约束计算
闭环检测的策略:搜索闭环,通过匹配检测是否是闭环,采用了分支定界法。
前已经述及PoseGraph的内容,此处继续。位姿图类定义了pose_graph::ConstraintBuilder constraint_builder_对象。
1.ConstraintBuilder类图
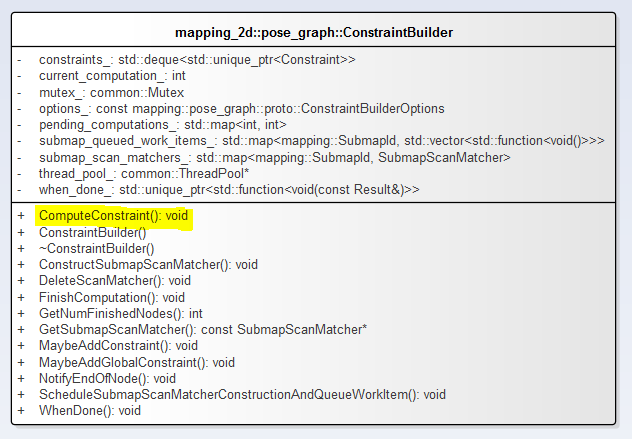
定义了SubmapScanMatcher的键值对。
1 // Map of already constructed scan matchers by 'submap_id'. 2 std::map<mapping::SubmapId, SubmapScanMatcher> submap_scan_matchers_ GUARDED_BY(mutex_);
SubmapScanMatcher结构体定义如下:
1 struct SubmapScanMatcher 2 { 3 const ProbabilityGrid* probability_grid; 4 std::unique_ptr<scan_matching::FastCorrelativeScanMatcher> 5 fast_correlative_scan_matcher; 6 };
注意ConstraintBuilder::ComputeConstraint方法,MaybeAddConstraint和MaybeAddGlobalConstraint都调用了该方法。
1 void ConstraintBuilder::ComputeConstraint( 2 const mapping::SubmapId& submap_id, const Submap* const submap, 3 const mapping::NodeId& node_id, bool match_full_submap, 4 const mapping::TrajectoryNode::Data* const constant_data, 5 const transform::Rigid2d& initial_relative_pose, 6 std::unique_ptr<ConstraintBuilder::Constraint>* constraint) { 7 const transform::Rigid2d initial_pose = 8 ComputeSubmapPose(*submap) * initial_relative_pose; 9 const SubmapScanMatcher* const submap_scan_matcher = 10 GetSubmapScanMatcher(submap_id); 11 12 // The 'constraint_transform' (submap i <- node j) is computed from: 13 // - a 'filtered_gravity_aligned_point_cloud' in node j, 14 // - the initial guess 'initial_pose' for (map <- node j), 15 // - the result 'pose_estimate' of Match() (map <- node j). 16 // - the ComputeSubmapPose() (map <- submap i) 17 float score = 0.; 18 transform::Rigid2d pose_estimate = transform::Rigid2d::Identity(); 19 20 // Compute 'pose_estimate' in three stages: 21 // 1. Fast estimate using the fast correlative scan matcher. 22 // 2. Prune if the score is too low. 23 // 3. Refine. 24 if (match_full_submap) { 25 if (submap_scan_matcher->fast_correlative_scan_matcher->MatchFullSubmap( 26 constant_data->filtered_gravity_aligned_point_cloud, 27 options_.global_localization_min_score(), &score, &pose_estimate)) { 28 CHECK_GT(score, options_.global_localization_min_score()); 29 CHECK_GE(node_id.trajectory_id, 0); 30 CHECK_GE(submap_id.trajectory_id, 0); 31 } else { 32 return; 33 } 34 } else { 35 if (submap_scan_matcher->fast_correlative_scan_matcher->Match( 36 initial_pose, constant_data->filtered_gravity_aligned_point_cloud, 37 options_.min_score(), &score, &pose_estimate)) { 38 // We've reported a successful local match. 39 CHECK_GT(score, options_.min_score()); 40 } else { 41 return; 42 } 43 } 44 { 45 common::MutexLocker locker(&mutex_); 46 score_histogram_.Add(score); 47 } 48 49 // Use the CSM estimate as both the initial and previous pose. This has the 50 // effect that, in the absence of better information, we prefer the original 51 // CSM estimate. 52 ceres::Solver::Summary unused_summary; 53 ceres_scan_matcher_.Match(pose_estimate.translation(), pose_estimate, 54 constant_data->filtered_gravity_aligned_point_cloud, 55 *submap_scan_matcher->probability_grid, 56 &pose_estimate, &unused_summary); 57 58 const transform::Rigid2d constraint_transform = 59 ComputeSubmapPose(*submap).inverse() * pose_estimate; 60 constraint->reset(new Constraint{submap_id, 61 node_id, 62 {transform::Embed3D(constraint_transform), 63 options_.loop_closure_translation_weight(), 64 options_.loop_closure_rotation_weight()}, 65 Constraint::INTER_SUBMAP}); 66 67 if (options_.log_matches()) { 68 std::ostringstream info; 69 info << "Node " << node_id << " with " 70 << constant_data->filtered_gravity_aligned_point_cloud.size() 71 << " points on submap " << submap_id << std::fixed; 72 if (match_full_submap) { 73 info << " matches"; 74 } else { 75 const transform::Rigid2d difference = 76 initial_pose.inverse() * pose_estimate; 77 info << " differs by translation " << std::setprecision(2) 78 << difference.translation().norm() << " rotation " 79 << std::setprecision(3) << std::abs(difference.normalized_angle()); 80 } 81 info << " with score " << std::setprecision(1) << 100. * score << "%."; 82 LOG(INFO) << info.str(); 83 } 84 }
