Golang并发编程-select实战篇
作者:尹正杰
版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任。
一.select概述
Go里面提供了一个关键字select,通过select可以监听channel上的数据流动。
有时候我们希望能够借助channel发送或接收数据,并避免因为发送或者接收导致的阻塞,尤其是当channel没有准备好写或者读时。select语句就可以实现这样的功能。
select的用法与switch语言非常类似,由select开始一个新的选择块,每个选择条件由case语句来描述。
与switch语句相比,select有比较多的限制,其中最大的一条限制就是每个case语句里必须是一个IO操作,
二.select的应用案例
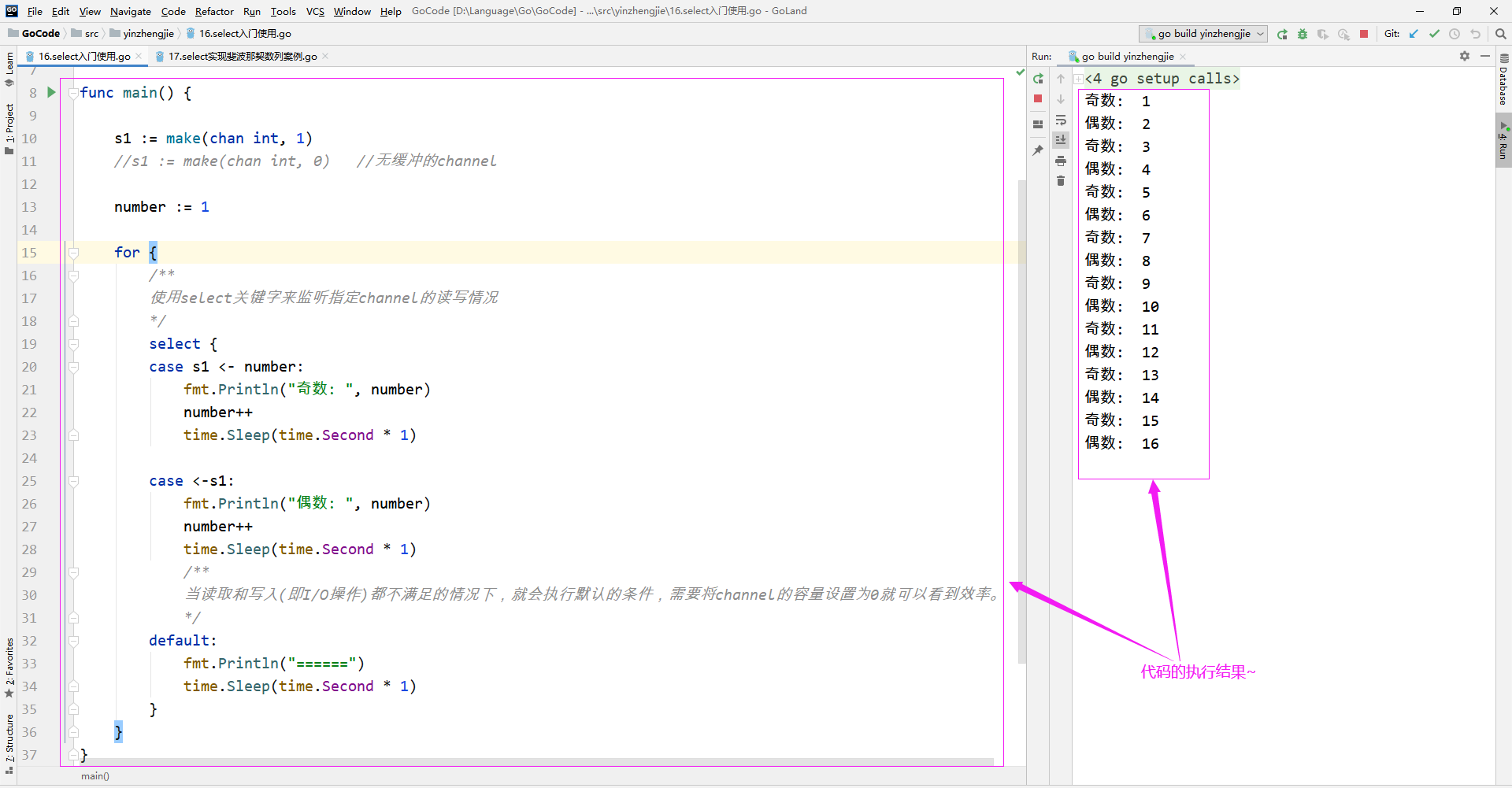
1>.select入门案例
package main import ( "fmt" "time" ) func main() { s1 := make(chan int, 1) //s1 := make(chan int, 0) //无缓冲的channel number := 1 for { /** 使用select关键字来监听指定channel的读写情况 */ select { case s1 <- number: fmt.Println("奇数: ", number) number++ time.Sleep(time.Second * 1) case <-s1: fmt.Println("偶数: ", number) number++ time.Sleep(time.Second * 1) /** 当读取和写入(即I/O操作)都不满足的情况下,就会执行默认的条件,需要将channel的容量设置为0就可以看到效率。 */ default: fmt.Println("======") time.Sleep(time.Second * 1) } } }
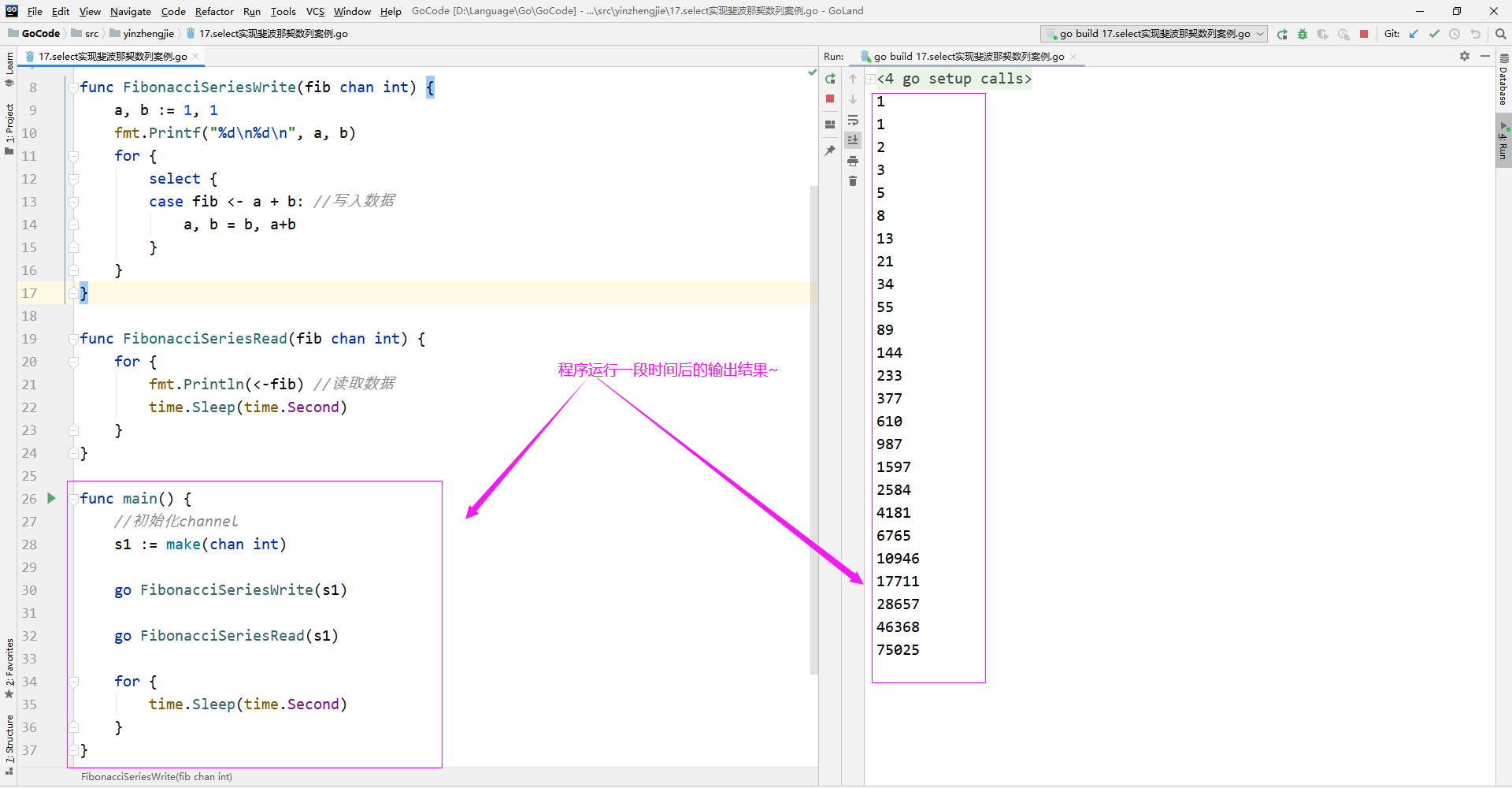
2>.select实现斐波那契数列案例
package main import ( "fmt" "time" ) func FibonacciSeriesWrite(fib chan int) { a, b := 1, 1 fmt.Printf("%d %d ", a, b) for { select { case fib <- a + b: //写入数据 a, b = b, a+b } } } func FibonacciSeriesRead(fib chan int) { for { fmt.Println(<-fib) //读取数据 time.Sleep(time.Second) } } func main() { //初始化channel s1 := make(chan int) go FibonacciSeriesWrite(s1) go FibonacciSeriesRead(s1) for { time.Sleep(time.Second) } }
