参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/LiaHon/p/11221634.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3310928.html
TreeMap原理实现及常用方法
一. TreeMap概述
- TreeMap存储K-V键值对,通过红黑树(R-B tree)实现;
- TreeMap继承了NavigableMap接口,NavigableMap接口继承了SortedMap接口,可支持一系列的导航定位以及导航操作的方法,当然只是提供了接口,需要TreeMap自己去实现;
- TreeMap实现了Cloneable接口,可被克隆,实现了Serializable接口,可序列化;
- TreeMap因为是通过红黑树实现,红黑树结构天然支持排序,默认情况下通过Key值的自然顺序进行排序;
二. 红黑树回顾
因为TreeMap的存储结构是红黑树,我们回顾一下红黑树的特点以及基本操作,红黑树的原理可参考关于红黑树(R-B tree)原理,看这篇如何。下图为典型的红黑树:
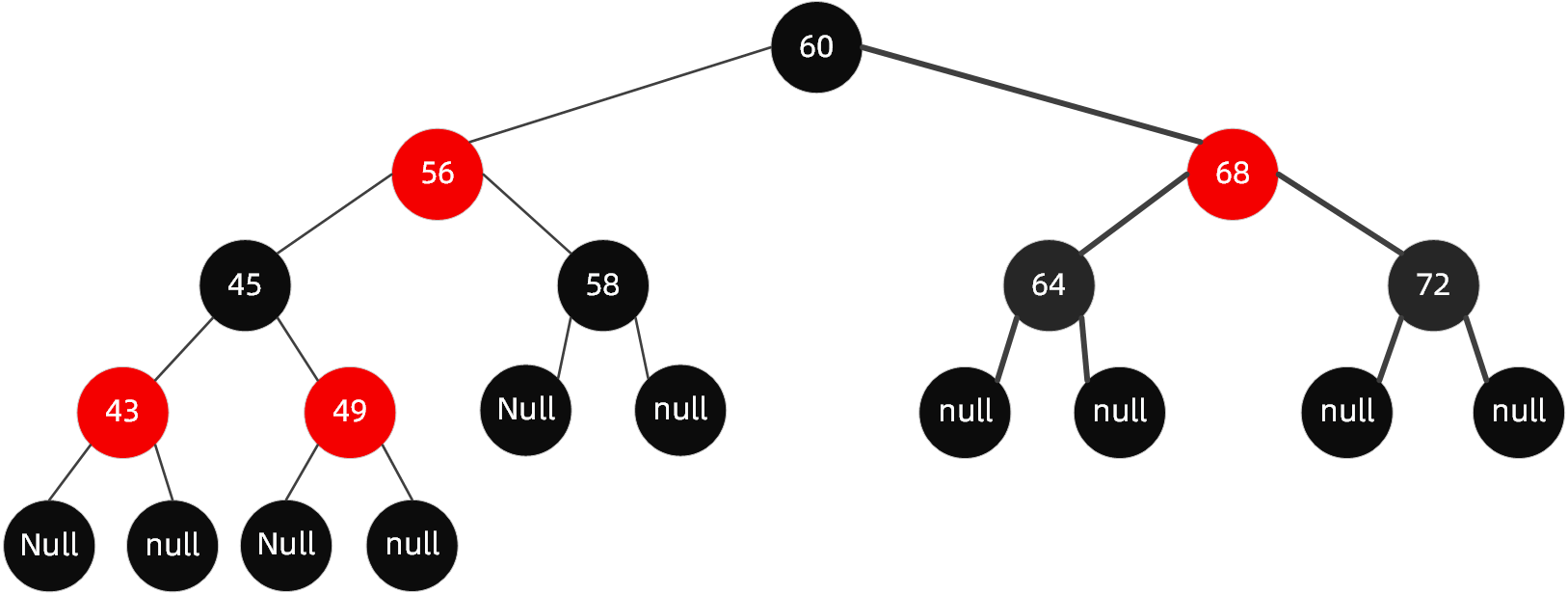
红黑树规则特点:
- 节点分为红色或者黑色;
- 根节点必为黑色;
- 叶子节点都为黑色,且为null;
- 连接红色节点的两个子节点都为黑色(红黑树不会出现相邻的红色节点);
- 从任意节点出发,到其每个叶子节点的路径中包含相同数量的黑色节点;
- 新加入到红黑树的节点为红色节点;
红黑树自平衡基本操作:
- 变色:在不违反上述红黑树规则特点情况下,将红黑树某个node节点颜色由红变黑,或者由黑变红;
- 左旋:逆时针旋转两个节点,让一个节点被其右子节点取代,而该节点成为右子节点的左子节点
- 右旋:顺时针旋转两个节点,让一个节点被其左子节点取代,而该节点成为左子节点的右子节点
三. TreeMap构造
我们先看一下TreeMap中主要的成员变量
/**
* 我们前面提到TreeMap是可以自动排序的,默认情况下comparator为null,这个时候按照key的自然顺序进行排
* 序,然而并不是所有情况下都可以直接使用key的自然顺序,有时候我们想让Map的自动排序按照我们自己的规则,
* 这个时候你就需要传递Comparator的实现类
*/
private final Comparator<? super K> comparator;
/**
* TreeMap的存储结构既然是红黑树,那么必然会有唯一的根节点。
*/
private transient Entry<K,V> root;
/**
* Map中key-val对的数量,也即是红黑树中节点Entry的数量
*/
private transient int size = 0;
/**
* 红黑树结构的调整次数
*/
private transient int modCount = 0;
上面的主要成员变量根节点root是Entry类的实体,我们来看一下Entry类的源码
static final class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
//key,val是存储的原始数据
K key;
V value;
//定义了节点的左孩子
Entry<K,V> left;
//定义了节点的右孩子
Entry<K,V> right;
//通过该节点可以反过来往上找到自己的父亲
Entry<K,V> parent;
//默认情况下为黑色节点,可调整
boolean color = BLACK;
/**
* 构造器
*/
Entry(K key, V value, Entry<K,V> parent) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.parent = parent;
}
/**
* 获取节点的key值
*/
public K getKey() {return key;}
/**
* 获取节点的value值
*/
public V getValue() {return value;}
/**
* 用新值替换当前值,并返回当前值
*/
public V setValue(V value) {
V oldValue = this.value;
this.value = value;
return oldValue;
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
return valEquals(key,e.getKey()) && valEquals(value,e.getValue());
}
public int hashCode() {
int keyHash = (key==null ? 0 : key.hashCode());
int valueHash = (value==null ? 0 : value.hashCode());
return keyHash ^ valueHash;
}
public String toString() {
return key + "=" + value;
}
}
Entry静态内部类实现了Map的内部接口Entry,提供了红黑树存储结构的java实现,通过left属性可以建立左子树,通过right属性可以建立右子树,通过parent可以往上找到父节点。
大体的实现结构图如下:

TreeMap构造函数:
//默认构造函数,按照key的自然顺序排列
public TreeMap() {comparator = null;}
//传递Comparator具体实现,按照该实现规则进行排序
public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) {this.comparator = comparator;}
//传递一个map实体构建TreeMap,按照默认规则排序
public TreeMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
comparator = null;
putAll(m);
}
//传递一个map实体构建TreeMap,按照传递的map的排序规则进行排序
public TreeMap(SortedMap<K, ? extends V> m) {
comparator = m.comparator();
try {
buildFromSorted(m.size(), m.entrySet().iterator(), null, null);
} catch (java.io.IOException cannotHappen) {
} catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) {
}
}
四. put方法
put方法为Map的核心方法,TreeMap的put方法大概流程如下:
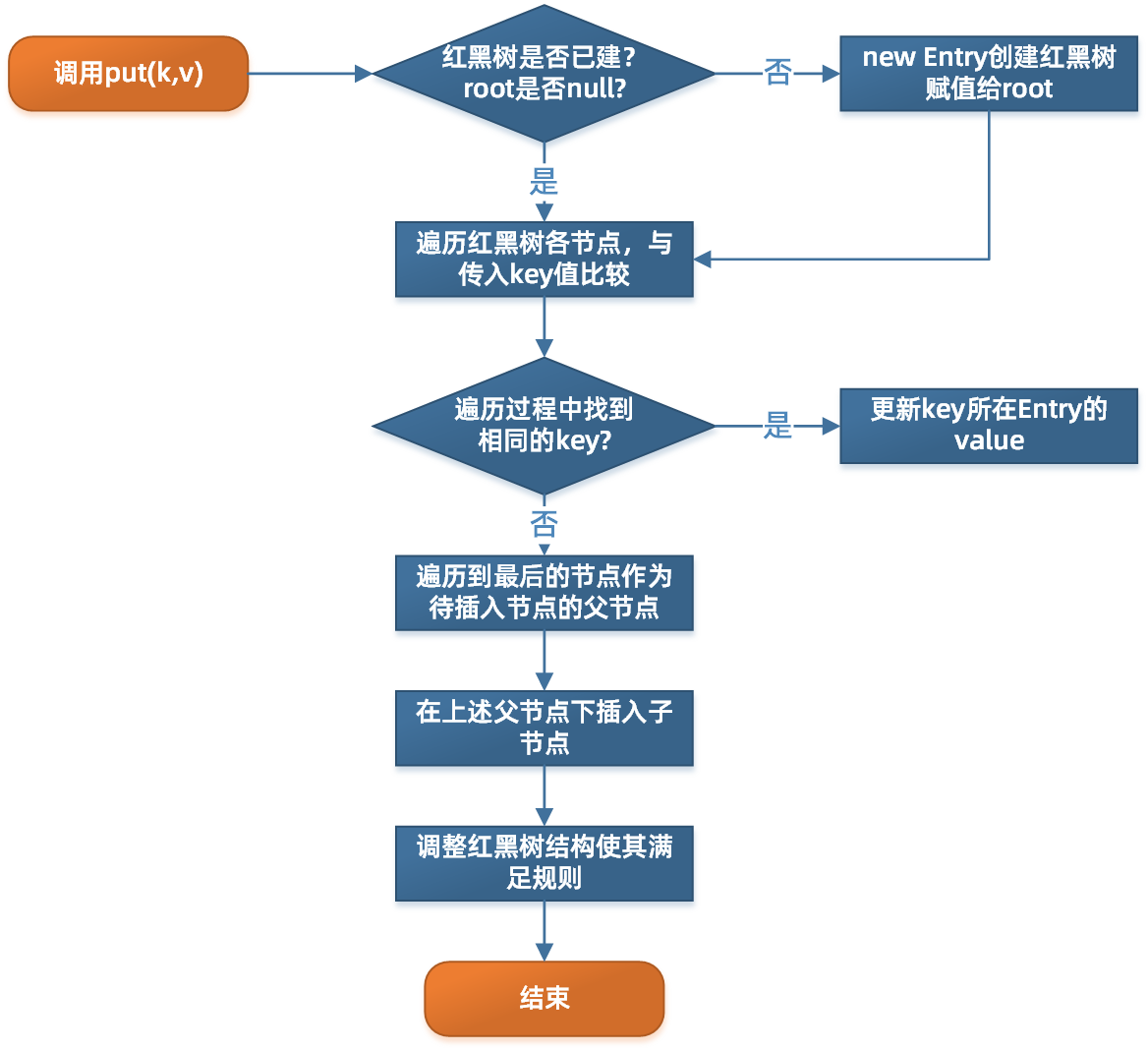
我们来分析一下源码
public V put(K key, V value) {
Entry<K,V> t = root;
/**
* 如果根节点都为null,还没建立起来红黑树,我们先new Entry并赋值给root把红黑树建立起来,这个时候红
* 黑树中已经有一个节点了,同时修改操作+1。
*/
if (t == null) {
compare(key, key);
root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
/**
* 如果节点不为null,定义一个cmp,这个变量用来进行二分查找时的比较;定义parent,是new Entry时必须
* 要的参数
*/
int cmp;
Entry<K,V> parent;
// cpr表示有无自己定义的排序规则,分两种情况遍历执行
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) {
/**
* 从root节点开始遍历,通过二分查找逐步向下找
* 第一次循环:从根节点开始,这个时候parent就是根节点,然后通过自定义的排序算法
* cpr.compare(key, t.key)比较传入的key和根节点的key值,如果传入的key<root.key,那么
* 继续在root的左子树中找,从root的左孩子节点(root.left)开始:如果传入的key>root.key,
* 那么继续在root的右子树中找,从root的右孩子节点(root.right)开始;如果恰好key==root.key,
* 那么直接根据root节点的value值即可。
* 后面的循环规则一样,当遍历到的当前节点作为起始节点,逐步往下找
*
* 需要注意的是:这里并没有对key是否为null进行判断,建议自己的实现Comparator时应该要考虑在内
*/
do {
parent = t;
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
else {
//从这里看出,当默认排序时,key值是不能为null的
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
//这里的实现逻辑和上面一样,都是通过二分查找,就不再多说了
do {
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
/**
* 能执行到这里,说明前面并没有找到相同的key,节点已经遍历到最后了,我们只需要new一个Entry放到
* parent下面即可,但放到左子节点上还是右子节点上,就需要按照红黑树的规则来。
*/
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
if (cmp < 0)
parent.left = e;
else
parent.right = e;
/**
* 节点加进去了,并不算完,我们在前面红黑树原理章节提到过,一般情况下加入节点都会对红黑树的结构造成
* 破坏,我们需要通过一些操作来进行自动平衡处置,如【变色】【左旋】【右旋】
*/
fixAfterInsertion(e);
size++;
modCount++;
return null;
}
put方法源码中通过fixAfterInsertion(e)方法来进行自平衡处理,我们回顾一下插入时自平衡调整的逻辑,下表中看不懂的名词可以参考关于红黑树(R-B tree)原理,看这篇如何
| 无需调整 | 【变色】即可实现平衡 | 【旋转+变色】才可实现平衡 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 情况1: | 当父节点为黑色时插入子节点 | 空树插入根节点,将根节点红色变为黑色 | 父节点为红色左节点,叔父节点为黑色,插入左子节点,那么通过【左左节点旋转】 |
| 情况2: | - | 父节点和叔父节点都为红色 | 父节点为红色左节点,叔父节点为黑色,插入右子节点,那么通过【左右节点旋转】 |
| 情况3: | - | - | 父节点为红色右节点,叔父节点为黑色,插入左子节点,那么通过【右左节点旋转】 |
| 情况4: | - | - | 父节点为红色右节点,叔父节点为黑色,插入右子节点,那么通过【右右节点旋转】 |
接下来我们看一看这个方法
private void fixAfterInsertion(Entry<K,V> x) {
//新插入的节点为红色节点
x.color = RED;
//我们知道父节点为黑色时,并不需要进行树结构调整,只有当父节点为红色时,才需要调整
while (x != null && x != root && x.parent.color == RED) {
//如果父节点是左节点,对应上表中情况1和情况2
if (parentOf(x) == leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)))) {
Entry<K,V> y = rightOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
//如果叔父节点为红色,对应于“父节点和叔父节点都为红色”,此时通过变色即可实现平衡
//此时父节点和叔父节点都设置为黑色,祖父节点设置为红色
if (colorOf(y) == RED) {
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(y, BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
x = parentOf(parentOf(x));
} else {
//如果插入节点是黑色,插入的是右子节点,通过【左右节点旋转】(这里先进行父节点左旋)
if (x == rightOf(parentOf(x))) {
x = parentOf(x);
rotateLeft(x);
}
//设置父节点和祖父节点颜色
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
//进行祖父节点右旋(这里【变色】和【旋转】并没有严格的先后顺序,达成目的就行)
rotateRight(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
}
} else {
//父节点是右节点的情况
Entry<K,V> y = leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
//对应于“父节点和叔父节点都为红色”,此时通过变色即可实现平衡
if (colorOf(y) == RED) {
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(y, BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
x = parentOf(parentOf(x));
} else {
//如果插入节点是黑色,插入的是左子节点,通过【右左节点旋转】(这里先进行父节点右旋)
if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) {
x = parentOf(x);
rotateRight(x);
}
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
//进行祖父节点左旋(这里【变色】和【旋转】并没有严格的先后顺序,达成目的就行)
rotateLeft(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
}
}
}
//根节点必须为黑色
root.color = BLACK;
}
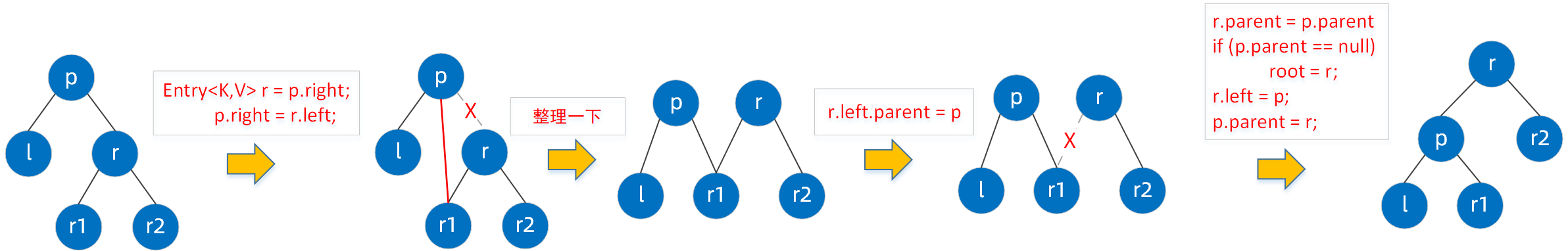
源码中通过 rotateLeft 进行【左旋】,通过 rotateRight 进行【右旋】。都非常类似,我们就看一下【左旋】的代码,【左旋】规则如下:“逆时针旋转两个节点,让一个节点被其右子节点取代,而该节点成为右子节点的左子节点”。
private void rotateLeft(Entry<K,V> p) {
if (p != null) {
/**
* 断开当前节点p与其右子节点的关联,重新将节点p的右子节点的地址指向节点p的右子节点的左子节点
* 这个时候节点r没有父节点
*/
Entry<K,V> r = p.right;
p.right = r.left;
//将节点p作为节点r的父节点
if (r.left != null)
r.left.parent = p;
//将节点p的父节点和r的父节点指向同一处
r.parent = p.parent;
//p的父节点为null,则将节点r设置为root
if (p.parent == null)
root = r;
//如果节点p是左子节点,则将该左子节点替换为节点r
else if (p.parent.left == p)
p.parent.left = r;
//如果节点p为右子节点,则将该右子节点替换为节点r
else
p.parent.right = r;
//重新建立p与r的关系
r.left = p;
p.parent = r;
}
}
就算是看了上面的注释还是并不清晰,看下图你就懂了
五. get 方法
get方法是通过二分查找的思想,我们看一下源码
public V get(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
return (p==null ? null : p.value);
}
/**
* 从root节点开始遍历,通过二分查找逐步向下找
* 第一次循环:从根节点开始,这个时候parent就是根节点,然后通过k.compareTo(p.key)比较传入的key和
* 根节点的key值;
* 如果传入的key<root.key, 那么继续在root的左子树中找,从root的左孩子节点(root.left)开始;
* 如果传入的key>root.key, 那么继续在root的右子树中找,从root的右孩子节点(root.right)开始;
* 如果恰好key==root.key,那么直接根据root节点的value值即可。
* 后面的循环规则一样,当遍历到的当前节点作为起始节点,逐步往下找
*/
//默认排序情况下的查找
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
if (comparator != null)
return getEntryUsingComparator(key);
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key);
if (cmp < 0)
p = p.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
}
return null;
}
/**
* 从root节点开始遍历,通过二分查找逐步向下找
* 第一次循环:从根节点开始,这个时候parent就是根节点,然后通过自定义的排序算法
* cpr.compare(key, t.key)比较传入的key和根节点的key值,如果传入的key<root.key,那么
* 继续在root的左子树中找,从root的左孩子节点(root.left)开始:如果传入的key>root.key,
* 那么继续在root的右子树中找,从root的右孩子节点(root.right)开始;如果恰好key==root.key,
* 那么直接根据root节点的value值即可。
* 后面的循环规则一样,当遍历到的当前节点作为起始节点,逐步往下找
*/
//自定义排序规则下的查找
final Entry<K,V> getEntryUsingComparator(Object key) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
K k = (K) key;
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = cpr.compare(k, p.key);
if (cmp < 0)
p = p.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
}
}
return null;
}
六. remove方法
remove方法可以分为两个步骤,先是找到这个节点,直接调用了上面介绍的getEntry(Object key),这个步骤我们就不说了,直接说第二个步骤,找到后的删除操作。
public V remove(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
if (p == null)
return null;
V oldValue = p.value;
deleteEntry(p);
return oldValue;
}
通过deleteEntry(p)进行删除操作,删除操作的原理我们在前面已经讲过
- 删除的是根节点,则直接将根节点置为null;
- 待删除节点的左右子节点都为null,删除时将该节点置为null;
- 待删除节点的左右子节点有一个有值,则用有值的节点替换该节点即可;
- 待删除节点的左右子节点都不为null,则找前驱或者后继,将前驱或者后继的值复制到该节点中,然后删除前驱或者后继(前驱:左子树中值最大的节点,后继:右子树中值最小的节点);
private void deleteEntry(Entry<K,V> p) {
modCount++;
size--;
//当左右子节点都不为null时,通过successor(p)遍历红黑树找到前驱或者后继
if (p.left != null && p.right != null) {
Entry<K,V> s = successor(p);
//将前驱或者后继的key和value复制到当前节点p中,然后删除节点s(通过将节点p引用指向s)
p.key = s.key;
p.value = s.value;
p = s;
}
Entry<K,V> replacement = (p.left != null ? p.left : p.right);
