- 树的应用:表达式解析
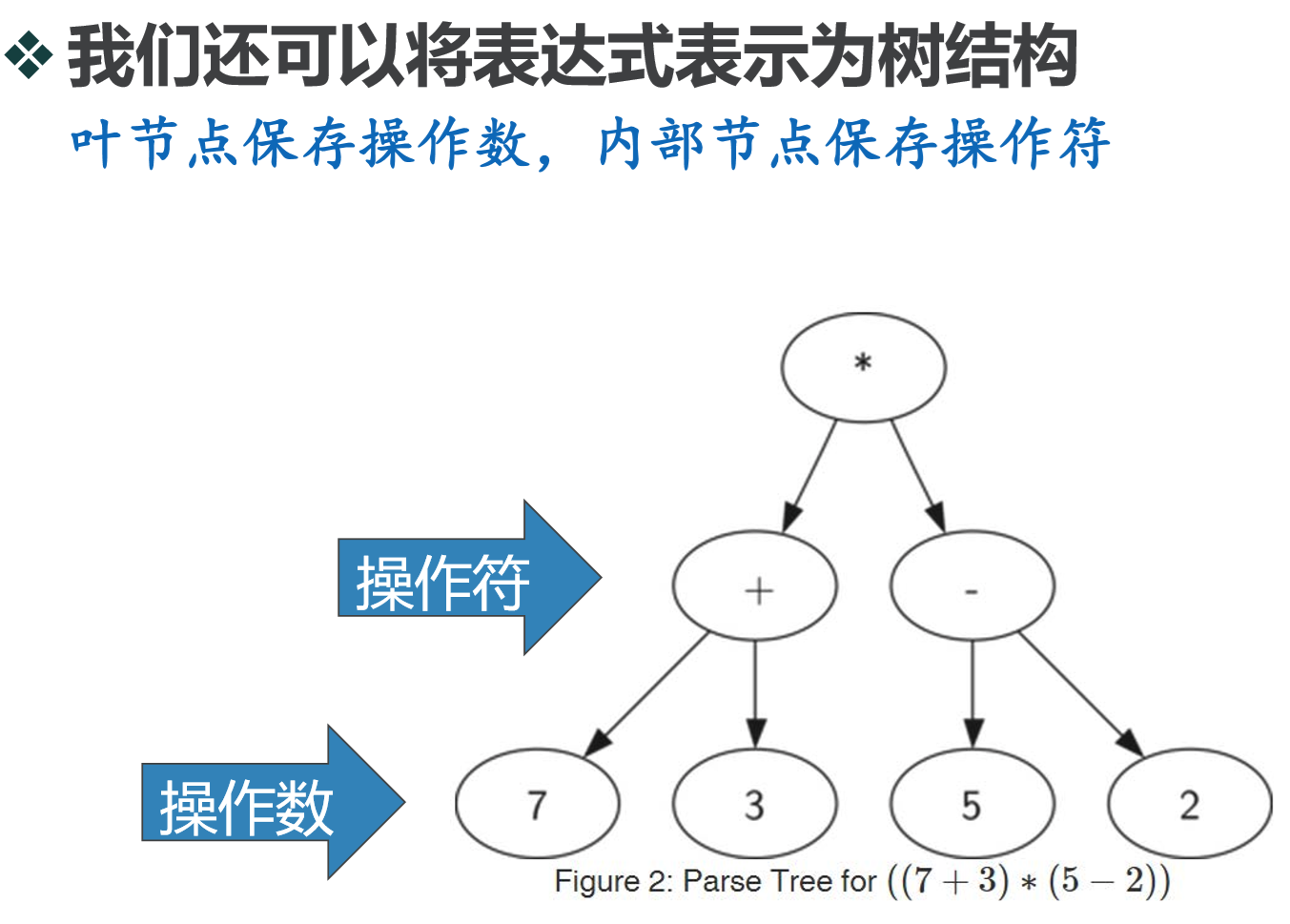
解析全括号表达式:(3+(4*5))

- 创建过程:
创建空树,当前节点为根节点
读入'(',创建了左子节点,当前节点下降
读入'3',当前节点设置为3,上升到父节点
读入'+',当前节点设置为+,创建右子节点,当前节点下降。

读入'(',创建左子节点,当前节点下降
读入'4',当前节点设置为4,上升到父节点
读入'*',当前节点设置为*,创建右子节点,当 前节点下降
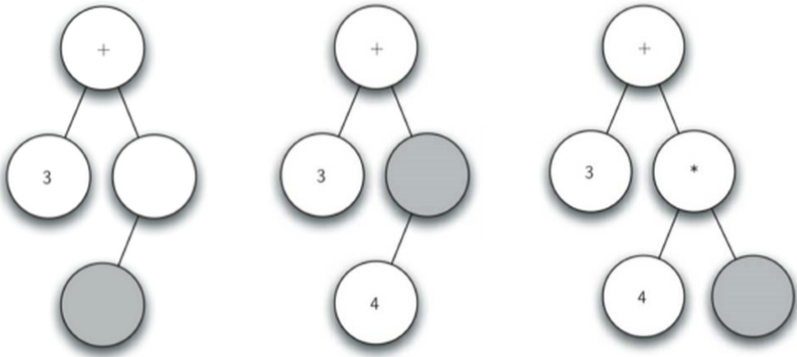
读入'5',当前节点设置为5,上升到父节点
读入')',上升到父节点
读入')',再上升到父节点
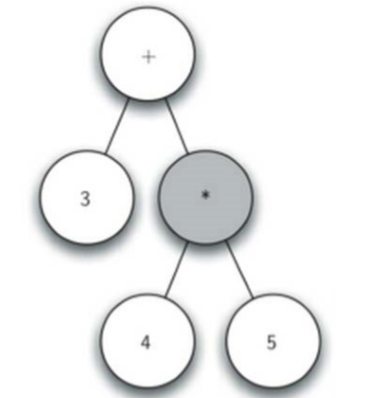
总结下:如果当前单词是"(":为当前节点添加一个新节 点作为其左子节点,当前节点下降为这个新节点 如果当前单词是操作符"+,-,/,*":将当前节点 的值设为此符号,为当前节点添加一个新节点作 为其右子节点,当前节点下降为这个新节点 如果当前单词是操作数:将当前节点的值设为此 数,当前节点上升到父节点 如果当前单词是")":则当前节点上升到父节点。
创建左右子树可调用insertLeft/Right
当前节点设置值,可以调用setRootVal
下降到左右子树可调用getLeft/RightChild
创建一个栈来跟踪父节点:当前节点下降时,将下降前的节点push入栈 当前节点需要上升到父节点时,上升到pop出栈的节点即可!
from Stack import Stack from Binary_Tree import BinaryTree def buildParseTree(fpexp): fplist = fpexp.split() pStack = Stack() eTree = BinaryTree('') #创建一个空树 pStack.push(eTree) currentTree = eTree for i in fplist: if i == "(": currentTree.insertLeft('') pStack.push(currentTree) #将老的当前节点入栈下降 currentTree = currentTree.getLeftChild() elif i not in ['+', '-', '*', '/', ')']: currentTree.setRootVal(int(i)) #设置当前节点的值,为操作数 parent = pStack.pop() #出栈上升 currentTree = parent #上升 elif i in ['+', '-', '*', '/']: currentTree.setRootVal(i) #将当前阶段设置成操作符 currentTree.insertRight('') #创建右子树 