列车调度(Train)
Description
Figure 1 shows the structure of a station for train dispatching.
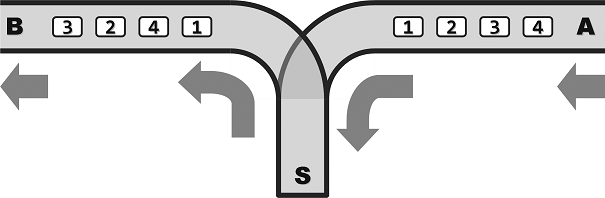
Figure 1
In this station, A is the entrance for each train and B is the exit. S is the transfer end. All single tracks are one-way, which means that the train can enter the station from A to S, and pull out from S to B. Note that the overtaking is not allowed. Because the compartments can reside in S, the order that they pull out at B may differ from that they enter at A. However, because of the limited capacity of S, no more that m compartments can reside at S simultaneously.
Assume that a train consist of n compartments labeled {1, 2, …, n}. A dispatcher wants to know whether these compartments can pull out at B in the order of {a1, a2, …, an} (a sequence). If can, in what order he should operate it?
Input
Two lines:
1st line: two integers n and m;
2nd line: n integers separated by spaces, which is a permutation of {1, 2, …, n}. This is a compartment sequence that is to be judged regarding the feasibility.
Output
If the sequence is feasible, output the sequence. “Push” means one compartment goes from A to S, while “pop” means one compartment goes from S to B. Each operation takes up one line.
If the sequence is infeasible, output a “no”.
Example 1
Input
5 2
1 2 3 5 4
Output
push
pop
push
pop
push
pop
push
push
pop
pop
Example 2
Input
5 5
3 1 2 4 5
Output
No
Restrictions
1 <= n <= 1,600,000
0 <= m <= 1,600,000
Time: 2 sec
Memory: 256 MB
感觉很简单的题目,就是难以下手,还是自己不行,加油吧!

1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <cstring> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 const int MAX_SIZE = 1600000 + 10; 7 int Stack1[MAX_SIZE], Stack2[MAX_SIZE]; 8 int out[MAX_SIZE]; 9 int pointer = 0; 10 11 void push(int a) 12 { 13 pointer++; 14 Stack1[pointer] = a; 15 Stack2[pointer] = a; 16 } 17 18 void pop() 19 { 20 pointer--; 21 } 22 23 int top1() 24 { 25 return Stack1[pointer]; 26 } 27 28 int top2() 29 { 30 return Stack2[pointer]; 31 } 32 33 int main() 34 { 35 int n, m; 36 scanf("%d %d", &n, &m); 37 38 for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) 39 { 40 scanf("%d", &out[i]); 41 } 42 43 int j = 0; 44 for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) 45 { 46 ///3个if 1个while 就模拟了栈混洗过程 47 if(out[i] < top1()) 48 { 49 printf("No"); 50 return 0; 51 } 52 53 while(j < out[i]) 54 { 55 push(++j); 56 printf("push(%d) ", j); 57 } 58 59 if(m < pointer) 60 { 61 printf("No"); 62 return 0; 63 } 64 65 if(out[i] == top1()) 66 { 67 printf("pop "); 68 pop(); 69 } 70 } 71 72 j = 0; 73 for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) 74 { 75 while(j < out[i]) 76 { 77 push(++j); 78 puts("push"); 79 } 80 81 if(out[i] == top2()) 82 { 83 pop(); 84 puts("pop"); 85 } 86 } 87 return 0; 88 }
