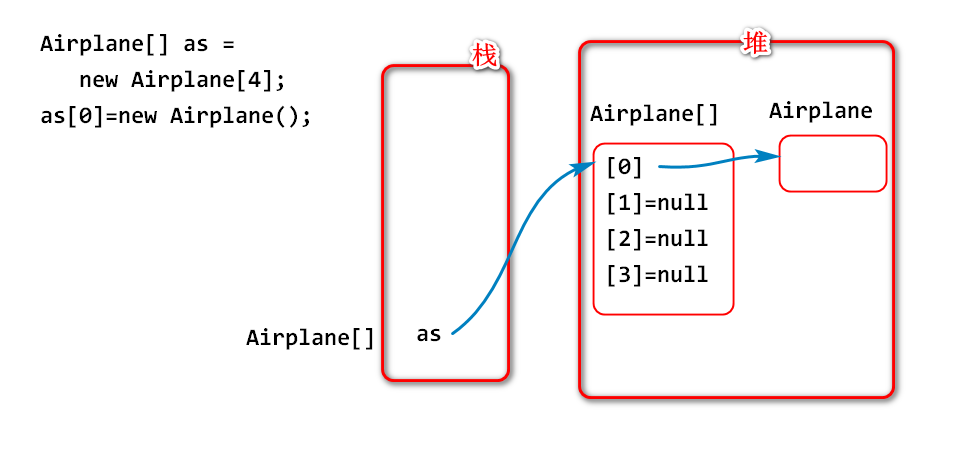
对象数组
用引用类型声明的数组称为对象数组
数组中没有元素是引用类型
数组中默认值是null
使用之前必须初始化,否则可能引起空指针异常。
案例:
public class ArrayDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
* 创建引用类型的数组
* 数组中每个元素都是一个引用
* 数组元素默认值是null
*/
Airplane[] as = new Airplane[4];
for(int i=0; i<as.length; i++) {
System.out.println(as[i]);
}
//创建一个飞机对象,将飞机的引用存储到数组的
//第一个元素中
as[0] = new Airplane();
for(int i=0; i<as.length; i++) {
System.out.println(as[i]);
}
}
}
class Airplane{
}
原理:
使用对象数组优化飞机大战案例:
Airplane[] as = new Airplane[10];
BigAirplane[] bas = new BigAirplane[10];
Bee[] bees = new Bee[10];
Bullet[] bullets = new Bullet[10];
void action() { //测试代码
sky = new Sky();
hero = new Hero();
for(int i=0; i<as.length; i++ ) {
as[i]=new Airplane();
}
for(int i=0; i<10; i++) {
System.out.println("小敌机as["+i+"]的宽:"+
as[i].width+",小敌机a1的高:"+
as[i].height+",小敌机a1的x:"+
as[i].x+",小敌机a1的y:"+as[i].y+","
+ "小敌机a1的speed:"+as[i].speed);
}
//System.out.println("小敌机a2的宽:"+a2.width+",小敌机a2的高:"+a2.height+",小敌机a2的x:"+a2.x+",小敌机a2的y:"+a2.y+",小敌机a2的speed:"+a2.speed);
//a1 = new Airplane();
//a2 = new Airplane();
//System.out.println("小敌机a1的宽:"+a1.width+",小敌机a1的高:"+a1.height+",小敌机a1的x:"+a1.x+",小敌机a1的y:"+a1.y+",小敌机a1的speed:"+a1.speed);
//System.out.println("小敌机a2的宽:"+a2.width+",小敌机a2的高:"+a2.height+",小敌机a2的x:"+a2.x+",小敌机a2的y:"+a2.y+",小敌机a2的speed:"+a2.speed);
}
继承
继承的概念:
子类可以继承父类中声明的属性和方法。
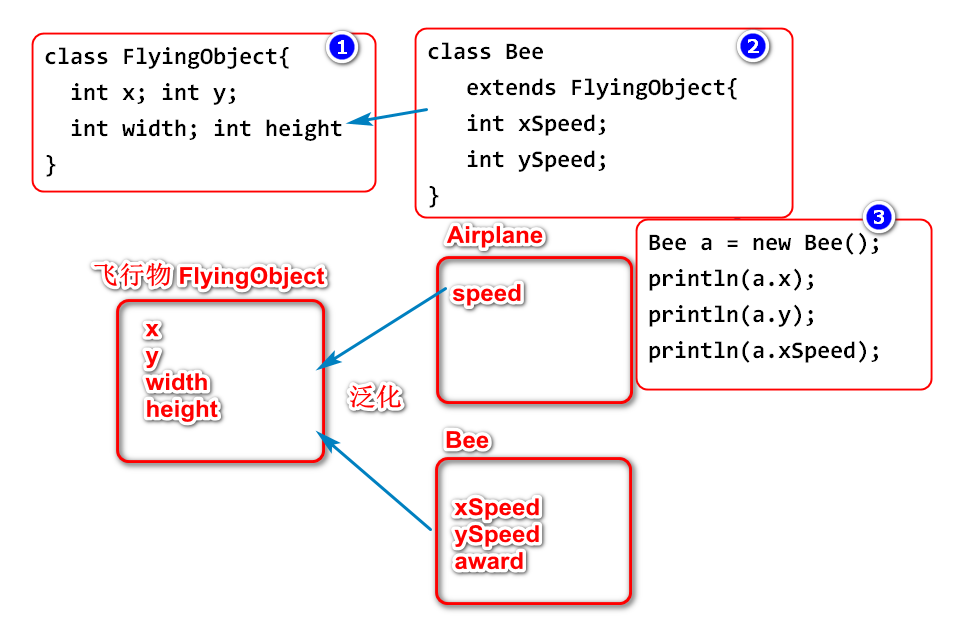
泛化
将多个子类中的公共属性和方法抽取到父类的过程称为泛化。
实际开发中设计父类时候,是通过泛化子类实现的。 所以继承也是一个泛化的过程。
原理:
案例:
public class ExtendDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 演示继承功能
*/
Bee b = new Bee();
System.out.println(b.x); //继承了父类的属性
System.out.println(b.y);
System.out.println(b.width);
b.fly();//继承了父类的
}
}
class FlyingObject{
int x;
int y;
int width;
int height;
public void fly() {
System.out.println("I can fly!");
}
}
class Bee extends FlyingObject{
int xSpeed;
int ySpeed;
}
