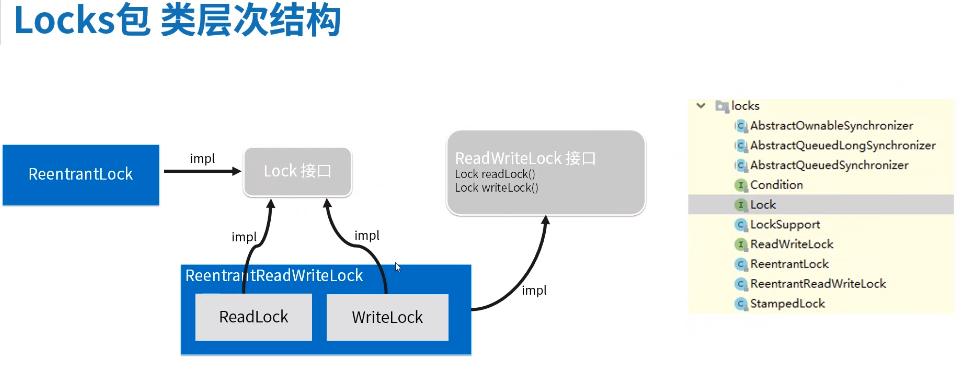
1.锁的本质
2.Lock接口使用ReentrenLock
3.读写锁使用
4.读写锁实现
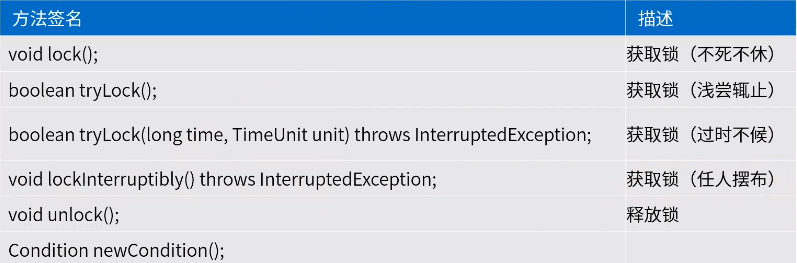
Lock接口方法
有点意思的是lockInterruptibly(), 只要没有获取到锁就会一直等待,直到某一地方对当前线程执行interrupt()方法后,
lockInterruptibly()处会抛出异常,可以在catch中对此异常情况进行处理

synchronized+wait+notify 对比 reentrantLock+condition+await+signal:
两种方式思想差不多,wait和await都会释放锁,最明显的不同是condition有多个等待队列,wait/notify只有一个等待队列
/*
1、自己实现一个阻塞队列,只能存储 n个元素
put时,若队列未满,直接put,
若队列满,就阻塞,直到再有空间
get时,若队列中有元素,则获取到元素
若无元素,则等待元素
*/
class JamesQueue{
List<Object> list = new ArrayList<>();
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition putCondition = lock.newCondition();
Condition takeCondition = lock.newCondition();
private int length;
public JamesQueue(int length){
this.length = length;
}
public void put(Object obj){
lock.lock();
try {
if (list.size() < length){
list.add(obj);
System.out.println("put:" + obj);
takeCondition.signal();
}else{
putCondition.await();
}
}catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public Object take(){
lock.lock();
Object obj = null;
try {
for (;;) {
if (list.size() > 0) {
obj = list.get(0);
list.remove(0);
System.out.println("take:" + obj);
putCondition.signal();
break;
} else {
takeCondition.await();
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
return obj;
}
}
public class Demo4_Condition3 {
public static void main(String args[]) throws InterruptedException {
JamesQueue bb = new JamesQueue(5);
new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
bb.put("x" + i);
}
}
}.start();
Thread.sleep(3000L);
System.out.println("开始从队列中取元素...");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
bb.take();
Thread.sleep(3000L);
}
}
}
ReentrantLock可重入锁
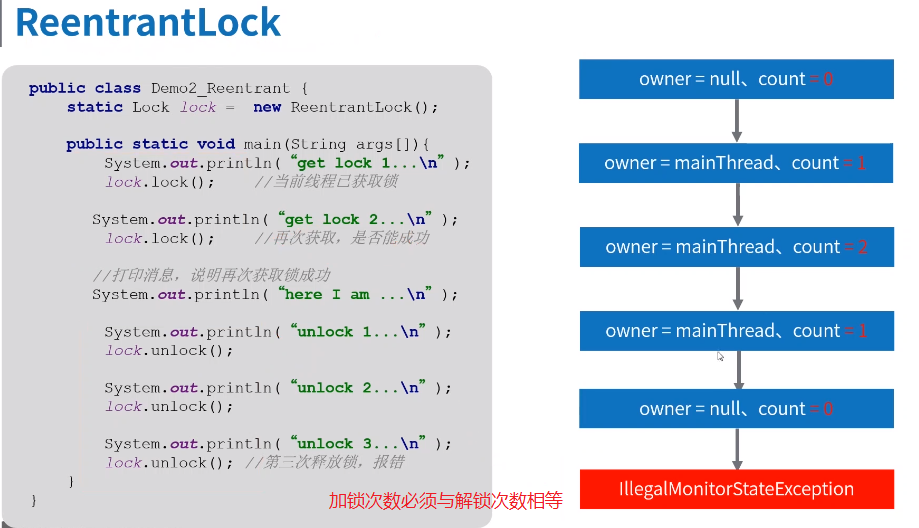
ReentrantLock基本原理
线程通过ReentrantLock.lock()加锁时:
判断count是否是0,若是则代表锁未被占用,开始抢锁,若抢到锁则CAS修改count值,并将owner设置为自身线程的引用;若否,则判断当前锁的占用者owner是不是自己,若是自己则count+1,若不是则进入等待队列waiters
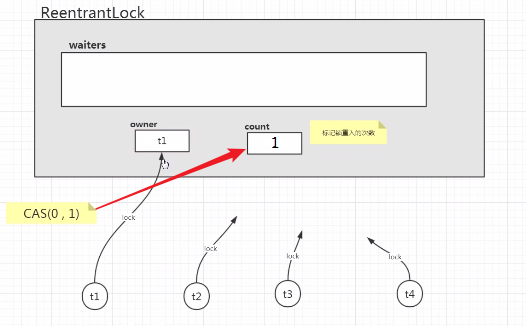
手写ReentrantLock
package com.study.lock.locks1;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport;
public class JamesReentrantLock implements Lock {
// 锁的拥有者
AtomicReference<Thread> owner = new AtomicReference<>();
// 等待队列
private LinkedBlockingQueue<Thread> waiters = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
// 标记重入次数的count值
AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(0);
@Override
public boolean tryLock() {// 浅尝辄止
// 判断count是否为0,若count!=0,说明锁被占用
int ct = count.get();
if (ct != 0) {
// 判断锁是否被当前线程占用,若被当前线程占用,做重入操作,count+=1
if (owner.get() == Thread.currentThread()) {
count.set(ct + 1);
return true;
} else {
// 若不是当前线程占用,互斥,抢锁失败,return false
return false;
}
} else {
// 若count=0, 说明锁未被占用,通过CAS(0,1) 来抢锁
if (count.compareAndSet(ct, ct + 1)) {
// 若抢锁成功,设置owner为当前线程的引用
owner.set(Thread.currentThread());
return true;
} else {
// CAS操作失败,说明情锁失败 返回false
return false;
}
}
}
@Override
public void lock() {// 不死不休
// 尝试抢锁
if (!tryLock()) {
// 如果失败,进入等待队列
waiters.offer(Thread.currentThread());
// 自旋
for (;;) {
// 判断是否是队列头部,如果是
Thread head = waiters.peek();
if (head == Thread.currentThread()) {
// 再次尝试抢锁
if (!tryLock()) {
// 若抢锁失败,挂起线程,继续等待
LockSupport.park();
} else {
// 若成功,就出队列
waiters.poll();
return;
}
} else {
// 如果不是,就挂起线程
LockSupport.park();
}
}
}
}
@Override
public void unlock() {
if (tryUnlock()) {
Thread th = waiters.peek();
if (th != null) {
LockSupport.unpark(th);
}
}
}
public boolean tryUnlock() {
// 判断,是否是当前线程占有锁,若不是,抛异常
if (owner.get() != Thread.currentThread()) {
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
} else {
// 如果是,就将count-1 若count变为0 ,则解锁成功
int ct = count.get();
int nextc = ct - 1;
count.set(nextc);
// 判断count值是否为0
if (nextc == 0) {
owner.compareAndSet(Thread.currentThread(), null);
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
@Override
public void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException {
}
@Override
public boolean tryLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
int ct = count.get();
if (ct == 0) {
// 未被占用,CAS修改count
long end = System.currentTimeMillis() + unit.toMillis(time);
for (;;) {
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (now > end) {
return false;
} else {
if (count.compareAndSet(0, 1)) {
owner.set(Thread.currentThread());
return true;
}
}
}
} else {
long end = System.currentTimeMillis() + unit.toMillis(time);
for (;;) {
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (now > end) {
return false;
} else {
if (count.compareAndSet(0, 1)) {
owner.set(Thread.currentThread());
return true;
}
}
}
}
}
@Override
public Condition newCondition() {
return null;
}
}
Lock与Synchronized对比
