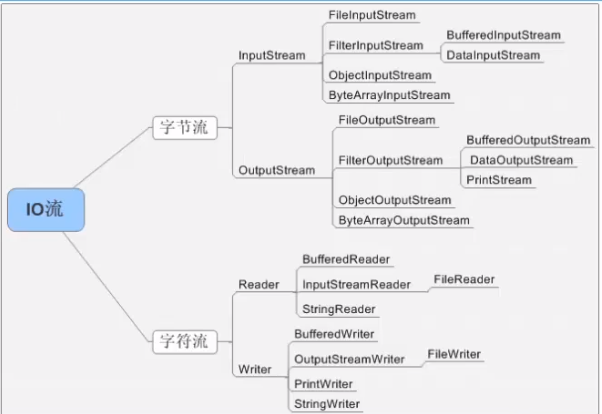
使用
如果需要将一个read()后的字节数组读取到内存中,并不断的追加,使用字节数组流非常合适
字节流和字符流
一.字节流在操作时不会用到缓冲区(内存),是直接对文件本身进行操作的。而字符流在操作时使用了缓冲区,通过缓冲区再操作文件。
字节流值read出来的是字节,我们需要自己手动转换成字符,write()也要写入字节,我们需要手动将字符转换字节
二.在硬盘上的所有文件都是以字节形式存在的(图片,声音,视频),而字符值在内存中才会形成。
字符流read出来的是字符,write()也要写入字符
对于图片,我们不能采用字符流,往图片文件写入一个字符串,那么图片还能打的开吗?
注意事项
1、我们的系统是在linux部署的,所以对文件路径的拼接尤其注意,使用C:/Users/zhengyan/Desktop/test1/x.txt 是不会有问题的,或者使用File.separator获取系统指定的路劲分割符,来拼接路劲
2、所有的关闭流需要使用标准的格式,在finally中判断如果read!=null,在close(),下面的示例代码为了简单化,没有按要求写
File基本使用
file.getPath() 返回自己传入的路径
file.getAbsolutePath() 返回绝对路径(如果new file()的时候传入的是文件名,路径为当前的项目目录+文件名,如果传入的是一个目录+文件名,或者目录,可能返回的结果并不是我们想要的)
file.getParent() 返回上一级目录,如果没有就返回null,new file("/x/xx.txt"),上一级为/x/
file.getParentFile() 返回上一级的目录生成的file对象
file.makir() 上一级路径必须存在,才可以被创建
file.mkdirs() 上一级目录如果不存在,连同上一级目录一起创建
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileFilter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//三种写法
//"C:/Users/zhengyan/Desktop/test"
//"C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test"
//"C:"+File.separator+"Users"+File.separator+"zhengyan"+File.separator+"Desktop"+File.separator+"test"
File f1 = new File("C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test");
File f2 = new File("C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test\t.js");
System.out.println(f1.isDirectory());//判断该目录是否是一个文件夹
System.out.println(f2.isFile()); //判断该目录是否是一个文件
System.out.println(f1.length()); //文件的大小(字节),如果文件不存在或者文件大小为空或者路径是一个目录都返回0
File f3 = new File("C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test11");
if(!f3.exists()){ //判断指定的目录是否存在(包括文件和目录)
try {
f3.createNewFile(); //不存在创建文件,存在返回false
f3.mkdir(); //创建目录
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}else{
String[] name = f3.list(); //列出当前目录下的所有的文件名(第一层)
File[] name1 = f3.listFiles(); //列出当前目录下的所有的文件对象(第一层);
File[] name2 = f3.listFiles(new FileFilter() {
@Override
public boolean accept(File pathname) {
return pathname.getName().endsWith(".txt");
}
}); //列出当前目录下的所有的(.txt)文件;
for(File i:name1){
System.out.println(i.getName()); //获取文件名
Date date = new Date(i.lastModified());
SimpleDateFormat simpledateformat = new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println(simpledateformat.format(date));//文件的最后修改时间
}
f3.delete(); //删除一个文件夹,只能是空文件夹,才可以删除
}
File f4 = new File("C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test");
f4.renameTo(new File("C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\new_test")); //重命名
f4.renameTo(new File("C:\Users\zhengyan\new_test")); //移动文件
}
}
示例:递归所有某个目录下的指定扩展名的文件
import java.io.File;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
showfile("C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1","txt");
}
public static void showfile(String filepath,String ext){
File f = new File(filepath);
if(!f.exists()){ //目录或者文件都可以判断
return;
}
else{
File[] file_list = f.listFiles();
for(File i:file_list){
if(i.isDirectory()){
showfile(i.getAbsolutePath(),ext);
}else{
if(i.getName().endsWith(ext)){
System.out.println(i.getName());
}
}
}
}
}
}
文件的读取和写入(字节流)
对于read(byte[]),返回的结果len,内部应该是这样判断的,首先判断读取的最后一个字节是不是-1,如果不是返回len为插入bytes数据的个数(并不是数组的长度),如果是-1,判断数据插入的个数如果为0,就返回-1,如果不是0,就返回插入数组的个数,此时下一次read的时候,一定返回的是-1。
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//文件写入
output("C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\x.txt","你好
");
//文件读出
input("C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\x.txt");
}
//对程序来说,将程序中的数据往文件写入,叫输出流
public static void output(String filepath,String s){
File file = new File(filepath);
try {
//如果指定的目录中的文件不存在,会自动创建,如果指定的目录不存在就会报错
// OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file);//需要捕获异常
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file,true);//追加写入
out.write(s.getBytes());//需要捕获异常
out.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void input(String filepath){
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
StringBuilder strbuilder = new StringBuilder();
File file = new File(filepath);
try {
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(file);
int len = -1;
while((len=in.read(bytes))!=-1){ //从输入流读取一些字节数,并将它们存储到
//缓冲区 bytes中,并且返回读取的字节的大小,当返回值为-1,表明数据读取完毕
System.out.println(len);
strbuilder.append(new String(bytes,0,len));//从数组的起始位置,到len长度位置,截取,转成字符串,(否则会出现多出字符的情况)
}
in.close();
System.out.println(strbuilder);
}catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
