1. 树的定义


2. 相关名词,
a)有序树、无序树 b)孩子、双亲、兄弟
3. 因度为2的树最节省空间,并且任意树可以向二叉树转化,因此着重研究二叉树的性质
二叉树
1.基本形态

2.满二叉树与完全二叉树
满二叉树: 完全二叉树:
1 1
2 3 2 3
4 5 6 7 4 5
3.二叉树一个很重要的性质:
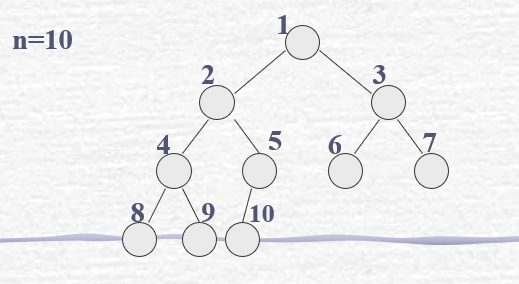

其中,以上三条可以作为二叉树一维数组存储的实现方法。
4. 二叉树的存储方法
a) 一维数组作顺序存储,数组编号与二叉树编号相对应,该数组即为二叉树的顺序存储结构,并且某个元素的双亲或兄弟的查找方法可以通过以上3.中的三条性质确定。
但是,一维数组存储对于完全二叉树或满二叉树可以较好的实现,但对于一般二叉树,会浪费大量的空间。因此,衍生出第二种存储方法--链表存储。
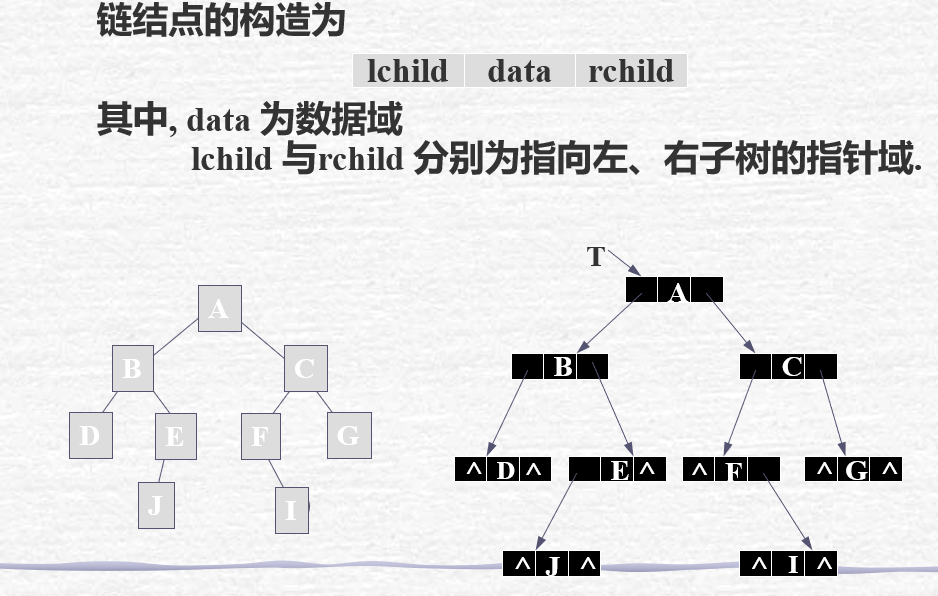
b) 二叉链表
结构示意:
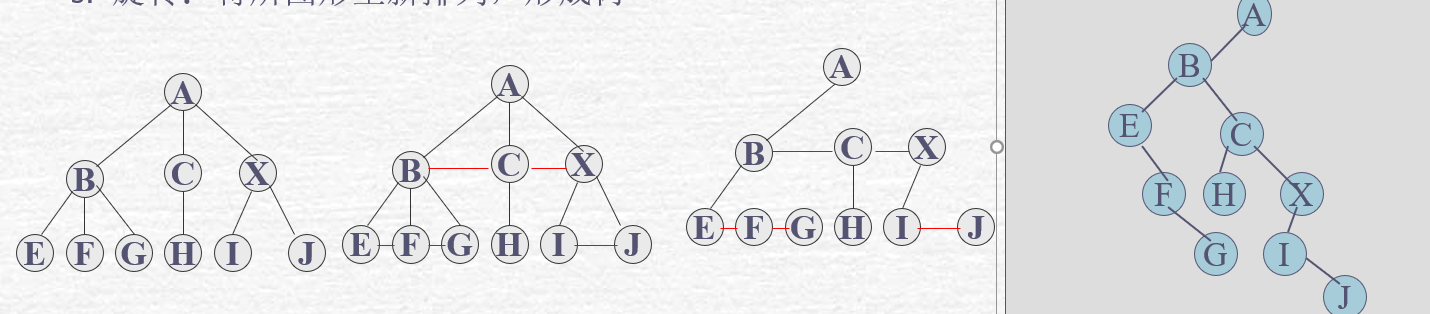
5. 普通树向二叉树的转化方法

