStage(stage)
if (jobId.isDefined) {
logDebug("submitStage(" + stage + ")")
if (!waitingStages(stage) && !runningStages(stage) && !failedStages(stage)) {
val missing = getMissingParentStages(stage).sortBy(_.id) //获取到Parent Stage后,递归调用上面那个方法按照StageId小的先提交的原则
logDebug("missing: " + missing)
if (missing.isEmpty) {
logInfo("Submitting " + stage + " (" + stage.rdd + "), which has no missing parents")
submitMissingTasks(stage, jobId.get)
} else {
for (parent <- missing) {
submitStage(parent)
}
waitingStages += stage
}
}
} else {
abortStage(stage, "No active job for stage " + stage.id, None)
}
}
DAGScheduler#getMissingParentStages
private def getMissingParentStages(stage: Stage): List[Stage] = {
val missing = new HashSet[Stage]
val visited = new HashSet[RDD[_]]
// We are manually maintaining a stack here to prevent StackOverflowError
// caused by recursively visiting
val waitingForVisit = new Stack[RDD[_]]
def visit(rdd: RDD[_]) {
if (!visited(rdd)) {
visited += rdd
val rddHasUncachedPartitions = getCacheLocs(rdd).contains(Nil)
if (rddHasUncachedPartitions) {
for (dep <- rdd.dependencies) {
dep match {
case shufDep: ShuffleDependency[_, _, _] =>
val mapStage = getShuffleMapStage(shufDep, stage.firstJobId)
if (!mapStage.isAvailable) {
missing += mapStage
}
case narrowDep: NarrowDependency[_] =>
waitingForVisit.push(narrowDep.rdd)
}
}
}
}
}
waitingForVisit.push(stage.rdd)
while (waitingForVisit.nonEmpty) {
visit(waitingForVisit.pop())
}
missing.toList
}
DAGScheduler#submitMissingTasks
private def submitMissingTasks(stage: Stage, jobId: Int) {
logDebug("submitMissingTasks(" + stage + ")")
// Get our pending tasks and remember them in our pendingTasks entry
stage.pendingPartitions.clear()
// First figure out the indexes of partition ids to compute.
val partitionsToCompute: Seq[Int] = stage.findMissingPartitions()
// Create internal accumulators if the stage has no accumulators initialized.
// Reset internal accumulators only if this stage is not partially submitted
// Otherwise, we may override existing accumulator values from some tasks
if (stage.internalAccumulators.isEmpty || stage.numPartitions == partitionsToCompute.size) {
stage.resetInternalAccumulators()
}
// Use the scheduling pool, job group, description, etc. from an ActiveJob associated
// with this Stage
val properties = jobIdToActiveJob(jobId).properties
runningStages += stage
// SparkListenerStageSubmitted should be posted before testing whether tasks are
// serializable. If tasks are not serializable, a SparkListenerStageCompleted event
// will be posted, which should always come after a corresponding SparkListenerStageSubmitted
// event.
stage match {
case s: ShuffleMapStage =>
outputCommitCoordinator.stageStart(stage = s.id, maxPartitionId = s.numPartitions - 1)
case s: ResultStage =>
outputCommitCoordinator.stageStart(
stage = s.id, maxPartitionId = s.rdd.partitions.length - 1)
}
val taskIdToLocations: Map[Int, Seq[TaskLocation]] = try {
stage match {
case s: ShuffleMapStage =>
partitionsToCompute.map { id => (id, getPreferredLocs(stage.rdd, id))}.toMap
case s: ResultStage =>
val job = s.activeJob.get
partitionsToCompute.map { id =>
val p = s.partitions(id)
(id, getPreferredLocs(stage.rdd, p))
}.toMap
}
} catch {
case NonFatal(e) =>
stage.makeNewStageAttempt(partitionsToCompute.size)
listenerBus.post(SparkListenerStageSubmitted(stage.latestInfo, properties))
abortStage(stage, s"Task creation failed: $e
${e.getStackTraceString}", Some(e))
runningStages -= stage
return
}
stage.makeNewStageAttempt(partitionsToCompute.size, taskIdToLocations.values.toSeq)
listenerBus.post(SparkListenerStageSubmitted(stage.latestInfo, properties))
// TODO: Maybe we can keep the taskBinary in Stage to avoid serializing it multiple times.