jdk1.7之后可以try()..来帮我们进行关闭流操作
try(FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("xx.txt")){
fileOutputStream.write("x".getBytes());
}
文件的读取和写入(字符流)
package com.zy;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.Reader;
import java.io.Writer;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// write();
read();
}
public static void write(){
String pathfile = "C:/Users/zhengyan/Desktop/test1/x.txt";
File file = new File(pathfile);
try {
Writer out = new FileWriter(file);
out.write("你好,小明");
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void read() {
String pathfile = "C:/Users/zhengyan/Desktop/test1/x.txt";
File file = new File(pathfile);
try {
Reader read = new FileReader(file);
char cr[] = new char[10];
StringBuilder strbuilder = new StringBuilder();
int len = -1;
while((len=read.read(cr))!=-1){
strbuilder.append(cr,0,len);
}
read.close();
System.out.println(strbuilder);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
字节操作流:每次执行写入会直接将数据写入文件;
字符操作流:执行完写入后,先将数据放入缓存区(1024字节),1.如果缓存区满了,会将数据吸入文件中,2.如果没有满,认为flush.将数据写入文件。3.执行close。会自动将数据写入文件。(字符流是基于字节流的)
示例:文件的copy
示例1
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
copy("C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\x.txt","C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\1\x.txt");
}
public static void copy(String old_path,String new_path){
File old_file = new File(old_path);
File new_file = new File(new_path);
InputStream file_read = null;
OutputStream file_write = null;
try {
file_read = new FileInputStream(old_file);
file_write = new FileOutputStream(new_file);
byte bytes[] = new byte[1024];
int len = -1;
while((len=file_read.read(bytes))!=-1){
file_write.write(bytes,0,len);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try {
file_read.close();
file_write.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
示例2:利用RandomAccessFile进行文件的复制
其中有一个seek方法,可以用来断点续传;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
run();
}
public static void run(){
try {
RandomAccessFile rf = new RandomAccessFile("C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\all.jpg", "r");
RandomAccessFile wf = new RandomAccessFile("C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\new_all.jpg", "rw");
byte bytes[] = new byte[1024];
int len=-1;
while((len=rf.read(bytes))!=-1){
wf.write(bytes,0,len);
}
System.out.println("复制成功");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
使用RandomAccessFile可以实现多线程并发下载文件(省略了多线程,可以自己实现)
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Demo.filedown("a.txt",2);
}
public static void filedown(String filepath,int file_count) throws IOException {
File file = new File(filepath);
long length = file.length();
//每一个文件的最大大小是one_file_size
int one_file_size = (int) Math.ceil(length*1.0/file_count);
for (int i = 0; i < file_count; i++) {
Demo.filedown1(new RandomAccessFile(file,"rw"),i*one_file_size,one_file_size);
}
}
public static void filedown1(RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile,int seek_count,int one_file_size) throws IOException {
randomAccessFile.seek(seek_count);
byte[] bytes = new byte[10];
int len = -1;
while ((len = randomAccessFile.read(bytes))!=-1){
if (len<=one_file_size){
String s = new String(bytes, 0, len);
System.out.println(s);
one_file_size -= len;
}else {
String s = new String(bytes, 0, one_file_size);
System.out.println(s);
break;
}
}
}
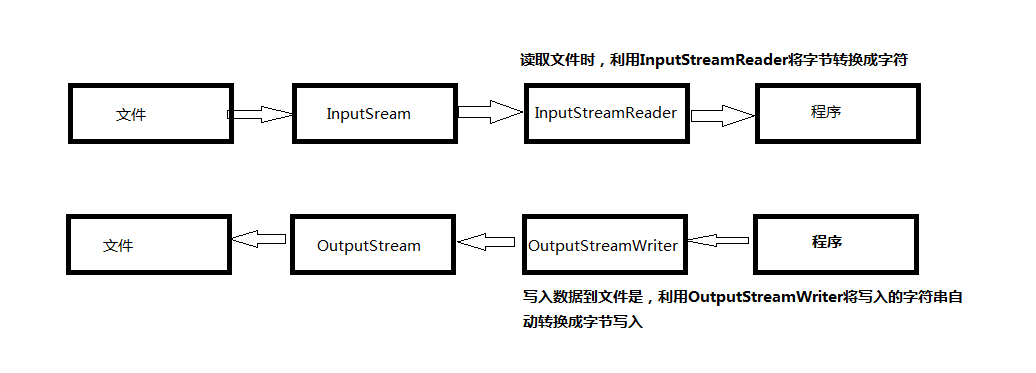
字节流和字符流相互转换(必要时需要指定编码防止乱码)
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.Reader;
import java.io.Writer;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\x.txt");
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file);
write(out);
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(file);
read(in);
}
//将输入的字节流转换成输入的字符流
public static void read(InputStream in) throws IOException{
//输入流必须转换成输出流时指定的编码
Reader rd = new InputStreamReader(in,Charset.forName("gbk"));//将字节流转换成字符流;
//Reader rd = new InputStreamReader(in,Charset.forName(charsetName));//转换默认编码;
char cr[] = new char[1024];
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder();
int len = -1;
while((len=rd.read(cr))!=-1){
str.append(new String(cr,0,len));
}
rd.close();
System.out.println(str);
}
//将输出字节流转换成输出字符流
public static void write(OutputStream out) throws IOException{
//输出流指定什么编码都可以;
Writer wr = new OutputStreamWriter(out,Charset.forName("gbk"));
