微软Visual C++是Win32最广泛使用的编译器,因此Win32反向器对其内部工作非常熟悉。能够识别编译器生成的粘合代码有助于快速集中于程序员编写的实际代码。它还有助于恢复程序的高级结构。我将集中讨论MSVC编译程序中的堆栈布局、异常处理和相关结构。假设对汇编程序、寄存器、调用约定等有一定的了解。
名词解释:
- Stack frame---堆栈帧,函数使用的堆栈段的片段。通常包含函数参数、返回调用方地址、保存的寄存器、局部变量和其他特定于此函数的数据。在x86(和大多数其他架构)上,调用者和被调用者堆栈帧是连续的。
- Frame pointer---帧指针,指向堆栈帧内固定位置的寄存器或其他变量。通常堆栈帧中的所有数据都是相对于帧指针寻址的。在x86上,它通常是ebp,通常指向返回地址的正下方。
- Object---对象,(C++)类的一个实例。
- Unwindable Object---不可逆转的对象,具有自动存储类说明符的本地对象,在堆栈上分配,超出范围时需要销毁。
- Stack UInwinding---堆栈展开:当控制由于异常而离开作用域时,自动销毁此类对象。
win32里C/C++异常分类
在C或C++程序中可以使用两种类型的异常。
- SEH异常(来自“结构化异常处理”)。也称为Win32或系统异常。著名的Matt Pietrek文章[1]详尽地介绍了这些内容。它们是C程序唯一可用的例外。编译器级别的支持包括关键字try、except、finally和其他一些关键字。
- C++异常(有时称为“EH”)。在SEH之上实现,C++异常允许任意类型的抛出和捕获。C++的一个非常重要的特点是在异常处理过程中自动堆栈展开,而MSVC使用一个非常复杂的底层框架来保证它在所有情况下都能正常工作。
栈基本布局
...
Local variables
Other saved registers
Saved ebp
Return address
Function arguments
..
注意:如果启用帧指针省略,则保存的ebp可能不存在。
SEH栈
在使用编译器级SEH(__try/__except/__finally)的情况下,堆栈布局会变得更复杂一些。
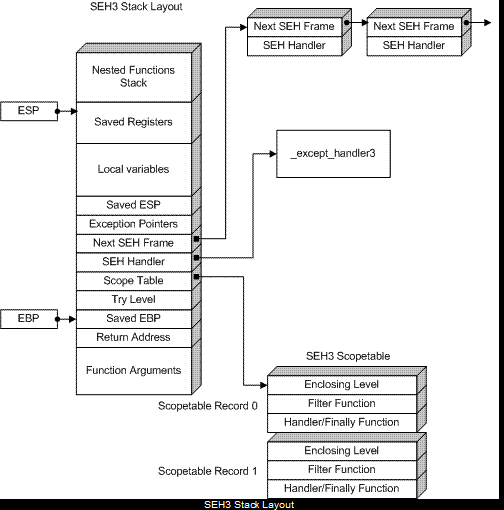
当函数中只有__finally块而没有__except块时,保存ESP是没有用的。Scopetable是一个记录数组,它描述每个__try块及其之间的关系:
struct _SCOPETABLE_ENTRY {
DWORD EnclosingLevel;
void* FilterFunc;
void* HandlerFunc;
}
要恢复try块,请查看try level变量的更新方式。它为每个try块分配一个唯一的数字,嵌套由scopetable条目之间的关系描述。例如,如果scopetable条目i包含EnclosingLevel=j,则try块j包含try块i。函数体被认为具有try level-1。
缓冲区溢出保护
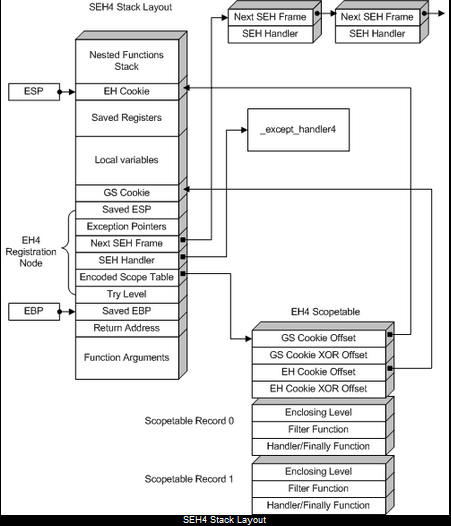
只有使用/GS开关编译函数时,才存在GS cookie。EHcookie总是存在的。SEH4 scopetable与SEH3基本相同,只是添加了头:
struct _EH4_SCOPETABLE {
DWORD GSCookieOffset;
DWORD GSCookieXOROffset;
DWORD EHCookieOffset;
DWORD EHCookieXOROffset;
_EH4_SCOPETABLE_RECORD ScopeRecord[1];
