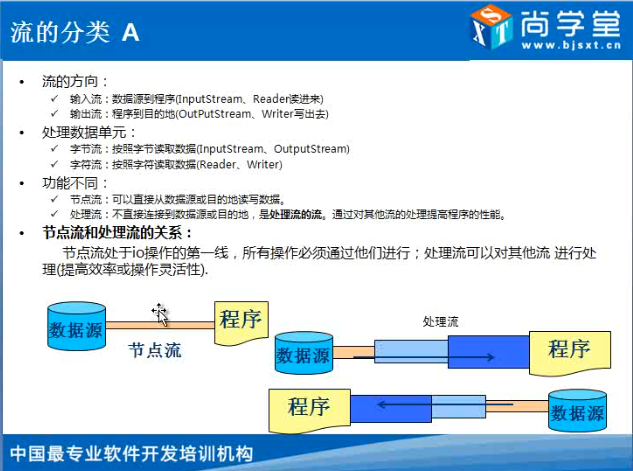
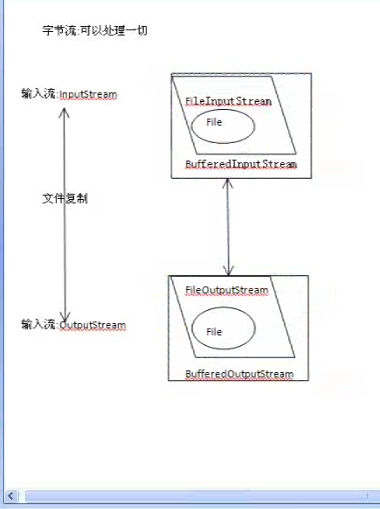
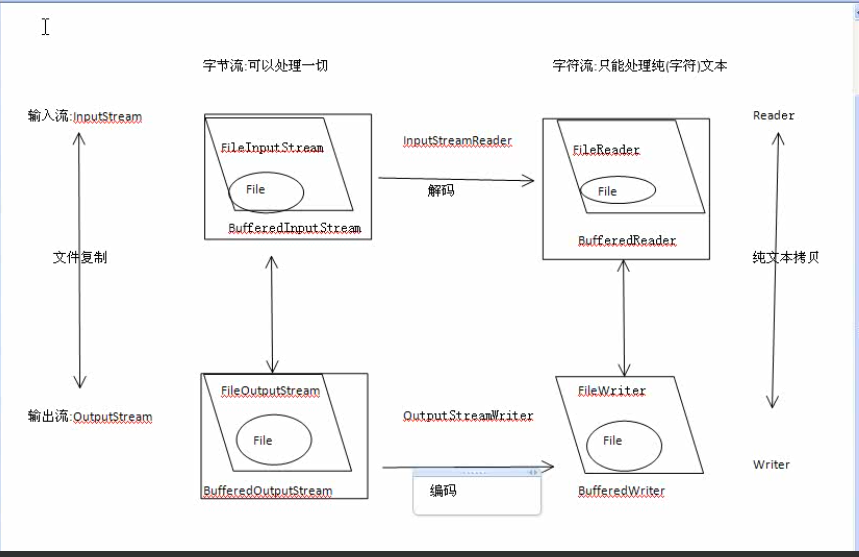
流的方向: 1.输入流:数据源到程序(InputStream,Reader读进来)。 2.输出流:程序到目的地(OutPutStream,Writer写出来)。 处理数据单元: 字节流:按照字节读取数据(InputStream,OutPutStream)。 字符流:按照字符读取数据(Reader,Writer) 功能不同: 节点流:可以直接从数据源或目的地读写数据。 处理流:不直接连接到数据源或者目的地,是处理流的流,通过对其他流的处理提高程序的性能。 处理流:增强功能,提供性能,处理流在节点流之上。 一、缓冲流 1)针对字节有字节缓冲流 BufferedInputStream readLine() BufferedOutPutStream 2)针对字符有字符缓冲流 BufferedReader newLine() BufferedWriter /** * 字节流文件拷贝+缓冲流 ,以后使用建议加上缓冲流提高性能。 * 节点流上面包一层缓冲流。 */ public class BufferedByteDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { } /** * 文件的拷贝 * @param 源文件路径 * @param 目录文件路径 * @throws FileNotFoundException,IOException * @return */ public static void copyFile(String srcPath,String destPath) throws FileNotFoundException,IOException { //1、建立联系 源(存在且为文件) +目的地(文件可以不存在) File src =new File(srcPath); File dest =new File(destPath); if(! src.isFile()){ //不是文件或者为null System.out.println("只能拷贝文件"); throw new IOException("只能拷贝文件"); } //2、选择流,利用缓冲流提高性能, InputStream is =new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(src)); OutputStream os =new BufferedOutputStream( new FileOutputStream(dest)); //3、文件拷贝 循环+读取+写出 byte[] flush =new byte[1024]; int len =0; //读取 while(-1!=(len=is.read(flush))){ //写出 os.write(flush, 0, len); } os.flush(); //强制刷出 //关闭流 os.close(); is.close(); } } /** * 字符缓冲流 +新增方法(不能发生多态),字符流外面包一层缓冲流。 */ public class BufferedCharDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建源 仅限于 字符的纯文本 File src =new File("E:/xp/test/1.java"); File dest =new File("e:/xp/test/2.txt"); //选择流 BufferedReader reader =null; BufferedWriter wr =null; try { reader =new BufferedReader(new FileReader(src)); wr =new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(dest)); //读取操作 /* char[] flush =new char[1024]; int len =0; while(-1!=(len=reader.read(flush))){ wr.write(flush, 0, len); }*/ //新增方法的操作 String line =null; while(null!=(line=reader.readLine())){//line每次为一行内容 wr.write(line); //wr.append(" "); wr.newLine(); //换行符号 } wr.flush();//强制刷出,流关闭的时候也可以刷出,这里是养成良好的编程习惯。 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("源文件不存在"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("文件读取失败"); }finally{ try { if (null != wr) { wr.close(); } } catch (Exception e2) { } try { if (null != reader) { reader.close(); } } catch (Exception e2) { } } } } 二、转换流:字节流转为字符流,作用是为了处理乱码(编码集、解码集)。 1.编码与解码的概念: 解码:二进制(计算机只认二进制)解码成字符(人只懂字符)。 编码:字符编码成二进制。 