wr.write("哈哈哈");
wr.close();
}
}
字节缓冲流 BufferedOutputStream / BufferedInputStream
利用装饰者设计模式
解决写入数据到文件过程中,频繁的操作文件;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
bytewrite();
byteread();
}
public static void bytewrite() throws IOException{
File file = new File("C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\x.txt");
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file);
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(out); //缓冲默认大小8192字节,可以指定大小
bos.write("你好".getBytes());
bos.close();//直接关闭bos,会自动关闭out
}
public static void byteread() throws IOException{
File file = new File("C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\x.txt");
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(file);
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(in);
byte bytes[] = new byte[1024];
int len = -1;
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder();
while((len=bis.read(bytes))!=-1){
str.append(new String(bytes),0,len);
}
System.out.println(str);
bis.close();
}
}
字符缓冲流 BufferedWriter / BufferedRead
package com.zy;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.Reader;
import java.io.Writer;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// charwrite();
charread();
}
public static void charwrite(){
String pathfile = "C:/Users/zhengyan/Desktop/test1/x.txt";
File file = new File(pathfile);
try {
Writer out = new FileWriter(file);
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(out);
bw.write("你好,小明");
bw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void charread() {
String pathfile = "C:/Users/zhengyan/Desktop/test1/x.txt";
File file = new File(pathfile);
try {
Reader in = new FileReader(file);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(in);
char cr[] = new char[10];
StringBuilder strbuilder = new StringBuilder();
int len = -1;
while((len=br.read(cr))!=-1){
strbuilder.append(cr,0,len);
}
br.close();
System.out.println(strbuilder);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
可以直接逐行输出
String line=null;
while((line=br.readline())!=null){
System.out.println(line);
}
打印流
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.io.Writer;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
byteprint();
charprint();
}
public static void byteprint(){
String pathfile = "C:/Users/zhengyan/Desktop/test1/x.txt";
File file = new File(pathfile);
try {
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file);
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(out);
//增强打印功能
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(bos);
ps.print("你好,小明");
ps.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void charprint(){
String pathfile = "C:/Users/zhengyan/Desktop/test1/x.txt";
File file = new File(pathfile);
try {
Writer in = new FileWriter(file);
BufferedWriter bos = new BufferedWriter(in);
//增强打印功能
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(bos);
pw.print("你好,小明");
pw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
PrintStream out = System.out;
out.println("输出到控制端");
//不能关闭
//out.close();
//输出到文件
out = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("a.txt"),true);
out.println("输出到文件中");
//out.close();
//重定向输出端
System.setOut(out);
System.out.println("xx");
//重定向控制台
System.setOut(new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream(FileDescriptor.out)));
System.out.println("xxx");
}
补充
InputStream in = System.in; BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in)); System.out.println(bufferedReader.readLine());
对象流
对象序列化
如果多个对象写入,将对象放入数组中,读取的时候读到的也是一个数组
写:oos.writeObject(dogs); dogs=[dog,dog]
读:Dog dog[] = (Dog[])(ois.readObject());
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//序列化
// Dog dog = new Dog(10,"花花");
// File file = new File("C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\dog.dog");
// OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file);
// ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(out);
// oos.writeObject(dog);
// oos.close();
//反序列化
File file = new File("C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\dog.dog");
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(file);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(in);
Dog dog[] = (Dog[])(ois.readObject());
ois.close();
System.out.println(dog);
}
}
//如果对象需要序列化,就必须实现Serializable接口
//序列化写入的是:类名,属性名,属性类型,属性值,方法名 等
//Serializable接口为标记接口,告诉jvm该类可以被序列化
