1 package cn.bjsxt.test;
2
3 public class TestStudent {
4 public static void main(String[] args){
5 Student s1 = new Student();
6 s1.name = "yisa";
7 s1.study();
8 s1.sayHello("gujan");
9 }
10 }
11
12
13 class Student{
14 public String name;
15 int id;
16 public int age;
17 public String gender;
18 public int weight;
19
20 public void study() {
21 System.out.println(this.name+" is lerning!");
22 }
23
24 public void sayHello(String sname) {
25 System.out.println(this.name+" say Hello to "+sname);
26 }
27
28 }
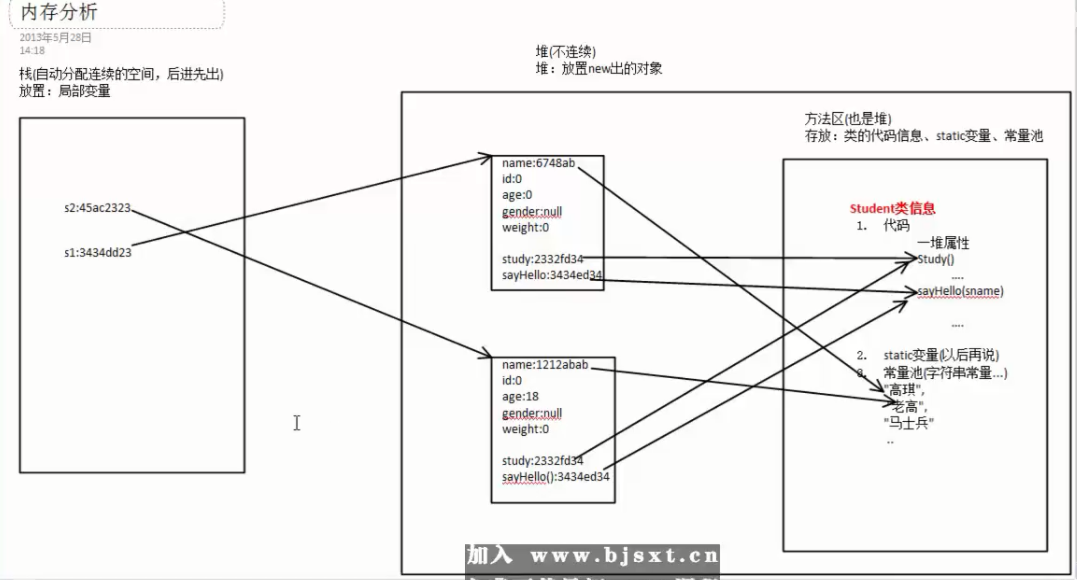
从头开始一行一行地分析Java在运行过程中的内存地址是如何分配的。
第5行:Student s1 = new Student(); 1.当JVM看到Student的时候,知道它是个类,于是通过Loader将类加载到方法区中。s1是局部变量放到栈里。
new Student 的意思是在堆中创建一个对象,并把该对象(连续空间)的首地址放入S1中(s1指向了该对象),此时对象属性全为默认值。
| 属性(方法) |
值(地址) |
| name |
null |
| id |
0 |
| age |
0 |
| gender |
null |
| study |
null |
| sayHello |
null |
第六行:s1.name = "yisa"; s1:找到栈里的s1,通过存放在它里的首地址找到对象(以上的表格),在方法区(堆)里创建一个字符串yisa,将其首地址付给对象里name.所以表格发生以下变化
name对应的nulll变成xx,(加入xx为“yisa”在方法区的地址)。
图如下