1、条件变量
条件变量是利用线程间共享的全局变量进行同步的一种机制,主要包括两个动作:一个线程等待"条件变量的条件成立"而挂起;另一个线程使"条件成立"(给出条件成立信号)。为了防止竞争,条件变量的使用总是和一个互斥
(1)创建和注销
条件变量和互斥锁一样,都有静态&动态两种创建方式,静态方式使用PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER常量,如下:
pthread_cond_t cond=PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER
动态方式调用pthread_cond_init()函数,API定义如下:
int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *cond, pthread_condattr_t *cond_attr)
尽管POSIX标准中为条件变量定义了属性,但在LinuxThreads中没有实现,因此cond_attr值通常为NULL,且被忽略。
注销一个条件变量需要调用pthread_cond_destroy(),只有在没有线程在该条件变量上等待的时候才能注销这个条件变量,否则返回EBUSY。因为Linux实现的条件变量没有分配什么资源,所以注销动作只包括检查是否有等待线程。API定义如下:
int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t *cond)
(2)等待和激发
int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *cond, pthread_mutex_t *mutex)
int pthread_cond_timedwait(pthread_cond_t *cond, pthread_mutex_t *mutex, const struct timespec *abstime)
等待条件有两种方式:无条件等待pthread_cond_wait()和计时等待pthread_cond_timedwait(),其中计时等待方式如果在给定时刻前条件没有满足,则返回ETIMEOUT,结束等待,其中abstime以与time()系统调用相同意义的绝对时间形式出现,0表示格林尼治时间1970年1月1日0时0分0秒。
无论哪种等待方式,都必须和一个互斥锁配合,以防止多个线程同时请求pthread_cond_wait()(或pthread_cond_timedwait(),下同)的竞争条件(Race Condition)。mutex互斥锁必须是普通锁(PTHREAD_MUTEX_TIMED_NP)或者适应锁(PTHREAD_MUTEX_ADAPTIVE_NP),且在调用pthread_cond_wait()前必须由本线程加锁(pthread_mutex_lock()),而在更新条件等待队列以前,mutex保持锁定状态,并在线程挂起进入等待前解锁。在条件满足从而离开pthread_cond_wait()之前,mutex将被重新加锁,以与进入pthread_cond_wait()前的加锁动作对应。
激发条件有两种形式,pthread_cond_signal()激活一个等待该条件的线程,存在多个等待线程时按入队顺序激活其中一个;而pthread_cond_broadcast()则激活所有等待线程。
(3)互斥变量举例:生产者&消费者
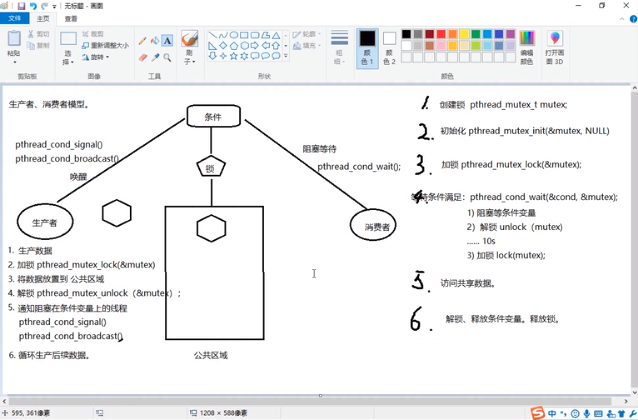
(4)举例:
《举例1》
1 /************************************************************************* 2 > File Name: pthread_cond1.c 3 > Summary: 条件变量应用---生产者&消费者 version1 单个生产者&单个消费者情形 4 > Author: xuelisheng 5 > Created Time: 2018年12月18日 6 ************************************************************************/ 7 8 #include <stdio.h> 9 #include <unistd.h> 10 #include <malloc.h> 11 #include <pthread.h> 12 13 // 链表作为共享数据,需要被互斥量保护 14 struct msg{ 15 struct msg *next; 16 int num; 17 }; 18 19 struct msg *head; 20 21 // 静态初始化,一个条件变量和一个互斥量 22 pthread_cond_t has_product = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER; 23 pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER; 24 25 void *consumer(void *p) 26 { 27 struct msg *mp; 28 for( ; ; ) 29 { 30 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); 31 while(head == NULL) // 说明此时没有节点,这里当只有一个消费者时,使用while和if都可以。如果有多个消费者则必须使用while 32 { 33 // 一开始 阻塞等待,并解锁mutex 34 // 收到signal信号之后,解除阻塞,加锁mutex 35 pthread_cond_wait(&has_product, &mutex); 36 } 37 mp = head; 38 head = mp->next; // 消费掉一个产品 39 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); 40 41 printf("Consume %lu --- %d ", pthread_self(), mp->num); 42 free(mp); 43 sleep(rand()%5); // 休眠:为了打印效果明显 44 } 45 } 46 47 void *producer(void *p) 48 { 49 struct msg *mp; 50 for(; ;) 51 { 52 mp = malloc(sizeof(struct msg)); 53 mp->num = rand() % 1000 + 1; // 模拟生产一个产品(1-1000之间的一个数字) 54 printf("Produce ---------------- %d ", mp->num); 55 56 // 加互斥锁:mp为共享数据 57 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); 58 mp->next = head; 59 head = mp; 60 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); 61 62 pthread_cond_signal(&has_product); // 将等待在该条件变量上的一个线程唤醒,通知阻塞在条件变量上的线程 63 sleep(rand()%5); // 休眠:为了打印效果明显 64 } 65 } 66 67 int main() 68 { 69 pthread_t pid, cid; 70 srand(time(NULL)); 71 72 // 创建线程 73 pthread_create(&pid, NULL, producer, NULL); 74 pthread_create(&pid, NULL, consumer, NULL); 75 76 // 等待回收 77 pthread_join(pid, NULL); 78 pthread_join(cid, NULL); 79 80 return 0; 81 }
运行结果(截取部分):