class Dog implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; //可以忽略;
private int age;
private String name;
private transient int id; //表示序列化的时候将该字段忽略掉,还原对象是,为默认值0(int);
public Dog(int age, String name) {
super();
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog [age=" + age + ", name=" + name + "]";
}
}
字节数组流
ByteArrayOutputStream :可以将用户程序数据写进去,然后直接操作这个内存数据;
ByteArrayInputStream :将内存中的数组数据可以输入到用户程序中
对于普通的字节流或者字符流
源头都是对硬盘中的文件进行操作。java程序需要借助操作系统资源来操作文件,所以我们必须手动通知操作系统释放资源
对于字节数组流
源头是内存(字节数组)。不需要和硬盘打交道,java程序可以直接访问,不需要操作系统参与,所以字节数组有垃圾回收机制来释放,不需要我们手动关闭。注意字节数组流空间不宜过大。
基于内存操作,内部维护着一个字节数组,我们可以利用流的读取机制来处理字符串;
无需关闭(close):
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args){
byteArray();
}
public static void byteArray(){
String s = "sdf34543GDFSDF";
ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(s.getBytes());
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); //不需要指定目的地,目的地就是内存
int curs = -1;
while((curs=bais.read())!=-1){
if(48<=curs&&curs<=57){
baos.write(curs);
}
}
System.out.println(baos);
}
}
数据流
数据按照什么字节存储;数据就按照什么字节读出
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
//datawrite();
dataread();
}
public static void dataread() throws IOException{
File file = new File("C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\x.txt");
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(bis);
int a = dis.readInt();
byte c = dis.readByte();
String d = dis.readUTF();
System.out.println(a+","+c+","+d);
}
public static void datawrite() throws IOException{
File file = new File("C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\x.txt");
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file));
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(bos);
dos.writeInt(33);
dos.writeByte(1);
dos.writeUTF("哈哈");
dos.close();
}
}
文件的分块传输
思路1:指定分割的文件大小
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String old_path = "C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\test.txt";
String new_path = "C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\1";
// 将old_path文件以每一份11kb,存放在new_path目录下,
filecuteload(old_path, new_path, 11);
}
public static void filecuteload(String old_path, String new_path, int cutesize) throws IOException {
int file_cute_count;
cutesize = cutesize * 1024;
int count;
File old_file = new File(old_path);
// 首先计算文件应该被切割成几份
if (old_file.length() <= cutesize) {
file_cute_count = 1;
} else {
file_cute_count = (int) (old_file.length() % cutesize) == 0 ? (int) (old_file.length() / cutesize)
: (int) (old_file.length() / cutesize + 1);
}
// 表示每次循环读取多少次old_file;
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File(old_path)));
for (int i = 1; i <= file_cute_count; i++) {
bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File(new_path + "\" + i + "-temp-" + old_file.getName())));
byte bytes[] = null;
if (file_cute_count == 1) {
bytes = new byte[(int) old_file.length()];
count = 1;
} else {
bytes = new byte[1024];
count = cutesize / 1024;
}
int len = -1;
//count>0的判断条件必须要在前面;
while (count > 0 && (len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1) {
bos.write(bytes, 0, len);
bos.flush();
count--;
}
// 每一次循环写入数据时候,如果cutesize/1024没有整除时,就将剩下的数据在写到每次循环的文件中
// 本代码由于设置了cutesize为1024整数倍,所以下面的代码可以舍去;
if ((cutesize % 1024) != 0) {
bytes = new byte[cutesize % 1024];
len = bis.read(bytes);
if (len != -1) {
bos.write(bytes, 0, len);
bos.flush();
}
}
bos.close();
}
bis.close();
}
}
思路2:指定分割的文件个数
public class DemoTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String old_path = "C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test.txt";
String new_path = "C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\1";
filecuteload(old_path, new_path, 5);
}
public static void filecuteload(String old_path, String new_path, int cutesize) throws IOException {
File file = new File(old_path);
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
long length = file.length();
int size = (int) (length/cutesize);
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < cutesize; i++) {
if (count==cutesize-1){
size = (int) (length-(size*count));
}
String filepath = new_path+"\"+count+".txt";
System.out.println(filepath);
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filepath);
int len = -1;
byte[] bytes = null;
//将size赋值给size_if,之后判断size_if,是否被读写完
int size_if = size;
//一开始判读每一个文件是否小于1024字节
if (size_if<=1024){
bytes = new byte[size_if];