/**
* 至少有一个子节点不为null,直接用这个有值的节点替换掉当前节点,给replacement的parent属性赋值,给
* parent节点的left属性和right属性赋值,同时要记住叶子节点必须为null,然后用fixAfterDeletion方法
* 进行自平衡处理
*/
if (replacement != null) {
//将待删除节点的子节点挂到待删除节点的父节点上。
replacement.parent = p.parent;
if (p.parent == null)
root = replacement;
else if (p == p.parent.left)
p.parent.left = replacement;
else
p.parent.right = replacement;
p.left = p.right = p.parent = null;
/**
* p如果是红色节点的话,那么其子节点replacement必然为红色的,并不影响红黑树的结构
* 但如果p为黑色节点的话,那么其父节点以及子节点都可能是红色的,那么很明显可能会存在红色相连的情
* 况,因此需要进行自平衡的调整
*/
if (p.color == BLACK)
fixAfterDeletion(replacement);
} else if (p.parent == null) {//这种情况就不用多说了吧
root = null;
} else {
/**
* 如果p节点为黑色,那么p节点删除后,就可能违背每个节点到其叶子节点路径上黑色节点数量一致的规则,
* 因此需要进行自平衡的调整
*/
if (p.color == BLACK)
fixAfterDeletion(p);
if (p.parent != null) {
if (p == p.parent.left)
p.parent.left = null;
else if (p == p.parent.right)
p.parent.right = null;
p.parent = null;
}
}
}
操作的操作其实很简单,场景也不多,我们看一下删除后的自平衡操作方法fixAfterDeletion
private void fixAfterDeletion(Entry<K,V> x) {
/**
* 当x不是root节点且颜色为黑色时
*/
while (x != root && colorOf(x) == BLACK) {
/**
* 首先分为两种情况,当前节点x是左节点或者当前节点x是右节点,这两种情况下面都是四种场景,这里通过
* 代码分析一下x为左节点的情况,右节点可参考左节点理解,因为它们非常类似
*/
if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) {
Entry<K,V> sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));
/**
* 场景1:当x是左黑色节点,兄弟节点sib是红色节点
* 兄弟节点由红转黑,父节点由黑转红,按父节点左旋,
* 左旋后树的结构变化了,这时重新赋值sib,这个时候sib指向了x的兄弟节点
*/
if (colorOf(sib) == RED) {
setColor(sib, BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(x), RED);
rotateLeft(parentOf(x));
sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));
}
/**
* 场景2:节点x、x的兄弟节点sib、sib的左子节点和右子节点都为黑色时,需要将该节点sib由黑变
* 红,同时将x指向当前x的父节点
*/
if (colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK &&
colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
setColor(sib, RED);
x = parentOf(x);
} else {
/**
* 场景3:节点x、x的兄弟节点sib、sib的右子节点都为黑色,sib的左子节点为红色时,
* 需要将sib左子节点设置为黑色,sib节点设置为红色,同时按sib右旋,再将sib指向x的
* 兄弟节点
*/
if (colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
setColor(leftOf(sib), BLACK);
setColor(sib, RED);
rotateRight(sib);
sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));
}
/**
* 场景4:节点x、x的兄弟节点sib都为黑色,而sib的左右子节点都为红色或者右子节点为红色、
* 左子节点为黑色,此时需要将sib节点的颜色设置成和x的父节点p相同的颜色,
* 设置x的父节点为黑色,设置sib右子节点为黑色,左旋x的父节点p,然后将x赋值为root
*/
setColor(sib, colorOf(parentOf(x)));
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(rightOf(sib), BLACK);
rotateLeft(parentOf(x));
x = root;
}
} else {//x是右节点的情况
Entry<K,V> sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));
if (colorOf(sib) == RED) {
setColor(sib, BLACK);
setColor(parentOf(x), RED);
rotateRight(parentOf(x));
sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));
}
if (colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK &&
colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
setColor(sib, RED);
x = parentOf(x);
} else {
if (colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
setColor(rightOf(sib), BLACK);
setColor(sib, RED);
rotateLeft(sib);
sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));
}
setColor(sib, colorOf(parentOf(x)));
setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
setColor(leftOf(sib), BLACK);
rotateRight(parentOf(x));
x = root;
}
}
}
setColor(x, BLACK);
}
当待操作节点为左节点时,上面描述了四种场景,而且场景之间可以相互转换,如deleteEntry后进入了场景1,经过场景1的一些列操作后,红黑树的结构并没有调整完成,而是进入了场景2,场景2执行完成后跳出循环,将待操作节点设置为黑色,完成。我们下面用图来说明一下四种场景帮助理解,当然大家最好自己手动画一下。
场景1:
当x是左黑色节点,兄弟节点sib是红色节点,需要兄弟节点由红转黑,父节点由黑转红,按父节点左旋,左旋后树的结构变化了,这时重新赋值sib,这个时候sib指向了x的兄弟节点。
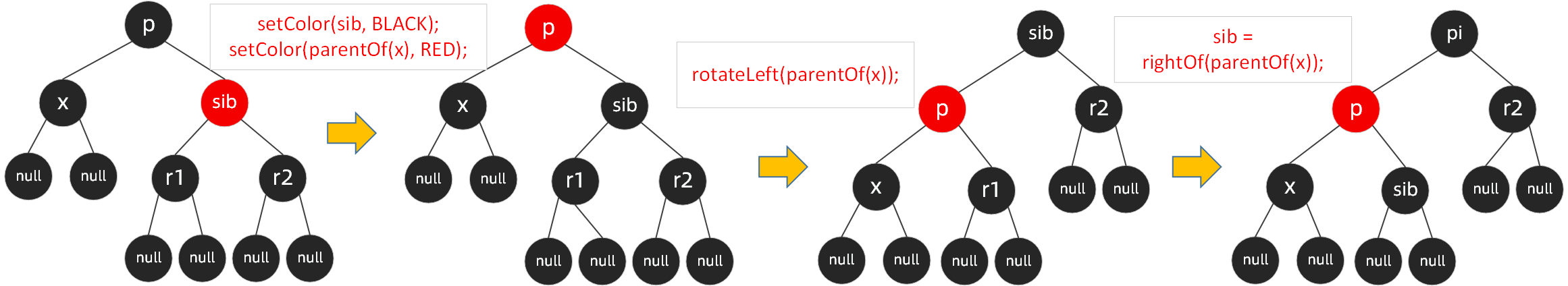
但经过这一系列操作后,并没有结束,而是可能到了场景2,或者场景3和4
场景2:
节点x、x的兄弟节点sib、sib的左子节点和右子节点都为黑色时,需要将该节点sib由黑变红,同时将x指向当前x的父节点
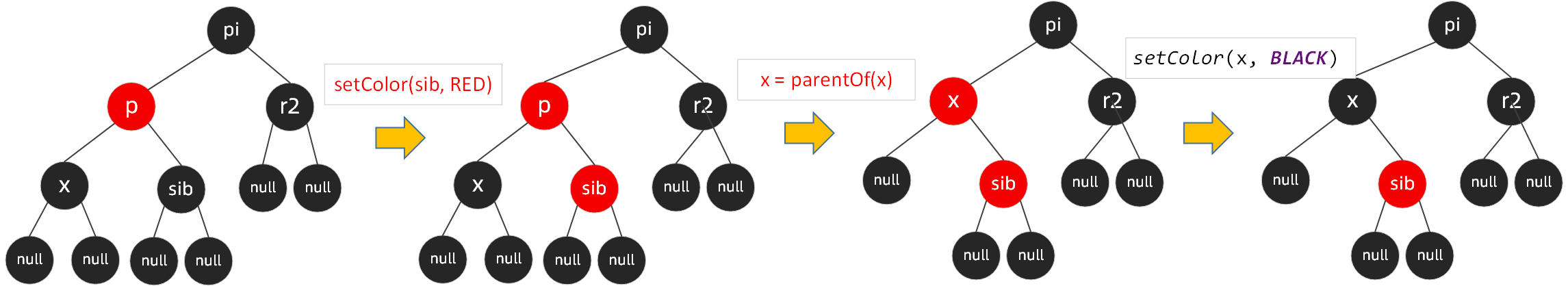
经过场景2的一系列操作后,循环就结束了,我们跳出循环,将节点x设置为黑色,自平衡调整完成。
场景3:
节点x、x的兄弟节点sib、sib的右子节点都为黑色,sib的左子节点为红色时,需要将sib左子节点设置为黑色,sib节点设置为红色,同时按sib右旋,再将sib指向x的兄弟节点
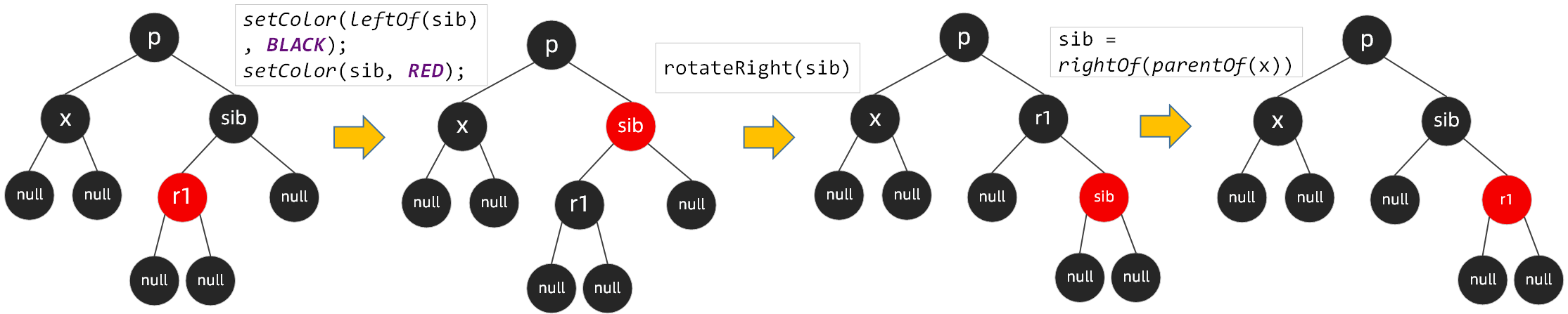
并没有完,场景3的一系列操作后,会进入到场景4
场景4:
节点x、x的兄弟节点sib都为黑色,而sib的左右子节点都为红色或者右子节点为红色、左子节点为黑色,此时需要将sib节点的颜色设置成和x的父节点p相同的颜色,设置x的父节点颜色为黑色,设置sib右孩子的颜色为黑色,左旋x的父节点p,然后将x赋值为root
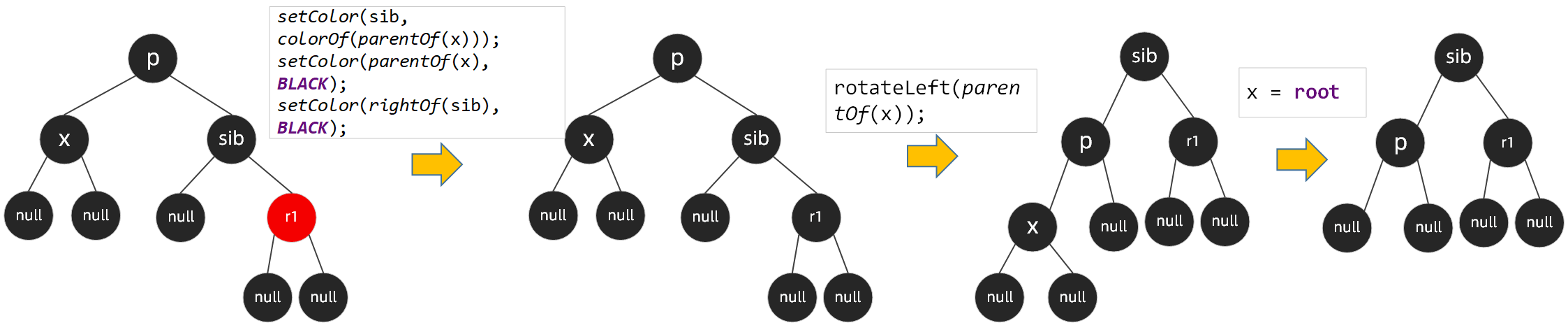
四种场景讲完了,删除后的自平衡操作不太好理解,代码层面的已经弄明白了,但如果让我自己去实现的话,还是差了一些,还需要再研究。
七. 遍历
遍历比较简单,TreeMap的遍历可以使用map.values(), map.keySet(),map.entrySet(),map.forEach(),这里不再多说。
八. 总结
本文详细介绍了TreeMap的基本特点,并对其底层数据结构红黑树进行了回顾,同时讲述了其自动排序的原理,并从源码的角度结合红黑树图形对put方法、get方法、remove方法进行了讲解,最后简单提了一下遍历操作,若有不对之处,请批评指正,望共同进步,谢谢!
Java 集合系列12之 TreeMap详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
第1部分 TreeMap介绍
TreeMap 简介
TreeMap 是一个有序的key-value集合,它是通过红黑树实现的。
TreeMap 继承于AbstractMap,所以它是一个Map,即一个key-value集合。
TreeMap 实现了NavigableMap接口,意味着它支持一系列的导航方法。比如返回有序的key集合。
TreeMap 实现了Cloneable接口,意味着它能被克隆。
TreeMap 实现了java.io.Serializable接口,意味着它支持序列化。
TreeMap基于红黑树(Red-Black tree)实现。该映射根据其键的自然顺序进行排序,或者根据创建映射时提供的 Comparator 进行排序,具体取决于使用的构造方法。
TreeMap的基本操作 containsKey、get、put 和 remove 的时间复杂度是 log(n) 。
另外,TreeMap是非同步的。 它的iterator 方法返回的迭代器是fail-fastl的。
TreeMap的构造函数
// 默认构造函数。使用该构造函数,TreeMap中的元素按照自然排序进行排列。 TreeMap() // 创建的TreeMap包含Map TreeMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> copyFrom) // 指定Tree的比较器 TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) // 创建的TreeSet包含copyFrom TreeMap(SortedMap<K, ? extends V> copyFrom)
TreeMap的API
Entry<K, V> ceilingEntry(K key) K ceilingKey(K key) void clear() Object clone() Comparator<? super K> comparator() boolean containsKey(Object key) NavigableSet<K> descendingKeySet() NavigableMap<K, V> descendingMap() Set<Entry<K, V>> entrySet() Entry<K, V> firstEntry() K firstKey() Entry<K, V> floorEntry(K key) K floorKey(K key) V get(Object key) NavigableMap<K, V> headMap(K to, boolean inclusive) SortedMap<K, V> headMap(K toExclusive) Entry<K, V> higherEntry(K key) K higherKey(K key) boolean isEmpty() Set<K> keySet() Entry<K, V> lastEntry() K lastKey() Entry<K, V> lowerEntry(K key) K lowerKey(K key) NavigableSet<K> navigableKeySet() Entry<K, V> pollFirstEntry() Entry<K, V> pollLastEntry() V put(K key, V value) V remove(Object key) int size() SortedMap<K, V> subMap(K fromInclusive, K toExclusive) NavigableMap<K, V> subMap(K from, boolean fromInclusive, K to, boolean toInclusive) NavigableMap<K, V> tailMap(K from, boolean inclusive) SortedMap<K, V> tailMap(K fromInclusive)
第2部分 TreeMap数据结构
TreeMap的继承关系
java.lang.Object
↳ java.util.AbstractMap<K, V>
↳ java.util.TreeMap<K, V>
public class TreeMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements NavigableMap<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {}
TreeMap与Map关系如下图:
从图中可以看出:
(01) TreeMap实现继承于AbstractMap,并且实现了NavigableMap接口。
(02) TreeMap的本质是R-B Tree(红黑树),它包含几个重要的成员变量: root, size, comparator。
root 是红黑数的根节点。它是Entry类型,Entry是红黑数的节点,它包含了红黑数的6个基本组成成分:key(键)、value(值)、left(左孩子)、right(右孩子)、parent(父节点)、color(颜色)。Entry节点根据key进行排序,Entry节点包含的内容为value。
红黑数排序时,根据Entry中的key进行排序;Entry中的key比较大小是根据比较器comparator来进行判断的。
size是红黑数中节点的个数。
关于红黑数的具体算法,请参考"红黑树(一) 原理和算法详细介绍"。
第3部分 TreeMap源码解析(基于JDK1.6.0_45)
为了更了解TreeMap的原理,下面对TreeMap源码代码作出分析。我们先给出源码内容,后面再对源码进行详细说明,当然,源码内容中也包含了详细的代码注释。读者阅读的时候,建议先看后面的说明,先建立一个整体印象;之后再阅读源码。

1 package java.util;
2
3 public class TreeMap<K,V>
4 extends AbstractMap<K,V>
5 implements NavigableMap<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
6 {
7
8 // 比较器。用来给TreeMap排序
9 private final Comparator<? super K> comparator;
10
11 // TreeMap是红黑树实现的,root是红黑书的根节点
12 private transient Entry<K,V> root = null;
13
14 // 红黑树的节点总数
15 private transient int size = 0;
16
17 // 记录红黑树的修改次数
18 private transient int modCount = 0;
19
20 // 默认构造函数
21 public TreeMap() {
22 comparator = null;
23 }
24
25 // 带比较器的构造函数
26 public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) {
27 this.comparator = comparator;
28 }
29
30 // 带Map的构造函数,Map会成为TreeMap的子集
31 public TreeMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
32 comparator = null;
33 putAll(m);
34 }
35
36 // 带SortedMap的构造函数,SortedMap会成为TreeMap的子集
37 public TreeMap(SortedMap<K, ? extends V> m) {
38 comparator = m.comparator();
39 try {
40 buildFromSorted(m.size(), m.entrySet().iterator(), null, null);
41 } catch (java.io.IOException cannotHappen) {
42 } catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) {
43 }
44 }
45
46 public int size() {
47 return size;
48 }
49
50 // 返回TreeMap中是否保护“键(key)”
51 public boolean containsKey(Object key) {
52 return getEntry(key) != null;
53 }
54
55 // 返回TreeMap中是否保护"值(value)"
56 public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
57 // getFirstEntry() 是返回红黑树的第一个节点
58 // successor(e) 是获取节点e的后继节点
59 for (Entry<K,V> e = getFirstEntry(); e != null; e = successor(e))
60 if (valEquals(value, e.value))
61 return true;
62 return false;
63 }
64
65 // 获取“键(key)”对应的“值(value)”
66 public V get(Object key) {
67 // 获取“键”为key的节点(p)
68 Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
69 // 若节点(p)为null,返回null;否则,返回节点对应的值
70 return (p==null ? null : p.value);
71 }
72
73 public Comparator<? super K> comparator() {
74 return comparator;
75 }
76
77 // 获取第一个节点对应的key
78 public K firstKey() {
79 return key(getFirstEntry());
80 }
81
82 // 获取最后一个节点对应的key
83 public K lastKey() {
84 return key(getLastEntry());
85 }
86
87 // 将map中的全部节点添加到TreeMap中
88 public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> map) {
89 // 获取map的大小
90 int mapSize = map.size();
91 // 如果TreeMap的大小是0,且map的大小不是0,且map是已排序的“key-value对”
92 if (size==0 && mapSize!=0 && map instanceof SortedMap) {
93 Comparator c = ((SortedMap)map).comparator();
94 // 如果TreeMap和map的比较器相等;
95 // 则将map的元素全部拷贝到TreeMap中,然后返回!
