第五章:Python高级编程-深入Python的dict和set
目录
5.1 dict的abc继承关系
class Mapping(Collection):
__slots__ = ()
"""A Mapping is a generic container for associating key/value
pairs.
This class provides concrete generic implementations of all
methods except for __getitem__, __iter__, and __len__.
"""
@abstractmethod
def __getitem__(self, key):
raise KeyError
def get(self, key, default=None):
'D.get(k[,d]) -> D[k] if k in D, else d. d defaults to None.'
try:
return self[key]
except KeyError:
return default
def __contains__(self, key):
try:
self[key]
except KeyError:
return False
else:
return True
def keys(self):
"D.keys() -> a set-like object providing a view on D's keys"
return KeysView(self)
def items(self):
"D.items() -> a set-like object providing a view on D's items"
return ItemsView(self)
def values(self):
"D.values() -> an object providing a view on D's values"
return ValuesView(self)
def __eq__(self, other):
if not isinstance(other, Mapping):
return NotImplemented
return dict(self.items()) == dict(other.items())
__reversed__ = None
class MutableMapping(Mapping):
__slots__ = ()
"""A MutableMapping is a generic container for associating
key/value pairs.
This class provides concrete generic implementations of all
methods except for __getitem__, __setitem__, __delitem__,
__iter__, and __len__.
"""
@abstractmethod
def __setitem__(self, key, value):
raise KeyError
@abstractmethod
def __delitem__(self, key):
raise KeyError
__marker = object()
def pop(self, key, default=__marker):
'''D.pop(k[,d]) -> v, remove specified key and return the corresponding value.
If key is not found, d is returned if given, otherwise KeyError is raised.
'''
try:
value = self[key]
except KeyError:
if default is self.__marker:
raise
return default
else:
del self[key]
return value
def popitem(self):
'''D.popitem() -> (k, v), remove and return some (key, value) pair
as a 2-tuple; but raise KeyError if D is empty.
'''
try:
key = next(iter(self))
except StopIteration:
raise KeyError from None
value = self[key]
del self[key]
return key, value
def clear(self):
'D.clear() -> None. Remove all items from D.'
try:
while True:
self.popitem()
except KeyError:
pass
def update(*args, **kwds):
''' D.update([E, ]**F) -> None. Update D from mapping/iterable E and F.
If E present and has a .keys() method, does: for k in E: D[k] = E[k]
If E present and lacks .keys() method, does: for (k, v) in E: D[k] = v
In either case, this is followed by: for k, v in F.items(): D[k] = v
'''
if not args:
raise TypeError("descriptor 'update' of 'MutableMapping' object "
"needs an argument")
self, *args = args
if len(args) > 1:
raise TypeError('update expected at most 1 arguments, got %d' %
len(args))
if args:
other = args[0]
if isinstance(other, Mapping):
for key in other:
self[key] = other[key]
elif hasattr(other, "keys"):
for key in other.keys():
self[key] = other[key]
else:
for key, value in other:
self[key] = value
for key, value in kwds.items():
self[key] = value
def setdefault(self, key, default=None):
'D.setdefault(k[,d]) -> D.get(k,d), also set D[k]=d if k not in D'
try:
return self[key]
except KeyError:
self[key] = default
return default
5.2 dict的常用方法
class dict(object):
"""
dict() -> new empty dictionary
dict(mapping) -> new dictionary initialized from a mapping object's
(key, value) pairs
dict(iterable) -> new dictionary initialized as if via:
d = {}
for k, v in iterable:
d[k] = v
dict(**kwargs) -> new dictionary initialized with the name=value pairs
in the keyword argument list. For example: dict(one=1, two=2)
"""
def clear(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" D.clear() -> None. Remove all items from D. """
pass
def copy(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" D.copy() -> a shallow copy of D """
pass
@staticmethod # known case
def fromkeys(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Create a new dictionary with keys from iterable and values set to value. """
pass
def get(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return the value for key if key is in the dictionary, else default. """
pass
def items(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" D.items() -> a set-like object providing a view on D's items """
pass
def keys(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" D.keys() -> a set-like object providing a view on D's keys """
pass
def pop(self, k, d=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
D.pop(k[,d]) -> v, remove specified key and return the corresponding value.
If key is not found, d is returned if given, otherwise KeyError is raised
"""
pass
def popitem(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
D.popitem() -> (k, v), remove and return some (key, value) pair as a
2-tuple; but raise KeyError if D is empty.
"""
pass
def setdefault(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Insert key with a value of default if key is not in the dictionary.
Return the value for key if key is in the dictionary, else default.
