setState更新数组
你会发现,如果直接使用push等方法改变state,按理来说,push会改变原数组,数组应该更新,但渲染出来的state并不会更改
let newValue = 1;
const [array, setArray] = useState([]);
const handleChange = (newValue: number) =>{
array.push(newValue);
setState(array);//array更新了,但无法触发渲染
console.log(array);//[1]
//array增加了newValue,但渲染并未发生改变
}
render:
<p>This array is {JSON.stringify(array)}</p> //[]
这是由于js中,数组的赋值是引用传递的,array.push相当于直接更改了数组对应的内存块,但react内部用于对比的array的内存并没有更改,是指向同一个内存的,setState只做shallow compare,因此没有触发re-render。
可以使用扩展运算符,创建一个新数组,更改内存引用
const handleChange = (newValue: number) =>{
const newArray = [...array, newValue];
setState(newArray);//此处本质上是改变了引用
console.log(array);//[]
//array并未改变,但渲染改变了
}
render:
<p>This array is {JSON.stringify(array)}</p> //[1]
或者触发展示组件的re-render,这样即使不改变数组的引用,依然可以正确显示变动。
const handleChange = (newValue: number) =>{
setValue(newValue);
setState(array.push(newValue));//其他更新触发了组件的re-render,此时可以正常显示变动
console.log(array);//[1]
//array改变,且渲染改变
}
render:
<p>This array is {JSON.stringify(array)}</p> //[1]
再给一个直观的例子(感谢我的同事@ling)
直接尝试:https://codepen.io/ling-cao/pen/NWrMRrq
const { useRef, useEffect, useState } = React
const useMemoryState = (init) => {
const [arr, setArr] = useState(init)
const lastArrRef = useRef(null)
const updateArr = next => {
lastArrRef.current = [...arr];
console.log(next);
setArr(next)
}
return [arr, updateArr, lastArrRef.current]
}
let i = 0;
const App = () => {
const [arr, setArr, lastArr] = useMemoryState([0])
const [updateSign, setUpdateSign] = useState(false)
return(
<>
<div className="text"><label>Current array :</label> {JSON.stringify(arr)}</div>
<div className="box-container">
<div className="box">
<h1>Push a number to array</h1>
<pre>setArr(arr.push(i) && arr)</pre>
<br />
<button
onClick={() => {
i++;
setArr(arr.push(i) && arr)
}}
className="btn btn-2 btn-2c">
Try it
</button>
</div>
<div className="box">
<h1>Push a number to array and renew array</h1>
<pre>setArr(arr.push(i) && [...arr])</pre>
<br />
<button
onClick={() => {
i++;
setArr(arr.push(i) && [...arr])
}}
className="btn btn-2 btn-2c">
Try it
</button>
</div>
<div className="box">
<h1>Push a number to array and update another state</h1>
<pre>setArr(arr.push(i) && arr); setUpdateSign(x => !x)</pre>