96 if (c == comparator || (c != null && c.equals(comparator))) {
97 ++modCount;
98 try {
99 buildFromSorted(mapSize, map.entrySet().iterator(),
100 null, null);
101 } catch (java.io.IOException cannotHappen) {
102 } catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) {
103 }
104 return;
105 }
106 }
107 // 调用AbstractMap中的putAll();
108 // AbstractMap中的putAll()又会调用到TreeMap的put()
109 super.putAll(map);
110 }
111
112 // 获取TreeMap中“键”为key的节点
113 final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
114 // 若“比较器”为null,则通过getEntryUsingComparator()获取“键”为key的节点
115 if (comparator != null)
116 return getEntryUsingComparator(key);
117 if (key == null)
118 throw new NullPointerException();
119 Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
120 // 将p设为根节点
121 Entry<K,V> p = root;
122 while (p != null) {
123 int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key);
124 // 若“p的key” < key,则p=“p的左孩子”
125 if (cmp < 0)
126 p = p.left;
127 // 若“p的key” > key,则p=“p的左孩子”
128 else if (cmp > 0)
129 p = p.right;
130 // 若“p的key” = key,则返回节点p
131 else
132 return p;
133 }
134 return null;
135 }
136
137 // 获取TreeMap中“键”为key的节点(对应TreeMap的比较器不是null的情况)
138 final Entry<K,V> getEntryUsingComparator(Object key) {
139 K k = (K) key;
140 Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
141 if (cpr != null) {
142 // 将p设为根节点
143 Entry<K,V> p = root;
144 while (p != null) {
145 int cmp = cpr.compare(k, p.key);
146 // 若“p的key” < key,则p=“p的左孩子”
147 if (cmp < 0)
148 p = p.left;
149 // 若“p的key” > key,则p=“p的左孩子”
150 else if (cmp > 0)
151 p = p.right;
152 // 若“p的key” = key,则返回节点p
153 else
154 return p;
155 }
156 }
157 return null;
158 }
159
160 // 获取TreeMap中不小于key的最小的节点;
161 // 若不存在(即TreeMap中所有节点的键都比key大),就返回null
162 final Entry<K,V> getCeilingEntry(K key) {
163 Entry<K,V> p = root;
164 while (p != null) {
165 int cmp = compare(key, p.key);
166 // 情况一:若“p的key” > key。
167 // 若 p 存在左孩子,则设 p=“p的左孩子”;
168 // 否则,返回p
169 if (cmp < 0) {
170 if (p.left != null)
171 p = p.left;
172 else
173 return p;
174 // 情况二:若“p的key” < key。
175 } else if (cmp > 0) {
176 // 若 p 存在右孩子,则设 p=“p的右孩子”
177 if (p.right != null) {
178 p = p.right;
179 } else {
180 // 若 p 不存在右孩子,则找出 p 的后继节点,并返回
181 // 注意:这里返回的 “p的后继节点”有2种可能性:第一,null;第二,TreeMap中大于key的最小的节点。
182 // 理解这一点的核心是,getCeilingEntry是从root开始遍历的。
183 // 若getCeilingEntry能走到这一步,那么,它之前“已经遍历过的节点的key”都 > key。
184 // 能理解上面所说的,那么就很容易明白,为什么“p的后继节点”又2种可能性了。
185 Entry<K,V> parent = p.parent;
186 Entry<K,V> ch = p;
187 while (parent != null && ch == parent.right) {
188 ch = parent;
189 parent = parent.parent;
190 }
191 return parent;
192 }
193 // 情况三:若“p的key” = key。
194 } else
195 return p;
196 }
197 return null;
198 }
199
200 // 获取TreeMap中不大于key的最大的节点;
201 // 若不存在(即TreeMap中所有节点的键都比key小),就返回null
202 // getFloorEntry的原理和getCeilingEntry类似,这里不再多说。
203 final Entry<K,V> getFloorEntry(K key) {
204 Entry<K,V> p = root;
205 while (p != null) {
206 int cmp = compare(key, p.key);
207 if (cmp > 0) {
208 if (p.right != null)
209 p = p.right;
210 else
211 return p;
212 } else if (cmp < 0) {
213 if (p.left != null) {
214 p = p.left;
215 } else {
216 Entry<K,V> parent = p.parent;
217 Entry<K,V> ch = p;
218 while (parent != null && ch == parent.left) {
219 ch = parent;
220 parent = parent.parent;
221 }
222 return parent;
223 }
224 } else
225 return p;
226
227 }
228 return null;
229 }
230
231 // 获取TreeMap中大于key的最小的节点。
232 // 若不存在,就返回null。
233 // 请参照getCeilingEntry来对getHigherEntry进行理解。
234 final Entry<K,V> getHigherEntry(K key) {
235 Entry<K,V> p = root;
236 while (p != null) {
237 int cmp = compare(key, p.key);
238 if (cmp < 0) {
239 if (p.left != null)
240 p = p.left;
241 else
242 return p;
243 } else {
244 if (p.right != null) {
245 p = p.right;
246 } else {
247 Entry<K,V> parent = p.parent;
248 Entry<K,V> ch = p;
249 while (parent != null && ch == parent.right) {
250 ch = parent;
251 parent = parent.parent;
252 }
253 return parent;
254 }
255 }
256 }
257 return null;
258 }
259
260 // 获取TreeMap中小于key的最大的节点。
261 // 若不存在,就返回null。
262 // 请参照getCeilingEntry来对getLowerEntry进行理解。
263 final Entry<K,V> getLowerEntry(K key) {
264 Entry<K,V> p = root;
265 while (p != null) {
266 int cmp = compare(key, p.key);
267 if (cmp > 0) {
268 if (p.right != null)
269 p = p.right;
270 else
271 return p;
272 } else {
273 if (p.left != null) {
274 p = p.left;
275 } else {
276 Entry<K,V> parent = p.parent;
277 Entry<K,V> ch = p;
278 while (parent != null && ch == parent.left) {
279 ch = parent;
280 parent = parent.parent;
281 }
282 return parent;
283 }
284 }
285 }
286 return null;
287 }
288
289 // 将“key, value”添加到TreeMap中
290 // 理解TreeMap的前提是掌握“红黑树”。
291 // 若理解“红黑树中添加节点”的算法,则很容易理解put。
292 public V put(K key, V value) {
293 Entry<K,V> t = root;
294 // 若红黑树为空,则插入根节点
295 if (t == null) {
296 // TBD:
297 // 5045147: (coll) Adding null to an empty TreeSet should
298 // throw NullPointerException
299 //
300 // compare(key, key); // type check
301 root = new Entry<K,V>(key, value, null);
302 size = 1;
303 modCount++;
304 return null;
305 }
306 int cmp;
307 Entry<K,V> parent;
308 // split comparator and comparable paths
309 Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
310 // 在二叉树(红黑树是特殊的二叉树)中,找到(key, value)的插入位置。
311 // 红黑树是以key来进行排序的,所以这里以key来进行查找。
312 if (cpr != null) {
313 do {
314 parent = t;
315 cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
316 if (cmp < 0)
317 t = t.left;
318 else if (cmp > 0)
319 t = t.right;
320 else
321 return t.setValue(value);
322 } while (t != null);
323 }
324 else {
325 if (key == null)
326 throw new NullPointerException();
327 Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
328 do {
329 parent = t;
330 cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
331 if (cmp < 0)
332 t = t.left;
333 else if (cmp > 0)
334 t = t.right;
335 else
336 return t.setValue(value);
337 } while (t != null);
338 }
339 // 新建红黑树的节点(e)
340 Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<K,V>(key, value, parent);
341 if (cmp < 0)
342 parent.left = e;
343 else
344 parent.right = e;
345 // 红黑树插入节点后,不再是一颗红黑树;
346 // 这里通过fixAfterInsertion的处理,来恢复红黑树的特性。
347 fixAfterInsertion(e);
348 size++;
349 modCount++;
350 return null;
351 }
352
353 // 删除TreeMap中的键为key的节点,并返回节点的值
354 public V remove(Object key) {
355 // 找到键为key的节点
356 Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
357 if (p == null)
358 return null;
359
360 // 保存节点的值
361 V oldValue = p.value;
362 // 删除节点
363 deleteEntry(p);
364 return oldValue;
365 }
366
367 // 清空红黑树
368 public void clear() {
369 modCount++;
370 size = 0;
371 root = null;
372 }
373
374 // 克隆一个TreeMap,并返回Object对象
375 public Object clone() {
376 TreeMap<K,V> clone = null;
377 try {
378 clone = (TreeMap<K,V>) super.clone();
379 } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
380 throw new InternalError();
381 }
382
383 // Put clone into "virgin" state (except for comparator)
384 clone.root = null;
385 clone.size = 0;
386 clone.modCount = 0;
387 clone.entrySet = null;
388 clone.navigableKeySet = null;
389 clone.descendingMap = null;
390
391 // Initialize clone with our mappings
392 try {
393 clone.buildFromSorted(size, entrySet().iterator(), null, null);
394 } catch (java.io.IOException cannotHappen) {
395 } catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) {
396 }
397
398 return clone;
399 }
400
401 // 获取第一个节点(对外接口)。
402 public Map.Entry<K,V> firstEntry() {
403 return exportEntry(getFirstEntry());
404 }
405
406 // 获取最后一个节点(对外接口)。
407 public Map.Entry<K,V> lastEntry() {
408 return exportEntry(getLastEntry());
409 }
410
411 // 获取第一个节点,并将改节点从TreeMap中删除。
412 public Map.Entry<K,V> pollFirstEntry() {
413 // 获取第一个节点
414 Entry<K,V> p = getFirstEntry();
415 Map.Entry<K,V> result = exportEntry(p);
416 // 删除第一个节点
417 if (p != null)
418 deleteEntry(p);
419 return result;
420 }
421
422 // 获取最后一个节点,并将改节点从TreeMap中删除。
423 public Map.Entry<K,V> pollLastEntry() {
424 // 获取最后一个节点
425 Entry<K,V> p = getLastEntry();
426 Map.Entry<K,V> result = exportEntry(p);
427 // 删除最后一个节点
428 if (p != null)
429 deleteEntry(p);
430 return result;
431 }
432
433 // 返回小于key的最大的键值对,没有的话返回null
434 public Map.Entry<K,V> lowerEntry(K key) {
435 return exportEntry(getLowerEntry(key));
436 }
437
438 // 返回小于key的最大的键值对所对应的KEY,没有的话返回null
439 public K lowerKey(K key) {
440 return keyOrNull(getLowerEntry(key));
441 }
442
443 // 返回不大于key的最大的键值对,没有的话返回null
444 public Map.Entry<K,V> floorEntry(K key) {
445 return exportEntry(getFloorEntry(key));
446 }
447
448 // 返回不大于key的最大的键值对所对应的KEY,没有的话返回null
449 public K floorKey(K key) {
450 return keyOrNull(getFloorEntry(key));
451 }
452
453 // 返回不小于key的最小的键值对,没有的话返回null
454 public Map.Entry<K,V> ceilingEntry(K key) {
455 return exportEntry(getCeilingEntry(key));
456 }
457
458 // 返回不小于key的最小的键值对所对应的KEY,没有的话返回null
459 public K ceilingKey(K key) {
460 return keyOrNull(getCeilingEntry(key));
461 }
462
463 // 返回大于key的最小的键值对,没有的话返回null
464 public Map.Entry<K,V> higherEntry(K key) {
465 return exportEntry(getHigherEntry(key));
466 }
467
468 // 返回大于key的最小的键值对所对应的KEY,没有的话返回null
469 public K higherKey(K key) {
470 return keyOrNull(getHigherEntry(key));
471 }
472
473 // TreeMap的红黑树节点对应的集合
474 private transient EntrySet entrySet = null;
475 // KeySet为KeySet导航类
476 private transient KeySet<K> navigableKeySet = null;
477 // descendingMap为键值对的倒序“映射”
478 private transient NavigableMap<K,V> descendingMap = null;
479
480 // 返回TreeMap的“键的集合”
481 public Set<K> keySet() {
482 return navigableKeySet();
483 }
484
485 // 获取“可导航”的Key的集合
486 // 实际上是返回KeySet类的对象。
487 public NavigableSet<K> navigableKeySet() {
488 KeySet<K> nks = navigableKeySet;
489 return (nks != null) ? nks : (navigableKeySet = new KeySet(this));
490 }
491
492 // 返回“TreeMap的值对应的集合”
493 public Collection<V> values() {
494 Collection<V> vs = values;
495 return (vs != null) ? vs : (values = new Values());
496 }
497
498 // 获取TreeMap的Entry的集合,实际上是返回EntrySet类的对象。
499 public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {
500 EntrySet es = entrySet;
501 return (es != null) ? es : (entrySet = new EntrySet());
502 }
503
504 // 获取TreeMap的降序Map
505 // 实际上是返回DescendingSubMap类的对象
506 public NavigableMap<K, V> descendingMap() {
507 NavigableMap<K, V> km = descendingMap;
508 return (km != null) ? km :
509 (descendingMap = new DescendingSubMap(this,
510 true, null, true,
511 true, null, true));
512 }
513
514 // 获取TreeMap的子Map
515 // 范围是从fromKey 到 toKey;fromInclusive是是否包含fromKey的标记,toInclusive是是否包含toKey的标记
516 public NavigableMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, boolean fromInclusive,
517 K toKey, boolean toInclusive) {
518 return new AscendingSubMap(this,
519 false, fromKey, fromInclusive,
520 false, toKey, toInclusive);
521 }
522
523 // 获取“Map的头部”
524 // 范围从第一个节点 到 toKey, inclusive是是否包含toKey的标记
525 public NavigableMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey, boolean inclusive) {
526 return new AscendingSubMap(this,
527 true, null, true,
528 false, toKey, inclusive);
529 }
530
531 // 获取“Map的尾部”。
532 // 范围是从 fromKey 到 最后一个节点,inclusive是是否包含fromKey的标记
533 public NavigableMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey, boolean inclusive) {
534 return new AscendingSubMap(this,
535 false, fromKey, inclusive,
536 true, null, true);
537 }
538
539 // 获取“子Map”。
540 // 范围是从fromKey(包括) 到 toKey(不包括)
541 public SortedMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, K toKey) {
542 return subMap(fromKey, true, toKey, false);
543 }
544
545 // 获取“Map的头部”。
546 // 范围从第一个节点 到 toKey(不包括)
547 public SortedMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey) {
548 return headMap(toKey, false);
549 }
550
551 // 获取“Map的尾部”。
552 // 范围是从 fromKey(包括) 到 最后一个节点
553 public SortedMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey) {
554 return tailMap(fromKey, true);
555 }
556
557 // ”TreeMap的值的集合“对应的类,它集成于AbstractCollection
558 class Values extends AbstractCollection<V> {
559 // 返回迭代器
560 public Iterator<V> iterator() {
561 return new ValueIterator(getFirstEntry());
562 }
563
564 // 返回个数
565 public int size() {
566 return TreeMap.this.size();
567 }
568
569 // "TreeMap的值的集合"中是否包含"对象o"
570 public boolean contains(Object o) {
571 return TreeMap.this.containsValue(o);
572 }
573
574 // 删除"TreeMap的值的集合"中的"对象o"
575 public boolean remove(Object o) {
576 for (Entry<K,V> e = getFirstEntry(); e != null; e = successor(e)) {
577 if (valEquals(e.getValue(), o)) {
578 deleteEntry(e);
579 return true;
580 }
581 }
582 return false;
583 }
584
585 // 清空删除"TreeMap的值的集合"
586 public void clear() {
587 TreeMap.this.clear();
588 }
589 }
590
591 // EntrySet是“TreeMap的所有键值对组成的集合”,
592 // EntrySet集合的单位是单个“键值对”。
593 class EntrySet extends AbstractSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
594 public Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() {
595 return new EntryIterator(getFirstEntry());
596 }
597
598 // EntrySet中是否包含“键值对Object”
599 public boolean contains(Object o) {
600 if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
601 return false;
602 Map.Entry<K,V> entry = (Map.Entry<K,V>) o;
603 V value = entry.getValue();
604 Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(entry.getKey());
605 return p != null && valEquals(p.getValue(), value);
606 }
607
608 // 删除EntrySet中的“键值对Object”
609 public boolean remove(Object o) {
610 if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
611 return false;
612 Map.Entry<K,V> entry = (Map.Entry<K,V>) o;
613 V value = entry.getValue();
614 Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(entry.getKey());
615 if (p != null && valEquals(p.getValue(), value)) {
616 deleteEntry(p);
617 return true;
618 }
619 return false;
620 }
621
622 // 返回EntrySet中元素个数
623 public int size() {
624 return TreeMap.this.size();
625 }
626
627 // 清空EntrySet
628 public void clear() {
629 TreeMap.this.clear();
630 }
631 }
632
633 // 返回“TreeMap的KEY组成的迭代器(顺序)”
634 Iterator<K> keyIterator() {
635 return new KeyIterator(getFirstEntry());
636 }
637
638 // 返回“TreeMap的KEY组成的迭代器(逆序)”
639 Iterator<K> descendingKeyIterator() {
640 return new DescendingKeyIterator(getLastEntry());
641 }
642
643 // KeySet是“TreeMap中所有的KEY组成的集合”
644 // KeySet继承于AbstractSet,而且实现了NavigableSet接口。
645 static final class KeySet<E> extends AbstractSet<E> implements NavigableSet<E> {
646 // NavigableMap成员,KeySet是通过NavigableMap实现的
647 private final NavigableMap<E, Object> m;
648 KeySet(NavigableMap<E,Object> map) { m = map; }
649
650 // 升序迭代器
651 public Iterator<E> iterator() {
652 // 若是TreeMap对象,则调用TreeMap的迭代器keyIterator()
653 // 否则,调用TreeMap子类NavigableSubMap的迭代器keyIterator()
654 if (m instanceof TreeMap)
655 return ((TreeMap<E,Object>)m).keyIterator();
656 else
657 return (Iterator<E>)(((TreeMap.NavigableSubMap)m).keyIterator());
658 }
659
660 // 降序迭代器
661 public Iterator<E> descendingIterator() {
662 // 若是TreeMap对象,则调用TreeMap的迭代器descendingKeyIterator()
663 // 否则,调用TreeMap子类NavigableSubMap的迭代器descendingKeyIterator()
664 if (m instanceof TreeMap)
665 return ((TreeMap<E,Object>)m).descendingKeyIterator();
666 else
667 return (Iterator<E>)(((TreeMap.NavigableSubMap)m).descendingKeyIterator());
668 }
669
670 public int size() { return m.size(); }
671 public boolean isEmpty() { return m.isEmpty(); }
672 public boolean contains(Object o) { return m.containsKey(o); }
673 public void clear() { m.clear(); }
674 public E lower(E e) { return m.lowerKey(e); }
675 public E floor(E e) { return m.floorKey(e); }
676 public E ceiling(E e) { return m.ceilingKey(e); }
677 public E higher(E e) { return m.higherKey(e); }
678 public E first() { return m.firstKey(); }
679 public E last() { return m.lastKey(); }
680 public Comparator<? super E> comparator() { return m.comparator(); }
681 public E pollFirst() {
682 Map.Entry<E,Object> e = m.pollFirstEntry();
683 return e == null? null : e.getKey();
684 }
685 public E pollLast() {
686 Map.Entry<E,Object> e = m.pollLastEntry();
687 return e == null? null : e.getKey();
688 }
689 public boolean remove(Object o) {
690 int oldSize = size();
691 m.remove(o);
692 return size() != oldSize;
693 }
694 public NavigableSet<E> subSet(E fromElement, boolean fromInclusive,
695 E toElement, boolean toInclusive) {
696 return new TreeSet<E>(m.subMap(fromElement, fromInclusive,
697 toElement, toInclusive));
698 }
699 public NavigableSet<E> headSet(E toElement, boolean inclusive) {
700 return new TreeSet<E>(m.headMap(toElement, inclusive));
701 }
702 public NavigableSet<E> tailSet(E fromElement, boolean inclusive) {
703 return new TreeSet<E>(m.tailMap(fromElement, inclusive));
704 }
705 public SortedSet<E> subSet(E fromElement, E toElement) {
706 return subSet(fromElement, true, toElement, false);
707 }
708 public SortedSet<E> headSet(E toElement) {
709 return headSet(toElement, false);
710 }
711 public SortedSet<E> tailSet(E fromElement) {
712 return tailSet(fromElement, true);
713 }
714 public NavigableSet<E> descendingSet() {
715 return new TreeSet(m.descendingMap());
716 }
717 }
718
719 // 它是TreeMap中的一个抽象迭代器,实现了一些通用的接口。
720 abstract class PrivateEntryIterator<T> implements Iterator<T> {
721 // 下一个元素
722 Entry<K,V> next;
723 // 上一次返回元素
724 Entry<K,V> lastReturned;
725 // 期望的修改次数,用于实现fast-fail机制
726 int expectedModCount;
727
728 PrivateEntryIterator(Entry<K,V> first) {
729 expectedModCount = modCount;
730 lastReturned = null;
731 next = first;
732 }
733
734 public final boolean hasNext() {
735 return next != null;
736 }
737
738 // 获取下一个节点
739 final Entry<K,V> nextEntry() {
740 Entry<K,V> e = next;
741 if (e == null)
742 throw new NoSuchElementException();
743 if (modCount != expectedModCount)
744 throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
745 next = successor(e);
746 lastReturned = e;
747 return e;
748 }
749
750 // 获取上一个节点
751 final Entry<K,V> prevEntry() {
752 Entry<K,V> e = next;
753 if (e == null)
754 throw new NoSuchElementException();
755 if (modCount != expectedModCount)
756 throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
757 next = predecessor(e);
758 lastReturned = e;
759 return e;
760 }
761
762 // 删除当前节点
763 public void remove() {
764 if (lastReturned == null)
765 throw new IllegalStateException();
766 if (modCount != expectedModCount)
767 throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
768 // 这里重点强调一下“为什么当lastReturned的左右孩子都不为空时,要将其赋值给next”。
769 // 目的是为了“删除lastReturned节点之后,next节点指向的仍然是下一个节点”。
770 // 根据“红黑树”的特性可知:
771 // 当被删除节点有两个儿子时。那么,首先把“它的后继节点的内容”复制给“该节点的内容”;之后,删除“它的后继节点”。
772 // 这意味着“当被删除节点有两个儿子时,删除当前节点之后,'新的当前节点'实际上是‘原有的后继节点(即下一个节点)’”。
773 // 而此时next仍然指向"新的当前节点"。也就是说next是仍然是指向下一个节点;能继续遍历红黑树。
774 if (lastReturned.left != null && lastReturned.right != null)
775 next = lastReturned;
776 deleteEntry(lastReturned);
777 expectedModCount = modCount;
778 lastReturned = null;
779 }
780 }
781
782 // TreeMap的Entry对应的迭代器
783 final class EntryIterator extends PrivateEntryIterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
784 EntryIterator(Entry<K,V> first) {
785 super(first);
786 }
787 public Map.Entry<K,V> next() {
788 return nextEntry();
789 }
790 }
791
792 // TreeMap的Value对应的迭代器
793 final class ValueIterator extends PrivateEntryIterator<V> {
794 ValueIterator(Entry<K,V> first) {
795 super(first);
796 }
797 public V next() {
798 return nextEntry().value;
799 }
800 }
801
802 // reeMap的KEY组成的迭代器(顺序)
803 final class KeyIterator extends PrivateEntryIterator<K> {
804 KeyIterator(Entry<K,V> first) {
805 super(first);
806 }
807 public K next() {
808 return nextEntry().key;
809 }
810 }
811
812 // TreeMap的KEY组成的迭代器(逆序)
813 final class DescendingKeyIterator extends PrivateEntryIterator<K> {
814 DescendingKeyIterator(Entry<K,V> first) {
815 super(first);
816 }
817 public K next() {
818 return prevEntry().key;
819 }
820 }
821
822 // 比较两个对象的大小
823 final int compare(Object k1, Object k2) {
824 return comparator==null ? ((Comparable<? super K>)k1).compareTo((K)k2)
825 : comparator.compare((K)k1, (K)k2);
826 }
827
828 // 判断两个对象是否相等
829 final static boolean valEquals(Object o1, Object o2) {
830 return (o1==null ? o2==null : o1.equals(o2));
831 }
832
833 // 返回“Key-Value键值对”的一个简单拷贝(AbstractMap.SimpleImmutableEntry<K,V>对象)
834 // 可用来读取“键值对”的值
835 static <K,V> Map.Entry<K,V> exportEntry(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e) {
836 return e == null? null :
837 new AbstractMap.SimpleImmutableEntry<K,V>(e);
838 }
839
840 // 若“键值对”不为null,则返回KEY;否则,返回null
841 static <K,V> K keyOrNull(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e) {
842 return e == null? null : e.key;
843 }
844
845 // 若“键值对”不为null,则返回KEY;否则,抛出异常
846 static <K> K key(Entry<K,?> e) {
847 if (e==null)
848 throw new NoSuchElementException();
849 return e.key;
850 }
851
852 // TreeMap的SubMap,它一个抽象类,实现了公共操作。
853 // 它包括了"(升序)AscendingSubMap"和"(降序)DescendingSubMap"两个子类。
854 static abstract class NavigableSubMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V>
855 implements NavigableMap<K,V>, java.io.Serializable {
856 // TreeMap的拷贝
857 final TreeMap<K,V> m;
858 // lo是“子Map范围的最小值”,hi是“子Map范围的最大值”;
859 // loInclusive是“是否包含lo的标记”,hiInclusive是“是否包含hi的标记”
860 // fromStart是“表示是否从第一个节点开始计算”,
861 // toEnd是“表示是否计算到最后一个节点 ”
862 final K lo, hi;
863 final boolean fromStart, toEnd;
864 final boolean loInclusive, hiInclusive;
865
866 // 构造函数
867 NavigableSubMap(TreeMap<K,V> m,
868 boolean fromStart, K lo, boolean loInclusive,
869 boolean toEnd, K hi, boolean hiInclusive) {
870 if (!fromStart && !toEnd) {
871 if (m.compare(lo, hi) > 0)
872 throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromKey > toKey");
873 } else {
874 if (!fromStart) // type check
875 m.compare(lo, lo);
876 if (!toEnd)
877 m.compare(hi, hi);
878 }
879
880 this.m = m;
881 this.fromStart = fromStart;
882 this.lo = lo;
883 this.loInclusive = loInclusive;
884 this.toEnd = toEnd;
885 this.hi = hi;
886 this.hiInclusive = hiInclusive;
887 }
888
889 // 判断key是否太小
890 final boolean tooLow(Object key) {
891 // 若该SubMap不包括“起始节点”,
892 // 并且,“key小于最小键(lo)”或者“key等于最小键(lo),但最小键却没包括在该SubMap内”
893 // 则判断key太小。其余情况都不是太小!