文件都是二进制,读进程序(转成字符)就是解码,写出去就是编码(转成二进制写出到另一个文件)。 2.乱码问题:(解码的时候要知道原先的编码的字符集) 1)编码与解码字符集不统一。 2)字节缺少,长度丢失。 public class ConverDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException { test1(); //解码(把二进制的中国转成中国让你看得懂,默认gbk),byte->char String str ="中国"; //编码,字符转字节,char->byte byte[] data =str.getBytes();//data=[-42, -48, -71, -6] //字节数不完整 System.out.println(new String(data,0,3));//String(byte[] bytes, int offset, int length)通过byte数组构建一个String,输出中? } /** * 编码与解码字符集必须相同,否则乱码 * @throws UnsupportedEncodingException */ public static void test1() throws UnsupportedEncodingException{ //解码(把二进制的中国转成中国让你看得懂,默认gbk), byte -->char String str ="中国"; //gbk //编码,字符转字节, char -->byte byte[] data =str.getBytes();//data=[-42, -48, -71, -6] //编码与解码字符集同一 System.out.println(new String(data));//中国 data =str.getBytes("utf-8"); //设定编码字符集,data=[-28, -72, -83, -27, -101, -67] //不同一出现乱码 System.out.println(new String(data));//涓�浗 //编码 byte[] data2 = "中国".getBytes("utf-8");//data2=[-28, -72, -83, -27, -101, -67] //解码 str=new String(data2,"utf-8");//中国 System.out.println(str); } } /*字节————(解码)————>字符————(编码)————>字节 源文件(二进制文件,字节)————(解码)————>程序(在程序中为字符)————(编码)————>目标文件(二进制文件)*/ /** * 转换流: 只能字节转为字符 * 1、输出流 OutputStreamWriter 编码, * 2、输入流 InputStreamReader 解码,读取是解码(字节转为字符),ANSI就是GBK的编码方式。 * 确保源不能为乱码 */ public class ConverDemo02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { /*BufferedReader br =new BufferedReader( new FileReader(new File("E:/xp/test/Demo03.java")) );//指定不了解码的字符集,所以只能底层使用字节流,因为字节给你可以解码,字符给你不能解码。*/ //指定解码字符集 BufferedReader br =new BufferedReader(//读进程序,1.java的文件的编码使用UTF-8编码的,所以这里的解码要UTF-8。 new InputStreamReader(//字符流和字节流不能直接操作,所以要用一个转换流。 new BufferedInputStream( new FileInputStream( new File("E:/xp/test/1.java"))),"UTF-8") ); //写出文件 编码 BufferedWriter bw =new BufferedWriter( new OutputStreamWriter(//用于编码的转换流 new BufferedOutputStream( new FileOutputStream(new File("E:/xp/test/2.java"))))); String info =null; while(null!=(info=br.readLine())){//读取源文件,每次读一行。 System.out.println(info); bw.write(info); bw.newLine(); } bw.flush(); bw.close(); br.close(); } } 其他流(数据在网络中传输都是通过流,不可能是传字符串): 一、字节数组(其他电脑的内存,服务器的内存): 输入流:ByteArrayInputStream read(byte[] byte int off,int len) + close() 输出流:ByteArrayOutputStream write(byte[] byte int off,int len) /** * 字节数组 节点流 * 数组的长度有限 ,数据量不会很大 * * 文件内容不用太大 * 1、文件 --程序->字节数组 * 2、字节数组 --程序->文件 */ public class ByteArrayDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { read(write()); } /** * 输出流 操作与文件输出流 有些不同, 有新增方法,不能使用多态 * @throws IOException */ public static byte[] write() throws IOException{ //目的地,一个字节数组。 