1、线程同步概念
线程同步:在多个线程访问共享数据时,有先后次序。
在一般情况下,创建一个线程是不能提高程序的执行效率的,所以要创建多个线程。但是多个线程同时运行的时候可能调用线程函数,在多个线程同时对同一个内存地址进行写入,由于CPU时间调度上的问题,写入数据会被多次的覆盖,所以就要使线程同步。
线程同步:即当有一个线程在对内存进行操作时,其他线程都不可以对这个内存地址进行操作,直到该线程完成操作, 其他线程才能对该内存地址进行操作,而其他线程又处于等待状态,目前实现线程同步的方法有很多,临界区对象就是其中一种。
常见的多线程同步的方式:临界区、互斥量、事件、信号量。
临界区(Critical Section)、互斥量(Mutex)、信号量(Semaphore)、事件(Event)的区别如下:
1、临界区:通过对多线程的串行化来访问公共资源或一段代码,速度快,适合控制数据访问。在任意时刻只允许一个线程对共享资源进行访问,如果有多个线程试图访问公共资源,那么在有一个线程进入后,其他试图访问公共资源的线程将被挂起,并一直等到进入临界区的线程离开,临界区在被释放后,其他线程才可以抢占。
2、互斥量:采用互斥对象机制。 只有拥有互斥对象的线程才有访问公共资源的权限,因为互斥对象只有一个,所以能保证公共资源不会同时被多个线程访问。互斥不仅能实现同一应用程序的公共资源安全共享,还能实现不同应用程序的公共资源安全共享。
3、信号量:它允许多个线程在同一时刻访问同一资源,但是需要限制在同一时刻访问此资源的最大线程数目。
4、事 件: 通过通知操作的方式来保持线程的同步,还可以方便实现对多个线程的优先级比较的操作。
2、互斥锁
posix下抽象了一个锁类型的结构:ptread_mutex_t。通过对该结构的操作,来判断资源是否可以访问。顾名思义,加锁(lock)后,别人就无法打开,只有当锁没有关闭(unlock)的时候才能访问资源。
主要有如下5个函数:
(1)pthread_mutex_init(pthread_mutex_t *mutex, const pthread_mutex attr_t *attr); // 初始化锁变量mutex。 // attr为锁属性(自己的值只能被自己的指针改变),NULL值为默认属性。 (2)pthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex); // 加锁(阻塞操作) (3)pthread_mutex_trylock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex); // 试图加锁(不阻塞操作) // 当互斥锁空闲时将占有该锁;否则立即返回 // 但是与2不一样的是当锁已经在使用的时候,返回为EBUSY,而不是挂起等待。 (4)pthread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex); // 释放锁 (5)pthread_mutex_destroy(pthread_mutex_t *mutex); // 使用完后删除
举例1:
1 /************************************************************************* 2 > File Name: pthread_mutex1.c 3 > Summary: 互斥锁举例1 4 > Author: xuelisheng 5 > Created Time: 2018年12月17日 6 ************************************************************************/ 7 /* 8 #include <stdio.h> 9 #include <stdlib.h> 10 #include <unistd.h> 11 #include <pthread.h> 12 typedef struct ct_sum 13 { 14 int sum; 15 pthread_mutex_t lock; 16 }ct_sum; 17 18 void * add1(void * cnt) 19 { 20 // 加互斥锁 21 pthread_mutex_lock(&(((ct_sum*)cnt)->lock)); 22 int i; 23 for(i=0; i<50; i++) 24 { 25 (*(ct_sum*)cnt).sum+=i; 26 } 27 printf("thread 1 printf sum = %d ", ((ct_sum *)cnt)->sum); 28 pthread_mutex_unlock(&(((ct_sum*)cnt)->lock)); 29 pthread_exit(NULL); 30 return 0; 31 } 32 33 void * add2(void *cnt) 34 { 35 int i; 36 cnt= (ct_sum*)cnt; 37 pthread_mutex_lock(&(((ct_sum*)cnt)->lock)); 38 for(i=50; i<101; i++) 39 { 40 (*(ct_sum*)cnt).sum+=i; 41 } 42 printf("thread 2 printf sum = %d ", ((ct_sum *)cnt)->sum); 43 pthread_mutex_unlock(&(((ct_sum*)cnt)->lock)); 44 pthread_exit(NULL); 45 return 0; 46 } 47 48 int main(void) 49 { 50 int i; 51 pthread_t ptid1, ptid2; 52 int sum = 0; 53 ct_sum cnt; 54 //初始化互斥锁 55 