};
struct _EH4_SCOPETABLE_RECORD {
DWORD EnclosingLevel;
long (*FilterFunc)();
union {
void (*HandlerAddress)();
void (*FinallyFunc)();
};
};
GSCookieOffset=-2表示不使用GS cookie。EH cookie总是存在的。偏移具有相对ebp。检查方式如下:(ebp+CookieXOROffset) ^ [ebp+CookieOffset]==指向堆栈中scopetable的“_security_cookie"指针也与“_security_cookie"进行异或。所以,在SEH4中,最外层的作用域级别是-2,而不是像SEH3中的-1。
C++异常模型的实现
当C++异常处理(try/catch)或不可展开对象出现在函数中时,情况变得非常复杂。
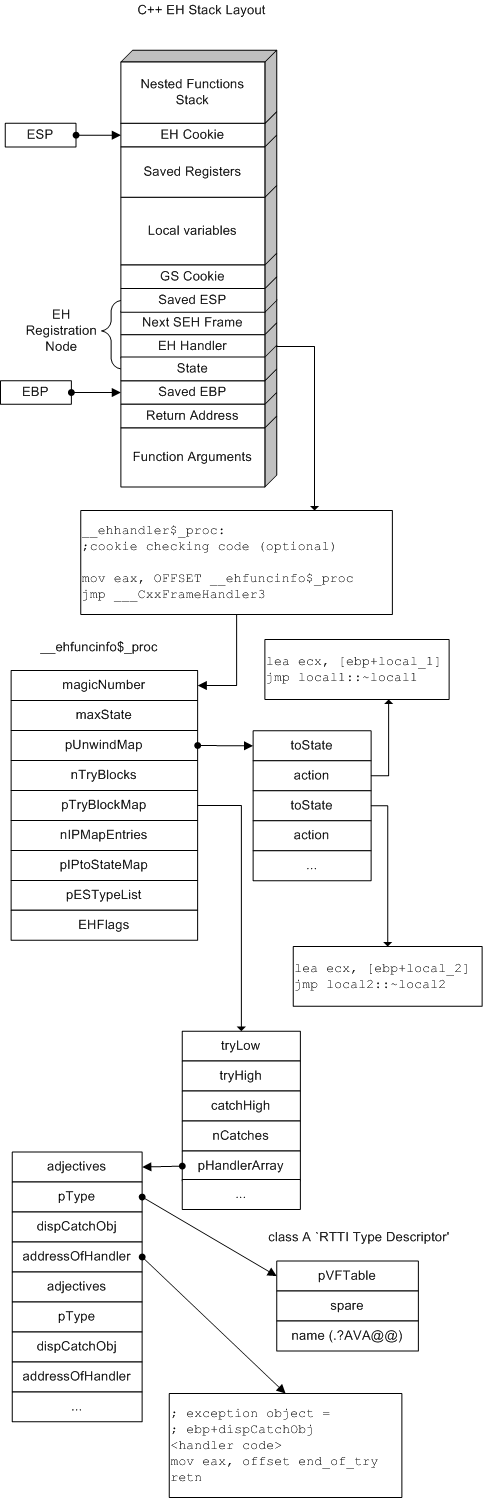
EH处理程序对于每个函数都是不同的(与SEH情况不同),通常如下所示:
(VC7+)
mov eax, OFFSET __ehfuncinfo
jmp ___CxxFrameHandler
__ehfuncinfo is a structure of type FuncInfo which fully describes all try/catch blocks and unwindable objects in the function.
struct FuncInfo {
// compiler version.
// 0x19930520: up to VC6, 0x19930521: VC7.x(2002-2003), 0x19930522: VC8 (2005)
DWORD magicNumber;
// number of entries in unwind table
int maxState;
// table of unwind destructors
UnwindMapEntry* pUnwindMap;
// number of try blocks in the function
DWORD nTryBlocks;
// mapping of catch blocks to try blocks
TryBlockMapEntry* pTryBlockMap;
// not used on x86
DWORD nIPMapEntries;
// not used on x86
void* pIPtoStateMap;
// VC7+ only, expected exceptions list (function "throw" specifier)
ESTypeList* pESTypeList;
// VC8+ only, bit 0 set if function was compiled with /EHs
int EHFlags;
};
Unwind map is similar to the SEH scopetable, only without filter functions:
struct UnwindMapEntry {
int toState; // target state
void (*action)(); // action to perform (unwind funclet address)
};
Try block descriptor. Describes a try{} block with associated catches.