894 if (!fromStart) {
895 int c = m.compare(key, lo);
896 if (c < 0 || (c == 0 && !loInclusive))
897 return true;
898 }
899 return false;
900 }
901
902 // 判断key是否太大
903 final boolean tooHigh(Object key) {
904 // 若该SubMap不包括“结束节点”,
905 // 并且,“key大于最大键(hi)”或者“key等于最大键(hi),但最大键却没包括在该SubMap内”
906 // 则判断key太大。其余情况都不是太大!
907 if (!toEnd) {
908 int c = m.compare(key, hi);
909 if (c > 0 || (c == 0 && !hiInclusive))
910 return true;
911 }
912 return false;
913 }
914
915 // 判断key是否在“lo和hi”开区间范围内
916 final boolean inRange(Object key) {
917 return !tooLow(key) && !tooHigh(key);
918 }
919
920 // 判断key是否在封闭区间内
921 final boolean inClosedRange(Object key) {
922 return (fromStart || m.compare(key, lo) >= 0)
923 && (toEnd || m.compare(hi, key) >= 0);
924 }
925
926 // 判断key是否在区间内, inclusive是区间开关标志
927 final boolean inRange(Object key, boolean inclusive) {
928 return inclusive ? inRange(key) : inClosedRange(key);
929 }
930
931 // 返回最低的Entry
932 final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absLowest() {
933 // 若“包含起始节点”,则调用getFirstEntry()返回第一个节点
934 // 否则的话,若包括lo,则调用getCeilingEntry(lo)获取大于/等于lo的最小的Entry;
935 // 否则,调用getHigherEntry(lo)获取大于lo的最小Entry
936 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e =
937 (fromStart ? m.getFirstEntry() :
938 (loInclusive ? m.getCeilingEntry(lo) :
939 m.getHigherEntry(lo)));
940 return (e == null || tooHigh(e.key)) ? null : e;
941 }
942
943 // 返回最高的Entry
944 final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absHighest() {
945 // 若“包含结束节点”,则调用getLastEntry()返回最后一个节点
946 // 否则的话,若包括hi,则调用getFloorEntry(hi)获取小于/等于hi的最大的Entry;
947 // 否则,调用getLowerEntry(hi)获取大于hi的最大Entry
948 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e =
949 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e =
950 (toEnd ? m.getLastEntry() :
951 (hiInclusive ? m.getFloorEntry(hi) :
952 m.getLowerEntry(hi)));
953 return (e == null || tooLow(e.key)) ? null : e;
954 }
955
956 // 返回"大于/等于key的最小的Entry"
957 final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absCeiling(K key) {
958 // 只有在“key太小”的情况下,absLowest()返回的Entry才是“大于/等于key的最小Entry”
959 // 其它情况下不行。例如,当包含“起始节点”时,absLowest()返回的是最小Entry了!
960 if (tooLow(key))
961 return absLowest();
962 // 获取“大于/等于key的最小Entry”
963 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = m.getCeilingEntry(key);
964 return (e == null || tooHigh(e.key)) ? null : e;
965 }
966
967 // 返回"大于key的最小的Entry"
968 final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absHigher(K key) {
969 // 只有在“key太小”的情况下,absLowest()返回的Entry才是“大于key的最小Entry”
970 // 其它情况下不行。例如,当包含“起始节点”时,absLowest()返回的是最小Entry了,而不一定是“大于key的最小Entry”!
971 if (tooLow(key))
972 return absLowest();
973 // 获取“大于key的最小Entry”
974 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = m.getHigherEntry(key);
975 return (e == null || tooHigh(e.key)) ? null : e;
976 }
977
978 // 返回"小于/等于key的最大的Entry"
979 final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absFloor(K key) {
980 // 只有在“key太大”的情况下,(absHighest)返回的Entry才是“小于/等于key的最大Entry”
981 // 其它情况下不行。例如,当包含“结束节点”时,absHighest()返回的是最大Entry了!
982 if (tooHigh(key))
983 return absHighest();
984 // 获取"小于/等于key的最大的Entry"
985 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = m.getFloorEntry(key);
986 return (e == null || tooLow(e.key)) ? null : e;
987 }
988
989 // 返回"小于key的最大的Entry"
990 final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absLower(K key) {
991 // 只有在“key太大”的情况下,(absHighest)返回的Entry才是“小于key的最大Entry”
992 // 其它情况下不行。例如,当包含“结束节点”时,absHighest()返回的是最大Entry了,而不一定是“小于key的最大Entry”!
993 if (tooHigh(key))
994 return absHighest();
995 // 获取"小于key的最大的Entry"
996 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = m.getLowerEntry(key);
997 return (e == null || tooLow(e.key)) ? null : e;
998 }
999
1000 // 返回“大于最大节点中的最小节点”,不存在的话,返回null
1001 final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absHighFence() {
1002 return (toEnd ? null : (hiInclusive ?
1003 m.getHigherEntry(hi) :
1004 m.getCeilingEntry(hi)));
1005 }
1006
1007 // 返回“小于最小节点中的最大节点”,不存在的话,返回null
1008 final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absLowFence() {
1009 return (fromStart ? null : (loInclusive ?
1010 m.getLowerEntry(lo) :
1011 m.getFloorEntry(lo)));
1012 }
1013
1014 // 下面几个abstract方法是需要NavigableSubMap的实现类实现的方法
1015 abstract TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subLowest();
1016 abstract TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subHighest();
1017 abstract TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subCeiling(K key);
1018 abstract TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subHigher(K key);
1019 abstract TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subFloor(K key);
1020 abstract TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subLower(K key);
1021 // 返回“顺序”的键迭代器
1022 abstract Iterator<K> keyIterator();
1023 // 返回“逆序”的键迭代器
1024 abstract Iterator<K> descendingKeyIterator();
1025
1026 // 返回SubMap是否为空。空的话,返回true,否则返回false
1027 public boolean isEmpty() {
1028 return (fromStart && toEnd) ? m.isEmpty() : entrySet().isEmpty();
1029 }
1030
1031 // 返回SubMap的大小
1032 public int size() {
1033 return (fromStart && toEnd) ? m.size() : entrySet().size();
1034 }
1035
1036 // 返回SubMap是否包含键key
1037 public final boolean containsKey(Object key) {
1038 return inRange(key) && m.containsKey(key);
1039 }
1040
1041 // 将key-value 插入SubMap中
1042 public final V put(K key, V value) {
1043 if (!inRange(key))
1044 throw new IllegalArgumentException("key out of range");
1045 return m.put(key, value);
1046 }
1047
1048 // 获取key对应值
1049 public final V get(Object key) {
1050 return !inRange(key)? null : m.get(key);
1051 }
1052
1053 // 删除key对应的键值对
1054 public final V remove(Object key) {
1055 return !inRange(key)? null : m.remove(key);
1056 }
1057
1058 // 获取“大于/等于key的最小键值对”
1059 public final Map.Entry<K,V> ceilingEntry(K key) {
1060 return exportEntry(subCeiling(key));
1061 }
1062
1063 // 获取“大于/等于key的最小键”
1064 public final K ceilingKey(K key) {
1065 return keyOrNull(subCeiling(key));
1066 }
1067
1068 // 获取“大于key的最小键值对”
1069 public final Map.Entry<K,V> higherEntry(K key) {
1070 return exportEntry(subHigher(key));
1071 }
1072
1073 // 获取“大于key的最小键”
1074 public final K higherKey(K key) {
1075 return keyOrNull(subHigher(key));
1076 }
1077
1078 // 获取“小于/等于key的最大键值对”
1079 public final Map.Entry<K,V> floorEntry(K key) {
1080 return exportEntry(subFloor(key));
1081 }
1082
1083 // 获取“小于/等于key的最大键”
1084 public final K floorKey(K key) {
1085 return keyOrNull(subFloor(key));
1086 }
1087
1088 // 获取“小于key的最大键值对”
1089 public final Map.Entry<K,V> lowerEntry(K key) {
1090 return exportEntry(subLower(key));
1091 }
1092
1093 // 获取“小于key的最大键”
1094 public final K lowerKey(K key) {
1095 return keyOrNull(subLower(key));
1096 }
1097
1098 // 获取"SubMap的第一个键"
1099 public final K firstKey() {
1100 return key(subLowest());
1101 }
1102
1103 // 获取"SubMap的最后一个键"
1104 public final K lastKey() {
1105 return key(subHighest());
1106 }
1107
1108 // 获取"SubMap的第一个键值对"
1109 public final Map.Entry<K,V> firstEntry() {
1110 return exportEntry(subLowest());
1111 }
1112
1113 // 获取"SubMap的最后一个键值对"
1114 public final Map.Entry<K,V> lastEntry() {
1115 return exportEntry(subHighest());
1116 }
1117
1118 // 返回"SubMap的第一个键值对",并从SubMap中删除改键值对
1119 public final Map.Entry<K,V> pollFirstEntry() {
1120 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = subLowest();
1121 Map.Entry<K,V> result = exportEntry(e);
1122 if (e != null)
1123 m.deleteEntry(e);
1124 return result;
1125 }
1126
1127 // 返回"SubMap的最后一个键值对",并从SubMap中删除改键值对
1128 public final Map.Entry<K,V> pollLastEntry() {
1129 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = subHighest();
1130 Map.Entry<K,V> result = exportEntry(e);
1131 if (e != null)
1132 m.deleteEntry(e);
1133 return result;
1134 }
1135
1136 // Views
1137 transient NavigableMap<K,V> descendingMapView = null;
1138 transient EntrySetView entrySetView = null;
1139 transient KeySet<K> navigableKeySetView = null;
1140
1141 // 返回NavigableSet对象,实际上返回的是当前对象的"Key集合"。
1142 public final NavigableSet<K> navigableKeySet() {
1143 KeySet<K> nksv = navigableKeySetView;
1144 return (nksv != null) ? nksv :
1145 (navigableKeySetView = new TreeMap.KeySet(this));
1146 }
1147
1148 // 返回"Key集合"对象
1149 public final Set<K> keySet() {
1150 return navigableKeySet();
1151 }
1152
1153 // 返回“逆序”的Key集合
1154 public NavigableSet<K> descendingKeySet() {
1155 return descendingMap().navigableKeySet();
1156 }
1157
1158 // 排列fromKey(包含) 到 toKey(不包含) 的子map
1159 public final SortedMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, K toKey) {
1160 return subMap(fromKey, true, toKey, false);
1161 }
1162
1163 // 返回当前Map的头部(从第一个节点 到 toKey, 不包括toKey)
1164 public final SortedMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey) {
1165 return headMap(toKey, false);
1166 }
1167
1168 // 返回当前Map的尾部[从 fromKey(包括fromKeyKey) 到 最后一个节点]
1169 public final SortedMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey) {
1170 return tailMap(fromKey, true);
1171 }
1172
1173 // Map的Entry的集合
1174 abstract class EntrySetView extends AbstractSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
1175 private transient int size = -1, sizeModCount;
1176
1177 // 获取EntrySet的大小
1178 public int size() {
1179 // 若SubMap是从“开始节点”到“结尾节点”,则SubMap大小就是原TreeMap的大小
1180 if (fromStart && toEnd)
1181 return m.size();
1182 // 若SubMap不是从“开始节点”到“结尾节点”,则调用iterator()遍历EntrySetView中的元素
1183 if (size == -1 || sizeModCount != m.modCount) {
1184 sizeModCount = m.modCount;
1185 size = 0;
1186 Iterator i = iterator();
1187 while (i.hasNext()) {
1188 size++;
1189 i.next();
1190 }
1191 }
1192 return size;
1193 }
1194
1195 // 判断EntrySetView是否为空
1196 public boolean isEmpty() {
1197 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> n = absLowest();
1198 return n == null || tooHigh(n.key);
1199 }
1200
1201 // 判断EntrySetView是否包含Object
1202 public boolean contains(Object o) {
1203 if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
1204 return false;
1205 Map.Entry<K,V> entry = (Map.Entry<K,V>) o;
1206 K key = entry.getKey();
1207 if (!inRange(key))
1208 return false;
1209 TreeMap.Entry node = m.getEntry(key);
1210 return node != null &&
1211 valEquals(node.getValue(), entry.getValue());
1212 }
1213
1214 // 从EntrySetView中删除Object
1215 public boolean remove(Object o) {
1216 if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
1217 return false;
1218 Map.Entry<K,V> entry = (Map.Entry<K,V>) o;
1219 K key = entry.getKey();
1220 if (!inRange(key))
1221 return false;
1222 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> node = m.getEntry(key);
1223 if (node!=null && valEquals(node.getValue(),entry.getValue())){
1224 m.deleteEntry(node);
1225 return true;
1226 }
1227 return false;
1228 }
1229 }
1230
1231 // SubMap的迭代器
1232 abstract class SubMapIterator<T> implements Iterator<T> {
1233 // 上一次被返回的Entry
1234 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> lastReturned;
1235 // 指向下一个Entry
1236 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> next;
1237 // “栅栏key”。根据SubMap是“升序”还是“降序”具有不同的意义
1238 final K fenceKey;
1239 int expectedModCount;
1240
1241 // 构造函数
1242 SubMapIterator(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> first,
1243 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> fence) {
1244 // 每创建一个SubMapIterator时,保存修改次数
1245 // 若后面发现expectedModCount和modCount不相等,则抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常。
1246 // 这就是所说的fast-fail机制的原理!
