前言
我们知道,每一款框架产品在实际开发中,都是通过XML文件来培训框架的相关流程的,MyBatis也不例外,主要有两个配置文件:config.xml和Mapper.xml,当然,这两种配置文件可以自定义文件名。
- config.xml是全局配置文件,主要配置MyBatis的数据源(DataSource),事务管理(TransactionManager),以及打印SQL语句,开启二级缓存,设置实体类别名等功能。
- Mapper.xml的作用是什么?我们之前介绍过,MyBatis是"半自动"的ORM框架,即SQL语句需要开发者自定义,MyBatis的关注点在POJO与SQL之间的映射关系。那么SQL语句在哪里配置自定义呢?就在Mapper.xml中配置。
一、parameterType:参数数据类型
(1)基本数据类型,通过id查询User。
UserDAO:
//通过id查询User
public User getById(int id);UserDAO.xml:
<select id="getById" parameterType="int" resultType="com.southwind.entity.User">
select * from user where id=#{id}
</select>(2)String类型,通过name查询User。
UserDAO:
//通过name查询User
public User getByName(String name);UserDAO.xml:
<select id="get2" parameterType="java.lang.String" resultType="com.southwind.entity.User">
select * from user where name = #{name}
</select>
(3)包装类,通过id查询User。
UserDAO:
//统计id查询User
public User getById(Integer id);UserDAO.xml:
<select id="getById" parameterType="java.lang.Integer" resultType="com.southwind.entity.User">
select * from user where id=#{id}
</select>(4)多个参数,通过name和age查询User。两个参数分别是String类型和int类型,类型不一致,所以此时parameterType可以省略,通过参数下标取出参数值。
UserDAO:
//通过name和age查询User
public User getByNameAge(int id,String name);UserDAO.xml:
<select id="getByNameAge" resultType="com.southwind.entity.User">
select * from user where name = #{0} and age = #{1}
</select>也可以param0,param1 或 args0,args1
(5)POJO,很显然,当有多个参数时,一个一个写太麻烦了,这时候我们可以将参数列表进行封装,将封装对象作为parameterType的值。
UserDAO:
//根据Usesr封装对象查询User
public User getByUser(User user);UserDAO.xml:
<select id="getByUser" parameterType="com.southwind.entity.User" resultType="com.southwind.entity.User">
select * from user where name = #{name} and age = #{age}
</select>
二、resultType:结果类型
(1)基本数据类型,统计User总数。
UserDAO:
//通过User总数量
public int getCount()UserDAO.xml:<select id="getCount" resultType="int">
select count(*) from user
</select>(2)包装类,统计User总数。
UserDAO:
//通过User总数量
public Integer getCount();UserDAO.xml:
<select id="getCount" resultType="java.lang.Integer">
select count(*) from user
</select>(3)String类型,根据id查询User的name值。
UserDAO:
//根据id查询User的name
public String getNameById(int id);UserDAO.xml:
<select id="getNameById" parameterType="int" resultType="java.lang.String">
select name from user where id = #{name}
</select>(4)POJO,如通过id查询User,上面已经介绍过了,这里就不再重复了。
三、级联查询
(1)一对多
我们现在查询的User是单表查询,如果是多表关联查询,比如查询Student同时级联对应的Classes,如何处理呢?
使用resultType无法完成,我们以通过id查询Student来举例。
SQL:
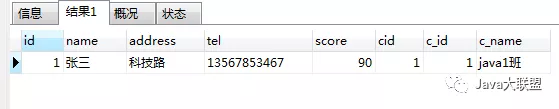
select * from student as s,classes as c where s.cid = c.c_id and s.id = 1;查询结果:
学生实体类Student:
package com.southwind.entity;
public class Student {
private int id;
private String name;
private String address;
private String tel;
private int score;
private Classes classes;
public Classes getClasses() {
return classes;
}
public void setClasses(Classes classes) {
this.classes = classes;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public String getTel() {
return tel;
}
public void setTel(String tel) {
this.tel = tel;
}
public int getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(int score) {
this.score = score;
}
}班级实体类Classes:
package com.southwind.entity;
import java.util.List;
public class Classes {
private int id;
private String name;
private List<Student> students;
public List<Student> getStudents() {
return students;
}
public void setStudents(List<Student> students) {
this.students = students;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}MyBatis会自动将结果与实体类进行映射,将字段的值赋给对应的属性,若字段名与属性名一致,完成赋值,那么问题来了。
如果字段不一致怎么办?