6. 二叉树的遍历
一、深度优先 实现方式:递归
a)前序遍历 : 根左右
b)中序遍历: 左根右
c)后序遍历:左右根
二、广度优先 实现方式:队列
// bintree.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 // #include "stdafx.h" #include "stdlib.h" #define M 1024 struct node * ccbl_chudui(); void ccbl_rudui(struct node * tree); struct node * queue[M]; int rear=-1; int front=-1; int flag=0; struct node { char data; struct node* l; struct node* r; }; struct node* Createtree(){ char ch; struct node* t; scanf("%c",&ch); getchar(); //fflush(stdin); if(ch=='#')t=NULL; else{ t = ( struct node* )malloc(sizeof( struct node)); t->data = ch; printf(" 请输入%c结点的左结点:",t->data); t->l = Createtree(); printf(" 请输入%c结点的右子结点:",t->data); t->r = Createtree(); } return t;//返回根节点 } int qxbl(struct node * tree) { if(tree==NULL) return 0; else { printf("%c ",tree->data); qxbl(tree->l); qxbl(tree->r); } } int zxbl(struct node * tree) { if(tree==NULL) return 0; else { zxbl(tree->l); printf("%c ",tree->data); zxbl(tree->r); } } int hxbl(struct node * tree) { if(tree==NULL) return 0; else { hxbl(tree->l); hxbl(tree->r); printf("%c ",tree->data); } } int ccbl(struct node * tree) { if(tree==NULL)return 0; printf("%c ",tree->data); if(tree->l!=NULL) ccbl_rudui(tree->l); //记录B if(tree->r!=NULL) ccbl_rudui(tree->r); //记录C tree=ccbl_chudui(); if(front==rear) { flag++; if(flag==1) ccbl(tree); return 0;} else ccbl(tree); } void ccbl_rudui(struct node * tree) { if(rear==M-1) printf(" 队列已满!"); else { rear++; queue[rear]=tree; } } struct node * ccbl_chudui() { if(front==rear) { printf("队列已空!"); return queue[front];} else { front++; return queue[front]; } } int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { struct node *tree; printf("请输入根节点的数据值 #代表NULL "); tree=Createtree(); printf(" 前序遍历: "); qxbl(tree); printf(" 中序遍历: "); zxbl(tree); printf(" 后序遍历: "); hxbl(tree); printf("层次遍历 "); ccbl(tree); system("pause"); return 0; }
三、二叉树的层次遍历(广度优先)
使用队列
void ccbl(struct node * root) { struct node * queue[1024]; struct node * p; int front, rear; if (root != NULL) { queue[0] = root; front = -1; rear = 0; } while (front < rear) //队列不空 { p = queue[++front]; printf("%c", p->data); //访问p if (p->l != NULL) queue[++rear] = p->l; if (p->r != NULL) queue[++rear] = p->r; } }
四、前序遍历的非递归算法 使用堆栈
void fdgbl(struct node * root) { struct node * p; p = root; while(p!=NULL) { printf("%c", root->data); if (root->r != NULL) push(root->r); if (root->l != NULL) p = p->l; else { if (!empty()) p = pop(); else p = NULL; } } }