1247 expectedModCount = m.modCount;
1248 lastReturned = null;
1249 next = first;
1250 fenceKey = fence == null ? null : fence.key;
1251 }
1252
1253 // 是否存在下一个Entry
1254 public final boolean hasNext() {
1255 return next != null && next.key != fenceKey;
1256 }
1257
1258 // 返回下一个Entry
1259 final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> nextEntry() {
1260 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = next;
1261 if (e == null || e.key == fenceKey)
1262 throw new NoSuchElementException();
1263 if (m.modCount != expectedModCount)
1264 throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
1265 // next指向e的后继节点
1266 next = successor(e);
1267 lastReturned = e;
1268 return e;
1269 }
1270
1271 // 返回上一个Entry
1272 final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> prevEntry() {
1273 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = next;
1274 if (e == null || e.key == fenceKey)
1275 throw new NoSuchElementException();
1276 if (m.modCount != expectedModCount)
1277 throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
1278 // next指向e的前继节点
1279 next = predecessor(e);
1280 lastReturned = e;
1281 return e;
1282 }
1283
1284 // 删除当前节点(用于“升序的SubMap”)。
1285 // 删除之后,可以继续升序遍历;红黑树特性没变。
1286 final void removeAscending() {
1287 if (lastReturned == null)
1288 throw new IllegalStateException();
1289 if (m.modCount != expectedModCount)
1290 throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
1291 // 这里重点强调一下“为什么当lastReturned的左右孩子都不为空时,要将其赋值给next”。
1292 // 目的是为了“删除lastReturned节点之后,next节点指向的仍然是下一个节点”。
1293 // 根据“红黑树”的特性可知:
1294 // 当被删除节点有两个儿子时。那么,首先把“它的后继节点的内容”复制给“该节点的内容”;之后,删除“它的后继节点”。
1295 // 这意味着“当被删除节点有两个儿子时,删除当前节点之后,'新的当前节点'实际上是‘原有的后继节点(即下一个节点)’”。
1296 // 而此时next仍然指向"新的当前节点"。也就是说next是仍然是指向下一个节点;能继续遍历红黑树。
1297 if (lastReturned.left != null && lastReturned.right != null)
1298 next = lastReturned;
1299 m.deleteEntry(lastReturned);
1300 lastReturned = null;
1301 expectedModCount = m.modCount;
1302 }
1303
1304 // 删除当前节点(用于“降序的SubMap”)。
1305 // 删除之后,可以继续降序遍历;红黑树特性没变。
1306 final void removeDescending() {
1307 if (lastReturned == null)
1308 throw new IllegalStateException();
1309 if (m.modCount != expectedModCount)
1310 throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
1311 m.deleteEntry(lastReturned);
1312 lastReturned = null;
1313 expectedModCount = m.modCount;
1314 }
1315
1316 }
1317
1318 // SubMap的Entry迭代器,它只支持升序操作,继承于SubMapIterator
1319 final class SubMapEntryIterator extends SubMapIterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
1320 SubMapEntryIterator(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> first,
1321 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> fence) {
1322 super(first, fence);
1323 }
1324 // 获取下一个节点(升序)
1325 public Map.Entry<K,V> next() {
1326 return nextEntry();
1327 }
1328 // 删除当前节点(升序)
1329 public void remove() {
1330 removeAscending();
1331 }
1332 }
1333
1334 // SubMap的Key迭代器,它只支持升序操作,继承于SubMapIterator
1335 final class SubMapKeyIterator extends SubMapIterator<K> {
1336 SubMapKeyIterator(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> first,
1337 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> fence) {
1338 super(first, fence);
1339 }
1340 // 获取下一个节点(升序)
1341 public K next() {
1342 return nextEntry().key;
1343 }
1344 // 删除当前节点(升序)
1345 public void remove() {
1346 removeAscending();
1347 }
1348 }
1349
1350 // 降序SubMap的Entry迭代器,它只支持降序操作,继承于SubMapIterator
1351 final class DescendingSubMapEntryIterator extends SubMapIterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
1352 DescendingSubMapEntryIterator(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> last,
1353 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> fence) {
1354 super(last, fence);
1355 }
1356
1357 // 获取下一个节点(降序)
1358 public Map.Entry<K,V> next() {
1359 return prevEntry();
1360 }
1361 // 删除当前节点(降序)
1362 public void remove() {
1363 removeDescending();
1364 }
1365 }
1366
1367 // 降序SubMap的Key迭代器,它只支持降序操作,继承于SubMapIterator
1368 final class DescendingSubMapKeyIterator extends SubMapIterator<K> {
1369 DescendingSubMapKeyIterator(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> last,
1370 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> fence) {
1371 super(last, fence);
1372 }
1373 // 获取下一个节点(降序)
1374 public K next() {
1375 return prevEntry().key;
1376 }
1377 // 删除当前节点(降序)
1378 public void remove() {
1379 removeDescending();
1380 }
1381 }
1382 }
1383
1384
1385 // 升序的SubMap,继承于NavigableSubMap
1386 static final class AscendingSubMap<K,V> extends NavigableSubMap<K,V> {
1387 private static final long serialVersionUID = 912986545866124060L;
1388
1389 // 构造函数
1390 AscendingSubMap(TreeMap<K,V> m,
1391 boolean fromStart, K lo, boolean loInclusive,
1392 boolean toEnd, K hi, boolean hiInclusive) {
1393 super(m, fromStart, lo, loInclusive, toEnd, hi, hiInclusive);
1394 }
1395
1396 // 比较器
1397 public Comparator<? super K> comparator() {
1398 return m.comparator();
1399 }
1400
1401 // 获取“子Map”。
1402 // 范围是从fromKey 到 toKey;fromInclusive是是否包含fromKey的标记,toInclusive是是否包含toKey的标记
1403 public NavigableMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, boolean fromInclusive,
1404 K toKey, boolean toInclusive) {
1405 if (!inRange(fromKey, fromInclusive))
1406 throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromKey out of range");
1407 if (!inRange(toKey, toInclusive))
1408 throw new IllegalArgumentException("toKey out of range");
1409 return new AscendingSubMap(m,
1410 false, fromKey, fromInclusive,
1411 false, toKey, toInclusive);
1412 }
1413
1414 // 获取“Map的头部”。
1415 // 范围从第一个节点 到 toKey, inclusive是是否包含toKey的标记
1416 public NavigableMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey, boolean inclusive) {
1417 if (!inRange(toKey, inclusive))
1418 throw new IllegalArgumentException("toKey out of range");
1419 return new AscendingSubMap(m,
1420 fromStart, lo, loInclusive,
1421 false, toKey, inclusive);
1422 }
1423
1424 // 获取“Map的尾部”。
1425 // 范围是从 fromKey 到 最后一个节点,inclusive是是否包含fromKey的标记
1426 public NavigableMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey, boolean inclusive){
1427 if (!inRange(fromKey, inclusive))
1428 throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromKey out of range");
1429 return new AscendingSubMap(m,
1430 false, fromKey, inclusive,
1431 toEnd, hi, hiInclusive);
1432 }
1433
1434 // 获取对应的降序Map
1435 public NavigableMap<K,V> descendingMap() {
1436 NavigableMap<K,V> mv = descendingMapView;
1437 return (mv != null) ? mv :
1438 (descendingMapView =
1439 new DescendingSubMap(m,
1440 fromStart, lo, loInclusive,
1441 toEnd, hi, hiInclusive));
1442 }
1443
1444 // 返回“升序Key迭代器”
1445 Iterator<K> keyIterator() {
1446 return new SubMapKeyIterator(absLowest(), absHighFence());
1447 }
1448
1449 // 返回“降序Key迭代器”
1450 Iterator<K> descendingKeyIterator() {
1451 return new DescendingSubMapKeyIterator(absHighest(), absLowFence());
1452 }
1453
1454 // “升序EntrySet集合”类
1455 // 实现了iterator()
1456 final class AscendingEntrySetView extends EntrySetView {
1457 public Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() {
1458 return new SubMapEntryIterator(absLowest(), absHighFence());
1459 }
1460 }
1461
1462 // 返回“升序EntrySet集合”
1463 public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {
1464 EntrySetView es = entrySetView;
1465 return (es != null) ? es : new AscendingEntrySetView();
1466 }
1467
1468 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subLowest() { return absLowest(); }
1469 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subHighest() { return absHighest(); }
1470 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subCeiling(K key) { return absCeiling(key); }
1471 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subHigher(K key) { return absHigher(key); }
1472 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subFloor(K key) { return absFloor(key); }
1473 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subLower(K key) { return absLower(key); }
1474 }
1475
1476 // 降序的SubMap,继承于NavigableSubMap
1477 // 相比于升序SubMap,它的实现机制是将“SubMap的比较器反转”!
1478 static final class DescendingSubMap<K,V> extends NavigableSubMap<K,V> {
1479 private static final long serialVersionUID = 912986545866120460L;
1480 DescendingSubMap(TreeMap<K,V> m,
1481 boolean fromStart, K lo, boolean loInclusive,
1482 boolean toEnd, K hi, boolean hiInclusive) {
1483 super(m, fromStart, lo, loInclusive, toEnd, hi, hiInclusive);
1484 }
1485
1486 // 反转的比较器:是将原始比较器反转得到的。
1487 private final Comparator<? super K> reverseComparator =
1488 Collections.reverseOrder(m.comparator);
1489
1490 // 获取反转比较器
1491 public Comparator<? super K> comparator() {
1492 return reverseComparator;
1493 }
1494
1495 // 获取“子Map”。
1496 // 范围是从fromKey 到 toKey;fromInclusive是是否包含fromKey的标记,toInclusive是是否包含toKey的标记
1497 public NavigableMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, boolean fromInclusive,
1498 K toKey, boolean toInclusive) {
1499 if (!inRange(fromKey, fromInclusive))
1500 throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromKey out of range");
1501 if (!inRange(toKey, toInclusive))
1502 throw new IllegalArgumentException("toKey out of range");
1503 return new DescendingSubMap(m,
1504 false, toKey, toInclusive,
1505 false, fromKey, fromInclusive);
1506 }
1507
1508 // 获取“Map的头部”。
1509 // 范围从第一个节点 到 toKey, inclusive是是否包含toKey的标记
1510 public NavigableMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey, boolean inclusive) {
1511 if (!inRange(toKey, inclusive))
1512 throw new IllegalArgumentException("toKey out of range");
1513 return new DescendingSubMap(m,
1514 false, toKey, inclusive,
1515 toEnd, hi, hiInclusive);
1516 }
1517
1518 // 获取“Map的尾部”。
1519 // 范围是从 fromKey 到 最后一个节点,inclusive是是否包含fromKey的标记
1520 public NavigableMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey, boolean inclusive){
1521 if (!inRange(fromKey, inclusive))
1522 throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromKey out of range");
1523 return new DescendingSubMap(m,
1524 fromStart, lo, loInclusive,
1525 false, fromKey, inclusive);
1526 }
1527
1528 // 获取对应的降序Map
1529 public NavigableMap<K,V> descendingMap() {
1530 NavigableMap<K,V> mv = descendingMapView;
1531 return (mv != null) ? mv :
1532 (descendingMapView =
1533 new AscendingSubMap(m,
1534 fromStart, lo, loInclusive,
1535 toEnd, hi, hiInclusive));
1536 }
1537
1538 // 返回“升序Key迭代器”
1539 Iterator<K> keyIterator() {
1540 return new DescendingSubMapKeyIterator(absHighest(), absLowFence());
1541 }
1542
1543 // 返回“降序Key迭代器”
1544 Iterator<K> descendingKeyIterator() {
1545 return new SubMapKeyIterator(absLowest(), absHighFence());
1546 }
1547
1548 // “降序EntrySet集合”类
1549 // 实现了iterator()
1550 final class DescendingEntrySetView extends EntrySetView {
1551 public Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() {
1552 return new DescendingSubMapEntryIterator(absHighest(), absLowFence());
1553 }
1554 }
1555
1556 // 返回“降序EntrySet集合”
1557 public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {
1558 EntrySetView es = entrySetView;
1559 return (es != null) ? es : new DescendingEntrySetView();
1560 }
1561
1562 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subLowest() { return absHighest(); }
1563 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subHighest() { return absLowest(); }
1564 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subCeiling(K key) { return absFloor(key); }
1565 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subHigher(K key) { return absLower(key); }
1566 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subFloor(K key) { return absCeiling(key); }
1567 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subLower(K key) { return absHigher(key); }
1568 }
1569
1570 // SubMap是旧版本的类,新的Java中没有用到。
1571 private class SubMap extends AbstractMap<K,V>
1572 implements SortedMap<K,V>, java.io.Serializable {
1573 private static final long serialVersionUID = -6520786458950516097L;
1574 private boolean fromStart = false, toEnd = false;
1575 private K fromKey, toKey;
1576 private Object readResolve() {
1577 return new AscendingSubMap(TreeMap.this,
1578 fromStart, fromKey, true,
1579 toEnd, toKey, false);
1580 }
1581 public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() { throw new InternalError(); }
1582 public K lastKey() { throw new InternalError(); }
1583 public K firstKey() { throw new InternalError(); }
1584 public SortedMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, K toKey) { throw new InternalError(); }
1585 public SortedMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey) { throw new InternalError(); }
1586 public SortedMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey) { throw new InternalError(); }
1587 public Comparator<? super K> comparator() { throw new InternalError(); }
1588 }
1589
1590
1591 // 红黑树的节点颜色--红色
1592 private static final boolean RED = false;
1593 // 红黑树的节点颜色--黑色
1594 private static final boolean BLACK = true;
1595
1596 // “红黑树的节点”对应的类。
1597 // 包含了 key(键)、value(值)、left(左孩子)、right(右孩子)、parent(父节点)、color(颜色)
1598 static final class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
1599 // 键
1600 K key;
1601 // 值
1602 V value;
1603 // 左孩子
1604 Entry<K,V> left = null;
1605 // 右孩子
1606 Entry<K,V> right = null;
1607 // 父节点
1608 Entry<K,V> parent;
1609 // 当前节点颜色
1610 boolean color = BLACK;
1611
1612 // 构造函数
1613 Entry(K key, V value, Entry<K,V> parent) {
1614 this.key = key;
1615 this.value = value;
1616 this.parent = parent;
1617 }
1618
1619 // 返回“键”
1620 public K getKey() {
1621 return key;
1622 }
1623
1624 // 返回“值”
1625 public V getValue() {
1626 return value;
1627 }
1628
1629 // 更新“值”,返回旧的值
1630 public V setValue(V value) {
1631 V oldValue = this.value;
1632 this.value = value;
1633 return oldValue;
1634 }
1635
1636 // 判断两个节点是否相等的函数,覆盖equals()函数。
1637 // 若两个节点的“key相等”并且“value相等”,则两个节点相等
1638 public boolean equals(Object o) {
1639 if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
1640 return false;
1641 Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
1642
1643 return valEquals(key,e.getKey()) && valEquals(value,e.getValue());
1644 }
1645
1646 // 覆盖hashCode函数。
1647 public int hashCode() {
1648 int keyHash = (key==null ? 0 : key.hashCode());
1649 int valueHash = (value==null ? 0 : value.hashCode());
1650 return keyHash ^ valueHash;
1651 }
1652
1653 // 覆盖toString()函数。
1654 public String toString() {
1655 return key + "=" + value;
1656 }
1657 }
1658
1659 // 返回“红黑树的第一个节点”
1660 final Entry<K,V> getFirstEntry() {
1661 Entry<K,V> p = root;
1662 if (p != null)
1663 while (p.left != null)
1664 p = p.left;
1665 return p;
1666 }
1667
1668 // 返回“红黑树的最后一个节点”
1669 final Entry<K,V> getLastEntry() {
1670 Entry<K,V> p = root;
1671 if (p != null)
1672 while (p.right != null)
1673 p = p.right;
1674 return p;
1675 }
1676
1677 // 返回“节点t的后继节点”
1678 static <K,V> TreeMap.Entry<K,V> successor(Entry<K,V> t) {
1679 if (t == null)
1680 return null;
1681 else if (t.right != null) {
1682 Entry<K,V> p = t.right;
1683 while (p.left != null)
1684 p = p.left;
1685 return p;
1686 } else {
1687 Entry<K,V> p = t.parent;
1688 Entry<K,V> ch = t;
1689 while (p != null && ch == p.right) {
1690 ch = p;
1691 p = p.parent;
1692 }
1693 return p;
1694 }
1695 }
1696
1697 // 返回“节点t的前继节点”
1698 static <K,V> Entry<K,V> predecessor(Entry<K,V> t) {
1699 if (t == null)
1700 return null;
1701 else if (t.left != null) {
1702 Entry<K,V> p = t.left;
1703 while (p.right != null)
1704 p = p.right;
1705 return p;
1706 } else {
1707 Entry<K,V> p = t.parent;
1708 Entry<K,V> ch = t;
1709 while (p != null && ch == p.left) {
1710 ch = p;
1711 p = p.parent;
1712 }
1713 return p;
1714 }
1715 }
1716
1717 // 返回“节点p的颜色”
1718 // 根据“红黑树的特性”可知:空节点颜色是黑色。
1719 private static <K,V> boolean colorOf(Entry<K,V> p) {
1720 return (p == null ? BLACK : p.color);
1721 }
1722
1723 // 返回“节点p的父节点”
1724 private static <K,V> Entry<K,V> parentOf(Entry<K,V> p) {
1725 return (p == null ? null: p.parent);
1726 }
1727
1728 // 设置“节点p的颜色为c”
1729 private static <K,V> void setColor(Entry<K,V> p, boolean c) {
1730 if (p != null)
1731 p.color = c;
1732 }
1733
1734 // 设置“节点p的左孩子”
1735 private static <K,V> Entry<K,V> leftOf(Entry<K,V> p) {
1736 return (p == null) ? null: p.left;
1737 }
1738
1739 // 设置“节点p的右孩子”
1740 private static <K,V> Entry<K,V> rightOf(Entry<K,V> p) {
1741 return (p == null) ? null: p.right;
1742 }
1743
1744 // 对节点p执行“左旋”操作
1745 private void rotateLeft(Entry<K,V> p) {
1746 if (p != null) {
1747 Entry<K,V> r = p.right;
1748 p.right = r.left;
1749 if (r.left != null)
1750 r.left.parent = p;
1751 r.parent = p.parent;
1752 if (p.parent == null)
1753 root = r;
1754 else if (p.parent.left == p)
1755 p.parent.left = r;
1756 else
1757 p.parent.right = r;
1758 r.left = p;
1759 p.parent = r;
1760 }
1761 }
1762
1763 // 对节点p执行“右旋”操作
1764 private void rotateRight(Entry<K,V> p) {
1765 if (p != null) {
1766 Entry<K,V> l = p.left;
1767 p.left = l.right;
1768 if (l.right != null) l.right.parent = p;
1769 l.parent = p.parent;
1770 if (p.parent == null)
1771 root = l;
1772 else if (p.parent.right == p)
1773 p.parent.right = l;
1774 else p.parent.left = l;
1775 l.right = p;
1776 p.parent = l;
1777 }
1778 }
1779
1780 // 插入之后的修正操作。
1781 // 目的是保证:红黑树插入节点之后,仍然是一颗红黑树
1782 private void fixAfterInsertion(Entry<K,V> x) {
1783 x.color = RED;
1784
1785 while (x != null && x != root && x.parent.color == RED) {
1786 if (parentOf(x) == leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)))) {
1787 Entry<K,V> y = rightOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
1788 if (colorOf(y) == RED) {
1789 setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
1790 setColor(y, BLACK);
1791 setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
1792 x = parentOf(parentOf(x));
1793 } else {
1794 if (x == rightOf(parentOf(x))) {
1795 x = parentOf(x);
1796 rotateLeft(x);
1797 }
1798 setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
1799 setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
1800 rotateRight(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
1801 }
1802 } else {
1803 Entry<K,V> y = leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
1804 if (colorOf(y) == RED) {
1805 setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
1806 setColor(y, BLACK);
1807 setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
1808 x = parentOf(parentOf(x));
1809 } else {
1810 if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) {
1811 x = parentOf(x);
1812 rotateRight(x);
1813 }
1814 setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
1815 setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);
1816 rotateLeft(parentOf(parentOf(x)));
1817 }
1818 }
1819 }
1820 root.color = BLACK;
1821 }
1822
1823 // 删除“红黑树的节点p”
1824 private void deleteEntry(Entry<K,V> p) {
1825 modCount++;
1826 size--;
1827
1828 // If strictly internal, copy successor's element to p and then make p
1829 // point to successor.
1830 if (p.left != null && p.right != null) {
1831 Entry<K,V> s = successor (p);
1832 p.key = s.key;
1833 p.value = s.value;
1834 p = s;
1835 } // p has 2 children
1836
1837 // Start fixup at replacement node, if it exists.
1838 Entry<K,V> replacement = (p.left != null ? p.left : p.right);
1839
1840 if (replacement != null) {
1841 // Link replacement to parent
1842 replacement.parent = p.parent;
1843 if (p.parent == null)
1844 root = replacement;
1845 else if (p == p.parent.left)
1846 p.parent.left = replacement;
1847 else
1848 p.parent.right = replacement;
1849
1850 // Null out links so they are OK to use by fixAfterDeletion.
1851 p.left = p.right = p.parent = null;
1852
1853 // Fix replacement
1854 if (p.color == BLACK)
1855 fixAfterDeletion(replacement);
1856 } else if (p.parent == null) { // return if we are the only node.
1857 root = null;
1858 } else { // No children. Use self as phantom replacement and unlink.
