二叉树的遍历及常用算法
遍历的定义:
按照某种次序访问二叉树上的所有结点,且每个节点仅被访问一次;
遍历的重要性:
当我们需要对一颗二叉树进行,插入,删除,查找等操作时,通常都需要先遍历二叉树,所有说:遍历是二叉树的基本操作;
遍历思路:
-
二叉树的数据结构是递归定义(每个节点都可能包含相同结构的子节点),所以遍历也可以使用递归,即结点不为空则继续递归调用
-
每个节点都有三个域,数据与,左孩子指针和右孩子之指针,每次遍历只需要读取数据,递归左子树,递归右子树,这三个操作
三种遍历次序:
根据访问三个域的不同顺序,可以有多种不同的遍历次序,而通常对于子树的访问都按照从左往右的顺序;
设:L为遍历左子树,D为访问根结点,R为遍历右子树,且L必须位于R的前面
可以得出以下三种不同的遍历次序:
先序遍历
操作次序为DLR,首先访问根结点,其次遍历 根的左子树,最后遍历根右子树,对每棵子树同样按 这三步(先根、后左、再右)进行
中序遍历
操作次序为LDR,首先遍历根的左子树,其次 访问根结点,最后遍历根右子树,对每棵子树同样按 这三步(先左、后根、再右)进行
后序遍历
操作次序为LRD,首先遍历根的左子树,其次 遍历根的右子树,最后访问根结点,对每棵子树同样 按这三步(先左、后右、最后根)进行
层次遍历
层次遍历即按照从上到下从左到右的顺序依次遍历所有节点,实现层次遍历通常需要借助一个队列,将接下来要遍历的结点依次加入队列中;
遍历的应用
“遍历”是二叉树各种操作的基础,可以在遍历 过程中对结点进行各种操作,如:对于一棵已知二叉树
- 求二叉树中结点的个数
- 求二叉树中叶子结点的个数;
- 求二叉树中度为1的结点个数
- 求二叉树中度为2的结点个数
- 5求二叉树中非终端结点个数
- 交换结点左右孩子
- 判定结点所在层次
等等...
C语言实现:
#include <stdio.h>
//二叉链表数据结构定义
typedef struct TNode {
char data;
struct TNode *lchild;
struct TNode *rchild;
} *BinTree, BinNode;
//初始化
//传入一个指针 令指针指向NULL
void initiate(BinTree *tree) {
*tree = NULL;
}
//创建树
void create(BinTree *BT) {
printf("输入当前结点值: (0则创建空节点)
");
char data;
scanf(" %c", &data);//连续输入整形和字符时.字符变量会接受到换行,所以加空格
if (data == 48) {
*BT = NULL;
return;
} else {
//创建根结点
//注意开辟的空间大小是结构体的大小 而不是结构体指针大小,写错了不会立马产生问题,但是后续在其中存储数据时极有可能出现内存访问异常(飙泪....)