struct TryBlockMapEntry {
int tryLow;
int tryHigh; // this try {} covers states ranging from tryLow to tryHigh
int catchHigh; // highest state inside catch handlers of this try
int nCatches; // number of catch handlers
HandlerType* pHandlerArray; //catch handlers table
};
Catch block descriptor. Describes a single catch() of a try block.
struct HandlerType {
// 0x01: const, 0x02: volatile, 0x08: reference
DWORD adjectives;
// RTTI descriptor of the exception type. 0=any (ellipsis)
TypeDescriptor* pType;
// ebp-based offset of the exception object in the function stack.
// 0 = no object (catch by type)
int dispCatchObj;
// address of the catch handler code.
// returns address where to continues execution (i.e. code after the try block)
void* addressOfHandler;
};
List of expected exceptions (implemented but not enabled in MSVC by default, use /d1ESrt to enable).
struct ESTypeList {
// number of entries in the list
int nCount;
// list of exceptions; it seems only pType field in HandlerType is used
HandlerType* pTypeArray;
};
RTTI type descriptor. Describes a single C++ type. Used here to match the thrown exception type with catch type.
struct TypeDescriptor {
// vtable of type_info class
const void * pVFTable;
// used to keep the demangled name returned by type_info::name()
void* spare;
// mangled type name, e.g. ".H" = "int", ".?AUA@@" = "struct A", ".?AVA@@" = "class A"
char name[0];
};
与SEH不同,每个try块没有一个关联的状态值。编译器不仅在进入/离开try块时更改状态值,而且还为每个构造/销毁的对象更改状态值。这样就可以知道发生异常时哪些对象需要展开。您仍然可以通过检查关联的状态范围和catch处理程序返回的地址来恢复try块边界。
抛出C++异常
throw语句被转换为_CxxThrowException()的调用,这实际上引发了一个Win32(SEH)异常,代码为0xE06D7363('msc'| 0xe000000)。Win32异常的自定义参数包括指向异常对象及其ThrowInfo结构的指针,使用这些指针,异常处理程序可以将抛出的异常类型与catch处理程序所期望的类型相匹配。
struct ThrowInfo {
// 0x01: const, 0x02: volatile
DWORD attributes;
// exception destructor
void (*pmfnUnwind)();
// forward compatibility handler
int (*pForwardCompat)();
// list of types that can catch this exception.
// i.e. the actual type and all its ancestors.
CatchableTypeArray* pCatchableTypeArray;
};
struct CatchableTypeArray {
// number of entries in the following array
int nCatchableTypes;
CatchableType* arrayOfCatchableTypes[0];
};
Describes a type that can catch this exception.
struct CatchableType {
// 0x01: simple type (can be copied by memmove), 0x02: can be caught by reference only, 0x04: has virtual bases
DWORD properties;
// see above
TypeDescriptor* pType;
// how to cast the thrown object to this type
PMD thisDisplacement;
// object size
int sizeOrOffset;
// copy constructor address
void (*copyFunction)();
};
// Pointer-to-member descriptor.
struct PMD {
// member offset
int mdisp;
// offset of the vbtable (-1 if not a virtual base)
int pdisp;
// offset to the displacement value inside the vbtable
int vdisp;
};
Prologs and Epilogs
编译器可以选择调用特定的prolog和epilog函数,而不是在函数体中发出用于设置堆栈帧的代码。有几个变体,每个都用于特定的函数类型:
| Name | Type | EH Cookie | GS Cookie | Catch Handlers |
| _SEH_prolog/_SEH_epilog | SEH3 | - | - | |
| _SEH_prolog4/_SEH_epilog4 S | EH4 | + | - | |
| _SEH_prolog4_GS/_SEH_epilog4_GS | SEH4 | + | + | |
| _EH_prolog | C++ EH | - | - | +/- |
| _EH_prolog3/_EH_epilog3 | C++ EH | + | - | - |
| _EH_prolog3_catch/_EH_epilog3 | C++ EH | + | - | + |
| _EH_prolog3_GS/_EH_epilog3_GS | C++ EH | + | + | - |
| _EH_prolog3_catch_GS/_EH_epilog3_catch_GS | C++ EH | + | + | + |
SEH2
显然是由MSVC 1.XX(由crtdll.dll导出)使用的。在一些旧的NT程序中遇到。
...
