Notes
在html中运行js的3种方式:
<!--1--> <h1>Testing alert</h1> <script>alert("hello!");</script> <!--2--> <h1>Testing alert</h1> <script src="code/hello.js"></script> <!--3--> <button onclick="alert('Boom!');">DO NOT PRESS</button>
js在浏览器中解释、运行,浏览器对js具有诸多限制,例如不允许js访问本地文件、不能修改任何和所访问网页无关的东西。因此js仿佛是在一个用钢板围起来的沙盒里活动,而html会被浏览器获取、解析为文档模型(一种特殊的数据结构),浏览器依据这个文档模型来渲染画面,这个文档模型是在js沙盒范围内的东西,js可以自由地读取和修改它。
html被解析为一种叫文档对象模型(Document Object Model)的东西,浏览器就是依据它来进行页面渲染的。全局绑定document是我们访问这些文档对象的入口,它的documentElement属性指向html标签所对应的对象,还有head和body属性,分别指向各种对应的对象。DOM是一种树形结构,document.documentElement即是根节点。再比如说document.body也是一个节点,它的孩子可以是元素节点,也可能是一段文本或者评论节点。
每个DOM节点对象都有一个nodeType属性,该属性包含标识节点类型的编码(数字)。元素的编码为Node.ELEMENT_NODE,该常量的真实值为数字1。 表示文档中一段文本的文本节点编码是3(Node.TEXT_NODE)。注释的编码为8(Node.COMMENT_NODE)。
DOM的可视化:
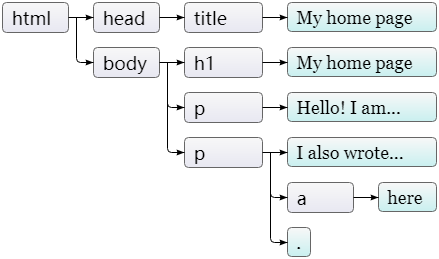
叶子是文本节点,箭头则表明了父子关系。
DOM并非是专门为js设计的,它最开始是想成为xml一样中立的东西。所以它本身和js集成得并不是特别好。一个典型的例子是childNodes属性,它类似array,却又不是真正的array,而是NodeList类型,所以它并不支持slice和map。再比如,DOM并没有提供一次性创建节点并添加子节点、属性的方法,而是必须要首先创建它,然后一个一个地添加子节点和属性。
当然,这些缺点都不是致命的,我们显然可以自定义函数来封装一些操作,以便更好地和DOM交互。(已经有许多现成的库做这件事情)
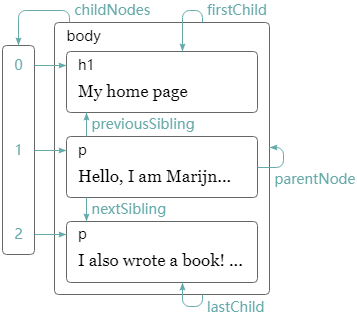
如果属性对应的节点不存在,则为null。
有个与childNodes类似的children属性,不过children属性只包含元素子女(编码为1的节点),当你对文本节点不感兴趣的时候这通常是有用的。可以通过递归来遍历DOM树,因为childNodes不是真正的数组,因此只能通过常规的循环来遍历它,不能用for/of循环。
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My home page</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>My home page</h1>
<p>Hello, I am Marijn and this is my home page.</p>
<p>I also wrote a book! Read it
<a href="http://eloquentjavascript.net">here</a>.</p>
<script type="text/javascript">
// 递归,深度优先搜索DOM树
function talksAbout(node, string) {
if (node.nodeType == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) {
for (let i = 0; i < node.childNodes.length; i++) {
if (talksAbout(node.childNodes[i], string)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
} else if (node.nodeType == Node.TEXT_NODE) {
// text节点的nodeValue储存着显示文本
return node.nodeValue.indexOf(string) > -1;
}
}
console.log(talksAbout(document.body, "book"));
// → true
</script>
</body>
</html>
根据子元素的标签类型:
let link = document.body.getElementsByTagName("a")[0];
console.log(link.href);
根据id:
<p>My ostrich Gertrude:</p> <p><img id="gertrude" src="img/ostrich.png"></p> <script> let ostrich = document.getElementById("gertrude"); console.log(ostrich.src); </script>
类似的还有getElementsByClassName
remove,移除元素:
<p>One</p>
<p>Two</p>
<p>Three</p>
<script>
let paragraphs = document.body.getElementsByTagName("p");
paragraphs[0].remove();
// two/three
</script>
appendChild,用于插入元素到某个父元素的孩子元素的最后一位:
<p>One</p>
<p>Two</p>
<p>Three</p>
<script>
let paragraphs = document.body.getElementsByTagName("p");
document.body.appendChild(paragraphs[1]);
// One/Three/Two
</script>
insertBefore,一个节点只能存在于文档中的一个地方,插入段落3会导致它在原来的位置移除,再被插入到相应位置:
<p>One</p>
<p>Two</p>
<p>Three</p>
<script>
let paragraphs = document.body.getElementsByTagName("p");
document.body.insertBefore(paragraphs[2], paragraphs[0]);
// insertBefore插入到某某之前,这里是把three插到one之前
// Three/One/Two
</script>
【All operations that insert a node somewhere will, as a side effect, cause it to be removed from its current position (if it has one).】
类似的还有replaceChild :
<p>One</p>
<p>Two</p>
<p>Three</p>
<script>
let paragraphs = document.body.getElementsByTagName("p");
document.body.replaceChild(paragraphs[0], paragraphs[1]);
// 第一个作为新元素,第二个是被淘汰的旧元素
// One/Three
</script>
点击按钮后将所有图片替换成其alt属性中的文字:
