先看下这个问题的背景:假设有一个spring应用,开发人员希望自定义一个注解@Log,可以加到指定的方法上,实现自动记录日志(入参、出参、响应耗时这些)
package com.cnblogs.yjmyzz.springbootdemo.aspect;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface Log {
}
然后再写一个Aspect来解析这个注解,对打了Log注解的方法进行增强处理
package com.cnblogs.yjmyzz.springbootdemo.aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
@Component
@Aspect
public class LogAspect {
@Pointcut("execution (* com.cnblogs.yjmyzz.springbootdemo.service..*.*(..))")
public void logPointcut() {
}
@Around("logPointcut()")
public void around(JoinPoint point) {
String methodName = point.getSignature().getName();
Object[] args = point.getArgs();
Class<?>[] argTypes = new Class[point.getArgs().length];
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
argTypes[i] = args[i].getClass();
}
Method method = null;
try {
method = point.getTarget().getClass().getMethod(methodName, argTypes);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//获取方法上的注解
Log log = method.getAnnotation(Log.class);
if (log != null) {
//演示方法执行前,记录一行日志
System.out.println("before:" + methodName);
}
try {
//执行方法
((ProceedingJoinPoint) point).proceed();
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (log != null) {
//演示方法执行后,记录一行日志
System.out.println("after:" + methodName);
}
}
}
}
写一个测试Service类:
package com.cnblogs.yjmyzz.springbootdemo.service;
import com.cnblogs.yjmyzz.springbootdemo.aspect.Log;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class HelloService {
