
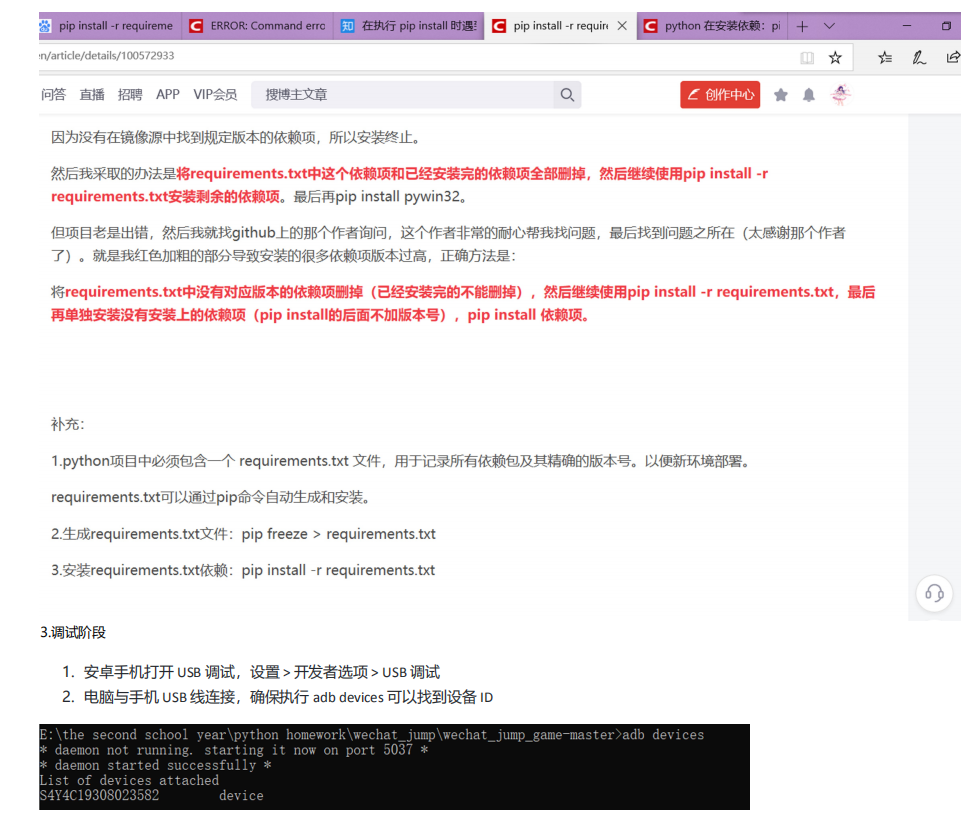

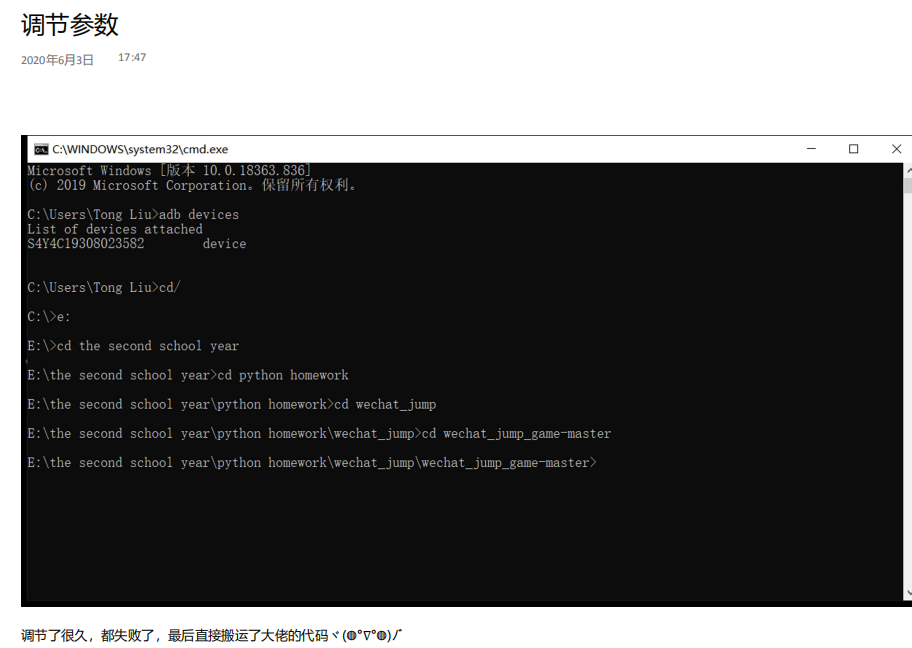
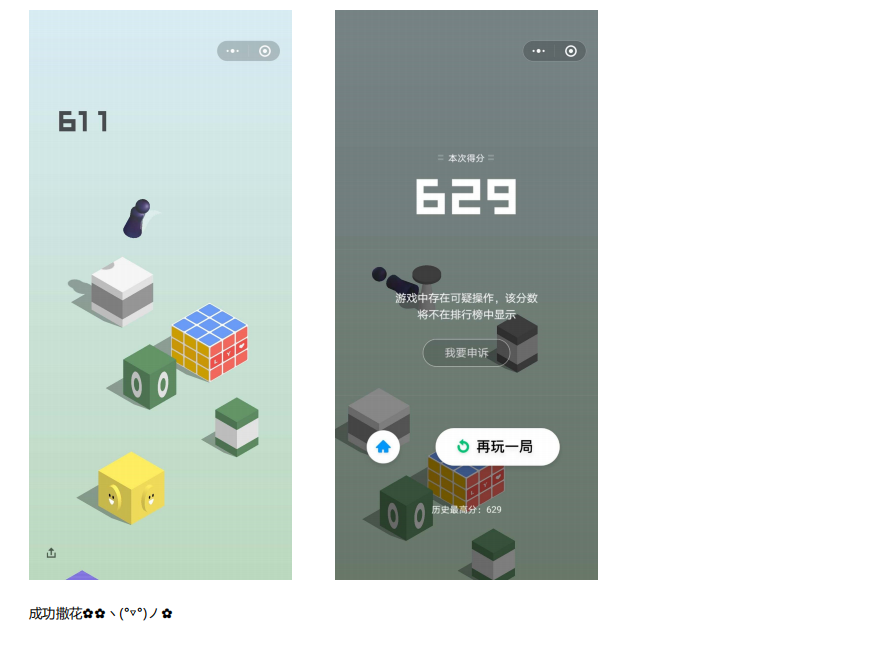
最后附上大佬的代码

from __future__ import print_function, division import os import sys import time import math import random from PIL import Image import subprocess # 分数y坐标 under_game_score_y = 300 # 长按的时间系数,请自己根据实际情况调节 press_coefficient = 1.392 # 二分之一的棋子底座高度,可能要调节 piece_base_height_1_2 = 20 # 棋子的宽度,比截图中量到的稍微大一点比较安全,可能要调节 piece_body_width = 70 def set_button_position(im): """ 将 swipe 设置为 `再来一局` 按钮的位置 """ global swipe_x1, swipe_y1, swipe_x2, swipe_y2 w, h = im.size left = int(w / 2) top = int(1584 * (h / 1920.0)) left = int(random.uniform(left-50, left+50)) top = int(random.uniform(top-10, top+10)) # 随机防 ban swipe_x1, swipe_y1, swipe_x2, swipe_y2 = left, top, left, top def jump(distance): """ 跳跃一定的距离 """ press_time = distance * press_coefficient press_time = max(press_time, 200) # 设置 200ms 是最小的按压时间 press_time = int(press_time) cmd = 'adb shell input swipe {x1} {y1} {x2} {y2} {duration}'.format( x1=swipe_x1, y1=swipe_y1, x2=swipe_x2, y2=swipe_y2, duration=press_time ) print(cmd) os.system(cmd) return press_time def find_piece_and_board(im): """ 寻找关键坐标 """ w, h = im.size piece_x_sum = 0 piece_x_c = 0 piece_y_max = 0 board_x = 0 board_y = 0 scan_x_border = int(w / 8) # 扫描棋子时的左右边界 scan_start_y = 0 # 扫描的起始 y 坐标 im_pixel = im.load() # 以 50px 步长,尝试探测 scan_start_y for i in range(int(h / 3), int(h*2 / 3), 50): last_pixel = im_pixel[0, i] for j in range(1, w): pixel = im_pixel[j, i] # 不是纯色的线,则记录 scan_start_y 