<p>The <img src="img/cat.png" alt="Cat"> in the <img src="img/hat.png" alt="Hat">.</p> <p><button onclick="replaceImages()">Replace</button></p> <script> function replaceImages() { let images = document.body.getElementsByTagName("img"); // image的长度内容都是随着document动态变化的 for(let i = images.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { // 所以才要从最后一个元素开始替换,这样移除元素 // 的时候才不会影响到访问其余兄弟元素的下标值 let image = images[i]; if(image.alt) { let text = document.createTextNode(image.alt); image.parentNode.replaceChild(text, image); // 必须获得父元素的引用才能替换孩子元素 } } // 主题无关↓:从DOM获取一个静态的数组Array.from let arrayish = { 0: "one", 1: "two", length: 2 }; let array = Array.from(arrayish); console.log(array.map(s => s.toUpperCase())); // → ["ONE", "TWO"] } </script>
document.createElement(tag name)返回一个相应类型的空元素,示例如下:
<blockquote id="quote"> No book can ever be finished. While working on it we learn just enough to find it immature the moment we turn away from it. </blockquote> <script> // 创建一个type类型的空元素 // children是它的孩子节点, // 该函数可以接受n个参数 function elt(type, ...children) { let node = document.createElement(type); for(let child of children) { if(typeof child != "string") node.appendChild(child); else node.appendChild(document.createTextNode(child)); // 如果是string类型就将其转换为一个文本节点再插入 } return node; // 返回这个创建好的节点 } document.getElementById("quote").appendChild( elt("footer"/*type*/, "—"/*child-0*/, elt("strong", "Karl Popper")/*child-1*/, ", preface to the second editon of "/*child-2*/, elt("em", "The Open Society and Its Enemies")/*child-3*/, ", 1950"/*child-4*/)); </script>
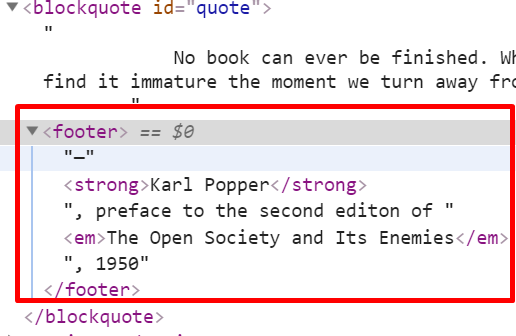

不仅可以在js中设置、获取元素的标准属性,还可以用getAttribute和setAttribute方法设置自定义的属性
(诸如alt、href等标准属性,直接node.alt就可以访问)
<p data-classified="secret">The launch code is 00000000.</p>
<p data-classified="unclassified">I have two feet.</p>
<script>
let paras = document.body.getElementsByTagName("p");
for(let para of Array.from(paras)) { // 将动态的nodelist转化为静态的数组
if(para.getAttribute("data-classified") == "secret") {
// 推荐用前缀修饰自定义属性,这样就不会与标准属性冲突了
para.remove();
}
}
</script>
getAttribute和setAttribute和属于通用方法,也可以用来访问标准属性。
访问元素所占空间大小:
<p style="border: 3px solid red"> I'm boxed in </p> <script> let para = document.body.getElementsByTagName("p")[0]; console.log("clientHeight:", para.clientHeight); // 21 不包括边框 console.log("offsetHeight:", para.offsetHeight); // 27 加上边框 2*3px </script>
访问元素位置最有效的方法:
<p style="border: 3px solid red"> I'm boxed in </p> <script> let para = document.body.getElementsByTagName("p")[0]; let boundingClientRect = para.getBoundingClientRect(); // html元素左上角相对于浏览器显示屏的准确位置 console.log("top:", boundingClientRect.top); // 16 console.log("buttom:", boundingClientRect.buttom); // undefined console.log("left:", boundingClientRect.left); // 8 console.log("right:", boundingClientRect.right); // 556 // 相对于document的位置,需要加上滚动条位置 console.log("pageXOffset:", window.pageXOffset); console.log("pageYOffset:", window.pageYOffset); </script>
进行文档布局需要做很多工作。为了速度,浏览器引擎不会在每次更改文档时立即重新布局文档,而是尽可能长时间的等待。当更改文档的JavaScript程序完成运行时,浏览器才必须计算新的布局以将更改的文档绘制到屏幕上。当程序通过诸如offsetHeight或者getBoundingClientRect读取某个东西的大小或者位置时,提供正确的信息也需要计算布局。在读取DOM布局信息和更改DOM之间反复交替的程序会强制执行大量布局计算,因此运行速度非常慢↓
<script>
function time(name, action) {
let start = Date.now(); // Current time in milliseconds
action();
console.log(name, "took", Date.now() - start, "ms");
}
time("naive", () => {
let target = document.getElementById("one");
while(target.offsetWidth < 2000) {
target.appendChild(document.createTextNode("X"));
}
});
// → naive took 32 ms
time("clever", function() {
let target = document.getElementById("two");
target.appendChild(document.createTextNode("XXXXX"));
let total = Math.ceil(2000 / (target.offsetWidth / 5));
target.firstChild.nodeValue = "X".repeat(total);
});
// → clever took 1 ms
</script>