byte[] dest; //选择流 不同点 ByteArrayOutputStream bos =new ByteArrayOutputStream(); //操作 写出 String msg ="操作与 文件输入流操作一致"; byte[] info =msg.getBytes(); bos.write(info, 0, info.length);//写到bos这个管道里去了 //获取数据 dest =bos.toByteArray(); //释放资源 bos.close(); return dest; } /** * 输入流 操作与 文件输入流操作一致 * 读取字节数组(之前是读文件),数组的长度有限,数据量不会很大。 * @throws IOException */ public static void read(byte[] src) throws IOException{ //数据源传入 String msg = "输入流 操作与 文件输入流操作一致"; ///byte[] src = msg.getBytes(); //选择流 InputStream is =new BufferedInputStream( new ByteArrayInputStream( src ) );//跟外界没有联系就不会有检查异常 //操作 byte[] flush =new byte[1024]; int len =0; while(-1!=(len=is.read(flush))){ System.out.println(new String(flush,0,len)); } //释放资源 is.close(); } } /** *1、文件 --通过程序->字节数组 *1)、文件输入流 * 字节数组输出流 * * 2、字节数组 --通过程序->文件 * 1)、字节数组输入流 * 文件输出流 */ public class ByteArrayDemo02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { byte[] data =getBytesFromFile("e:/xp/test/1.jpg");//文件 --通过程序->字节数组 toFileFromByteArray(data,"e:/xp/test/arr.jpg");//字节数组 --通过程序->文件 } /** * 2、字节数组 --程序->文件 */ public static void toFileFromByteArray(byte[] src,String destPath) throws IOException{ //创建源src //目的地 File dest=new File(destPath); //选择流(不同的文件类型,选择的流不一样) //字节数组输入流 InputStream is =new BufferedInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(src)); //文件输出流 OutputStream os =new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dest)); //操作 不断读取字节数组 byte[] flush =new byte[1]; int len =0; while(-1!=(len =is.read(flush))){ //写出到文件中 os.write(flush, 0, len); } os.flush(); //释放资源 os.close(); is.close(); } /** * 1、文件 --程序->字节数组 */ public static byte[] getBytesFromFile(String srcPath) throws IOException{ //创建文件源 File src =new File(srcPath); //创建字节数组目的地 byte[] dest =null; //选择流 //文件输入流 InputStream is =new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(src)); //字节数组输出流 不能使用多态 ByteArrayOutputStream bos =new ByteArrayOutputStream(); //操作 不断读取文件 写出到字节数组流中 byte[] flush =new byte[1024]; int len =0; while(-1!=(len =is.read(flush))){ //写出到字节数组流中 bos.write(flush, 0, len); } bos.flush();//输出流都要flush一下 //获取数据 dest =bos.toByteArray(); bos.close(); is.close(); return dest; } } 其他流 二、处理流: 1.