iOS开发UI篇—ios应用数据存储方式(归档)
一、简单说明
在使用plist进行数据存储和读取,只适用于系统自带的一些常用类型才能用,且必须先获取路径相对麻烦;
偏好设置(将所有的东西都保存在同一个文件夹下面,且主要用于存储应用的设置信息)
归档:因为前两者都有一个致命的缺陷,只能存储常用的类型。归档可以实现把自定义的对象存放在文件中。
二、代码示例
1.文件结构

2.代码示例
YYViewController.m文件
// // YYViewController.m // 02-归档 // // Created by apple on 14-6-7. // Copyright (c) 2014年 itcase. All rights reserved. // #import "YYViewController.h" #import "YYPerson.h" @interface YYViewController () - (IBAction)saveBtnOnclick:(id)sender; - (IBAction)readBtnOnclick:(id)sender; @end @implementation YYViewController - (void)viewDidLoad { [super viewDidLoad]; } - (IBAction)saveBtnOnclick:(id)sender { //1.创建对象 YYPerson *p=[[YYPerson alloc]init]; p.name=@"文顶顶"; p.age=23; p.height=1.7; //2.获取文件路径 NSString *docPath=[NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES)lastObject]; NSString *path=[docPath stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"person.yangyang"]; NSLog(@"path=%@",path); //3.将自定义的对象保存到文件中 [NSKeyedArchiver archiveRootObject:p toFile:path]; } - (IBAction)readBtnOnclick:(id)sender { //1.获取文件路径 NSString *docPath=[NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES)lastObject]; NSString *path=[docPath stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"person.yangyang"]; NSLog(@"path=%@",path); //2.从文件中读取对象 YYPerson *p=[NSKeyedUnarchiver unarchiveObjectWithFile:path]; NSLog(@"%@,%d,%.1f",p.name,p.age,p.height); } @end
新建一个person类
YYPerson.h文件
// // YYPerson.h // 02-归档 // // Created by apple on 14-6-7. // Copyright (c) 2014年 itcase. All rights reserved. // #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> // 如果想将一个自定义对象保存到文件中必须实现NSCoding协议 @interface YYPerson : NSObject<NSCoding> //姓名 @property(nonatomic,copy)NSString *name; //年龄 @property(nonatomic,assign)int age; //身高 @property(nonatomic,assign)double height; @end
YYPerson.m文件
// // YYPerson.m // 02-归档 // // Created by apple on 14-6-7. // Copyright (c) 2014年 itcase. All rights reserved. // #import "YYPerson.h" @implementation YYPerson // 当将一个自定义对象保存到文件的时候就会调用该方法 // 在该方法中说明如何存储自定义对象的属性 // 也就说在该方法中说清楚存储自定义对象的哪些属性 -(void)encodeWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aCoder { NSLog(@"调用了encodeWithCoder:方法"); [aCoder encodeObject:self.name forKey:@"name"]; [aCoder encodeInteger:self.age forKey:@"age"]; [aCoder encodeDouble:self.height forKey:@"height"]; } // 当从文件中读取一个对象的时候就会调用该方法 // 在该方法中说明如何读取保存在文件中的对象 // 也就是说在该方法中说清楚怎么读取文件中的对象 -(id)initWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aDecoder { NSLog(@"调用了initWithCoder:方法"); //注意:在构造方法中需要先初始化父类的方法 if (self=[super init]) { self.name=[aDecoder decodeObjectForKey:@"name"]; self.age=[aDecoder decodeIntegerForKey:@"age"]; self.height=[aDecoder decodeDoubleForKey:@"height"]; } return self; } @end
3.打印效果和两个重要的错误提示
点击保存按钮和读取按钮,成功打印结果如下:

关于不实现两个协议方法的错误提示:
-(void)encodeWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aCoder方法:
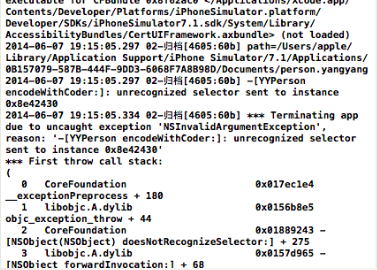
-(id)initWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aDecoder方法:
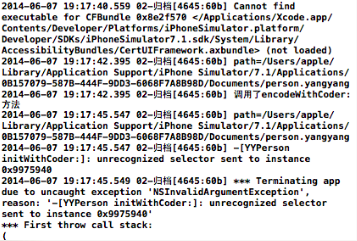
三、继承类中的使用
新建一个学生类,让这个类继承自Preson这个类,增加一个体重的属性。
YYstudent.h文件
// // YYstudent.h // 02-归档 // // Created by apple on 14-6-7. // Copyright (c) 2014年 itcase. All rights reserved. // #import "YYPerson.h" @interface YYstudent : YYPerson //增加一个体重属性 @property(nonatomic,assign) double weight; @end