}else {
bytes = new byte[1024];
}
while ((len=fileInputStream.read(bytes))!=-1){
fileOutputStream.write(bytes);
if (size_if<=1024){
fileOutputStream.close();
count++;
break;
}
size_if = size_if-1024;
if (size_if<1024){
bytes = new byte[size_if];
}
}
}
fileInputStream.close();
}
}
文件的合并
注意事项: 合并的时候注意文件的顺序的问题;(顺序不对会影响合并和的文件的正确性)
方式一;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//记住path和file不能再同一个目录下(或者在本代码下自动判断)
String path = "C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\1";
String file = "C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\all.txt";
filetogether(path,file);
}
private static void filetogether(String path,String file) throws IOException {
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File(file)));
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
File file_path = new File(path);
for(File f:file_path.listFiles()){
bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(f)); //顺序会发生错误(看下面的解决方式)
System.out.println(f);
byte bytes[] = new byte[1024];
int len=-1;
while((len=bis.read(bytes))!=-1){
bos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
bis.close();
}
bos.close();
}
}
解决顺序问题
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Object> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Object>() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
//判断
//返回-1:表示升序,返回1:降序
return -1;
}
});
}
方式二:使用合并流
将所需要的文件放到集合中,直接一次性读取
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.SequenceInputStream;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Vector;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//记住path和file不能再同一个目录下(或者在本代码下自动判断)
String path = "C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\1";
String file = "C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\1\all.txt";
filetogether(path,file);
}
private static void filetogether(String path,String file) throws IOException{
Vector<InputStream> v = new Vector<InputStream>();
File file_path = new File(path);
for(File f:file_path.listFiles()){
v.add(new FileInputStream(f));//顺序可能会发生错误
}
Enumeration<InputStream> es = v.elements();
SequenceInputStream sis = new SequenceInputStream(es);
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File(file)));
byte bytes[] = new byte[1024];
int len=-1;
while((len=sis.read(bytes))!=-1){
bos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
sis.close();
bos.close();
}
}
方式三:按照顺序读取文件,防止顺序读错
public class DemoTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String new_file = "C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\1\new_test.txt";
String old_path = "C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\1";
filetogether(old_path,new_file);
}
public static void filetogether(String old_path,String new_file) throws IOException {
File file = new File(old_path);
int length = file.list().length;
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(new_file);
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
String filepath = old_path+"\"+i+".txt";
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filepath);
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len = -1;
while ((len=fileInputStream.read(bytes))!=-1){
fileOutputStream.write(bytes,0,len);
}
fileInputStream.close();
}
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}
方式4:使用SequenceInputStream
Vector<InputStream> vi = new Vector<>();
//将所有的输入流按照顺序添加到vi中
vi.add(new FileInputStream("a"));
SequenceInputStream sequenceInputStream = new SequenceInputStream(vi.elements());
//读取操作
sequenceInputStream.read();
sequenceInputStream.close();
字符串流
以字符串为数据源来构造数据流
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.StreamTokenizer;
import java.io.StringReader;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
stringReader();
}
public static void stringReader() throws IOException{
String s = "dsfsdf sdfdsf sdfsd";
StringReader sr = new StringReader(s);
//流 标记器
StreamTokenizer st = new StreamTokenizer(sr);
int count = 0;
while(st.ttype!=StreamTokenizer.TT_EOF){//TT_EOF表示读到了字符串的结尾结束
//记录str中有多少个单词
if(st.nextToken()==StreamTokenizer.TT_WORD){
count++;
}
}
sr.close();
System.out.println("count="+count);
}
}
管道流
用于线程之间的通信
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PipedInputStream;
import java.io.PipedOutputStream;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
PipedInputStream pin = new PipedInputStream();