1859 if (p.color == BLACK)
1860 fixAfterDeletion(p);
1861
1862 if (p.parent != null) {
1863 if (p == p.parent.left)
1864 p.parent.left = null;
1865 else if (p == p.parent.right)
1866 p.parent.right = null;
1867 p.parent = null;
1868 }
1869 }
1870 }
1871
1872 // 删除之后的修正操作。
1873 // 目的是保证:红黑树删除节点之后,仍然是一颗红黑树
1874 private void fixAfterDeletion(Entry<K,V> x) {
1875 while (x != root && colorOf(x) == BLACK) {
1876 if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) {
1877 Entry<K,V> sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));
1878
1879 if (colorOf(sib) == RED) {
1880 setColor(sib, BLACK);
1881 setColor(parentOf(x), RED);
1882 rotateLeft(parentOf(x));
1883 sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));
1884 }
1885
1886 if (colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK &&
1887 colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
1888 setColor(sib, RED);
1889 x = parentOf(x);
1890 } else {
1891 if (colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
1892 setColor(leftOf(sib), BLACK);
1893 setColor(sib, RED);
1894 rotateRight(sib);
1895 sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));
1896 }
1897 setColor(sib, colorOf(parentOf(x)));
1898 setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
1899 setColor(rightOf(sib), BLACK);
1900 rotateLeft(parentOf(x));
1901 x = root;
1902 }
1903 } else { // symmetric
1904 Entry<K,V> sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));
1905
1906 if (colorOf(sib) == RED) {
1907 setColor(sib, BLACK);
1908 setColor(parentOf(x), RED);
1909 rotateRight(parentOf(x));
1910 sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));
1911 }
1912
1913 if (colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK &&
1914 colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
1915 setColor(sib, RED);
1916 x = parentOf(x);
1917 } else {
1918 if (colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK) {
1919 setColor(rightOf(sib), BLACK);
1920 setColor(sib, RED);
1921 rotateLeft(sib);
1922 sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));
1923 }
1924 setColor(sib, colorOf(parentOf(x)));
1925 setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);
1926 setColor(leftOf(sib), BLACK);
1927 rotateRight(parentOf(x));
1928 x = root;
1929 }
1930 }
1931 }
1932
1933 setColor(x, BLACK);
1934 }
1935
1936 private static final long serialVersionUID = 919286545866124006L;
1937
1938 // java.io.Serializable的写入函数
1939 // 将TreeMap的“容量,所有的Entry”都写入到输出流中
1940 private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
1941 throws java.io.IOException {
1942 // Write out the Comparator and any hidden stuff
1943 s.defaultWriteObject();
1944
1945 // Write out size (number of Mappings)
1946 s.writeInt(size);
1947
1948 // Write out keys and values (alternating)
1949 for (Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> i = entrySet().iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) {
1950 Map.Entry<K,V> e = i.next();
1951 s.writeObject(e.getKey());
1952 s.writeObject(e.getValue());
1953 }
1954 }
1955
1956
1957 // java.io.Serializable的读取函数:根据写入方式读出
1958 // 先将TreeMap的“容量、所有的Entry”依次读出
1959 private void readObject(final java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
1960 throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
1961 // Read in the Comparator and any hidden stuff
1962 s.defaultReadObject();
1963
1964 // Read in size
1965 int size = s.readInt();
1966
1967 buildFromSorted(size, null, s, null);
1968 }
1969
1970 // 根据已经一个排好序的map创建一个TreeMap
1971 private void buildFromSorted(int size, Iterator it,
1972 java.io.ObjectInputStream str,
1973 V defaultVal)
1974 throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
1975 this.size = size;
1976 root = buildFromSorted(0, 0, size-1, computeRedLevel(size),
1977 it, str, defaultVal);
1978 }
1979
1980 // 根据已经一个排好序的map创建一个TreeMap
1981 // 将map中的元素逐个添加到TreeMap中,并返回map的中间元素作为根节点。
1982 private final Entry<K,V> buildFromSorted(int level, int lo, int hi,
1983 int redLevel,
1984 Iterator it,
1985 java.io.ObjectInputStream str,
1986 V defaultVal)
1987 throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
1988
1989 if (hi < lo) return null;
1990
1991
1992 // 获取中间元素
1993 int mid = (lo + hi) / 2;
1994
1995 Entry<K,V> left = null;
1996 // 若lo小于mid,则递归调用获取(middel的)左孩子。
1997 if (lo < mid)
1998 left = buildFromSorted(level+1, lo, mid - 1, redLevel,
1999 it, str, defaultVal);
2000
2001 // 获取middle节点对应的key和value
2002 K key;
2003 V value;
2004 if (it != null) {
2005 if (defaultVal==null) {
2006 Map.Entry<K,V> entry = (Map.Entry<K,V>)it.next();
2007 key = entry.getKey();
2008 value = entry.getValue();
2009 } else {
2010 key = (K)it.next();
2011 value = defaultVal;
2012 }
2013 } else { // use stream
2014 key = (K) str.readObject();
2015 value = (defaultVal != null ? defaultVal : (V) str.readObject());
2016 }
2017
2018 // 创建middle节点
2019 Entry<K,V> middle = new Entry<K,V>(key, value, null);
2020
2021 // 若当前节点的深度=红色节点的深度,则将节点着色为红色。
2022 if (level == redLevel)
2023 middle.color = RED;
2024
2025 // 设置middle为left的父亲,left为middle的左孩子
2026 if (left != null) {
2027 middle.left = left;
2028 left.parent = middle;
2029 }
2030
2031 if (mid < hi) {
2032 // 递归调用获取(middel的)右孩子。
2033 Entry<K,V> right = buildFromSorted(level+1, mid+1, hi, redLevel,
2034 it, str, defaultVal);
2035 // 设置middle为left的父亲,left为middle的左孩子
2036 middle.right = right;
2037 right.parent = middle;
2038 }
2039
2040 return middle;
2041 }
2042
2043 // 计算节点树为sz的最大深度,也是红色节点的深度值。
2044 private static int computeRedLevel(int sz) {
2045 int level = 0;
2046 for (int m = sz - 1; m >= 0; m = m / 2 - 1)
2047 level++;
2048 return level;
2049 }
2050 }
说明:
在详细介绍TreeMap的代码之前,我们先建立一个整体概念。
TreeMap是通过红黑树实现的,TreeMap存储的是key-value键值对,TreeMap的排序是基于对key的排序。
TreeMap提供了操作“key”、“key-value”、“value”等方法,也提供了对TreeMap这颗树进行整体操作的方法,如获取子树、反向树。
后面的解说内容分为几部分,
首先,介绍TreeMap的核心,即红黑树相关部分;
然后,介绍TreeMap的主要函数;
再次,介绍TreeMap实现的几个接口;
最后,补充介绍TreeMap的其它内容。
TreeMap本质上是一颗红黑树。要彻底理解TreeMap,建议读者先理解红黑树。关于红黑树的原理,可以参考:红黑树(一) 原理和算法详细介绍
第3.1部分 TreeMap的红黑树相关内容
TreeMap中于红黑树相关的主要函数有:
1 数据结构
1.1 红黑树的节点颜色--红色
private static final boolean RED = false;
1.2 红黑树的节点颜色--黑色
private static final boolean BLACK = true;
1.3 “红黑树的节点”对应的类。
static final class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { ... }
Entry包含了6个部分内容:key(键)、value(值)、left(左孩子)、right(右孩子)、parent(父节点)、color(颜色)
Entry节点根据key进行排序,Entry节点包含的内容为value。
2 相关操作
2.1 左旋
private void rotateLeft(Entry<K,V> p) { ... }
2.2 右旋
private void rotateRight(Entry<K,V> p) { ... }
2.3 插入操作
public V put(K key, V value) { ... }
2.4 插入修正操作
红黑树执行插入操作之后,要执行“插入修正操作”。
目的是:保红黑树在进行插入节点之后,仍然是一颗红黑树
private void fixAfterInsertion(Entry<K,V> x) { ... }
2.5 删除操作
private void deleteEntry(Entry<K,V> p) { ... }
2.6 删除修正操作
红黑树执行删除之后,要执行“删除修正操作”。
目的是保证:红黑树删除节点之后,仍然是一颗红黑树
private void fixAfterDeletion(Entry<K,V> x) { ... }
关于红黑树部分,这里主要是指出了TreeMap中那些是红黑树的主要相关内容。具体的红黑树相关操作API,这里没有详细说明,因为它们仅仅只是将算法翻译成代码。读者可以参考“红黑树(一) 原理和算法详细介绍”进行了解。
第3.2部分 TreeMap的构造函数
1 默认构造函数
使用默认构造函数构造TreeMap时,使用java的默认的比较器比较Key的大小,从而对TreeMap进行排序。
public TreeMap() {
comparator = null;
}
2 带比较器的构造函数
public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
}
3 带Map的构造函数,Map会成为TreeMap的子集
public TreeMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
comparator = null;
putAll(m);
}
该构造函数会调用putAll()将m中的所有元素添加到TreeMap中。putAll()源码如下:
public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
for (Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e : m.entrySet())
put(e.getKey(), e.getValue());
}
从中,我们可以看出putAll()就是将m中的key-value逐个的添加到TreeMap中。
4 带SortedMap的构造函数,SortedMap会成为TreeMap的子集
public TreeMap(SortedMap<K, ? extends V> m) {
comparator = m.comparator();
try {
buildFromSorted(m.size(), m.entrySet().iterator(), null, null);
} catch (java.io.IOException cannotHappen) {
} catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) {
}
}
该构造函数不同于上一个构造函数,在上一个构造函数中传入的参数是Map,Map不是有序的,所以要逐个添加。
而该构造函数的参数是SortedMap是一个有序的Map,我们通过buildFromSorted()来创建对应的Map。
buildFromSorted涉及到的代码如下:

1 // 根据已经一个排好序的map创建一个TreeMap
2 // 将map中的元素逐个添加到TreeMap中,并返回map的中间元素作为根节点。
3 private final Entry<K,V> buildFromSorted(int level, int lo, int hi,
4 int redLevel,
5 Iterator it,
6 java.io.ObjectInputStream str,
7 V defaultVal)
8 throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
9
10 if (hi < lo) return null;
11
12
13 // 获取中间元素
14 int mid = (lo + hi) / 2;
15
16 Entry<K,V> left = null;
17 // 若lo小于mid,则递归调用获取(middel的)左孩子。
18 if (lo < mid)
19 left = buildFromSorted(level+1, lo, mid - 1, redLevel,
20 it, str, defaultVal);
21
22 // 获取middle节点对应的key和value
23 K key;
24 V value;
25 if (it != null) {
26 if (defaultVal==null) {
27 Map.Entry<K,V> entry = (Map.Entry<K,V>)it.next();
28 key = entry.getKey();
29 value = entry.getValue();
30 } else {
31 key = (K)it.next();
32 value = defaultVal;
33 }
34 } else { // use stream
35 key = (K) str.readObject();
36 value = (defaultVal != null ? defaultVal : (V) str.readObject());
37 }
38
39 // 创建middle节点
40 Entry<K,V> middle = new Entry<K,V>(key, value, null);
41
42 // 若当前节点的深度=红色节点的深度,则将节点着色为红色。
43 if (level == redLevel)
44 middle.color = RED;
45
46 // 设置middle为left的父亲,left为middle的左孩子
47 if (left != null) {
48 middle.left = left;
49 left.parent = middle;
50 }
51
52 if (mid < hi) {
53 // 递归调用获取(middel的)右孩子。
54 Entry<K,V> right = buildFromSorted(level+1, mid+1, hi, redLevel,
55 it, str, defaultVal);
56 // 设置middle为left的父亲,left为middle的左孩子
57 middle.right = right;
58 right.parent = middle;
59 }
60
61 return middle;
62 }
要理解buildFromSorted,重点说明以下几点:
第一,buildFromSorted是通过递归将SortedMap中的元素逐个关联。
第二,buildFromSorted返回middle节点(中间节点)作为root。
第三,buildFromSorted添加到红黑树中时,只将level == redLevel的节点设为红色。第level级节点,实际上是buildFromSorted转换成红黑树后的最底端(假设根节点在最上方)的节点;只将红黑树最底端的阶段着色为红色,其余都是黑色。
第3.3部分 TreeMap的Entry相关函数
TreeMap的 firstEntry()、 lastEntry()、 lowerEntry()、 higherEntry()、 floorEntry()、 ceilingEntry()、 pollFirstEntry() 、 pollLastEntry() 原理都是类似的;下面以firstEntry()来进行详细说明
我们先看看firstEntry()和getFirstEntry()的代码:
public Map.Entry<K,V> firstEntry() {
return exportEntry(getFirstEntry());
}
final Entry<K,V> getFirstEntry() {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
if (p != null)
while (p.left != null)
p = p.left;
return p;
}
从中,我们可以看出 firstEntry() 和 getFirstEntry() 都是用于获取第一个节点。
但是,firstEntry() 是对外接口; getFirstEntry() 是内部接口。而且,firstEntry() 是通过 getFirstEntry() 来实现的。那为什么外界不能直接调用 getFirstEntry(),而需要多此一举的调用 firstEntry() 呢?
先告诉大家原因,再进行详细说明。这么做的目的是:防止用户修改返回的Entry。getFirstEntry()返回的Entry是可以被修改的,但是经过firstEntry()返回的Entry不能被修改,只可以读取Entry的key值和value值。下面我们看看到底是如何实现的。
(01) getFirstEntry()返回的是Entry节点,而Entry是红黑树的节点,它的源码如下:
// 返回“红黑树的第一个节点”
final Entry<K,V> getFirstEntry() {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
if (p != null)
while (p.left != null)
p = p.left;
return p;
}
从中,我们可以调用Entry的getKey()、getValue()来获取key和value值,以及调用setValue()来修改value的值。
(02) firstEntry()返回的是exportEntry(getFirstEntry())。下面我们看看exportEntry()干了些什么?
static <K,V> Map.Entry<K,V> exportEntry(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e) {
return e == null? null :
new AbstractMap.SimpleImmutableEntry<K,V>(e);
}
实际上,exportEntry() 是新建一个AbstractMap.SimpleImmutableEntry类型的对象,并返回。
SimpleImmutableEntry的实现在AbstractMap.java中,下面我们看看AbstractMap.SimpleImmutableEntry是如何实现的,代码如下:

1 public static class SimpleImmutableEntry<K,V>
2 implements Entry<K,V>, java.io.Serializable
3 {
4 private static final long serialVersionUID = 7138329143949025153L;
5
6 private final K key;
7 private final V value;
8
9 public SimpleImmutableEntry(K key, V value) {
10 this.key = key;
11 this.value = value;
12 }
13
14 public SimpleImmutableEntry(Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> entry) {
15 this.key = entry.getKey();
16 this.value = entry.getValue();
17 }
18
19 public K getKey() {
20 return key;
21 }
22
23 public V getValue() {
24 return value;
25 }
26
27 public V setValue(V value) {
28 throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
29 }
30
31 public boolean equals(Object o) {
32 if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
33 return false;
34 Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry)o;
35 return eq(key, e.getKey()) && eq(value, e.getValue());
36 }
37
38 public int hashCode() {
39 return (key == null ? 0 : key.hashCode()) ^
40 (value == null ? 0 : value.hashCode());
41 }
42
43 public String toString() {
44 return key + "=" + value;
45 }
46 }
从中,我们可以看出SimpleImmutableEntry实际上是简化的key-value节点。
它只提供了getKey()、getValue()方法类获取节点的值;但不能修改value的值,因为调用 setValue() 会抛出异常UnsupportedOperationException();
再回到我们之前的问题:那为什么外界不能直接调用 getFirstEntry(),而需要多此一举的调用 firstEntry() 呢?
现在我们清晰的了解到:
(01) firstEntry()是对外接口,而getFirstEntry()是内部接口。
(02) 对firstEntry()返回的Entry对象只能进行getKey()、getValue()等读取操作;而对getFirstEntry()返回的对象除了可以进行读取操作之后,还可以通过setValue()修改值。
第3.4部分 TreeMap的key相关函数
TreeMap的firstKey()、lastKey()、lowerKey()、higherKey()、floorKey()、ceilingKey()原理都是类似的;下面以ceilingKey()来进行详细说明
ceilingKey(K key)的作用是“返回大于/等于key的最小的键值对所对应的KEY,没有的话返回null”,它的代码如下:
public K ceilingKey(K key) {
return keyOrNull(getCeilingEntry(key));
}
ceilingKey()是通过getCeilingEntry()实现的。keyOrNull()的代码很简单,它是获取节点的key,没有的话,返回null。
static <K,V> K keyOrNull(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e) {
return e == null? null : e.key;
}
getCeilingEntry(K key)的作用是“获取TreeMap中大于/等于key的最小的节点,若不存在(即TreeMap中所有节点的键都比key大),就返回null”。它的实现代码如下:

1 final Entry<K,V> getCeilingEntry(K key) {
2 Entry<K,V> p = root;
3 while (p != null) {
4 int cmp = compare(key, p.key);
5 // 情况一:若“p的key” > key。
6 // 若 p 存在左孩子,则设 p=“p的左孩子”;
7 // 否则,返回p
8 if (cmp < 0) {
9 if (p.left != null)
10 p = p.left;
11 else
12 return p;
13 // 情况二:若“p的key” < key。
14 } else if (cmp > 0) {
15 // 若 p 存在右孩子,则设 p=“p的右孩子”
16 if (p.right != null) {
17 p = p.right;
18 } else {
19 // 若 p 不存在右孩子,则找出 p 的后继节点,并返回
20 // 注意:这里返回的 “p的后继节点”有2种可能性:第一,null;第二,TreeMap中大于key的最小的节点。
21 // 理解这一点的核心是,getCeilingEntry是从root开始遍历的。
22 // 若getCeilingEntry能走到这一步,那么,它之前“已经遍历过的节点的key”都 > key。
23 // 能理解上面所说的,那么就很容易明白,为什么“p的后继节点”有2种可能性了。
24 Entry<K,V> parent = p.parent;
25 Entry<K,V> ch = p;
26 while (parent != null && ch == parent.right) {
27 ch = parent;
28 parent = parent.parent;
29 }
30 return parent;
31 }
32 // 情况三:若“p的key” = key。
33 } else
34 return p;
35 }
36 return null;
37 }
第3.5部分 TreeMap的values()函数
values() 返回“TreeMap中值的集合”
values()的实现代码如下:
public Collection<V> values() {
Collection<V> vs = values;
return (vs != null) ? vs : (values = new Values());
}
说明:从中,我们可以发现values()是通过 new Values() 来实现 “返回TreeMap中值的集合”。
那么Values()是如何实现的呢? 没错!由于返回的是值的集合,那么Values()肯定返回一个集合;而Values()正好是集合类Value的构造函数。Values继承于AbstractCollection,它的代码如下:

1 // ”TreeMap的值的集合“对应的类,它集成于AbstractCollection
2 class Values extends AbstractCollection<V> {
3 // 返回迭代器
4 public Iterator<V> iterator() {
5 return new ValueIterator(getFirstEntry());
6 }
7
8 // 返回个数
9 public int size() {
10 return TreeMap.this.size();
11 }
12
13 // "TreeMap的值的集合"中是否包含"对象o"
14 public boolean contains(Object o) {
15 return TreeMap.this.containsValue(o);
16 }
17
18 // 删除"TreeMap的值的集合"中的"对象o"
19 public boolean remove(Object o) {
20 for (Entry<K,V> e = getFirstEntry(); e != null; e = successor(e)) {
21 if (valEquals(e.getValue(), o)) {
22 deleteEntry(e);
23 return true;
24 }
25 }
26 return false;
27 }
28
29 // 清空删除"TreeMap的值的集合"
30 public void clear() {
31 TreeMap.this.clear();
32 }
33 }
说明:从中,我们可以知道Values类就是一个集合。而 AbstractCollection 实现了除 size() 和 iterator() 之外的其它函数,因此只需要在Values类中实现这两个函数即可。
size() 的实现非常简单,Values集合中元素的个数=该TreeMap的元素个数。(TreeMap每一个元素都有一个值嘛!)