"""
pass
def update(self, E=None, **F): # known special case of dict.update
"""
D.update([E, ]**F) -> None. Update D from dict/iterable E and F.
If E is present and has a .keys() method, then does: for k in E: D[k] = E[k]
If E is present and lacks a .keys() method, then does: for k, v in E: D[k] = v
In either case, this is followed by: for k in F: D[k] = F[k]
"""
pass
def values(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" D.values() -> an object providing a view on D's values """
pass
def __contains__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" True if the dictionary has the specified key, else False. """
pass
def __delitem__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Delete self[key]. """
pass
def __eq__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self==value. """
pass
def __getattribute__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return getattr(self, name). """
pass
def __getitem__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__getitem__(y) <==> x[y] """
pass
def __ge__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self>=value. """
pass
def __gt__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self>value. """
pass
def __init__(self, seq=None, **kwargs): # known special case of dict.__init__
"""
dict() -> new empty dictionary
dict(mapping) -> new dictionary initialized from a mapping object's
(key, value) pairs
dict(iterable) -> new dictionary initialized as if via:
d = {}
for k, v in iterable:
d[k] = v
dict(**kwargs) -> new dictionary initialized with the name=value pairs
in the keyword argument list. For example: dict(one=1, two=2)
# (copied from class doc)
"""
pass
def __iter__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Implement iter(self). """
pass
def __len__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return len(self). """
pass
def __le__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self<=value. """
pass
def __lt__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self<value. """
pass
@staticmethod # known case of __new__
def __new__(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Create and return a new object. See help(type) for accurate signature. """
pass
def __ne__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self!=value. """
pass
def __repr__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return repr(self). """
pass
def __setitem__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Set self[key] to value. """
pass
def __sizeof__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" D.__sizeof__() -> size of D in memory, in bytes """
pass
__hash__ = None
5.3 dict的子类
"""
不建议直接继承dict,而是collections.UserDict
"""
5.4 set和frozenset
"""
set 集合 frozenset(不可变集合) 无序 不重复
"""
s = set("abcde") # 迭代类型
print(s)
# 向set添加数据
s.add()
s.update()
difference() # 差值
- # 差集