class BigAirplane extends FlyingObject{
}
继承中的构造器
Constructor : 构造器也翻译为构造方法
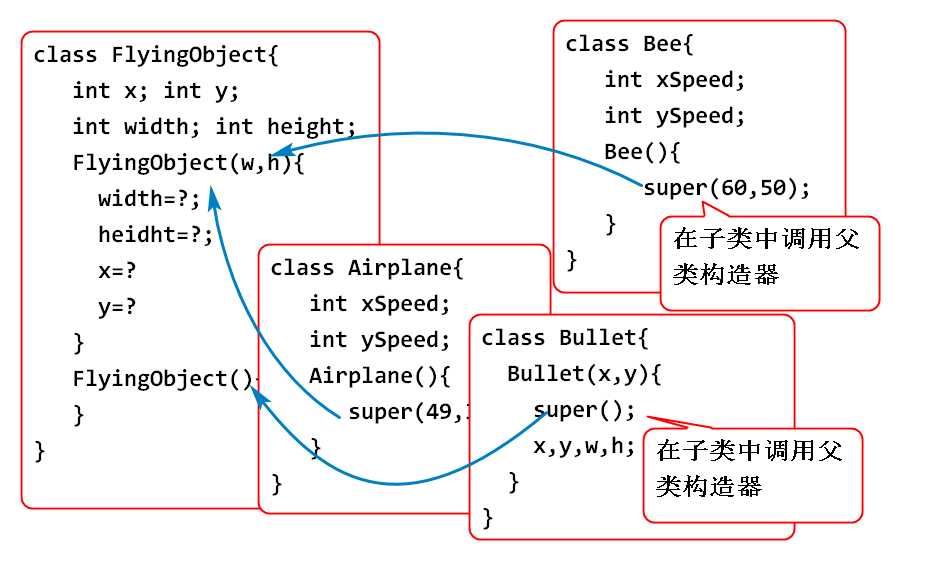
子类不能继承父类的构造方法
子类可以使用super()调用父类构造方法
这样可以实现多个子类重用父类构造方法的初始化算法
如果子类构造器中不写super()方法调用构造器,Java编译器会自动添加 super()
子类一定调用父类的构造器,如果不使用super()则Java自动添加 super(), 如果父类没有无参数构造器,则会发生编译错误。
为了避免子类出现编译错误,一般建议所有类都添加无参数构造器。
super() 必须写在构造器的第一行。
案例:
代码:
public class ConstructorDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 继承中的构造器演示:
* Constructor : 构造器也翻译为构造方法
* 1. 子类不能继承父类的构造方法
* 2. 子类可以使用super()调用父类构造方法
* 这样可以实现多个子类重用父类构造方法的
* 初始化算法
* 3. 如果子类不写super()方法调用构造器,
* Java编译器会自动添加 super()
* 4. 子类一定调用父类的构造器,如果不使用super()
* 则Java自动添加 super(), 如果父类没有
* 无参数构造器,则会发生编译错误。
* - 为了避免子类出现编译错误,一般建议
* 所有类都添加无参数构造器。
/
Bee1 b = new Bee1();
System.out.println("b.x:"+b.x);
Bullet1 bl = new Bullet1(200, 150);
System.out.println("bl.x:"+bl.x);
}
}
class FlyingObject1{
int x;
int y;
int width;
int height;
/*
* 留给屏幕上方掉落的飞行物体
/
public FlyingObject1(int w, int h) {
width = w;
height = h;
y = -height;
Random random = new Random();
x = random.nextInt(400-width);
}
/*
* 留给子弹或者其他对象的。
*/
public FlyingObject1() {
}
}
class Bullet1 extends FlyingObject1{
public Bullet1(int x, int y) {
//可以省略 super() 如果省略则自动调用super()
super();
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.width=8;
this.height=14;
}
}
class Airplane1 extends FlyingObject1{
int speed;
public Airplane1() {
//子类调用父类的构造器
super(49,36); //初始化了父类中的属性
speed = 2;
}
}
class Bee1 extends FlyingObject1{
int xSpeed;
int ySpeed;
public Bee1() {
super(60, 50);
xSpeed = 1;
ySpeed = 1;
}
}
super
super 在子类中代表当前对象的父类型
案例:
public class SuperDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 当局部变量,实例变量,以及父类变量无法区别时候
* 使用 this.访问当前对象的属性,super.访问
* 从父类型继承的属性。
* 如果能够区别变量,则无需使用 "super."
*/
Koo k = new Koo();
k.test(8);
}
}
class Foo{
int a = 5;
}
class Koo extends Foo{
int a = 6;
public void test(int a) {
System.out.println(a+","+this.a+","+super.a);
}
}