Saved edi
Saved esi
Saved ebx
Next SEH frame
Current SEH handler (__except_handler2)
Pointer to the scopetable
Try level
Saved ebp (of this function)
Exception pointers
Local variables
Saved ESP
Local variables
Callee EBP
Return address
Function arguments
...
附录一:SEH例子
让我们考虑下面的示例反汇编。
func1 proc near _excCode = dword ptr -28h buf = byte ptr -24h _saved_esp = dword ptr -18h _exception_info = dword ptr -14h _next = dword ptr -10h _handler = dword ptr -0Ch _scopetable = dword ptr -8 _trylevel = dword ptr -4 str = dword ptr 8 push ebp mov ebp, esp push -1 push offset _func1_scopetable push offset _except_handler3 mov eax, large fs:0 push eax mov large fs:0, esp add esp, -18h push ebx push esi push edi ; --- end of prolog --- mov [ebp+_trylevel], 0 ;trylevel -1 -> 0: beginning of try block 0 mov [ebp+_trylevel], 1 ;trylevel 0 -> 1: beginning of try block 1 mov large dword ptr ds:123, 456 mov [ebp+_trylevel], 0 ;trylevel 1 -> 0: end of try block 1 jmp short _endoftry1 _func1_filter1: ; __except() filter of try block 1 mov ecx, [ebp+_exception_info] mov edx, [ecx+EXCEPTION_POINTERS.ExceptionRecord] mov eax, [edx+EXCEPTION_RECORD.ExceptionCode] mov [ebp+_excCode], eax mov ecx, [ebp+_excCode] xor eax, eax cmp ecx, EXCEPTION_ACCESS_VIOLATION setz al retn _func1_handler1: ; beginning of handler for try block 1 mov esp, [ebp+_saved_esp] push offset aAccessViolatio ; "Access violation" call _printf add esp, 4 mov [ebp+_trylevel], 0 ;trylevel 1 -> 0: end of try block 1 _endoftry1: mov edx, [ebp+str] push edx lea eax, [ebp+buf] push eax call _strcpy add esp, 8 mov [ebp+_trylevel], -1 ; trylevel 0 -> -1: end of try block 0 call _func1_handler0 ; execute __finally of try block 0 jmp short _endoftry0 _func1_handler0: ; __finally handler of try block 0 push offset aInFinally ; "in finally" call _puts add esp, 4 retn _endoftry0: ; --- epilog --- mov ecx, [ebp+_next] mov large fs:0, ecx pop edi pop esi pop ebx mov esp, ebp pop ebp retn func1 endp _func1_scopetable ;try block 0 dd -1 ;EnclosingLevel dd 0 ;FilterFunc dd offset _func1_handler0 ;HandlerFunc ;try block 1 dd 0 ;EnclosingLevel dd offset _func1_filter1 ;FilterFunc dd offset _func1_handler1 ;HandlerFunc
0号try块没有筛选器,因此其处理程序是一个__finally{}块。1号try块的封闭级别为0,因此它位于0号try块中。考虑到这一点,我们可以尝试重建功能结构:
void func1 (char* str) { char buf[12]; __try // try block 0 { __try // try block 1 { *(int*)123=456; } __except(GetExceptCode() == EXCEPTION_ACCESS_VIOLATION) { printf("Access violation"); } strcpy(buf,str); } __finally { puts("in finally"); } }
附录II:用汇编实现C++异常的示例程序
func1 proc near _a1 = dword ptr -24h _exc = dword ptr -20h e = dword ptr -1Ch a2 = dword ptr -18h a1 = dword ptr -14h _saved_esp = dword ptr -10h _next = dword ptr -0Ch _handler = dword ptr -8 _state = dword ptr -4 push ebp mov ebp, esp push 0FFFFFFFFh push offset func1_ehhandler mov eax, large fs:0 push eax mov large fs:0, esp push ecx sub esp, 14h push ebx push esi push edi mov [ebp+_saved_esp], esp ; --- end of prolog --- lea ecx, [ebp+a1] call A::A(void) mov [ebp+_state], 0 ; state -1 -> 0: a1 constructed mov [ebp+a1], 1 ; a1.m1 = 1 mov byte ptr [ebp+_state], 1 ; state 0 -> 1: try { lea ecx, [ebp+a2] call A::A(void) mov [ebp+_a1], eax mov byte ptr [ebp+_state], 2 ; state 2: a2 constructed mov [ebp+a2], 2 ; a2.m1 = 2 mov eax, [ebp+a1] cmp eax, [ebp+a2] ; a1.m1 == a2.m1? jnz short loc_40109F mov [ebp+_exc], offset aAbc ; _exc = "abc" push offset __TI1?PAD ; char * lea ecx, [ebp+_exc] push ecx call _CxxThrowException ; throw "abc"; loc_40109F: mov byte ptr [ebp+_state], 1 ; state 2 -> 1: destruct a2 lea ecx, [ebp+a2] call A::~A(void) jmp short func1_try0end ; catch (char * e) func1_try0handler_pchar: mov edx, [ebp+e] push edx push offset aCaughtS ; "Caught %s " call ds:printf ; add esp, 8 mov eax, offset func1_try0end retn ; catch (...) func1_try0handler_ellipsis: push offset aCaught___ ; "Caught ... " call ds:printf add esp, 4 mov eax, offset func1_try0end retn func1_try0end: mov [ebp+_state], 0 ; state 1 -> 0: }//try push offset aAfterTry ; "after try " call ds:printf add esp, 4 mov [ebp+_state], -1 ; state 0 -> -1: destruct a1 lea ecx, [ebp+a1] call A::~A(void) ; --- epilog --- mov ecx, [ebp+_next] mov large fs:0, ecx pop edi pop esi pop ebx mov esp, ebp pop ebp retn func1 endp func1_ehhandler proc near mov eax, offset func1_funcinfo jmp __CxxFrameHandler func1_ehhandler endp func1_funcinfo dd 19930520h ; magicNumber dd 4 ; maxState dd offset func1_unwindmap ; pUnwindMap dd 1 ; nTryBlocks dd offset func1_trymap ; pTryBlockMap dd 0 ; nIPMapEntries dd 0 ; pIPtoStateMap dd 0 ; pESTypeList func1_unwindmap dd -1 dd offset func1_unwind_1tobase ; action dd 0 ; toState dd 0 ; action dd 1 ; toState dd offset func1_unwind_2to1 ; action dd 0 ; toState dd 0 ; action func1_trymap dd 1 ; tryLow dd 2 ; tryHigh dd 3 ; catchHigh dd 2 ; nCatches dd offset func1_tryhandlers_0 ; pHandlerArray dd 0 func1_tryhandlers_0 dd 0 ; adjectives dd offset char * `RTTI Type Descriptor' ; pType dd -1Ch ; dispCatchObj dd offset func1_try0handler_pchar ; addressOfHandler dd 0 ; adjectives dd 0 ; pType dd 0 ; dispCatchObj dd offset func1_try0handler_ellipsis ; addressOfHandler func1_unwind_1tobase proc near a1 = byte ptr -14h lea ecx, [ebp+a1] call A::~A(void) retn func1_unwind_1tobase endp func1_unwind_2to1 proc near a2 = byte ptr -18h lea ecx, [ebp+a2] call A::~A(void) retn func1_unwind_2to1 endp
让我们看看这里能找到什么。FuncInfo结构中的maxState字段是4,这意味着展开映射中有4个条目,从0到3。通过检查映射,我们可以看到在展开期间执行以下操作:
- 状态3->状态0(无操作)
- 状态2->状态1(销毁a2)
- 状态1->状态0(无操作)
- 状态0->状态-1(析构函数a1)
检查try map,我们可以推断状态1和2对应于try块体,状态3对应于catch块体。因此,从状态0更改为状态1表示try块的开始,从1更改为0表示try块的结束。从函数代码中我们还可以看到-1->0是a1的构造,1->2是a2的构造。所以状态图如下:
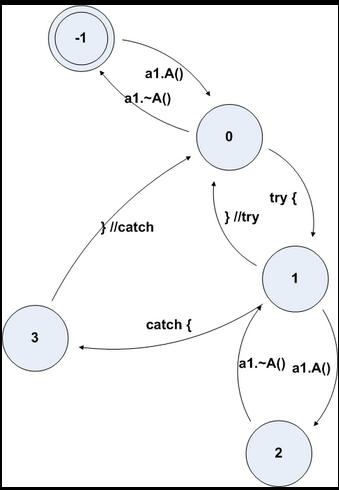
箭头1->3是从哪里来的?我们无法在函数代码或FuncInfo结构中看到它,因为它是由异常处理程序完成的。如果异常发生在try块中,异常处理程序首先将堆栈展开为tryLow值(在本例中为1),然后在调用catch处理程序之前将状态值设置为tryHigh+1(2+1=3)。
void func1 () { A a1; a1.m1 = 1; try { A a2; a2.m1 = 2; if (a1.m1 == a1.m2) throw "abc"; } catch(char* e) { printf("Caught %s ",e); } catch(...) { printf("Caught ... "); } printf("after try "); }