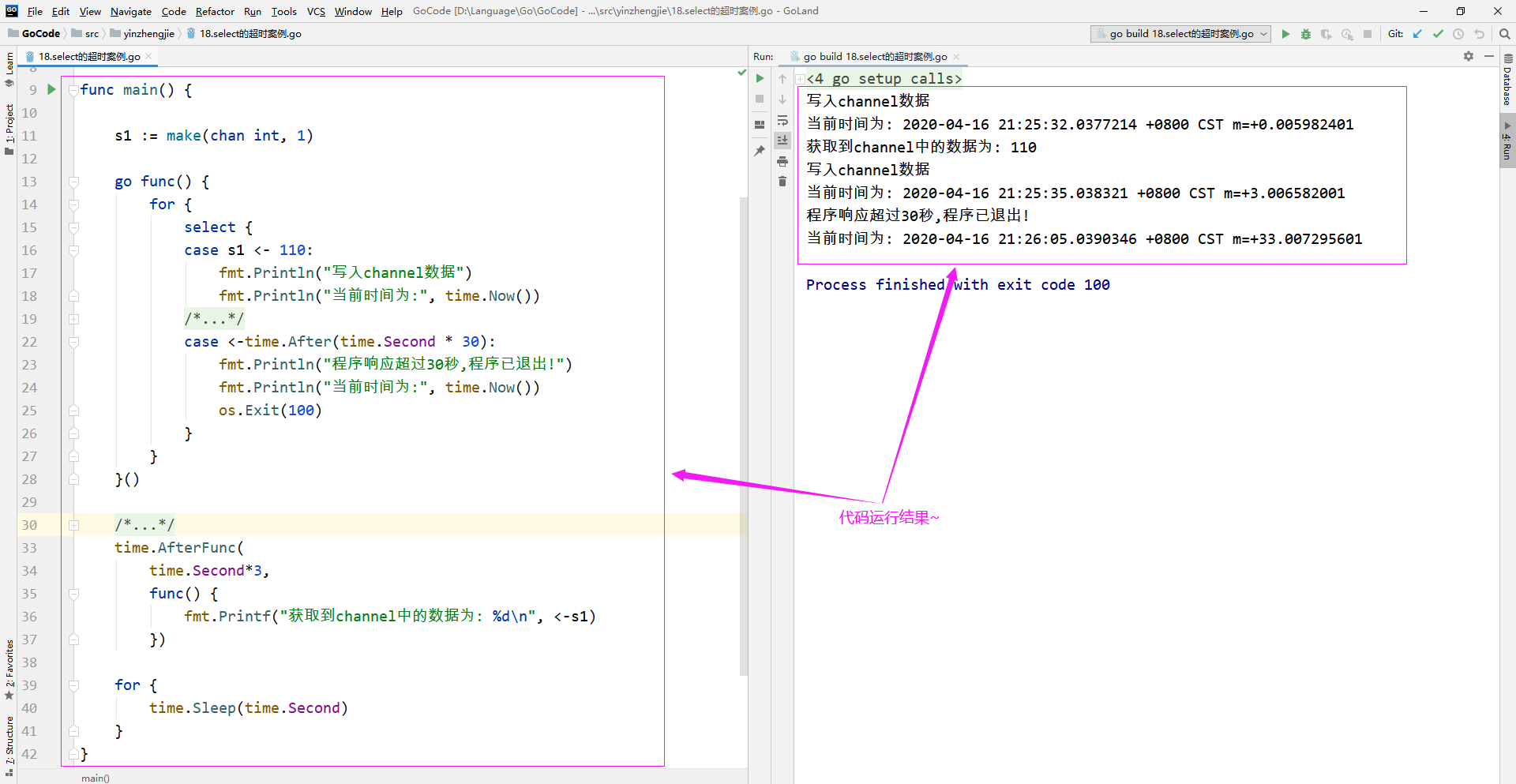
3>.select实现超时案例
package main import ( "fmt" "os" "time" ) func main() { s1 := make(chan int, 1) go func() { for { select { case s1 <- 110: fmt.Println("写入channel数据") fmt.Println("当前时间为:", time.Now()) /** 设置定时器,当channel中的数据在30秒内没有被消费时,就会退出程序。 */ case <-time.After(time.Second * 30): fmt.Println("程序响应超过30秒,程序已退出!") fmt.Println("当前时间为:", time.Now()) os.Exit(100) } } }() /** 设置一次性定时器,仅消费一次数据哟~ */ time.AfterFunc( time.Second*3, func() { fmt.Printf("获取到channel中的数据为: %d ", <-s1) }) for { time.Sleep(time.Second) } }