Produce ---------------- 395 Consume 140093303256832 --- 395 Produce ---------------- 506 Consume 140093303256832 --- 506 Produce ---------------- 553 Consume 140093303256832 --- 553 Produce ---------------- 139 Produce ---------------- 758 Consume 140093303256832 --- 758 Produce ---------------- 313 Produce ---------------- 267 Consume 140093303256832 --- 267 Produce ---------------- 739 Consume 140093303256832 --- 739 Produce ---------------- 718 Consume 140093303256832 --- 718 Consume 140093303256832 --- 313 Produce ---------------- 744 Consume 140093303256832 --- 744 Consume 140093303256832 --- 139 Produce ---------------- 619 Produce ---------------- 449 Produce ---------------- 948 Produce ---------------- 276 Consume 140093303256832 --- 276 Produce ---------------- 896 Consume 140093303256832 --- 896 Consume 140093303256832 --- 948 Produce ---------------- 837 Produce ---------------- 317 Consume 140093303256832 --- 317 Produce ---------------- 478 Consume 140093303256832 --- 478 Consume 140093303256832 --- 837 Produce ---------------- 545 Consume 140093303256832 --- 545
《举例2》
1 /************************************************************************* 2 > File Name: pthread_cond2.c 3 > Summary: 条件变量应用---生产者&消费者 version2 单个生产者&多个消费者情形 4 > Author: xuelisheng 5 > Created Time: 2018年12月18日 6 ************************************************************************/ 7 8 #include <stdio.h> 9 #include <unistd.h> 10 #include <malloc.h> 11 #include <pthread.h> 12 13 // 链表作为共享数据,需要被互斥量保护 14 struct msg{ 15 struct msg *next; 16 int num; 17 }; 18 19 struct msg *head; 20 21 // 静态初始化,一个条件变量和一个互斥量 22 pthread_cond_t has_product = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER; 23 pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER; 24 25 void *consumer(void *p) 26 { 27 struct msg *mp; 28 for( ; ; ) 29 { 30 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); 31 while(head == NULL) // 说明此时没有节点,这里当只有一个消费者时,使用while和if都可以。如果有多个消费者则必须使用while 32 { 33 // 一开始 阻塞等待,并解锁mutex 34 // 收到signal信号之后,解除阻塞,加锁mutex 35 pthread_cond_wait(&has_product, &mutex); // 多个消费者线程都阻塞在这里 36 } 37 mp = head; 38 head = mp->next; // 消费掉一个产品 39 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); 40 41 printf("Consume %lu --- %d ", pthread_self(), mp->num); 42 free(mp); 43 sleep(rand()%5); // 休眠:为了打印效果明显 44 } 45 } 46 47 void *producer(void *p) 48 { 49 struct msg *mp; 50 for(; ;) 51 { 52 mp = malloc(sizeof(struct msg)); 53 mp->num = rand() % 1000 + 1; // 模拟生产一个产品(1-1000之间的一个数字) 54 printf("Produce ---------------- %d ", mp->num); 55 56 // 加互斥锁:mp为共享数据 57 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); 58 mp->next = head; 59 head = mp; 60 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); 61 62 pthread_cond_signal(&has_product); // 将等待在该条件变量上的一个线程唤醒,通知阻塞在条件变量上的线程 63 sleep(rand()%5); // 休眠:为了打印效果明显 64 } 65 } 66 67 int main() 68 { 69 pthread_t pid, cid; 70 srand(time(NULL)); 71 72 // 创建线程 73 pthread_create(&pid, NULL, producer, NULL); 74 75 // 创建多个消费者 76 pthread_create(&pid, NULL, consumer, NULL); 77 pthread_create(&pid, NULL, consumer, NULL); 78 pthread_create(&pid, NULL, consumer, NULL); 79 pthread_create(&pid, NULL, consumer, NULL); 80 81 // 等待回收 82 pthread_join(pid, NULL); 83 pthread_join(cid, NULL); 84 85 return 0; 86 }
运行结果(截取部分):发现消费者线程id不同,即多个消费者
Produce ---------------- 913 Consume 139785213572864 --- 913 Produce ---------------- 509 Consume 139785213572864 --- 509 Produce ---------------- 970 Consume 139785292695296 --- 970 Produce ---------------- 3 Consume 139785196787456 --- 3 Produce ---------------- 41 Consume 139785205180160 --- 41 Produce ---------------- 917 Consume 139785213572864 --- 917 Produce ---------------- 417 Consume 139785196787456 --- 417 Produce ---------------- 768 Consume 139785292695296 --- 768 Produce ---------------- 354 Consume 139785213572864 --- 354 Produce ---------------- 706 Consume 139785205180160 --- 706 Produce ---------------- 412 Consume 139785292695296 --- 412 Produce ---------------- 359 Consume 139785196787456 --- 359 Produce ---------------- 144 Produce ---------------- 400 Consume 139785213572864 --- 144 Consume 139785205180160 --- 400 Produce ---------------- 809 Consume 139785213572864 --- 809