# / & -
#set 集合 fronzenset (不可变集合) 无序, 不重复
# s = set('abcdee')
# s = set(['a','b','c','d','e'])
s = {'a','b', 'c'}
# s = frozenset("abcde") #frozenset 可以作为dict的key
# print(s)
#向set添加数据
another_set = set("cef")
re_set = s.difference(another_set)
re_set = s - another_set
re_set = s & another_set
re_set = s | another_set
#set性能很高
# | & - #集合运算
print(re_set)
print (s.issubset(re_set))
# if "c" in re_set:
# print ("i am in set")
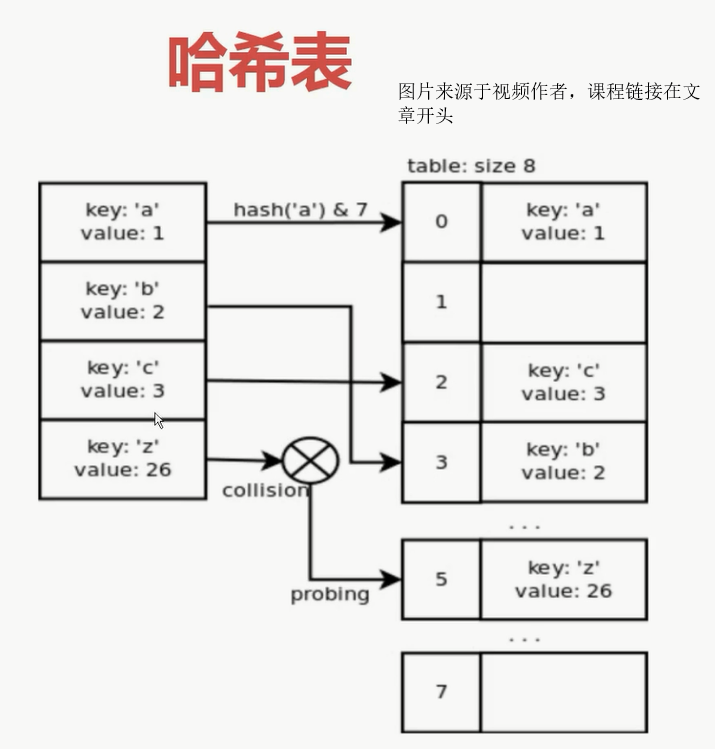
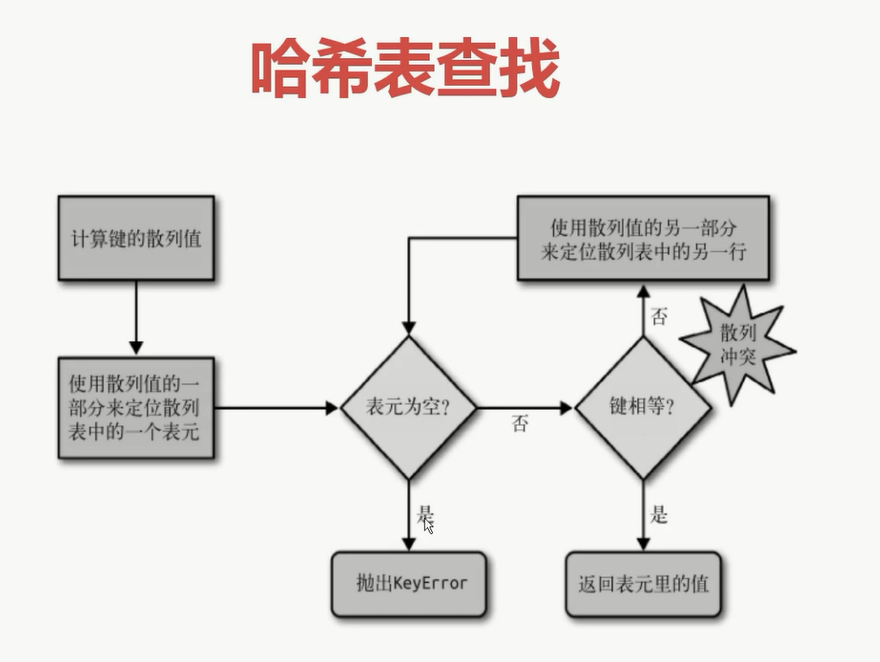
5.5 dict和set的实现原理
"""
测试list和dict的性能
"""
from random import randint
def load_list_data(total_nums, target_nums):
"""
从文件中读取数据,以list的方式返回
:param total_nums: 读取的数量
:param target_nums: 需要查询的数据的数量
"""
all_data = []
target_data = []
file_name = "G:/慕课网课程/AdvancePython/fbobject_idnew.txt"
with open(file_name, encoding="utf8", mode="r") as f_open:
for count, line in enumerate(f_open):
if count < total_nums:
all_data.append(line)
else:
break
for x in range(target_nums):
random_index = randint(0, total_nums)
if all_data[random_index] not in target_data:
target_data.append(all_data[random_index])
if len(target_data) == target_nums:
break
return all_data, target_data
def load_dict_data(total_nums, target_nums):
"""
从文件中读取数据,以dict的方式返回
:param total_nums: 读取的数量
:param target_nums: 需要查询的数据的数量
"""
all_data = {}
target_data = []
file_name = "G:/慕课网课程/AdvancePython/fbobject_idnew.txt"
with open(file_name, encoding="utf8", mode="r") as f_open:
for count, line in enumerate(f_open):
if count < total_nums:
all_data[line] = 0
else:
break
all_data_list = list(all_data)
for x in range(target_nums):
random_index = randint(0, total_nums-1)
if all_data_list[random_index] not in target_data:
target_data.append(all_data_list[random_index])
if len(target_data) == target_nums:
break
return all_data, target_data
def find_test(all_data, target_data):
#测试运行时间
test_times = 100
total_times = 0
import time
for i in range(test_times):
find = 0
start_time = time.time()
for data in target_data:
if data in all_data:
find += 1
last_time = time.time() - start_time
total_times += last_time
return total_times/test_times
if __name__ == "__main__":
# all_data, target_data = load_list_data(10000, 1000)
# all_data, target_data = load_list_data(100000, 1000)
# all_data, target_data = load_list_data(1000000, 1000)
# all_data, target_data = load_dict_data(10000, 1000)
# all_data, target_data = load_dict_data(100000, 1000)
# all_data, target_data = load_dict_data(1000000, 1000)
all_data, target_data = load_dict_data(2000000, 1000)
last_time = find_test(all_data, target_data)
#dict查找的性能远远大于list
#在list中随着list数据的增大 查找时间会增大
#在dict中查找元素不会随着dict的增大而增大
print(last_time)
#1. dict的key或者set的值 都必须是可以hash的
#不可变对象 都是可hash的, str, fronzenset, tuple,自己实现的类 __hash__
#2. dict的内存花销大,但是查询速度快, 自定义的对象 或者python内部的对象都是用dict包装的
# 3. dict的存储顺序和元素添加顺序有关
# 4. 添加数据有可能改变已有数据的顺序