的值,准备跳出循环 if pixel != last_pixel: scan_start_y = i - 50 break if scan_start_y: break print('scan_start_y: {}'.format(scan_start_y)) # 从 scan_start_y 开始往下扫描,棋子应位于屏幕上半部分,这里暂定不超过 2/3 for i in range(scan_start_y, int(h * 2 / 3)): # 横坐标方面也减少了一部分扫描开销 for j in range(scan_x_border, w - scan_x_border): pixel = im_pixel[j, i] # 根据棋子的最低行的颜色判断,找最后一行那些点的平均值,这个颜 # 色这样应该 OK,暂时不提出来 if (50 < pixel[0] < 60) and (53 < pixel[1] < 63) and (95 < pixel[2] < 110): piece_x_sum += j piece_x_c += 1 piece_y_max = max(i, piece_y_max) if not all((piece_x_sum, piece_x_c)): return 0, 0, 0, 0 piece_x = int(piece_x_sum / piece_x_c) piece_y = piece_y_max - piece_base_height_1_2 # 上移棋子底盘高度的一半 # 限制棋盘扫描的横坐标,避免音符 bug if piece_x < w/2: board_x_start = piece_x board_x_end = w else: board_x_start = 0 board_x_end = piece_x for i in range(int(h / 3), int(h * 2 / 3)): last_pixel = im_pixel[0, i] if board_x or board_y: break board_x_sum = 0 board_x_c = 0 for j in range(int(board_x_start), int(board_x_end)): pixel = im_pixel[j, i] # 修掉脑袋比下一个小格子还高的情况的 bug if abs(j - piece_x) < piece_body_ continue # 修掉圆顶的时候一条线导致的小 bug,这个颜色判断应该 OK,暂时不提出来 if abs(pixel[0] - last_pixel[0]) + abs(pixel[1] - last_pixel[1]) + abs(pixel[2] - last_pixel[2]) > 10: board_x_sum += j board_x_c += 1 if board_x_sum: board_x = board_x_sum / board_x_c last_pixel = im_pixel[board_x, i] # 从上顶点往下 +274 的位置开始向上找颜色与上顶点一样的点,为下顶点 # 该方法对所有纯色平面和部分非纯色平面有效,对高尔夫草坪面、木纹桌面、 # 药瓶和非菱形的碟机(好像是)会判断错误 for k in range(i+274, i, -1): # 274 取开局时最大的方块的上下顶点距离 pixel = im_pixel[board_x, k] if