In computer science, merge sort (also commonly spelled mergesort) is an efficient, general-purpose, comparison-based sorting algorithm. Most implementations produce a stable sort, which means that the implementation preserves the input order of equal elements in the sorted output. Mergesort is a divide and conquer algorithm that was invented by John von Neumann in 1945.[1] A detailed description and analysis of bottom-up mergesort appeared in a report by Goldstine and Neumann as early as 1948.[2]
来自 <https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Merge_sort>
翻译如下:
在CS领域,归并排序(merge sort)是一个高效的、多用途的、基于比较的排序算法。它的大多数实现是稳定的。这意味着,在排序过程中,值相等的元素的相对顺序不会发生改变。归并排序是一种分治算法(divide and conquer algorithm),由约翰·冯·诺依曼在1945年发明。
归并排序的最差时间复杂度为O(n log n)。

归并操作:
归并操作(merge),也叫归并算法,指的是将两个已经排序的序列合并成一个序列的操作。归并排序算法依赖归并操作。
迭代法[编辑]
- 申请空间,使其大小为两个已经排序序列之和,该空间用来存放合并后的序列
- 设定两个指针,最初位置分别为两个已经排序序列的起始位置
- 比较两个指针所指向的元素,选择相对小的元素放入到合并空间,并移动指针到下一位置
- 重复步骤3直到某一指针到达序列尾
- 将另一序列剩下的所有元素直接复制到合并序列尾
递归法[编辑]
原理如下(假设序列共有n个元素):
- 将序列每相邻两个数字进行归并操作,形成
 个序列,排序后每个序列包含两个元素
个序列,排序后每个序列包含两个元素
- 将上述序列再次归并,形成
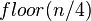 个序列,每个序列包含四个元素
个序列,每个序列包含四个元素
- 重复步骤2,直到所有元素排序完毕
来自 <https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E5%BD%92%E5%B9%B6%E6%8E%92%E5%BA%8F>
1 package com.yan.algorithm; 2 3 import java.util.Arrays; 4 /** 5 * merge sort java implementation. 6 * @author Yan 7 * 8 */ 9 public class MergeSort { 10 private static int[] data = new int[] { 6, 5, 3, 1, 8, 7, 2, 4 }; 11 12 public MergeSort() { 13 } 14 15 public static void main(String[] args) { 16 mergeSort(data); 17 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(data)); 18 } 19 20 public static void mergeSort(int[] data) { 21 int[] temp = new int[data.length]; 22 mergeSort(data, temp, 0, data.length - 1); 23 } 24 25 public static void mergeSort(int[] data, int[] temp, int left, int right) { 26 if (left < right) { 27 int mid = (left + right) >> 1; 28 // recursively divide the array to two parts by the median index. 29 mergeSort(data, temp, left, mid); 30 mergeSort(data, temp, mid + 1, right); 31 // merge the divided two fragments to one sorted fragment. 32 merge(data, temp, left, mid, right); 33 } 34 } 35 36 public static void merge(int[] data, int[] temp, int left, int mid, int right) { 37 // declare a indexPoint to step move in the right part; 38 // for the left part the "left" can be used as a indexPoint. 39 int rightPoint = mid + 1; 40 // declare a indexPoint to step move in the temporary array. 41 int tempPoint = left; 42 // mark the whole length of the two parts, to control to write the 43 // temporary array into the original array. 44 int num = right - left + 1; 45 /* 46 * merge the two part array in sequence. 47 */ 48 while (left <= mid && rightPoint <= right) { 49 if (data[left] <= data[rightPoint]) { 50 temp[tempPoint++] = data[left++]; 51 } else { 52 temp[tempPoint++] = data[rightPoint++]; 53 } 54 } 55 /* 56 * if the left part has rest, copy the left rest elements into the temp 57 * array. 58 */ 59 if (left <= mid) { 60 for (int i = left; i <= mid; i++) { 61 temp[tempPoint++] = data[i]; 62 } 63 } 64 /* 65 * if the right part has rest, copy the right rest elements into the 66 * temp array. 67 */ 68 if (rightPoint <= right) { 69 for (int i = rightPoint; i <= right; i++) { 70 temp[tempPoint++] = data[i]; 71 } 72 } 73 /* 74 * write the sorted temp array back to the original data array. num 75 * controls the number to write. 76 */ 77 78 for (int i = 0; i < num; i++, right--) { 79 data[right] = temp[right]; 80 } 81 } 82 83 }