pthread_mutex_init(&(cnt.lock),NULL); 56 cnt.sum=0; 57 // 创建线程1 58 pthread_create(&ptid1,NULL,add1,&cnt); 59 // 创建线程2 60 pthread_create(&ptid2,NULL,add2,&cnt); 61 62 pthread_mutex_lock(&(cnt.lock)); 63 printf("sum %d ",cnt.sum); 64 pthread_mutex_unlock(&(cnt.lock)); 65 pthread_join(ptid1,NULL); 66 pthread_join(ptid2,NULL); 67 pthread_mutex_destroy(&(cnt.lock)); 68 return 0; 69 } 70 */ 71 72 /* 73 关于pthread_exit和pthread_join的联合使用 74 一般都是pthread_exit在线程内退出,然后返回一个值。这个时候就跳到主线程的pthread_join了(因为一直在等你结束),这个返回值会直接送到pthread_join,实现了主与分线程的通信。 75 */ 76 #include <stdio.h> 77 #include <stdlib.h> 78 #include <unistd.h> 79 #include <pthread.h> 80 typedef struct ct_sum1 81 { 82 int sum; 83 pthread_mutex_t lock; 84 }; 85 86 struct ct_sum1 ct_sum; 87 88 void * add1() 89 { 90 // 加互斥锁 91 pthread_mutex_lock(&ct_sum.lock); 92 int i; 93 for(i=0; i<50; i++) 94 { 95 ct_sum.sum+=i; 96 } 97 printf("thread 1 printf sum = %d ", ct_sum.sum); 98 // 解锁 99 pthread_mutex_unlock(&ct_sum.lock); 100 // pthread_exit用于强制退出一个线程(非执行完毕退出),一般用于线程内部。 101 pthread_exit(NULL); 102 return 0; 103 } 104 105 void * add2() 106 { 107 int i; 108 // 加互斥锁 109 pthread_mutex_lock(&ct_sum.lock); 110 for(i=50; i<101; i++) 111 { 112 ct_sum.sum+=i; 113 } 114 printf("thread 2 printf sum = %d ", ct_sum.sum); 115 // 解锁 116 pthread_mutex_unlock(&ct_sum.lock); 117 // pthread_exit用于强制退出一个线程(非执行完毕退出),一般用于线程内部。 118 pthread_exit(NULL); 119 return 0; 120 } 121 122 int main(void) 123 { 124 ct_sum.sum = 0; 125 pthread_t ptid1, ptid2; 126 int sum = 0; 127 //初始化互斥锁 128 pthread_mutex_init(&(ct_sum.lock),NULL); 129 // 创建线程1 130 pthread_create(&ptid1,NULL,add1,NULL); 131 // 创建线程2 132 pthread_create(&ptid2,NULL,add2,NULL); 133 // 阻塞主线程,回收子线程 134 pthread_join(ptid1,NULL); 135 pthread_join(ptid2,NULL); 136 137 printf("sum %d ",ct_sum.sum); 138 // 销毁互斥锁 139 pthread_mutex_destroy(&(ct_sum.lock)); 140 return 0; 141 }
运行结果:
thread 1 printf sum = 1225 thread 2 printf sum = 5050 sum 5050
举例2:
1 /************************************************************************* 2 > File Name: pthread_mutex2.c 3 > Summary: 互斥锁举例2(多线程写文件---没有加锁的情形) 4 > Author: xuelisheng 5 > Created Time: 2018年12月17日 6 ************************************************************************/ 7 #include <stdio.h> 8 #include <pthread.h> 9 #include <malloc.h> 10 11 const char filename[] = "hello"; 12 void* thread(void *id) 13 { 14 int num = *(int *)id; // 写文件的操作 15 FILE *fp = fopen(filename, "a+"); 16 int start = *((int *)id); 17 int end = start + 1; 18 setbuf(fp, NULL);// 设置缓冲区的大小 19 fprintf(stdout, "%d ", start); 20 for (int i = (start * 10); i < (end * 10); i ++) 21 { 22 // 写文件 23 fprintf(fp, "%d ", i); 24 } 25 fprintf(fp, " "); 26 fclose(fp); 27 return NULL; 28 } 29 30 int main() 31 { 32 // 设置线程个数 33 int num_thread = 5; 34 // 堆上申请指向每个线程的指针 35 pthread_t *pt = (pthread_t *)malloc(sizeof(pthread_t) * num_thread); 36 int * id = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * num_thread); 37 for (int i = 0; i < num_thread; i++) 38 { 39 id[i] = i; 40 if (pthread_create(&pt[i], NULL, thread, &id[i]) != 0) 41 { 42 printf("thread create failed! "); 43 return 1; 44 } 45 } 46 for (int i = 0; i < num_thread; i++) 47 { 48 pthread_join(pt[i], NULL); 49 } // 释放资源 50 free(pt); 51 free(id); 52 return 0; 53 }
运行结果:
屏幕输出:
1 0 2 3 4
输出文件(hello):
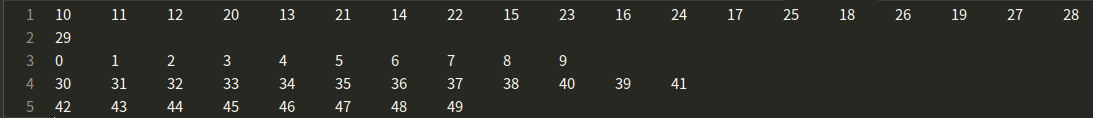
举例3(更改举例2出现的问题):
1 /************************************************************************* 2 > File Name: pthread_mutex3.c 3 > Summary: 互斥锁举例3(多线程写文件---加锁的情形) 4 > Author: xuelisheng 5 > Created Time: 2018年12月17日 6 ************************************************************************/ 7 #include <stdio.h> 8 #include <pthread.h> 9 #include <malloc.h> 10 11 pthread_mutex_t mutex; 12 const char filename[] = "hello"; 13 void* thread(void *id) 14 { 15 int num = *(int *)id; // 写文件的操作 16 // 加锁 17 if (pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex) != 0){ 18 fprintf(stdout, "lock error! "); 19 } 20 FILE *fp = fopen(filename, "a+"); 21 int start = *((int *)id); 22 int end = start + 1; 23 setbuf(fp, NULL);// 设置缓冲区的大小 24 fprintf(stdout, "%d ", start); 25 for (int i = (start * 10); i < (end * 10); i ++) 26 { 27 // 写文件 28 fprintf(fp, "%d ", i); 29 } 30 fprintf(fp, " "); 31 fclose(fp); 32 // 解锁 33 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); 34 return NULL; 35 } 36 37 int main() 38 { 39 // 设置线程个数 40 int num_thread = 5; 41 // 堆上申请指向每个线程的指针 42 pthread_t *pt = (pthread_t *)malloc(sizeof(pthread_t) * num_thread); 43 int * id = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * num_thread); 44 // 初始化互斥锁 45 if (pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL) != 0) 46 { 47 // 互斥锁初始化失败 48 free(pt); 49 free(id); 50 return 1; 51 } 52 53 for (int i = 0; i < num_thread; i++) 54 { 55 id[i] = i; 56 if (pthread_create(&pt[i], NULL, thread, &id[i]) != 0) 57 { 58 printf("thread create failed! "); 59 return 1; 60 } 61 } 62 for (int i = 0; i < num_thread; i++) 63 { 64 pthread_join(pt[i], NULL); 65 } // 释放资源 66 67 pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex); 68 free(pt); 69 free(id); 70 return 0; 71 }
运行结果:
屏幕输出:
0 1 2 3 4
输出文件(hello):