// Broadcasted binary for the task, used to dispatch tasks to executors. Note that we broadcast
// the serialized copy of the RDD and for each task we will deserialize it, which means each
// task gets a different copy of the RDD. This provides stronger isolation between tasks that
// might modify state of objects referenced in their closures. This is necessary in Hadoop
// where the JobConf/Configuration object is not thread-safe.
var taskBinary: Broadcast[Array[Byte]] = null
try {
// For ShuffleMapTask, serialize and broadcast (rdd, shuffleDep).
// For ResultTask, serialize and broadcast (rdd, func).
val taskBinaryBytes: Array[Byte] = stage match {
case stage: ShuffleMapStage =>
closureSerializer.serialize((stage.rdd, stage.shuffleDep): AnyRef).array()
case stage: ResultStage =>
closureSerializer.serialize((stage.rdd, stage.func): AnyRef).array()
}
taskBinary = sc.broadcast(taskBinaryBytes)
} catch {
// In the case of a failure during serialization, abort the stage.
case e: NotSerializableException =>
abortStage(stage, "Task not serializable: " + e.toString, Some(e))
runningStages -= stage
// Abort execution
return
case NonFatal(e) =>
abortStage(stage, s"Task serialization failed: $e
${e.getStackTraceString}", Some(e))
runningStages -= stage
return
}
val tasks: Seq[Task[_]] = try {
stage match {
case stage: ShuffleMapStage =>
partitionsToCompute.map { id =>
val locs = taskIdToLocations(id)
val part = stage.rdd.partitions(id)
new ShuffleMapTask(stage.id, stage.latestInfo.attemptId,
taskBinary, part, locs, stage.internalAccumulators)
}
case stage: ResultStage =>
val job = stage.activeJob.get
partitionsToCompute.map { id =>
val p: Int = stage.partitions(id)
val part = stage.rdd.partitions(p)
val locs = taskIdToLocations(id)
new ResultTask(stage.id, stage.latestInfo.attemptId,
taskBinary, part, locs, id, stage.internalAccumulators)
}
}
} catch {
case NonFatal(e) =>
abortStage(stage, s"Task creation failed: $e
${e.getStackTraceString}", Some(e))
runningStages -= stage
return
}
if (tasks.size > 0) {
logInfo("Submitting " + tasks.size + " missing tasks from " + stage + " (" + stage.rdd + ")")
stage.pendingPartitions ++= tasks.map(_.partitionId)
logDebug("New pending partitions: " + stage.pendingPartitions)
taskScheduler.submitTasks(new TaskSet(
tasks.toArray, stage.id, stage.latestInfo.attemptId, jobId, properties))
stage.latestInfo.submissionTime = Some(clock.getTimeMillis())
} else {
// Because we posted SparkListenerStageSubmitted earlier, we should mark
// the stage as completed here in case there are no tasks to run
markStageAsFinished(stage, None)
val debugString = stage match {
case stage: ShuffleMapStage =>
s"Stage ${stage} is actually done; " +
s"(available: ${stage.isAvailable}," +
s"available outputs: ${stage.numAvailableOutputs}," +
s"partitions: ${stage.numPartitions})"
case stage : ResultStage =>
s"Stage ${stage} is actually done; (partitions: ${stage.numPartitions})"
}
logDebug(debugString)
}
}
DAGScheduler#submitWaitingStages
private def submitWaitingStages() {
// TODO: We might want to run this less often, when we are sure that something has become
// runnable that wasn't before.
logTrace("Checking for newly runnable parent stages")
logTrace("running: " + runningStages)
logTrace("waiting: " + waitingStages)
logTrace("failed: " + failedStages)
val waitingStagesCopy = waitingStages.toArray
waitingStages.clear()
for (stage <- waitingStagesCopy.sortBy(_.firstJobId)) {
submitStage(stage)
}
}