*BT = malloc(sizeof(struct TNode));
//数据域赋值
(*BT)->data = data;
printf("输入节点 %c 的左孩子
", data);
create(&((*BT)->lchild));//递归创建左子树
printf("输入节点 %c 的右孩子
", data);
create(&((*BT)->rchild));//递归创建右子树
}
}
//求双亲结点(父结点)
BinNode *Parent(BinTree tree, char x) {
if (tree == NULL)
return NULL;
else if ((tree->lchild != NULL && tree->lchild->data == x) ||
(tree->rchild != NULL && tree->rchild->data == x))
return tree;
else{
BinNode *node1 = Parent(tree->lchild, x);
BinNode *node2 = Parent(tree->rchild, x);
return node1 != NULL ? node1 : node2;
}
}
//先序遍历
void PreOrder(BinTree tree) {
if (tree) {
//输出数据
printf("%c ", tree->data);
//不为空则按顺序继续递归判断该节点的两个子节点
PreOrder(tree->lchild);
PreOrder(tree->rchild);
}
}
//中序
void InOrder(BinTree tree) {
if (tree) {
InOrder(tree->lchild);
printf("%c ", tree->data);
InOrder(tree->rchild);
}
}
//后序
void PostOrder(BinTree tree) {
if (tree) {
PostOrder(tree->lchild);
PostOrder(tree->rchild);
printf("%c ", tree->data);
}
}
//销毁结点 递归free所有节点
void DestroyTree(BinTree *tree) {
if (*tree != NULL) {
printf("free %c
", (*tree)->data);
if ((*tree)->lchild) {
DestroyTree(&((*tree)->lchild));
}
if ((*tree)->rchild) {
DestroyTree(&((*tree)->rchild));
}
free(*tree);
*tree = NULL;
}
}
// 查找元素为X的结点 使用的是层次遍历
BinNode *FindNode(BinTree tree, char x) {
if (tree == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
//队列
BinNode *nodes[1000] = {};
//队列头尾位置
int front = 0, real = 0;
//将根节点插入到队列尾
nodes[real] = tree;
real += 1;
//若队列不为空则继续
while (front != real) {
//取出队列头结点输出数据
BinNode *current = nodes[front];
if (current->data == x) {
return current;
}
front++;
//若当前节点还有子(左/右)节点则将结点加入队列
if (current->lchild != NULL) {
nodes[real] = current->lchild;
real++;
}
if (current->rchild != NULL) {
nodes[real] = current->rchild;
real++;
}
}
return NULL;
}
//层次遍历
// 查找元素为X的结点 使用的是层次遍历
void LevelOrder(BinTree tree) {
if (tree == NULL) {
return;
}
//队列
BinNode *nodes[1000] = {};
//队列头尾位置
int front = 0, real = 0;
//将根节点插入到队列尾
nodes[real] = tree;
real += 1;
//若队列不为空则继续
while (front != real) {
//取出队列头结点输出数据
BinNode *current = nodes[front];
printf("%2c", current->data);
front++;
//若当前节点还有子(左/右)节点则将结点加入队列
if (current->lchild != NULL) {
nodes[real] = current->lchild;
real++;
}
if (current->rchild != NULL) {
nodes[real] = current->rchild;
real++;
}
}
}
//查找x的左孩子
BinNode *Lchild(BinTree tree, char x) {