PipedOutputStream pout = new PipedOutputStream();
pin.connect(pout);
ReadThread readTh = new ReadThread(pin);
WriteThread writeTh = new WriteThread(pout);
new Thread(readTh).start();
new Thread((Runnable) writeTh).start();
}
}
class WriteThread implements Runnable{
private PipedOutputStream pout;
public WriteThread(PipedOutputStream pout) {
this.pout = pout;
}
public void run(){
try {
pout.write("测试".getBytes());
pout.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class ReadThread implements Runnable{
private PipedInputStream pin;
public ReadThread(PipedInputStream pin) {
this.pin = pin;
}
public void run(){
byte bytes[] = new byte[1024];
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder();
int len;
try {
while((len=pin.read(bytes))!=-1){
str.append(new String(bytes,0,len));
}
System.out.println(str);
pin.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
};
}
}
文件的压缩 ZipOutputStream
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.zip.ZipEntry;
import java.util.zip.ZipOutputStream;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
String from_path = "C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\1";
String to_path = "C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\test.zip";
compression(from_path,to_path);
System.out.println("压缩完成");
}
private static void compression(String from_path,String to_path){
try {
//要生成的压缩的文件;
ZipOutputStream zipout = new ZipOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File(to_path)));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(zipout);
File from_file = new File(from_path);
zip(from_file,from_file.getName(),zipout,bos);
bos.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void zip(File from_file, String name, ZipOutputStream zipout, BufferedOutputStream bos) throws IOException {
if(from_file.isDirectory()){
if(from_file.length()==0){//如果from_file是一个空文件
System.out.println("空文件");
zipout.putNextEntry(new ZipEntry(name+"/"));//name+"/":表示写入一个文件夹;
}else{
for(File f:from_file.listFiles()){
zip(f, name+"/"+f.getName(), zipout, bos);//表示在当前的目录下压缩文件,否在所有的文件都会压缩到一个目录下了
}
}
}else{
zipout.putNextEntry(new ZipEntry(name));
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(from_file);
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(in);
byte bytes[] = new byte[1024];
int len = -1;
while((len=bis.read(bytes))!=-1){
bos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
bis.close();
}
}
}
文件解压
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.zip.ZipEntry;
import java.util.zip.ZipInputStream;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
String from_path = "C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\test.zip";
String to_path = "C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\down";
decompression(from_path,to_path);
}
public static void decompression(String from_path,String to_path) {
try {
ZipInputStream zis = new ZipInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File(from_path)));
ZipEntry entry;
File file = null;
while((entry = zis.getNextEntry())!=null&&!entry.isDirectory()){
file = new File(to_path,entry.getName());
if(!file.exists()){
System.out.println(file.getParent());
new File(file.getParent()).mkdirs();//创建此文件的上级目录
}
FileOutputStream ops = new FileOutputStream(file);
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(ops);
byte bytes[] = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len=zis.read(bytes))!=-1){
bos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
bos.close();
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
NIO
Java NIO和IO的主要区别 :https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaoxi/p/6576588.html
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
//申请8个字节的缓冲区
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(8);
System.out.println("buf.positon="+buf.position()); //0
System.out.println("buf.limit="+buf.limit()); //8
System.out.println("buf.limit="+buf.capacity()); //8
buf.put((byte) (10));
buf.put((byte)(20));
buf.put((byte)(30));
buf.put((byte)(40));
System.out.println("----------------------------");
System.out.println("buf.positon="+buf.position()); //4
System.out.println("buf.limit="+buf.limit()); //8
System.out.println("buf.limit="+buf.capacity()); //8
System.out.println("----------------------------");
buf.flip();//缓冲区反转
System.out.println("----------------------------");
System.out.println("buf.positon="+buf.position()); //0