处理基本类型+字符串(保留数据和类型),是处理流就要借助于节点流(把东西存到哪个地方去), 输入流:DataInputStream(看到InputStream就要字节流不能用字符流) readXxx 输出流:DataOutputStream writeXxx /** * 数据类型(类型只能是基本类型+String)处理流 * 1、输入流 DataInputStream readXxx() * 2、输出流 DataOutputStream writeXxx() * 新增方法不能使用多态 * java.io.EOFException :没有读取到相关的内容 */ public class DataDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { try { write("e:/xp/test/data.txt"); //read("e:/xp/test/arr.txt"); //非法内容 read("e:/xp/test/data.txt"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 从文件读取数据+类型 * @throws IOException */ public static void read(String destPath) throws IOException{ //创建源 File src =new File(destPath); //选择流 DataInputStream dis =new DataInputStream( new BufferedInputStream( new FileInputStream(src) ) ); //操作 读取的顺序与写出一致 必须存在才能读取 //读取的顺序不一致,数据输出会存在问题 long num2 =dis.readLong(); double num1 =dis.readDouble(); String str =dis.readUTF(); dis.close(); System.out.println(num2+"-->"+str); } /** * 数据+类型输出到文件 * @throws IOException */ public static void write(String destPath) throws IOException{ double point =2.5; long num=100L; String str ="数据类型"; //创建源 File dest =new File(destPath); //选择流 DataOutputStream DataOutputStream dos =new DataOutputStream( new BufferedOutputStream(//OutputStream的子类 new FileOutputStream(dest) ) ); //操作 写出的顺序 为读取准备,写入到文件data.txt dos.writeDouble(point); dos.writeLong(num); dos.writeUTF(str); dos.flush(); //释放资源 dos.close(); } } /** * 数据类型(基本+String)处理流 * 1、输入流 DataInputStream readXxx() * 2、输出流 DataOutputStream writeXxx() * 新增方法不能使用多态 * java.io.EOFException :没有读取到相关的内容 */ public class DataDemo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { try { byte[] data=write(); read(data); System.out.println(data.length); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 从字节数组读取数据+类型 * @throws IOException */ public static void read(byte[] src) throws IOException{ //字节数组,选择流用字节数组输入流 DataInputStream dis =new DataInputStream( new BufferedInputStream( new ByteArrayInputStream(src) )); //操作 读取的顺序与写出一致 必须存在才能读取 double num1 =dis.readDouble(); long num2 =dis.readLong(); String str =dis.readUTF(); dis.close(); System.out.println(num1+"-->"+num2+"-->"+str); } /** * 数据+类型输出到字节数组中,输出到字节数组中用ByteArrayOutputStream。 * @throws IOException */ public static byte[] write() throws IOException{ //目标数组 byte[] dest =null; double point =2.5; long num=100L; String str ="数据类型"; //选择流 ByteArrayOutputStream DataOutputStream ByteArrayOutputStream bos =new ByteArrayOutputStream(); DataOutputStream dos =new DataOutputStream( new BufferedOutputStream( bos ) ); //操作 写出的顺序 为读取准备 dos.writeDouble(point); dos.writeLong(num); dos.writeUTF(str); dos.flush(); dest =bos.toByteArray(); //释放资源 dos.close(); return dest;//把double、long、String写入到字节数组dest中。 } }