iterator() 则返回一个迭代器,用于遍历Values。下面,我们一起可以看看iterator()的实现:
public Iterator<V> iterator() {
return new ValueIterator(getFirstEntry());
}
说明: iterator() 是通过ValueIterator() 返回迭代器的,ValueIterator是一个类。代码如下:
final class ValueIterator extends PrivateEntryIterator<V> {
ValueIterator(Entry<K,V> first) {
super(first);
}
public V next() {
return nextEntry().value;
}
}
说明:ValueIterator的代码很简单,它的主要实现应该在它的父类PrivateEntryIterator中。下面我们一起看看PrivateEntryIterator的代码:

1 abstract class PrivateEntryIterator<T> implements Iterator<T> {
2 // 下一节点
3 Entry<K,V> next;
4 // 上一次返回的节点
5 Entry<K,V> lastReturned;
6 // 修改次数统计数
7 int expectedModCount;
8
9 PrivateEntryIterator(Entry<K,V> first) {
10 expectedModCount = modCount;
11 lastReturned = null;
12 next = first;
13 }
14
15 // 是否存在下一个节点
16 public final boolean hasNext() {
17 return next != null;
18 }
19
20 // 返回下一个节点
21 final Entry<K,V> nextEntry() {
22 Entry<K,V> e = next;
23 if (e == null)
24 throw new NoSuchElementException();
25 if (modCount != expectedModCount)
26 throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
27 next = successor(e);
28 lastReturned = e;
29 return e;
30 }
31
32 // 返回上一节点
33 final Entry<K,V> prevEntry() {
34 Entry<K,V> e = next;
35 if (e == null)
36 throw new NoSuchElementException();
37 if (modCount != expectedModCount)
38 throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
39 next = predecessor(e);
40 lastReturned = e;
41 return e;
42 }
43
44 // 删除当前节点
45 public void remove() {
46 if (lastReturned == null)
47 throw new IllegalStateException();
48 if (modCount != expectedModCount)
49 throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
50 // deleted entries are replaced by their successors
51 if (lastReturned.left != null && lastReturned.right != null)
52 next = lastReturned;
53 deleteEntry(lastReturned);
54 expectedModCount = modCount;
55 lastReturned = null;
56 }
57 }
说明:PrivateEntryIterator是一个抽象类,它的实现很简单,只只实现了Iterator的remove()和hasNext()接口,没有实现next()接口。
而我们在ValueIterator中已经实现的next()接口。
至此,我们就了解了iterator()的完整实现了。
第3.6部分 TreeMap的entrySet()函数
entrySet() 返回“键值对集合”。顾名思义,它返回的是一个集合,集合的元素是“键值对”。
下面,我们看看它是如何实现的?entrySet() 的实现代码如下:
public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {
EntrySet es = entrySet;
return (es != null) ? es : (entrySet = new EntrySet());
}
说明:entrySet()返回的是一个EntrySet对象。
下面我们看看EntrySet的代码:

1 // EntrySet是“TreeMap的所有键值对组成的集合”,
2 // EntrySet集合的单位是单个“键值对”。
3 class EntrySet extends AbstractSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
4 public Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() {
5 return new EntryIterator(getFirstEntry());
6 }
7
8 // EntrySet中是否包含“键值对Object”
9 public boolean contains(Object o) {
10 if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
11 return false;
12 Map.Entry<K,V> entry = (Map.Entry<K,V>) o;
13 V value = entry.getValue();
14 Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(entry.getKey());
15 return p != null && valEquals(p.getValue(), value);
16 }
17
18 // 删除EntrySet中的“键值对Object”
19 public boolean remove(Object o) {
20 if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
21 return false;
22 Map.Entry<K,V> entry = (Map.Entry<K,V>) o;
23 V value = entry.getValue();
24 Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(entry.getKey());
25 if (p != null && valEquals(p.getValue(), value)) {
26 deleteEntry(p);
27 return true;
28 }
29 return false;
30 }
31
32 // 返回EntrySet中元素个数
33 public int size() {
34 return TreeMap.this.size();
35 }
36
37 // 清空EntrySet
38 public void clear() {
39 TreeMap.this.clear();
40 }
41 }
说明:
EntrySet是“TreeMap的所有键值对组成的集合”,而且它单位是单个“键值对”。
EntrySet是一个集合,它继承于AbstractSet。而AbstractSet实现了除size() 和 iterator() 之外的其它函数,因此,我们重点了解一下EntrySet的size() 和 iterator() 函数
size() 的实现非常简单,AbstractSet集合中元素的个数=该TreeMap的元素个数。
iterator() 则返回一个迭代器,用于遍历AbstractSet。从上面的源码中,我们可以发现iterator() 是通过EntryIterator实现的;下面我们看看EntryIterator的源码:
final class EntryIterator extends PrivateEntryIterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
EntryIterator(Entry<K,V> first) {
super(first);
}
public Map.Entry<K,V> next() {
return nextEntry();
}
}
说明:和Values类一样,EntryIterator也继承于PrivateEntryIterator类。
第3.7部分 TreeMap实现的Cloneable接口
TreeMap实现了Cloneable接口,即实现了clone()方法。
clone()方法的作用很简单,就是克隆一个TreeMap对象并返回。

1 // 克隆一个TreeMap,并返回Object对象
2 public Object clone() {
3 TreeMap<K,V> clone = null;
4 try {
5 clone = (TreeMap<K,V>) super.clone();
6 } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
7 throw new InternalError();
8 }
9
10 // Put clone into "virgin" state (except for comparator)
11 clone.root = null;
12 clone.size = 0;
13 clone.modCount = 0;
14 clone.entrySet = null;
15 clone.navigableKeySet = null;
16 clone.descendingMap = null;
17
18 // Initialize clone with our mappings
19 try {
20 clone.buildFromSorted(size, entrySet().iterator(), null, null);
21 } catch (java.io.IOException cannotHappen) {
22 } catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) {
23 }
24
25 return clone;
26 }
第3.8部分 TreeMap实现的Serializable接口
TreeMap实现java.io.Serializable,分别实现了串行读取、写入功能。
串行写入函数是writeObject(),它的作用是将TreeMap的“容量,所有的Entry”都写入到输出流中。
而串行读取函数是readObject(),它的作用是将TreeMap的“容量、所有的Entry”依次读出。
readObject() 和 writeObject() 正好是一对,通过它们,我能实现TreeMap的串行传输。

1 // java.io.Serializable的写入函数
2 // 将TreeMap的“容量,所有的Entry”都写入到输出流中
3 private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
4 throws java.io.IOException {
5 // Write out the Comparator and any hidden stuff
6 s.defaultWriteObject();
7
8 // Write out size (number of Mappings)
9 s.writeInt(size);
10
11 // Write out keys and values (alternating)
12 for (Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> i = entrySet().iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) {
13 Map.Entry<K,V> e = i.next();
14 s.writeObject(e.getKey());
15 s.writeObject(e.getValue());
16 }
17 }
18
19
20 // java.io.Serializable的读取函数:根据写入方式读出
21 // 先将TreeMap的“容量、所有的Entry”依次读出
22 private void readObject(final java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
23 throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
24 // Read in the Comparator and any hidden stuff
25 s.defaultReadObject();
26
27 // Read in size
28 int size = s.readInt();
29
30 buildFromSorted(size, null, s, null);
31 }
说到这里,就顺便说一下“关键字transient”的作用
transient是Java语言的关键字,它被用来表示一个域不是该对象串行化的一部分。
Java的serialization提供了一种持久化对象实例的机制。当持久化对象时,可能有一个特殊的对象数据成员,我们不想用serialization机制来保存它。为了在一个特定对象的一个域上关闭serialization,可以在这个域前加上关键字transient。
当一个对象被串行化的时候,transient型变量的值不包括在串行化的表示中,然而非transient型的变量是被包括进去的。
第3.9部分 TreeMap实现的NavigableMap接口
firstKey()、lastKey()、lowerKey()、higherKey()、ceilingKey()、floorKey();
firstEntry()、 lastEntry()、 lowerEntry()、 higherEntry()、 floorEntry()、 ceilingEntry()、 pollFirstEntry() 、 pollLastEntry();
上面已经讲解过这些API了,下面对其它的API进行说明。
1 反向TreeMap
descendingMap() 的作用是返回当前TreeMap的反向的TreeMap。所谓反向,就是排序顺序和原始的顺序相反。
我们已经知道TreeMap是一颗红黑树,而红黑树是有序的。
TreeMap的排序方式是通过比较器,在创建TreeMap的时候,若指定了比较器,则使用该比较器;否则,就使用Java的默认比较器。
而获取TreeMap的反向TreeMap的原理就是将比较器反向即可!
理解了descendingMap()的反向原理之后,再讲解一下descendingMap()的代码。
// 获取TreeMap的降序Map
public NavigableMap<K, V> descendingMap() {
NavigableMap<K, V> km = descendingMap;
return (km != null) ? km :
(descendingMap = new DescendingSubMap(this,
true, null, true,
true, null, true));
}
从中,我们看出descendingMap()实际上是返回DescendingSubMap类的对象。下面,看看DescendingSubMap的源码:

1 static final class DescendingSubMap<K,V> extends NavigableSubMap<K,V> {
2 private static final long serialVersionUID = 912986545866120460L;
3 DescendingSubMap(TreeMap<K,V> m,
4 boolean fromStart, K lo, boolean loInclusive,
5 boolean toEnd, K hi, boolean hiInclusive) {
6 super(m, fromStart, lo, loInclusive, toEnd, hi, hiInclusive);
7 }
8
9 // 反转的比较器:是将原始比较器反转得到的。
10 private final Comparator<? super K> reverseComparator =
11 Collections.reverseOrder(m.comparator);
12
13 // 获取反转比较器
14 public Comparator<? super K> comparator() {
15 return reverseComparator;
16 }
17
18 // 获取“子Map”。
19 // 范围是从fromKey 到 toKey;fromInclusive是是否包含fromKey的标记,toInclusive是是否包含toKey的标记
20 public NavigableMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, boolean fromInclusive,
21 K toKey, boolean toInclusive) {
22 if (!inRange(fromKey, fromInclusive))
23 throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromKey out of range");
24 if (!inRange(toKey, toInclusive))
25 throw new IllegalArgumentException("toKey out of range");
26 return new DescendingSubMap(m,
27 false, toKey, toInclusive,
28 false, fromKey, fromInclusive);
29 }
30
31 // 获取“Map的头部”。
32 // 范围从第一个节点 到 toKey, inclusive是是否包含toKey的标记
33 public NavigableMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey, boolean inclusive) {
34 if (!inRange(toKey, inclusive))
35 throw new IllegalArgumentException("toKey out of range");
36 return new DescendingSubMap(m,
37 false, toKey, inclusive,
38 toEnd, hi, hiInclusive);
39 }
40
41 // 获取“Map的尾部”。
42 // 范围是从 fromKey 到 最后一个节点,inclusive是是否包含fromKey的标记
43 public NavigableMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey, boolean inclusive){
44 if (!inRange(fromKey, inclusive))
45 throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromKey out of range");
46 return new DescendingSubMap(m,
47 fromStart, lo, loInclusive,
48 false, fromKey, inclusive);
49 }
50
51 // 获取对应的降序Map
52 public NavigableMap<K,V> descendingMap() {
53 NavigableMap<K,V> mv = descendingMapView;
54 return (mv != null) ? mv :
55 (descendingMapView =
56 new AscendingSubMap(m,
57 fromStart, lo, loInclusive,
58 toEnd, hi, hiInclusive));
59 }
60
61 // 返回“升序Key迭代器”
62 Iterator<K> keyIterator() {
63 return new DescendingSubMapKeyIterator(absHighest(), absLowFence());
64 }
65
66 // 返回“降序Key迭代器”
67 Iterator<K> descendingKeyIterator() {
68 return new SubMapKeyIterator(absLowest(), absHighFence());
69 }
70
71 // “降序EntrySet集合”类
72 // 实现了iterator()
73 final class DescendingEntrySetView extends EntrySetView {
74 public Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() {
75 return new DescendingSubMapEntryIterator(absHighest(), absLowFence());
76 }
77 }
78
79 // 返回“降序EntrySet集合”
80 public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {
81 EntrySetView es = entrySetView;
82 return (es != null) ? es : new DescendingEntrySetView();
83 }
84
85 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subLowest() { return absHighest(); }
86 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subHighest() { return absLowest(); }
87 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subCeiling(K key) { return absFloor(key); }
88 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subHigher(K key) { return absLower(key); }
89 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subFloor(K key) { return absCeiling(key); }
90 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subLower(K key) { return absHigher(key); }
91 }
从中,我们看出DescendingSubMap是降序的SubMap,它的实现机制是将“SubMap的比较器反转”。
它继承于NavigableSubMap。而NavigableSubMap是一个继承于AbstractMap的抽象类;它包括2个子类——"(升序)AscendingSubMap"和"(降序)DescendingSubMap"。NavigableSubMap为它的两个子类实现了许多公共API。
下面看看NavigableSubMap的源码。

1 static abstract class NavigableSubMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V>
2 implements NavigableMap<K,V>, java.io.Serializable {
3 // TreeMap的拷贝
4 final TreeMap<K,V> m;
5 // lo是“子Map范围的最小值”,hi是“子Map范围的最大值”;
6 // loInclusive是“是否包含lo的标记”,hiInclusive是“是否包含hi的标记”
7 // fromStart是“表示是否从第一个节点开始计算”,
8 // toEnd是“表示是否计算到最后一个节点 ”
9 final K lo, hi;
10 final boolean fromStart, toEnd;
11 final boolean loInclusive, hiInclusive;
12
13 // 构造函数
14 NavigableSubMap(TreeMap<K,V> m,
15 boolean fromStart, K lo, boolean loInclusive,
16 boolean toEnd, K hi, boolean hiInclusive) {
17 if (!fromStart && !toEnd) {
18 if (m.compare(lo, hi) > 0)
19 throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromKey > toKey");
20 } else {
21 if (!fromStart) // type check
22 m.compare(lo, lo);
23 if (!toEnd)
24 m.compare(hi, hi);
25 }
26
27 this.m = m;
28 this.fromStart = fromStart;
29 this.lo = lo;
30 this.loInclusive = loInclusive;
31 this.toEnd = toEnd;
32 this.hi = hi;
33 this.hiInclusive = hiInclusive;
34 }
35
36 // 判断key是否太小
37 final boolean tooLow(Object key) {
38 // 若该SubMap不包括“起始节点”,
39 // 并且,“key小于最小键(lo)”或者“key等于最小键(lo),但最小键却没包括在该SubMap内”
40 // 则判断key太小。其余情况都不是太小!
41 if (!fromStart) {
42 int c = m.compare(key, lo);
43 if (c < 0 || (c == 0 && !loInclusive))
44 return true;
45 }
46 return false;
47 }
48
49 // 判断key是否太大
50 final boolean tooHigh(Object key) {
51 // 若该SubMap不包括“结束节点”,
52 // 并且,“key大于最大键(hi)”或者“key等于最大键(hi),但最大键却没包括在该SubMap内”
53 // 则判断key太大。其余情况都不是太大!
54 if (!toEnd) {
55 int c = m.compare(key, hi);
56 if (c > 0 || (c == 0 && !hiInclusive))
57 return true;
58 }
59 return false;
60 }
61
62 // 判断key是否在“lo和hi”开区间范围内
63 final boolean inRange(Object key) {
64 return !tooLow(key) && !tooHigh(key);
65 }
66
67 // 判断key是否在封闭区间内
68 final boolean inClosedRange(Object key) {
69 return (fromStart || m.compare(key, lo) >= 0)
70 && (toEnd || m.compare(hi, key) >= 0);
71 }
72
73 // 判断key是否在区间内, inclusive是区间开关标志
74 final boolean inRange(Object key, boolean inclusive) {
75 return inclusive ? inRange(key) : inClosedRange(key);
76 }
77
78 // 返回最低的Entry
79 final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absLowest() {
80 // 若“包含起始节点”,则调用getFirstEntry()返回第一个节点
81 // 否则的话,若包括lo,则调用getCeilingEntry(lo)获取大于/等于lo的最小的Entry;
82 // 否则,调用getHigherEntry(lo)获取大于lo的最小Entry
83 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e =
84 (fromStart ? m.getFirstEntry() :
85 (loInclusive ? m.getCeilingEntry(lo) :
86 m.getHigherEntry(lo)));
87 return (e == null || tooHigh(e.key)) ? null : e;
88 }
89
90 // 返回最高的Entry
91 final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absHighest() {
92 // 若“包含结束节点”,则调用getLastEntry()返回最后一个节点
93 // 否则的话,若包括hi,则调用getFloorEntry(hi)获取小于/等于hi的最大的Entry;
94 // 否则,调用getLowerEntry(hi)获取大于hi的最大Entry
95 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e =
96 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e =
97 (toEnd ? m.getLastEntry() :
98 (hiInclusive ? m.getFloorEntry(hi) :
99 m.getLowerEntry(hi)));
100 return (e == null || tooLow(e.key)) ? null : e;
101 }
102
103 // 返回"大于/等于key的最小的Entry"
104 final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absCeiling(K key) {
105 // 只有在“key太小”的情况下,absLowest()返回的Entry才是“大于/等于key的最小Entry”
106 // 其它情况下不行。例如,当包含“起始节点”时,absLowest()返回的是最小Entry了!
107 if (tooLow(key))
108 return absLowest();
109 // 获取“大于/等于key的最小Entry”
110 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = m.getCeilingEntry(key);
111 return (e == null || tooHigh(e.key)) ? null : e;
112 }
113
114 // 返回"大于key的最小的Entry"
115 final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absHigher(K key) {
116 // 只有在“key太小”的情况下,absLowest()返回的Entry才是“大于key的最小Entry”
117 // 其它情况下不行。例如,当包含“起始节点”时,absLowest()返回的是最小Entry了,而不一定是“大于key的最小Entry”!
118 if (tooLow(key))
119 return absLowest();
120 // 获取“大于key的最小Entry”
121 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = m.getHigherEntry(key);
122 return (e == null || tooHigh(e.key)) ? null : e;
123 }
124
125 // 返回"小于/等于key的最大的Entry"
126 final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absFloor(K key) {
127 // 只有在“key太大”的情况下,(absHighest)返回的Entry才是“小于/等于key的最大Entry”
128 // 其它情况下不行。例如,当包含“结束节点”时,absHighest()返回的是最大Entry了!
129 if (tooHigh(key))
130 return absHighest();
131 // 获取"小于/等于key的最大的Entry"
132 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = m.getFloorEntry(key);
133 return (e == null || tooLow(e.key)) ? null : e;
134 }
135
136 // 返回"小于key的最大的Entry"
137 final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absLower(K key) {
138 // 只有在“key太大”的情况下,(absHighest)返回的Entry才是“小于key的最大Entry”
139 // 其它情况下不行。例如,当包含“结束节点”时,absHighest()返回的是最大Entry了,而不一定是“小于key的最大Entry”!
140 if (tooHigh(key))
141 return absHighest();
142 // 获取"小于key的最大的Entry"
143 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = m.getLowerEntry(key);
144 return (e == null || tooLow(e.key)) ? null : e;
145 }
146
147 // 返回“大于最大节点中的最小节点”,不存在的话,返回null
148 final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absHighFence() {
149 return (toEnd ? null : (hiInclusive ?
150 m.getHigherEntry(hi) :
151 m.getCeilingEntry(hi)));
152 }
153
154 // 返回“小于最小节点中的最大节点”,不存在的话,返回null
155 final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absLowFence() {
156 return (fromStart ? null : (loInclusive ?
157 m.getLowerEntry(lo) :
158 m.getFloorEntry(lo)));
159 }
160
161 // 下面几个abstract方法是需要NavigableSubMap的实现类实现的方法
162 abstract TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subLowest();
163 abstract TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subHighest();
164 abstract TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subCeiling(K key);
165 abstract TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subHigher(K key);
166 abstract TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subFloor(K key);
167 abstract TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subLower(K key);
168 // 返回“顺序”的键迭代器
169 abstract Iterator<K> keyIterator();
170 // 返回“逆序”的键迭代器
171 abstract Iterator<K> descendingKeyIterator();
172
173 // 返回SubMap是否为空。空的话,返回true,否则返回false
174 public boolean isEmpty() {
175 return (fromStart && toEnd) ? m.isEmpty() : entrySet().isEmpty();
176 }
177
178 // 返回SubMap的大小
179 public int size() {
180 return (fromStart && toEnd) ? m.size() : entrySet().size();
181 }
182
183 // 返回SubMap是否包含键key
184 public final boolean containsKey(Object key) {
185 return inRange(key) && m.containsKey(key);
186 }
187
188 // 将key-value 插入SubMap中
189 public final V put(K key, V value) {
190 if (!inRange(key))
191 throw new IllegalArgumentException("key out of range");
192 return m.put(key, value);
193 }
194
195 // 获取key对应值
196 public final V get(Object key) {
197 return !inRange(key)? null : m.get(key);
198 }
199
200 // 删除key对应的键值对
201 public final V remove(Object key) {
202 return !inRange(key)? null : m.remove(key);
203 }
204
205 // 获取“大于/等于key的最小键值对”
206 public final Map.Entry<K,V> ceilingEntry(K key) {
207 return exportEntry(subCeiling(key));
208 }
209
210 // 获取“大于/等于key的最小键”
211 public final K ceilingKey(K key) {
212 return keyOrNull(subCeiling(key));
213 }
214
215 // 获取“大于key的最小键值对”
216 public final Map.Entry<K,V> higherEntry(K key) {
217 return exportEntry(subHigher(key));
218 }
219
220 // 获取“大于key的最小键”
221 public final K higherKey(K key) {
222 return keyOrNull(subHigher(key));
223 }
224
225 // 获取“小于/等于key的最大键值对”
226 public final Map.Entry<K,V> floorEntry(K key) {
227 return exportEntry(subFloor(key));
228 }
229
230 // 获取“小于/等于key的最大键”
231 public final K floorKey(K key) {
232 return keyOrNull(subFloor(key));
233 }
234
235 // 获取“小于key的最大键值对”
236 public final Map.Entry<K,V> lowerEntry(K key) {
237 return exportEntry(subLower(key));
238 }
239
240 // 获取“小于key的最大键”
241 public final K lowerKey(K key) {
242 return keyOrNull(subLower(key));
243 }
244
245 // 获取"SubMap的第一个键"
246 public final K firstKey() {
247 return key(subLowest());
248 }
249
250 // 获取"SubMap的最后一个键"
251 public final K lastKey() {
252 return key(subHighest());
253 }
254
255 // 获取"SubMap的第一个键值对"
256 public final Map.Entry<K,V> firstEntry() {
257 return exportEntry(subLowest());
258 }
259
260 // 获取"SubMap的最后一个键值对"
261 public final Map.Entry<K,V> lastEntry() {
262 return exportEntry(subHighest());
263 }
264
265 // 返回"SubMap的第一个键值对",并从SubMap中删除改键值对
266 public final Map.Entry<K,V> pollFirstEntry() {
267 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = subLowest();
268 Map.Entry<K,V> result = exportEntry(e);
269 if (e != null)
270 m.deleteEntry(e);
271 return result;
272 }
273
274 // 返回"SubMap的最后一个键值对",并从SubMap中删除改键值对
275 public final Map.Entry<K,V> pollLastEntry() {
276 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = subHighest();
277 Map.Entry<K,V> result = exportEntry(e);
278 if (e != null)
279 m.deleteEntry(e);
280 return result;
281 }
282
283 // Views
284 transient NavigableMap<K,V> descendingMapView = null;
285 transient EntrySetView entrySetView = null;
286 transient KeySet<K> navigableKeySetView = null;
287
288 // 返回NavigableSet对象,实际上返回的是当前对象的"Key集合"。
289 public final NavigableSet<K> navigableKeySet() {
290 KeySet<K> nksv = navigableKeySetView;
291 return (nksv != null) ? nksv :
292 (navigableKeySetView = new TreeMap.KeySet(this));
293 }
294
295 // 返回"Key集合"对象
296 public final Set<K> keySet() {
297 return navigableKeySet();
298 }
299
300 // 返回“逆序”的Key集合
301 public NavigableSet<K> descendingKeySet() {
302 return descendingMap().navigableKeySet();
303 }
304
305 // 排列fromKey(包含) 到 toKey(不包含) 的子map
306 public final SortedMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, K toKey) {
307 return subMap(fromKey, true, toKey, false);
308 }
309
310 // 返回当前Map的头部(从第一个节点 到 toKey, 不包括toKey)
311 public final SortedMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey) {
312 return headMap(toKey, false);
313 }
314
315 // 返回当前Map的尾部[从 fromKey(包括fromKeyKey) 到 最后一个节点]
316 public final SortedMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey) {
317 return tailMap(fromKey, true);
318 }
319
320 // Map的Entry的集合
321 abstract class EntrySetView extends AbstractSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
322 private transient int size = -1, sizeModCount;
323
324 // 获取EntrySet的大小
325 public int size() {
326 // 若SubMap是从“开始节点”到“结尾节点”,则SubMap大小就是原TreeMap的大小
327 if (fromStart && toEnd)
328 return m.size();
329 // 若SubMap不是从“开始节点”到“结尾节点”,则调用iterator()遍历EntrySetView中的元素
330 if (size == -1 || sizeModCount != m.modCount) {
331 sizeModCount = m.modCount;
332 size = 0;
333 Iterator i = iterator();
334 while (i.hasNext()) {
335 size++;
336 i.next();
337 }
338 }
339 return size;
340 }
341
342 // 判断EntrySetView是否为空
343 public boolean isEmpty() {
344 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> n = absLowest();
345 return n == null || tooHigh(n.key);
346 }
347
348 // 判断EntrySetView是否包含Object
349 public boolean contains(Object o) {
350 if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
351 return false;
352 Map.Entry<K,V> entry = (Map.Entry<K,V>) o;
353 K key = entry.getKey();
354 if (!inRange(key))
355 return false;
356 TreeMap.Entry node = m.getEntry(key);
357 return node != null &&
358 valEquals(node.getValue(), entry.getValue());
359 }
360
361 // 从EntrySetView中删除Object
362 public boolean remove(Object o) {
363 if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
364 return false;
365 Map.Entry<K,V> entry = (Map.Entry<K,V>) o;
366 K key = entry.getKey();
367 if (!inRange(key))
368 return false;
369 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> node = m.getEntry(key);
370 if (node!=null && valEquals(node.getValue(),entry.getValue())){
371 m.deleteEntry(node);
372 return true;
373 }
374 return false;
375 }
376 }
377
378 // SubMap的迭代器
379 abstract class SubMapIterator<T> implements Iterator<T> {
380 // 上一次被返回的Entry
381 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> lastReturned;
382 // 指向下一个Entry
383 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> next;
384 // “栅栏key”。根据SubMap是“升序”还是“降序”具有不同的意义
385 final K fenceKey;
386 int expectedModCount;
387
388 // 构造函数
389 SubMapIterator(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> first,
390 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> fence) {
391 // 每创建一个SubMapIterator时,保存修改次数
392 // 若后面发现expectedModCount和modCount不相等,则抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常。
393 // 这就是所说的fast-fail机制的原理!