System.out.println("buf.limit="+buf.limit()); //4
System.out.println("buf.limit="+buf.capacity()); //8
if(buf.hasRemaining()){
for(int i=0;i<buf.remaining();i++){
System.out.println(buf.get(i));
}
}
}
}
利用NIO进行文件操作
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
String from_file = "C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\x.txt";
String to_file = "C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\t.txt";
copyFile(from_file,to_file);
}
private static void copyFile(String from_file, String to_file) {
try {
//创建输入文件通道
FileChannel fcIn = new FileInputStream(from_file).getChannel();
//创建输出文件通道
FileChannel fcOut = new FileOutputStream(to_file).getChannel();
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while(fcIn.read(buf)!=-1){
buf.flip();
fcOut.write(buf);
buf.clear();
}
fcIn.close();
fcOut.close();
System.out.println("copy successful");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
内存映射
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
import java.nio.MappedByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel.MapMode;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
String from_file = "C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\x.txt";
String to_file = "C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\w.txt";
copyFile(from_file,to_file);
}
private static void copyFile(String from_file, String to_file) {
try {
RandomAccessFile in = new RandomAccessFile(from_file, "r");
RandomAccessFile out = new RandomAccessFile(to_file, "rw");
FileChannel fin = in.getChannel();
FileChannel fout = out.getChannel();
long size = fin.size();
//输出流的缓冲区
MappedByteBuffer inbuf = fin.map(MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, size);
//输入流的缓冲区
MappedByteBuffer outbuf = fout.map(MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, size);
byte bytes[] = new byte[1024];
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
outbuf.put(inbuf.get());
}
//文件关闭写入数据块
fin.close();
fout.close();
in.close();
out.close();
System.out.println("copy successful");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
IO性能比较
内存映射速度最快
NIO读写文件
使用缓冲的IO流
无缓冲的IO流
Files工具类
文件的写入和读取
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.nio.file.StandardOpenOption;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
String from_file = "C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\x.txt";
wirte(from_file);
read(from_file);
}
private static void wirte(String from_file) {
Path p1 = Paths.get(from_file);
try {
//对文件写入;利用Files类
Files.write(p1, "sdf".getBytes(), StandardOpenOption.APPEND);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void read(String from_file){
Path p = Paths.get(from_file);
try {
byte bytes[] = Files.readAllBytes(p);
System.out.println(new String(bytes));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
文件和目录的增加,文件的删除,文件的复制,文件的移动
jdk1.7之后;
内部使用NIO
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.nio.file.StandardCopyOption;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
String from_file = "C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\b.txt";
String to_file = "C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\x.txt";
//copy(from_file,to_file);
//move(from_file,to_file);
delete(from_file);
create("C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test2");
}
private static void copy(String from_file, String to_file) {
Path p = Paths.get(from_file);
try {
//StandardCopyOption.REPLACE_EXISTING:文件存在就替换它
Files.copy(p, Paths.get(to_file),StandardCopyOption.REPLACE_EXISTING);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void move(String from_file, String to_file) {
Path p = Paths.get(from_file);
try {
Files.move(p, Paths.get(to_file), StandardCopyOption.REPLACE_EXISTING);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void delete(String from_file) {
Path p = Paths.get(from_file);
try {
//Files.delete(p);//文件不存在会报错
Files.deleteIfExists(p);//如果文件不存在,不会抛出异常;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void create(String string) {
try {
Files.createDirectories(Paths.get(string));//可以创建不存在的中间目录
//Files.createDirectory(Paths.get(string));//不能创建中间目录
Files.createFile(Paths.get(string)); //创建文件
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
StringUtils工具类
String response = StreamUtils.copyToString( conn.getInputStream(), Charset.forName("UTF-8")); //将输入流转成字符串