- 如图,id,name,address,tel,score属性可以对应字段,classes属性没有对应的字段,准确的讲,classes属性需要对应的对象为c_id,c_name封装起来的对象。
- 此时,需要使用resultMap来完成映射。
StudentDAO:
//通过id查询Student
public Student getById(int id);StudentDAO.xml,使用association标签配置classes级联,因为一个Student只能对应一个Classes。
<resultMap type="student" id="studentMap">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="name" column="name"/>
<result property="address" column="address"/>
<result property="tel" column="tel"/>
<result property="score" column="score"/>
<!-- 映射classes属性 -->
<association property="classes" javaType="com.southwind.entity.Classes">
<id property="id" column="c_id"/>
<result property="name" column="c_name"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
<select id="getById" parameterType="int" resultMap="studentMap">
select * from student as s,classes as c where s.cid = c.c_id and s.id = #{id};
</select>
同理,反过来查询Classes,将级联的所有Student一并查询。
ClassesDAO:
//根据id查询Classes
public Classes getById(int id);ClassesDAO.xml,使用collection标签配置students级联,因为一个Classes可以对应多个Student。
<resultMap type="classes" id="classesMap">
<id property="id" column="c_id"/>
<result property="name" column="c_name"/>
<!-- 映射students属性 -->
<collection property="students" ofType="student">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="name" column="name"/>
<result property="address" column="address"/>
<result property="tel" column="tel"/>
<result property="score" column="score"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="getById" parameterType="int" resultMap="classesMap">
select * from classes as c,student as s where c.c_id = s.cid and c.c_id = #{id};
</select>需要注意的是:association标签,通过设置javaType属性,映射实体类,
collection标签,通过设置ofType属性映射实体类。
(2)多对多
多对多其实是双向的一对多关系,我们用Customer和Goods来举例,
一个Customer可以对应多个Goods,一个Goods也可以对应多个Customer,所以双方都是用collection标签设置级联。
Customer:
package com.southwind.entity;
import java.util.List;
public class Customer {
private int id;
private String name;
private List<Goods> goods;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public List<Goods> getGoods() {
return goods;
}
public void setGoods(List<Goods> goods) {
this.goods = goods;
}
}Goods:
package com.southwind.entity;
import java.util.List;
public class Goods {
private int id;
private String name;
private List<Customer> customers;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public List<Customer> getCustomers() {
return customers;
}
public void setCustomers(List<Customer> customers) {
this.customers = customers;
}
}CustomerDAO:
//根据id查询Customer
public Customer getById(int id);CustomerDAO.xml:
<resultMap type="customer" id="customerMap">
<id property="id" column="c_id"/>
<result property="name" column="c_name"/>
<!-- 映射goods属性 -->
<collection property="goods" ofType="goods">
<id property="id" column="g_id"/>
<result property="name" column="g_name"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="getById" parameterType="int" resultMap="customerMap">
select * from customer as c,goods as g,
customer_goods as cg where c.c_id = cg.c_id
and g.g_id =c g.g_id and c.c_id = #{id};
</select>GoodsDAO:
//根据id查询Goods
public Goods getById(int id);GoodsDAO.xml:
<resultMap type="goods" id="goodsMap">
<id property="id" column="g_id"/>
<result property="name" column="g_name"/>
<!-- 映射customers属性 -->
<collection property="customers" ofType="customer">
<id property="id" column="c_id"/>
<result property="name" column="c_name"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="getById" parameterType="int" resultMap="goodsMap">
select * from customer as c,
goods as g,customer_goods as cg
where c.c_id = cg.c_id and g.g_id
= cg.g_id and g.g_id = #{id};
</select>
mybatis中Mapper.xml配置详解,小伙伴们加油~~~