YYstudent.m文件
// // YYstudent.m // 02-归档 // // Created by apple on 14-6-7. // Copyright (c) 2014年 itcase. All rights reserved. // #import "YYstudent.h" @implementation YYstudent //在子类中重写这两个方法 - (void)encodeWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aCoder { [super encodeWithCoder:aCoder]; NSLog(@"调用了YYStudent encodeWithCoder"); [aCoder encodeFloat:self.weight forKey:@"weight"]; } - (id)initWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aDecoder { if (self = [super initWithCoder:aDecoder]) { NSLog(@"调用了YYstudent initWithCoder"); self.weight = [aDecoder decodeFloatForKey:@"weight"]; } return self; } @end
YYViewController.m文件
// // YYViewController.m // 02-归档 // // Created by apple on 14-6-7. // Copyright (c) 2014年 itcase. All rights reserved. // #import "YYViewController.h" #import "YYPerson.h" #import "YYstudent.h" @interface YYViewController () - (IBAction)saveBtnOnclick:(id)sender; - (IBAction)readBtnOnclick:(id)sender; @end @implementation YYViewController - (void)viewDidLoad { [super viewDidLoad]; } - (IBAction)saveBtnOnclick:(id)sender { //1.创建对象 // YYPerson *p=[[YYPerson alloc]init]; // p.name=@"文顶顶"; // p.age=23; // p.height=1.7; YYstudent *s=[[YYstudent alloc]init]; s.name=@"wendingding"; s.age=23; s.height=1.7; s.weight=62; //2.获取文件路径 NSString *docPath=[NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES)lastObject]; NSString *path=[docPath stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"person.yangyang"]; NSLog(@"path=%@",path); //3.将自定义的对象保存到文件中 // [NSKeyedArchiver archiveRootObject:p toFile:path]; [NSKeyedArchiver archiveRootObject:s toFile:path]; } - (IBAction)readBtnOnclick:(id)sender { //1.获取文件路径 NSString *docPath=[NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES)lastObject]; NSString *path=[docPath stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"person.yangyang"]; NSLog(@"path=%@",path); //2.从文件中读取对象 // YYPerson *p=[NSKeyedUnarchiver unarchiveObjectWithFile:path]; // NSLog(@"%@,%d,%.1f",p.name,p.age,p.height); YYstudent *s=[NSKeyedUnarchiver unarchiveObjectWithFile:path]; NSLog(@"%@,%d,%.1f,%f",s.name,s.age,s.height,s.weight); } @end
点击保存按钮和读取按钮后的打印输出:
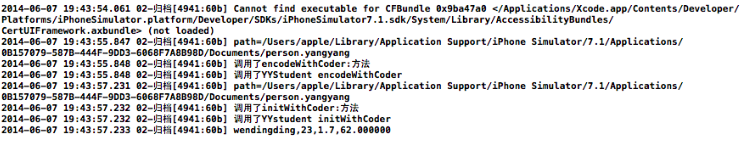
四、重要说明
1.保存数据过程:
//1.创建对象 YYstudent *s=[[YYstudent alloc]init]; s.name=@"wendingding"; s.age=23; s.height=1.7; s.weight=62; //2.获取文件路径 NSString *docPath=[NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES)lastObject]; NSString *path=[docPath stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"person.yangyang"]; NSLog(@"path=%@",path); //3.将自定义的对象保存到文件中 [NSKeyedArchiver archiveRootObject:s toFile:path];
2.读取数据过程:
//1.获取文件路径 NSString *docPath=[NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES)lastObject]; NSString *path=[docPath stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"person.yangyang"]; //2.从文件中读取对象 YYstudent *s=[NSKeyedUnarchiver unarchiveObjectWithFile:path];
3.遵守NSCoding协议,并实现该协议中的两个方法。
4.如果是继承,则子类一定要重写那两个方法。因为person的子类在存取的时候,会去子类中去找调用的方法,没找到那么它就去父类中找,所以最后保存和读取的时候新增加的属性会被忽略。需要先调用父类的方法,先初始化父类的,再初始化子类的。
5.保存数据的文件的后缀名可以随意命名。
6.通过plist保存的数据是直接显示的,不安全。通过归档方法保存的数据在文件中打开是乱码的,更安全。