这里出现了scan_matching::FastCorrelativeScanMatcher,另一种扫描匹配的方法。论文中介绍的分支定界法就在这个类中实现。
以上FastCorrelativeScanMatcher::Match和FastCorrelativeScanMatcher::MatchFullSubmap方法都调用了FastCorrelativeScanMatcher::MatchWithSearchParameters方法。
FastCorrelativeScanMatcher::MatchWithSearchParameters调用了FastCorrelativeScanMatcher::BranchAndBound方法。
|
Tips:总结一下出现的几种扫描匹配的方法? RealTimeCorrelativeScanMatcher FastCorrelativeScanMatcher |
1 bool FastCorrelativeScanMatcher::MatchWithSearchParameters( 2 SearchParameters search_parameters, 3 const transform::Rigid2d& initial_pose_estimate, 4 const sensor::PointCloud& point_cloud, float min_score, float* score, 5 transform::Rigid2d* pose_estimate) const 6 { 7 CHECK_NOTNULL(score); 8 CHECK_NOTNULL(pose_estimate); 9 10 const Eigen::Rotation2Dd initial_rotation = initial_pose_estimate.rotation(); 11 const sensor::PointCloud rotated_point_cloud = sensor::TransformPointCloud( 12 point_cloud, 13 transform::Rigid3f::Rotation(Eigen::AngleAxisf( 14 initial_rotation.cast<float>().angle(), Eigen::Vector3f::UnitZ()))); 15 const std::vector<sensor::PointCloud> rotated_scans = 16 GenerateRotatedScans(rotated_point_cloud, search_parameters); 17 const std::vector<DiscreteScan> discrete_scans = DiscretizeScans( 18 limits_, rotated_scans, 19 Eigen::Translation2f(initial_pose_estimate.translation().x(), 20 initial_pose_estimate.translation().y())); 21 search_parameters.ShrinkToFit(discrete_scans, limits_.cell_limits()); 22 23 const std::vector<Candidate> lowest_resolution_candidates = 24 ComputeLowestResolutionCandidates(discrete_scans, search_parameters); 25 const Candidate best_candidate = BranchAndBound( 26 discrete_scans, search_parameters, lowest_resolution_candidates, 27 precomputation_grid_stack_->max_depth(), min_score);//分支定界法 28 if (best_candidate.score > min_score) { 29 *score = best_candidate.score; 30 *pose_estimate = transform::Rigid2d( 31 {initial_pose_estimate.translation().x() + best_candidate.x, 32 initial_pose_estimate.translation().y() + best_candidate.y}, 33 initial_rotation * Eigen::Rotation2Dd(best_candidate.orientation)); 34 return true; 35 } 36 return false; 37 }
2.分支定界法
FastCorrelativeScanMatcher::BranchAndBound,......
1 Candidate FastCorrelativeScanMatcher::BranchAndBound( 2 const std::vector<DiscreteScan>& discrete_scans, 3 const SearchParameters& search_parameters, 4 const std::vector<Candidate>& candidates, const int candidate_depth, 5 float min_score) const 6 { 7 if (candidate_depth == 0) 8 { 9 // Return the best candidate. 10 return *candidates.begin(); 11 } 12 13 Candidate best_high_resolution_candidate(0, 0, 0, search_parameters); 14 best_high_resolution_candidate.score = min_score; 15 for (const Candidate& candidate : candidates) 16 { 17 if (candidate.score <= min_score) { break; } 18 std::vector<Candidate> higher_resolution_candidates; 19 const int half_width = 1 << (candidate_depth - 1); 20 for (int x_offset : {0, half_width}) 21 { 22 if (candidate.x_index_offset + x_offset > 23 search_parameters.linear_bounds[candidate.scan_index].max_x) { 24 break; 25 } 26 for (int y_offset : {0, half_width}) { 27 if (candidate.y_index_offset + y_offset > 28 search_parameters.linear_bounds[candidate.scan_index].max_y) { 29 break; 30 } 31 higher_resolution_candidates.emplace_back( 32 candidate.scan_index, candidate.x_index_offset + x_offset, 33 candidate.y_index_offset + y_offset, search_parameters); 34 } 35 } 36 ScoreCandidates(precomputation_grid_stack_->Get(candidate_depth - 1), 37 discrete_scans, search_parameters, 38 &higher_resolution_candidates); 39 best_high_resolution_candidate = std::max( 40 best_high_resolution_candidate, 41 BranchAndBound(discrete_scans, search_parameters, 42 higher_resolution_candidates, candidate_depth - 1, 43 best_high_resolution_candidate.score)); 44 } 45 return best_high_resolution_candidate; 46 }