BinTree node = FindNode(tree, x);
if (node != NULL) {
return node->lchild;
}
return NULL;
}
//查找x的右孩子
BinNode *Rchild(BinTree tree, char x) {
BinTree node = FindNode(tree, x);
if (node != NULL) {
return node->rchild;
}
return NULL;
}
//求叶子结点数量
int leafCount(BinTree *tree) {
if (*tree == NULL)
return 0;
//若左右子树都为空则该节点为叶子,且后续不用接续递归了
else if (!(*tree)->lchild && !(*tree)->rchild)
return 1;
else
//若当前结点存在子树,则递归左右子树, 结果相加
return leafCount(&((*tree)->lchild)) + leafCount(&((*tree)->rchild));
}
//求非叶子结点数量
int NotLeafCount(BinTree *tree) {
if (*tree == NULL)
return 0;
//若该结点左右子树均为空,则是叶子,且不用继续递归
else if (!(*tree)->lchild && !(*tree)->rchild)
return 0;
else
//若当前结点存在左右子树,则是非叶子结点(数量+1),在递归获取左右子树中的非叶子结点,结果相加
return NotLeafCount(&((*tree)->lchild)) + NotLeafCount(&((*tree)->rchild)) + 1;
}
//求树的高度(深度)
int DepthCount(BinTree *tree) {
if (*tree == NULL)
return 0;
else{
//当前节点不为空则深度+1 在加上子树的高度,
int lc = DepthCount(&((*tree)->lchild)) + 1;
int rc = DepthCount(&((*tree)->rchild)) + 1;
return lc > rc?lc:rc;// 取两子树深度的 最大值
}
}
//删除左子树
void RemoveLeft(BinNode *node){
if (!node)
return;
if (node->lchild)
DestroyTree(&(node->lchild));
node->lchild = NULL;
}
//删除右子树
void RemoveRight(BinNode *node){
if (!node)
return;
if (node->rchild)
DestroyTree(&(node->rchild));
node->rchild = NULL;
}
int main() {
BinTree tree;
create(&tree);
BinNode *node = Parent(tree, 'G');
printf("G的父结点为%c
",node->data);
BinNode *node2 = Lchild(tree, 'D');
printf("D的左孩子结点为%c
",node2->data);
BinNode *node3 = Rchild(tree, 'D');
printf("D的右孩子结点为%c
",node3->data);
printf("先序遍历为:");
PreOrder(tree);
printf("
");
printf("中序遍历为:");
InOrder(tree);
printf("
");
printf("后序遍历为:");
PostOrder(tree);
printf("
");
printf("层次遍历为:");
LevelOrder(tree);
printf("
");
int a = leafCount(&tree);
printf("叶子结点数为%d
",a);
int b = NotLeafCount(&tree);
printf("非叶子结点数为%d
",b);
int c = DepthCount(&tree);
printf("深度为%d
",c);
//查找F节点
BinNode *node4 = FindNode(tree,'C');
RemoveLeft(node4);
printf("删除C的左孩子后遍历:");
LevelOrder(tree);
printf("
");
RemoveRight(node4);
printf("删除C的右孩子后遍历:");
LevelOrder(tree);
printf("
");
//销毁树
printf("销毁树
");
DestroyTree(&tree);
printf("销毁后后遍历:");
LevelOrder(tree);
printf("
");
printf("Hello, World!
");
return 0;
}
测试:
测试数据为下列二叉树:
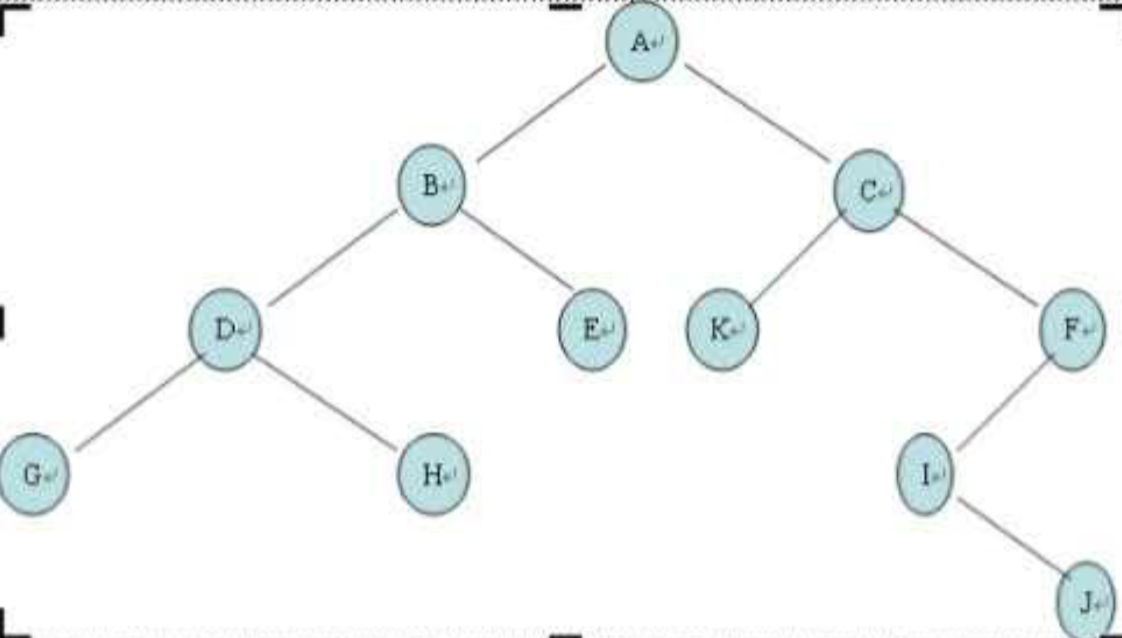
运行程序复制粘贴下列内容:
A
B
D
G
0
0
H
0
0
E
0
0
C
K
0
0
F
I
0
J
0
0
0
特别感谢:iammomo