List<泛型集合>
线性数据结构
概念
C#集合是来维护一组对象的数据结构,与数组不同,集合包含更多的功能。如:自动添加元素到指定位置,排序等。
C#中集合是指在system.Collection下的类型,他们大多数是通过实现此命名空间下的接口来实现的。泛型集合是指在system.Collection.Generic下的类型,他们在具体的集合类型的特性上增加了泛型的特性。泛型集合相对集合更安全,性能更好。
声明(定义)
当我们创建了一个泛型列表的时候在其内部会创建一个大小为4的数组
每次当添加的元素超过了这个大小,其内部数组的长度将会扩大一倍
使用泛型集合类型之前必须先using System.Collections.Generic;
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace _1208 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { List<int> list = new List<int>(10); //实例化 如果不给长度的话 默认长度为4 Console.WriteLine(list.Capacity); //获取最大长度 for (int i = list.Capacity; i > 0; i--) { list.Add(i); //遍历添加数据 Add() } foreach (int item in list) { Console.Write(item + " "); //打印数据 } Console.WriteLine(); list.RemoveAt(5); //移除指定索引位置的数据 RemoveAt(index) foreach (int item in list) { Console.Write(item + " "); } Console.WriteLine(); list[7] = 15; //指定索引位置赋值 list.Remove(15); //按元素删除 Remove(要删的数据内容) list.Insert(2, 100); //指定索引插入数据 Console.WriteLine(list.IndexOf(100)); //通过值找索引 从前往后 Console.WriteLine("从后往前 " +list.LastIndexOf(100)); //通过值找索引 从后往前找 bool isHave = list.Contains(100); //查找是否含有某个数据 Console.WriteLine(isHave); Console.WriteLine(list.Count); //实际长度 Console.WriteLine(list.Capacity); //总长度
注意
赋值:通过索引器赋值时,传入的索引要小于count的值
删除:需要删除的索引值必须小于count
插入:必须要在有值的范围内插入
查找:通过值查找索引,如果该集合中没有这个值,则返回-1
List排序
可以使用Sort方法直接对基本数据类型进行排序List可以对继承了IComparable<T>接口的类或结构体进行排序
返回值<0:此实例在排序顺序中位于other之前
返回值>0:此实例在排序顺序中位于other之后
返回值==0:此实例与other实例位置不变
排序练习

public int CompareTo(Drug other) { //判断类型是否相同,如果不同,两者类型互减,如果相同则判断品质谁前谁后 return !(this.type == other.type) ? (int)this.type - (int)other.type : (int)this.quality - (int)other.quality; }
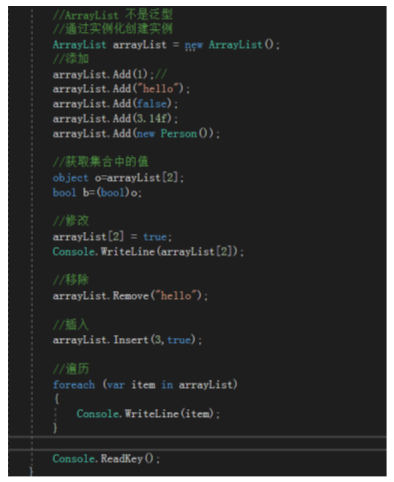
ArrayList
直接通过实例化创建
不是泛型的
ArrayList创建的集合可以存储任何类型
拆箱和装箱--慎用(消耗性能较大)
拆箱:Object转换成子类
装箱:将子类转换成Object类型
拆箱装箱都非常消耗性能
ArrayList和List的区别

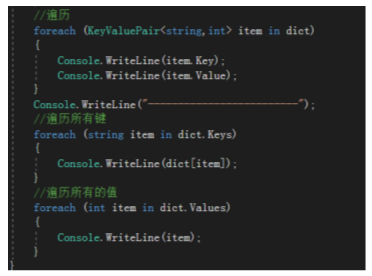
Dictionary字典
散列排列
字典的结构
字典在内存中为散列结构,用Key来索引对应Value,方便修改和查找(高于列表)
每对数据分为“键”和“值”
申请字典对象时需要指定键和值的类型
使用键值对的方式存取数据
字典也是泛型的
字典的特性
无序的
字典的元素是成对出现的
字典中的“键”不能重复
通过“键”去索引该键值对