abs(pixel[0] - last_pixel[0]) + abs(pixel[1] - last_pixel[1]) + abs(pixel[2] - last_pixel[2]) < 10: break board_y = int((i+k) / 2) # 如果上一跳命中中间,则下个目标中心会出现 r245 g245 b245 的点,利用这个 # 属性弥补上一段代码可能存在的判断错误 # 若上一跳由于某种原因没有跳到正中间,而下一跳恰好有无法正确识别花纹,则有 # 可能游戏失败,由于花纹面积通常比较大,失败概率较低 for j in range(i, i+200): pixel = im_pixel[board_x, j] if abs(pixel[0] - 245) + abs(pixel[1] - 245) + abs(pixel[2] - 245) == 0: board_y = j + 10 break if not all((board_x, board_y)): return 0, 0, 0, 0 return piece_x, piece_y, board_x, board_y def pull_screenshot(): os.system('adb shell screencap -p /sdcard/1.png') os.system('adb pull /sdcard/1.png .') def check_screenshot(): # 检查获取截图的方式 if os.path.isfile('1.png'): os.remove('1.png') pull_screenshot() Image.open('./1.png').load() def main(): check_screenshot() i, next_rest, next_rest_time = (0, random.randrange(3, 10), random.randrange(5, 10)) while True: pull_screenshot() im = Image.open('./1.png') # 获取棋子和 board 的位置 piece_x, piece_y, board_x, board_y = find_piece_and_board(im) ts = int(time.time()) print(ts, piece_x, piece_y, board_x, board_y) set_button_position(im) jump(math.sqrt((board_x - piece_x) ** 2 + (board_y - piece_y) ** 2)) im.close() i += 1 if i == next_rest: print('已经连续打了 {} 下,休息 {}s'.format(i, next_rest_time)) for j in range(next_rest_time): sys.stdout.write(' 程序将在 {}s 后继续'.format(next_rest_time - j)) sys.stdout.flush() time.sleep(1) print(' 继续') i, next_rest, next_rest_time = (0, random.randrange(30, 100), random.randrange(10, 60)) # 为了保证截图的时候应落稳了,多延迟一会儿,随机值防 ban time.sleep(random.uniform(0.9, 1.2)) if __name__ == '__main__': main()