<p id="para" style="color: purple"> Nice text </p> <script> let para = document.getElementById("para"); console.log(para.style.color); para.style.color = "magenta"; para.style['color'] = "red"; para.style.fontFamily = "cursive"; </script>
<p>And if you go chasing <span class="animal">rabbits</span></p> <p>And you know you're going to fall</p> <p>Tell 'em a <span class="character">hookah smoking <span class="animal">caterpillar</span></span></p> <p>Has given you the call</p> <script> function count(selector) { return document.querySelectorAll(selector).length; } console.log(count("p")); // All <p> elements // → 4 console.log(count(".animal")); // Class animal // → 2 console.log(count("p .animal")); // Animal inside of <p> // → 2 console.log(count("p > .animal")); // Direct child of <p> // → 1 </script>
querySelectorAll与querySelector后者只返回一个元素(第一个)。
<p>_</p> <p>_</p> <p>_</p> <p>_</p> <p>_</p> <p style="text-align: center"> <img src="img/cat.png" style="position: relative"> </p> <script> let cat = document.querySelector("img"); let angle = Math.PI / 2; function animate(time, lastTime) { if (lastTime != null) { angle += (time - lastTime) * 0.001; } cat.style.top = (Math.sin(angle) * 20) + "px"; cat.style.left = (Math.cos(angle) * 200) + "px"; requestAnimationFrame(newTime => animate(newTime, time)); } debugger; requestAnimationFrame(animate); </script>
Exercises
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> </head> <body> <h1>Mountains</h1> <div id="mountains"></div> <script> const MOUNTAINS = [ {name: "Kilimanjaro", height: 5895, place: "Tanzania"}, {name: "Everest", height: 8848, place: "Nepal"}, {name: "Mount Fuji", height: 3776, place: "Japan"}, {name: "Vaalserberg", height: 323, place: "Netherlands"}, {name: "Denali", height: 6168, place: "United States"}, {name: "Popocatepetl", height: 5465, place: "Mexico"}, {name: "Mont Blanc", height: 4808, place: "Italy/France"} ]; // Your code here function elt(type, ...children) { let node = document.createElement(type); for(let child of children) { if(typeof child != "string" && typeof child != "number") { node.appendChild(child); } else node.appendChild(document.createTextNode(child)); // 如果是string类型就将其转换为一个文本节点再插入 } return node; // 返回这个创建好的节点 } let table = document.createElement("table"); let ths = document.createElement("tr"); ths.appendChild(elt("th", "name")); ths.appendChild(elt("th", "height")); ths.appendChild(elt("th", "place")); table.appendChild(ths); for (let mountain of MOUNTAINS) { let tds = document.createElement("tr"); tds.appendChild(elt("td", mountain['name'])); let tdHeight = elt("td", mountain['height']); tdHeight.style.textAlign = "right"; tds.appendChild(tdHeight); tds.appendChild(elt("td", mountain['place'])); table.appendChild(tds); } document.getElementById("mountains").appendChild(table); </script> </body> </html>
————--- -- - ---- —— ——- -- -- - -- - -- - -- - - - -
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> </head> <body> <h1>Heading with a <span>span</span> element.</h1> <p>A paragraph with <span>one</span>, <span>two</span> spans. </p> <script> function byTagName(node, tagName) { // Your code here. let result = []; const byTagNameHelper = (node, tagName) => { for (let child of Array.from(node.children)) { if (child.nodeName == tagName.toUpperCase()) { result.push(child); } byTagNameHelper(child, tagName); } }; byTagNameHelper(node, tagName); return result; } console.log(byTagName(document.body, "h1").length); // → 1 console.log(byTagName(document.body, "span").length); // → 3 let para = document.querySelector("p"); console.log(byTagName(para, "span").length); // → 2 </script> </body> </html>
————--- -- - ---- —— ——- -- -- - -- - -- - -- - - - -
略