394 expectedModCount = m.modCount;
395 lastReturned = null;
396 next = first;
397 fenceKey = fence == null ? null : fence.key;
398 }
399
400 // 是否存在下一个Entry
401 public final boolean hasNext() {
402 return next != null && next.key != fenceKey;
403 }
404
405 // 返回下一个Entry
406 final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> nextEntry() {
407 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = next;
408 if (e == null || e.key == fenceKey)
409 throw new NoSuchElementException();
410 if (m.modCount != expectedModCount)
411 throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
412 // next指向e的后继节点
413 next = successor(e);
414 lastReturned = e;
415 return e;
416 }
417
418 // 返回上一个Entry
419 final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> prevEntry() {
420 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = next;
421 if (e == null || e.key == fenceKey)
422 throw new NoSuchElementException();
423 if (m.modCount != expectedModCount)
424 throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
425 // next指向e的前继节点
426 next = predecessor(e);
427 lastReturned = e;
428 return e;
429 }
430
431 // 删除当前节点(用于“升序的SubMap”)。
432 // 删除之后,可以继续升序遍历;红黑树特性没变。
433 final void removeAscending() {
434 if (lastReturned == null)
435 throw new IllegalStateException();
436 if (m.modCount != expectedModCount)
437 throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
438 // 这里重点强调一下“为什么当lastReturned的左右孩子都不为空时,要将其赋值给next”。
439 // 目的是为了“删除lastReturned节点之后,next节点指向的仍然是下一个节点”。
440 // 根据“红黑树”的特性可知:
441 // 当被删除节点有两个儿子时。那么,首先把“它的后继节点的内容”复制给“该节点的内容”;之后,删除“它的后继节点”。
442 // 这意味着“当被删除节点有两个儿子时,删除当前节点之后,'新的当前节点'实际上是‘原有的后继节点(即下一个节点)’”。
443 // 而此时next仍然指向"新的当前节点"。也就是说next是仍然是指向下一个节点;能继续遍历红黑树。
444 if (lastReturned.left != null && lastReturned.right != null)
445 next = lastReturned;
446 m.deleteEntry(lastReturned);
447 lastReturned = null;
448 expectedModCount = m.modCount;
449 }
450
451 // 删除当前节点(用于“降序的SubMap”)。
452 // 删除之后,可以继续降序遍历;红黑树特性没变。
453 final void removeDescending() {
454 if (lastReturned == null)
455 throw new IllegalStateException();
456 if (m.modCount != expectedModCount)
457 throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
458 m.deleteEntry(lastReturned);
459 lastReturned = null;
460 expectedModCount = m.modCount;
461 }
462
463 }
464
465 // SubMap的Entry迭代器,它只支持升序操作,继承于SubMapIterator
466 final class SubMapEntryIterator extends SubMapIterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
467 SubMapEntryIterator(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> first,
468 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> fence) {
469 super(first, fence);
470 }
471 // 获取下一个节点(升序)
472 public Map.Entry<K,V> next() {
473 return nextEntry();
474 }
475 // 删除当前节点(升序)
476 public void remove() {
477 removeAscending();
478 }
479 }
480
481 // SubMap的Key迭代器,它只支持升序操作,继承于SubMapIterator
482 final class SubMapKeyIterator extends SubMapIterator<K> {
483 SubMapKeyIterator(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> first,
484 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> fence) {
485 super(first, fence);
486 }
487 // 获取下一个节点(升序)
488 public K next() {
489 return nextEntry().key;
490 }
491 // 删除当前节点(升序)
492 public void remove() {
493 removeAscending();
494 }
495 }
496
497 // 降序SubMap的Entry迭代器,它只支持降序操作,继承于SubMapIterator
498 final class DescendingSubMapEntryIterator extends SubMapIterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
499 DescendingSubMapEntryIterator(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> last,
500 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> fence) {
501 super(last, fence);
502 }
503
504 // 获取下一个节点(降序)
505 public Map.Entry<K,V> next() {
506 return prevEntry();
507 }
508 // 删除当前节点(降序)
509 public void remove() {
510 removeDescending();
511 }
512 }
513
514 // 降序SubMap的Key迭代器,它只支持降序操作,继承于SubMapIterator
515 final class DescendingSubMapKeyIterator extends SubMapIterator<K> {
516 DescendingSubMapKeyIterator(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> last,
517 TreeMap.Entry<K,V> fence) {
518 super(last, fence);
519 }
520 // 获取下一个节点(降序)
521 public K next() {
522 return prevEntry().key;
523 }
524 // 删除当前节点(降序)
525 public void remove() {
526 removeDescending();
527 }
528 }
529 }
NavigableSubMap源码很多,但不难理解;读者可以通过源码和注释进行理解。
其实,读完NavigableSubMap的源码后,我们可以得出它的核心思想是:它是一个抽象集合类,为2个子类——"(升序)AscendingSubMap"和"(降序)DescendingSubMap"而服务;因为NavigableSubMap实现了许多公共API。它的最终目的是实现下面的一系列函数:
headMap(K toKey, boolean inclusive) headMap(K toKey) subMap(K fromKey, K toKey) subMap(K fromKey, boolean fromInclusive, K toKey, boolean toInclusive) tailMap(K fromKey) tailMap(K fromKey, boolean inclusive) navigableKeySet() descendingKeySet()
第3.10部分 TreeMap其它函数
1 顺序遍历和逆序遍历
TreeMap的顺序遍历和逆序遍历原理非常简单。
由于TreeMap中的元素是从小到大的顺序排列的。因此,顺序遍历,就是从第一个元素开始,逐个向后遍历;而倒序遍历则恰恰相反,它是从最后一个元素开始,逐个往前遍历。
我们可以通过 keyIterator() 和 descendingKeyIterator()来说明!
keyIterator()的作用是返回顺序的KEY的集合,
descendingKeyIterator()的作用是返回逆序的KEY的集合。
keyIterator() 的代码如下:
Iterator<K> keyIterator() {
return new KeyIterator(getFirstEntry());
}
说明:从中我们可以看出keyIterator() 是返回以“第一个节点(getFirstEntry)” 为其实元素的迭代器。
KeyIterator的代码如下:
final class KeyIterator extends PrivateEntryIterator<K> {
KeyIterator(Entry<K,V> first) {
super(first);
}
public K next() {
return nextEntry().key;
}
}
说明:KeyIterator继承于PrivateEntryIterator。当我们通过next()不断获取下一个元素的时候,就是执行的顺序遍历了。
descendingKeyIterator()的代码如下:
Iterator<K> descendingKeyIterator() {
return new DescendingKeyIterator(getLastEntry());
}
说明:从中我们可以看出descendingKeyIterator() 是返回以“最后一个节点(getLastEntry)” 为其实元素的迭代器。
再看看DescendingKeyIterator的代码:
final class DescendingKeyIterator extends PrivateEntryIterator<K> {
DescendingKeyIterator(Entry<K,V> first) {
super(first);
}
public K next() {
return prevEntry().key;
}
}
说明:DescendingKeyIterator继承于PrivateEntryIterator。当我们通过next()不断获取下一个元素的时候,实际上调用的是prevEntry()获取的上一个节点,这样它实际上执行的是逆序遍历了。
至此,TreeMap的相关内容就全部介绍完毕了。若有错误或纰漏的地方,欢迎指正!
第4部分 TreeMap遍历方式
4.1 遍历TreeMap的键值对
第一步:根据entrySet()获取TreeMap的“键值对”的Set集合。
第二步:通过Iterator迭代器遍历“第一步”得到的集合。
// 假设map是TreeMap对象
// map中的key是String类型,value是Integer类型
Integer integ = null;
Iterator iter = map.entrySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)iter.next();
// 获取key
key = (String)entry.getKey();
// 获取value
integ = (Integer)entry.getValue();
}
4.2 遍历TreeMap的键
第一步:根据keySet()获取TreeMap的“键”的Set集合。
第二步:通过Iterator迭代器遍历“第一步”得到的集合。
// 假设map是TreeMap对象
// map中的key是String类型,value是Integer类型
String key = null;
Integer integ = null;
Iterator iter = map.keySet().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
// 获取key
key = (String)iter.next();
// 根据key,获取value
integ = (Integer)map.get(key);
}
4.3 遍历TreeMap的值
第一步:根据value()获取TreeMap的“值”的集合。
第二步:通过Iterator迭代器遍历“第一步”得到的集合。
// 假设map是TreeMap对象
// map中的key是String类型,value是Integer类型
Integer value = null;
Collection c = map.values();
Iterator iter= c.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
value = (Integer)iter.next();
}
TreeMap遍历测试程序如下:

1 import java.util.Map;
2 import java.util.Random;
3 import java.util.Iterator;
4 import java.util.TreeMap;
5 import java.util.HashSet;
6 import java.util.Map.Entry;
7 import java.util.Collection;
8
9 /*
10 * @desc 遍历TreeMap的测试程序。
11 * (01) 通过entrySet()去遍历key、value,参考实现函数:
12 * iteratorTreeMapByEntryset()
13 * (02) 通过keySet()去遍历key、value,参考实现函数:
14 * iteratorTreeMapByKeyset()
15 * (03) 通过values()去遍历value,参考实现函数:
16 * iteratorTreeMapJustValues()
17 *
18 * @author skywang
19 */
20 public class TreeMapIteratorTest {
21
22 public static void main(String[] args) {
23 int val = 0;
24 String key = null;
25 Integer value = null;
26 Random r = new Random();
27 TreeMap map = new TreeMap();
28
29 for (int i=0; i<12; i++) {
30 // 随机获取一个[0,100)之间的数字
31 val = r.nextInt(100);
32
33 key = String.valueOf(val);
34 value = r.nextInt(5);
35 // 添加到TreeMap中
36 map.put(key, value);
37 System.out.println(" key:"+key+" value:"+value);
38 }
39 // 通过entrySet()遍历TreeMap的key-value
40 iteratorTreeMapByEntryset(map) ;
41
42 // 通过keySet()遍历TreeMap的key-value
43 iteratorTreeMapByKeyset(map) ;
44
45 // 单单遍历TreeMap的value
46 iteratorTreeMapJustValues(map);
47 }
48
49 /*
50 * 通过entry set遍历TreeMap
51 * 效率高!
52 */
53 private static void iteratorTreeMapByEntryset(TreeMap map) {
54 if (map == null)
55 return ;
56
57 System.out.println("
iterator TreeMap By entryset");
58 String key = null;
59 Integer integ = null;
60 Iterator iter = map.entrySet().iterator();
61 while(iter.hasNext()) {
62 Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)iter.next();
63
64 key = (String)entry.getKey();
65 integ = (Integer)entry.getValue();
66 System.out.println(key+" -- "+integ.intValue());
67 }
68 }
69
70 /*
71 * 通过keyset来遍历TreeMap
72 * 效率低!
73 */
74 private static void iteratorTreeMapByKeyset(TreeMap map) {
75 if (map == null)
76 return ;
77
78 System.out.println("
iterator TreeMap By keyset");
79 String key = null;
80 Integer integ = null;
81 Iterator iter = map.keySet().iterator();
82 while (iter.hasNext()) {
83 key = (String)iter.next();
84 integ = (Integer)map.get(key);
85 System.out.println(key+" -- "+integ.intValue());
86 }
87 }
88
89
90 /*
91 * 遍历TreeMap的values
92 */
93 private static void iteratorTreeMapJustValues(TreeMap map) {
94 if (map == null)
95 return ;
96
97 Collection c = map.values();
98 Iterator iter= c.iterator();
99 while (iter.hasNext()) {
100 System.out.println(iter.next());
101 }
102 }
103 }
第5部分 TreeMap示例
下面通过实例来学习如何使用TreeMap

1 import java.util.*;
2
3 /**
4 * @desc TreeMap测试程序
5 *
6 * @author skywang
7 */
8 public class TreeMapTest {
9
10 public static void main(String[] args) {
11 // 测试常用的API
12 testTreeMapOridinaryAPIs();
13
14 // 测试TreeMap的导航函数
15 //testNavigableMapAPIs();
16
17 // 测试TreeMap的子Map函数
18 //testSubMapAPIs();
19 }
20
21 /**
22 * 测试常用的API
23 */
24 private static void testTreeMapOridinaryAPIs() {
25 // 初始化随机种子
26 Random r = new Random();
27 // 新建TreeMap
28 TreeMap tmap = new TreeMap();
29 // 添加操作
30 tmap.put("one", r.nextInt(10));
31 tmap.put("two", r.nextInt(10));
32 tmap.put("three", r.nextInt(10));
33
34 System.out.printf("
---- testTreeMapOridinaryAPIs ----
");
35 // 打印出TreeMap
36 System.out.printf("%s
",tmap );
37
38 // 通过Iterator遍历key-value
39 Iterator iter = tmap.entrySet().iterator();
40 while(iter.hasNext()) {
41 Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)iter.next();
42 System.out.printf("next : %s - %s
", entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
43 }
44
45 // TreeMap的键值对个数
46 System.out.printf("size: %s
", tmap.size());
47
48 // containsKey(Object key) :是否包含键key
49 System.out.printf("contains key two : %s
",tmap.containsKey("two"));
50 System.out.printf("contains key five : %s
",tmap.containsKey("five"));
51
52 // containsValue(Object value) :是否包含值value
53 System.out.printf("contains value 0 : %s
",tmap.containsValue(new Integer(0)));
54
55 // remove(Object key) : 删除键key对应的键值对
56 tmap.remove("three");
57
58 System.out.printf("tmap:%s
",tmap );
59
60 // clear() : 清空TreeMap
61 tmap.clear();
62
63 // isEmpty() : TreeMap是否为空
64 System.out.printf("%s
", (tmap.isEmpty()?"tmap is empty":"tmap is not empty") );
65 }
66
67
68 /**
69 * 测试TreeMap的子Map函数
70 */
71 public static void testSubMapAPIs() {
72 // 新建TreeMap
73 TreeMap tmap = new TreeMap();
74 // 添加“键值对”
75 tmap.put("a", 101);
76 tmap.put("b", 102);
77 tmap.put("c", 103);
78 tmap.put("d", 104);
79 tmap.put("e", 105);
80
81 System.out.printf("
---- testSubMapAPIs ----
");
82 // 打印出TreeMap
83 System.out.printf("tmap:
%s
", tmap);
84
85 // 测试 headMap(K toKey)
86 System.out.printf("tmap.headMap("c"):
%s
", tmap.headMap("c"));
87 // 测试 headMap(K toKey, boolean inclusive)
88 System.out.printf("tmap.headMap("c", true):
%s
", tmap.headMap("c", true));
89 System.out.printf("tmap.headMap("c", false):
%s
", tmap.headMap("c", false));
90
91 // 测试 tailMap(K fromKey)
92 System.out.printf("tmap.tailMap("c"):
%s
", tmap.tailMap("c"));
93 // 测试 tailMap(K fromKey, boolean inclusive)
94 System.out.printf("tmap.tailMap("c", true):
%s
", tmap.tailMap("c", true));
95 System.out.printf("tmap.tailMap("c", false):
%s
", tmap.tailMap("c", false));
96
97 // 测试 subMap(K fromKey, K toKey)
98 System.out.printf("tmap.subMap("a", "c"):
%s
", tmap.subMap("a", "c"));
99 // 测试
100 System.out.printf("tmap.subMap("a", true, "c", true):
%s
",
101 tmap.subMap("a", true, "c", true));
102 System.out.printf("tmap.subMap("a", true, "c", false):
%s
",
103 tmap.subMap("a", true, "c", false));
104 System.out.printf("tmap.subMap("a", false, "c", true):
%s
",
105 tmap.subMap("a", false, "c", true));
106 System.out.printf("tmap.subMap("a", false, "c", false):
%s
",
107 tmap.subMap("a", false, "c", false));
108
109 // 测试 navigableKeySet()
110 System.out.printf("tmap.navigableKeySet():
%s
", tmap.navigableKeySet());
111 // 测试 descendingKeySet()
112 System.out.printf("tmap.descendingKeySet():
%s
", tmap.descendingKeySet());
113 }
114
115 /**
116 * 测试TreeMap的导航函数
117 */
118 public static void testNavigableMapAPIs() {
119 // 新建TreeMap
120 NavigableMap nav = new TreeMap();
121 // 添加“键值对”
122 nav.put("aaa", 111);
123 nav.put("bbb", 222);
124 nav.put("eee", 333);
125 nav.put("ccc", 555);
126 nav.put("ddd", 444);
127
128 System.out.printf("
---- testNavigableMapAPIs ----
");
129 // 打印出TreeMap
130 System.out.printf("Whole list:%s%n", nav);
131
132 // 获取第一个key、第一个Entry
133 System.out.printf("First key: %s First entry: %s%n",nav.firstKey(), nav.firstEntry());
134
135 // 获取最后一个key、最后一个Entry
136 System.out.printf("Last key: %s Last entry: %s%n",nav.lastKey(), nav.lastEntry());
137
138 // 获取“小于/等于bbb”的最大键值对
139 System.out.printf("Key floor before bbb: %s%n",nav.floorKey("bbb"));
140
141 // 获取“小于bbb”的最大键值对
142 System.out.printf("Key lower before bbb: %s%n", nav.lowerKey("bbb"));
143
144 // 获取“大于/等于bbb”的最小键值对
145 System.out.printf("Key ceiling after ccc: %s%n",nav.ceilingKey("ccc"));
146
147 // 获取“大于bbb”的最小键值对
148 System.out.printf("Key higher after ccc: %s%n
",nav.higherKey("ccc"));
149 }
150
151 }
运行结果:
{one=8, three=4, two=2}
next : one - 8
next : three - 4
next : two - 2
size: 3
contains key two : true
contains key five : false
contains value 0 : false
tmap:{one=8, two=2}
tmap is empty

