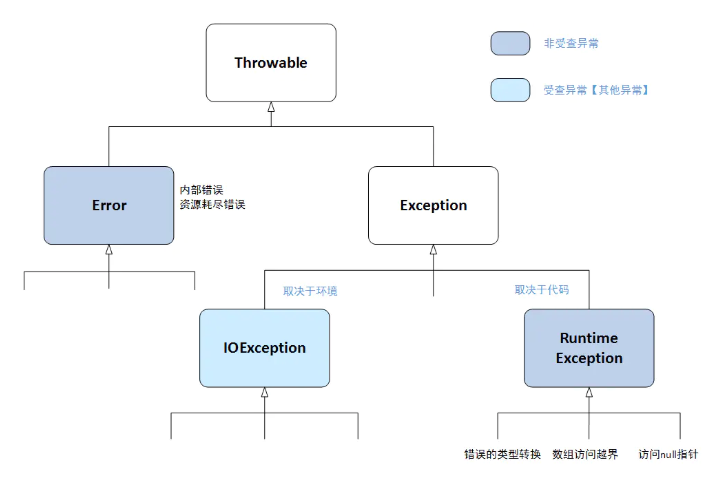
分类
- 编译时__异常__: 无法通过编译,必须显示处理。Exception下非RuntimeException类(Run..也是Ex..的子类),如IOException、SQLException等
- 运行时异常: 都是RuntimeException类及其子类异常,如NullPointerException(空指针异常)
异常处理
- try..catch..finally
- throws
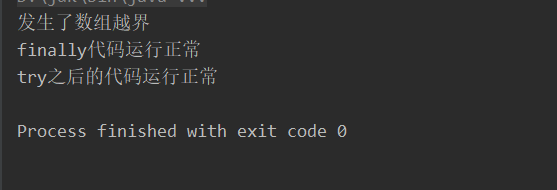
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] i = {1,2,3};
try {
i[3] = 10;
int j= 2/0;
System.out.println("try中异常代码之后部分不会执行");
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("发生了数组越界");
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("发生了被除数为0");
} finally {
System.out.println("finally代码运行正常"); // finally 中代码永远会执行
}
System.out.println("try之后的代码运行正常");
}
public static void main(String arg[]) {
try {
function();
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
System.out.println("e = " + e.toString());
} finally {
System.out.println("finally");
}
}
public static void function() throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException{
int a, b;
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
a = in.nextInt();
b = in.nextInt();
int c = a / b;
System.out.println(c);
int[] a1 = { 1, 3, 3 };
System.out.println(a1[3]);
System.out.println("异常后的语句");
}
finally
finally块不管异常是否发生,只要对应的try执行了,则它一定也执行。只有一种方法让finally块不执行:System.exit()。因此finally块通常用来做资源释放操作:关闭文件,关闭数据库连接等等。
良好的编程习惯是:在try块中打开资源,在finally块中清理释放这些资源。
需要注意的地方:
- finally块没有处理异常的能力。处理异常的只能是catch块。
- 在同一try…catch…finally块中 ,如果try中抛出异常,且有匹配的catch块,则先执行catch块,再执行finally块。如果没有catch块匹配,则先执行finally,然后去外面的调用者中寻找合适的catch块。
- 在同一try…catch…finally块中 ,try发生异常,且匹配的catch块中处理异常时也抛出异常,那么后面的finally也会执行:首先执行finally块,然后去外围调用者中寻找合适的catch块。
这是正常的情况,但是也有特例。关于finally有很多恶心,偏、怪、难的问题,我在本文最后统一介绍了,电梯速达->:finally块和return
自定义异常
[1] 继承Exception
public class MyException extends Exception {
public MyException(){
}
public MyException(String message){
super(message);
}
}
// test
public static void main(String[] args) throws MyException {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("男");
list.add("女");
if(!list.contains("中性")){
throw new MyException("性格不合适");
}
}
- 继承RuntimeException
public class MyRuntime extends RuntimeException{
public MyRuntime(){
super();
}
public MyRuntime(String message){
super(message);
}
// test
public static void main(String[] args) throws MyException {
try{
throw new MyRuntime("a runtime exception!");
} catch (MyRuntime myRuntime){
System.out.println("myRuntime = " + myRuntime);
}
}