pStack.push(currentTree) #把老的当前节点push到栈中 currentTree = currentTree.getRightChild() elif i == ")": currentTree = pStack.pop() else: raise ValueError return eTree flist = buildParseTree('( 3 + ( 4 * 5 ) )')
- 利用表达式解析树求值
创建了表达式解析树,可用来进行求值。由于二叉树BinaryTree是一个递归数据 结构,自然可以用递归算法来处理。由前述对子表达式的描述,可从树的底层子树开 始,逐步向上层求值,最终得到整个表达式的值。
求值函数evaluate的递归三要素:
基本结束条件:叶节点是最简单的子树,没有左 右子节点,其根节点的数据项即为子表达式树的值
缩小规模:将表达式树分为左子树、右子树,即为缩小规模
调用自身:分别调用evaluate计算左子树和右 子树的值,然后将左右子树的值依根节点的操作 符进行计算,从而得到表达式的值
这里引用函数引用包 operator。
from Stack import Stack from Binary_Tree import BinaryTree def buildParseTree(fpexp): fplist = fpexp.split() pStack = Stack() eTree = BinaryTree('') #创建一个空树 pStack.push(eTree) currentTree = eTree for i in fplist: if i == "(": currentTree.insertLeft('') pStack.push(currentTree) #将老的当前节点入栈下降 currentTree = currentTree.getLeftChild() elif i not in ['+', '-', '*', '/', ')']: currentTree.setRootVal(int(i)) #设置当前节点的值,为操作数 parent = pStack.pop() #出栈上升 currentTree = parent #上升 elif i in ['+', '-', '*', '/']: currentTree.setRootVal(i) #将当前阶段设置成操作符 currentTree.insertRight('') #创建右子树 pStack.push(currentTree) #把老的当前节点push到栈中 currentTree = currentTree.getRightChild() elif i == ")": currentTree = pStack.pop() else: raise ValueError return eTree flist = buildParseTree('( 3 + ( 4 * 5 ) )')