<br />
<button
onClick={() => {
i++;
{
setArr(arr.push(i) && arr)
setUpdateSign(x => !x)
}
}}
className="btn btn-2 btn-2c">
Try it
</button>
</div>
</div>
</>
);
}
逐次点击第二个按钮或第三个按钮都可以正常更新渲染。
点击第一个按钮,通过console可以看出来,array数组值有更新,但没有渲染(Current array 没变);再点其他两个按钮时,会把第一个按钮点击更新的结果一起渲染出来。
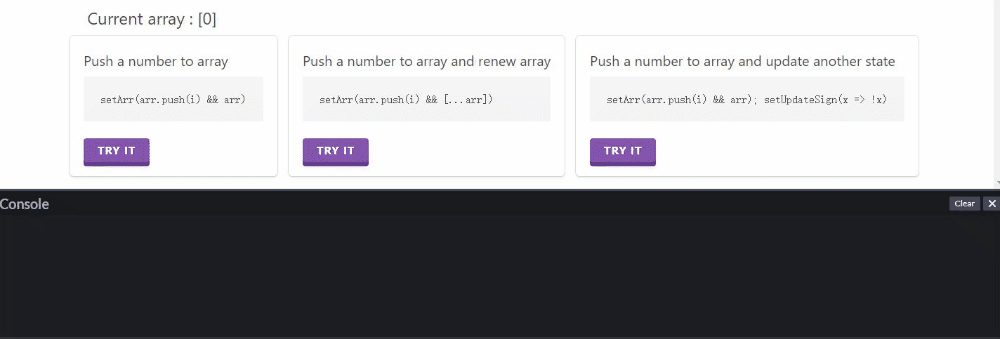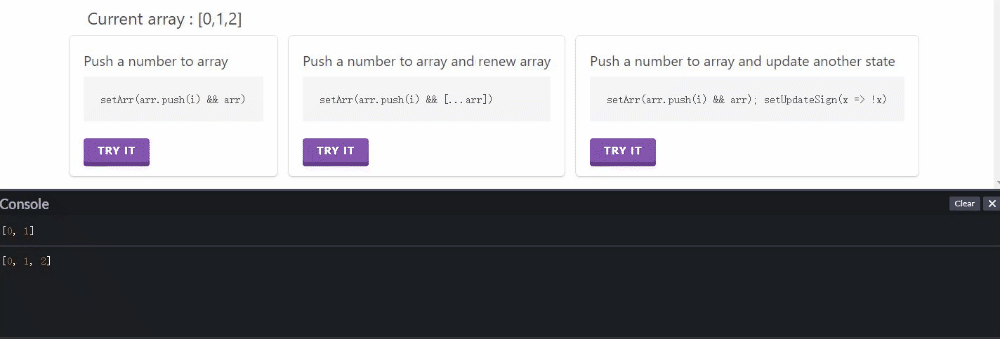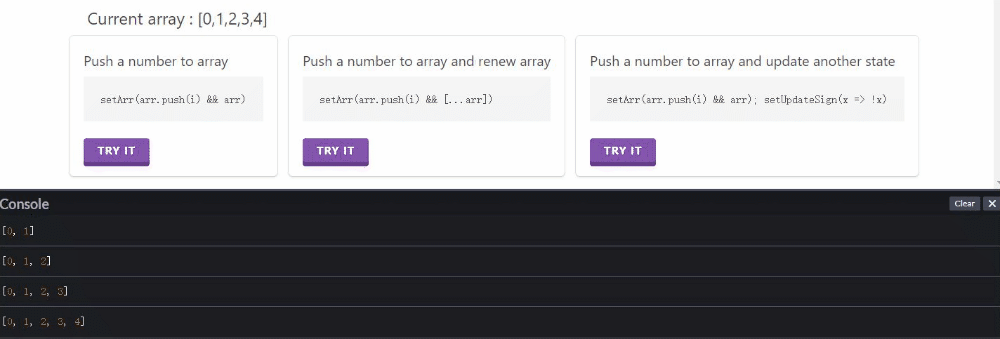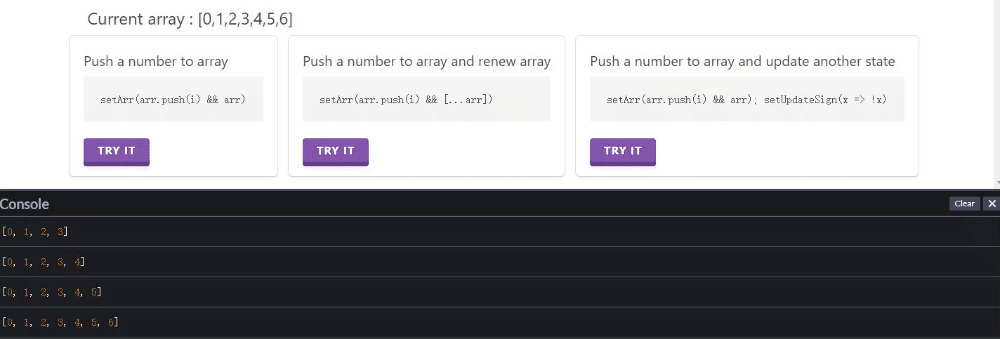
侧面展示并不是没有更新数组,而是更新后未渲染。
setState不会立即改变数据
setState某种意义上是类似于异步函数的。
// name is ""
this.setState({
name: "name"
})
console.log(`name is ${this.state.name}`)
这样写,name是不能正常显示。
最常用的办法就是使用回调函数
this.setState({
name: "name"
}, () => {
console.log(`name is ${this.state.name}`)
})
多个setState的更新
setState的“异步”是本身执行的过程和代码是同步的,只是合成事件和钩子函数的调用顺序在更新之前,导致在合成事件和钩子函数中没办法立马拿到更新后的值,形成了所谓的异步。批量更新优化也是建立在“异步”之上的,如果对同一个值进行多次setState,setState的批量更新策略会对其进行覆盖,取最后一次执行;如果是同时setState多个不同的值,在更新时会对其合并批量更新。
setState异步回调获取不到最新值
useEffect(() => {
const newModel = {
name: props.name,
datasetId: props.datasetId,
modelId: null,
trainingStatus: TrainingStatus.Init,
modelStatus: Status.NotStarted,
} as TrainingModel;
setModels([...models, newModel]);
startTraining(newModel);
}, [props.datasetId]);
const startTraining = async (newModel: TrainingModel) => {
const dataset = await getDataset(newModel.datasetId);
let newModels = [...models];
let currModel = newModels.find(x => x.datasetId == newModels.datasetId);
currModel.trainingStatus = TrainingStatus.CreateDataset;
//此时可通过页面的渲染效果知道models中已有值,但此处断点models为空
setModels(newModels);
};
类似的,老生常谈的,在useEffect里面设置一个Interval,过了Interval time,也同样是useEffect更新时的state值,而得不到最新的state值。
为解决异步导致的获取不到最新state的问题,使用setState的回调函数获取state的当前最新值
const startTraining = async (newModel: TrainingModel) => {
const dataset = await getDataset(newModel.datasetId);
setModels(lastModels => { //此时的lastModels是models的最新值
const nextModels = [...lastModels];
let currModel = nextModels.find(x => x.datasetId == newModel.datasetId);
currModel.trainingStatus = TrainingStatus.CreateDataset;
return nextModels;
});
};
原因是,组件内部的任何函数,包括事件处理函数和effect,都是从它被创建的那次渲染中被[看到]的,也就是说,组件内部的函数拿到的总是定义它的那次渲染中的props和state。想要解决,一般两种方法,一种是上述的使用setState回调函数获取state最新值,一种是使用ref保存修改并读取state。