@Log
public void sayHi(String msg) {
System.out.println(" sayHi:" + msg);
}
public void anotherSayHi(String msg) {
this.sayHi(msg);
}
}
最后来跑一把:
package com.cnblogs.yjmyzz.springbootdemo;
import com.cnblogs.yjmyzz.springbootdemo.service.HelloService;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
/**
* @author 菩提树下的杨过
*/
@ComponentScan("com.cnblogs.yjmyzz")
@Configuration
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class SampleApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SampleApplication.class);
HelloService helloService = context.getBean(HelloService.class);
helloService.sayHi("hi-1");
System.out.println("
");
helloService.anotherSayHi("hi-2");
}
}
输出如下:
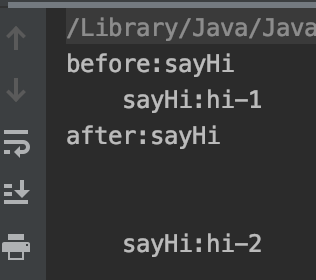
显然HelloService中的anotherSayHi方法,并未被aop增强。 原因其实很简单,了解AOP原理的同学想必都知道,AOP的实现有二类,如果是基于接口的,会采用动态代理,生成一个代理类,如果是基于类的,会采用CGLib生成子类,然后在子类中扩展父类中的方法。
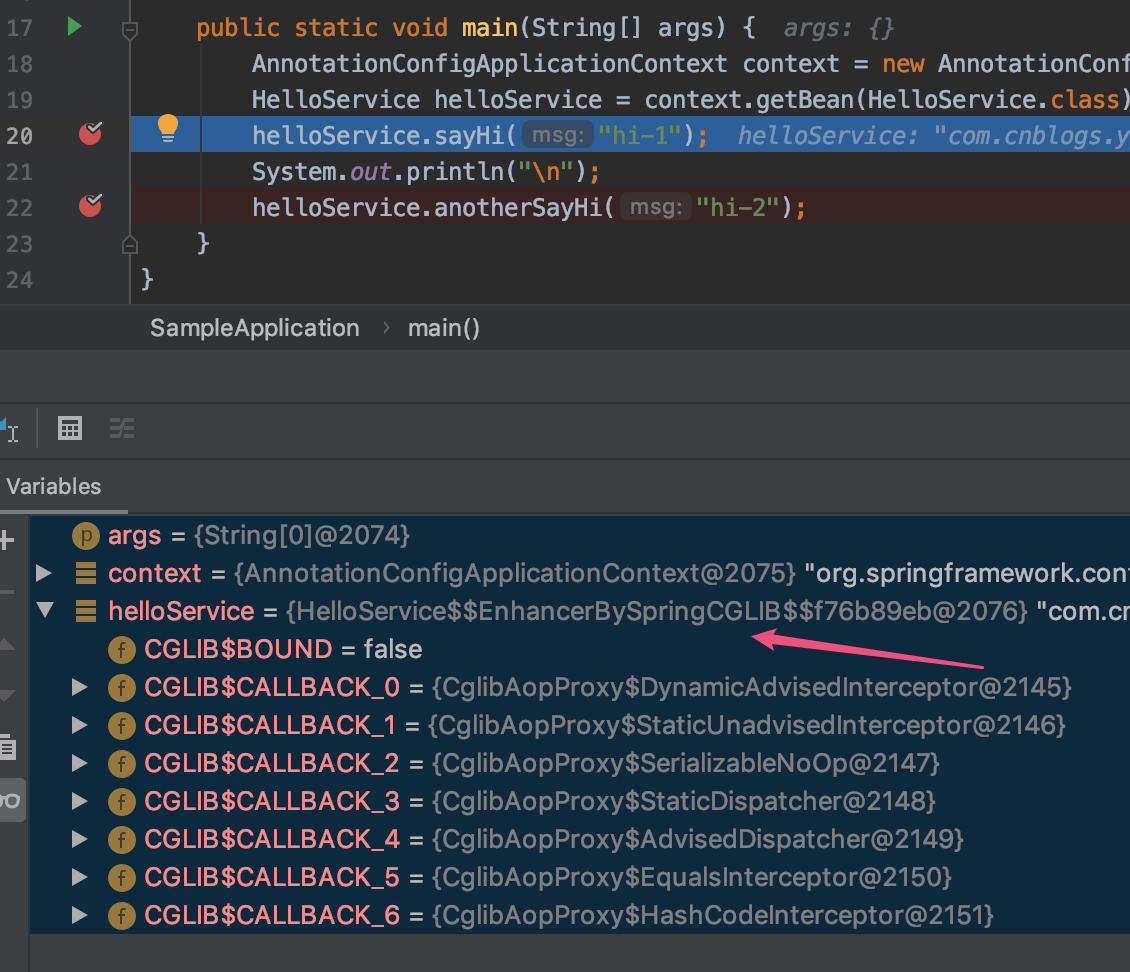
本文中HelloService并不是一个接口,所以从上图的断点中可以看出,当Spring运行时,HelloService被增加为...EnhancerBySpringCGLib...。但是当调用到anotherSayHi时
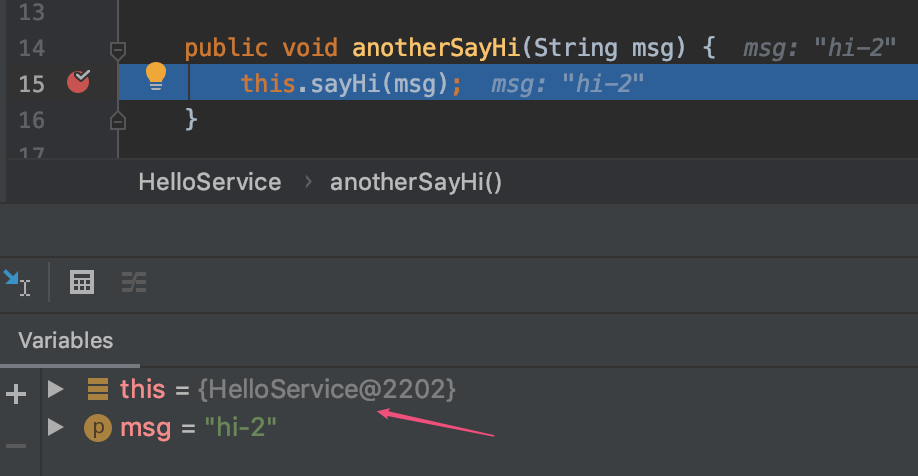
方法的调用方,其实是原始的HelloSerfvice实例,即:是未经过Spring AOP增强的对象实例。所以解决问题的思路就有了,想办法用增强后的HelloService实例来调用!
方法一:用Autowired 注入自身的实例
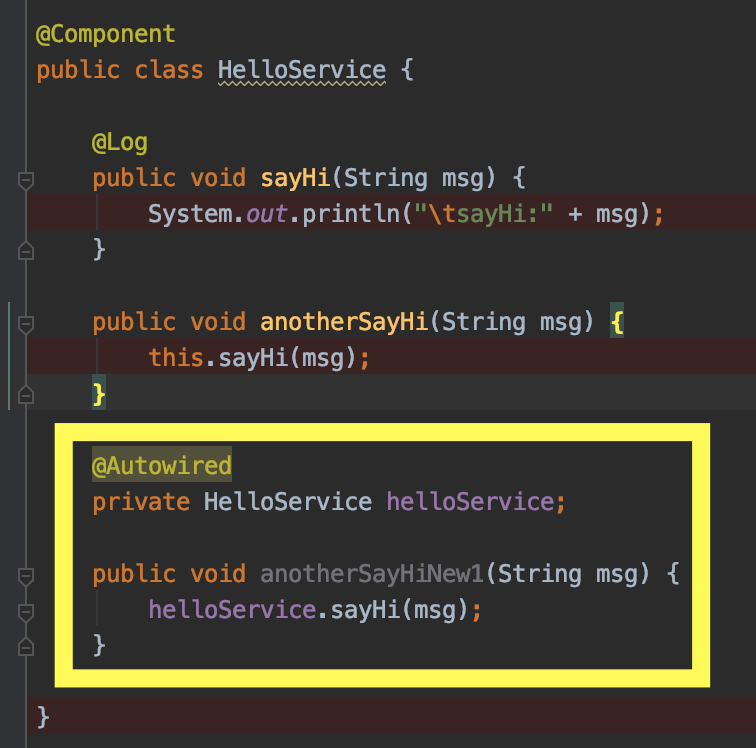
这个方法,第一眼看上去感觉有些怪,自己注入自己,感觉有点象递归/死循环的搞法,但确实可以work,Spring在解决循环依赖上有自己的处理方式,避免了死循环。
方法二:从Spring上下文获取增强后的实例引用
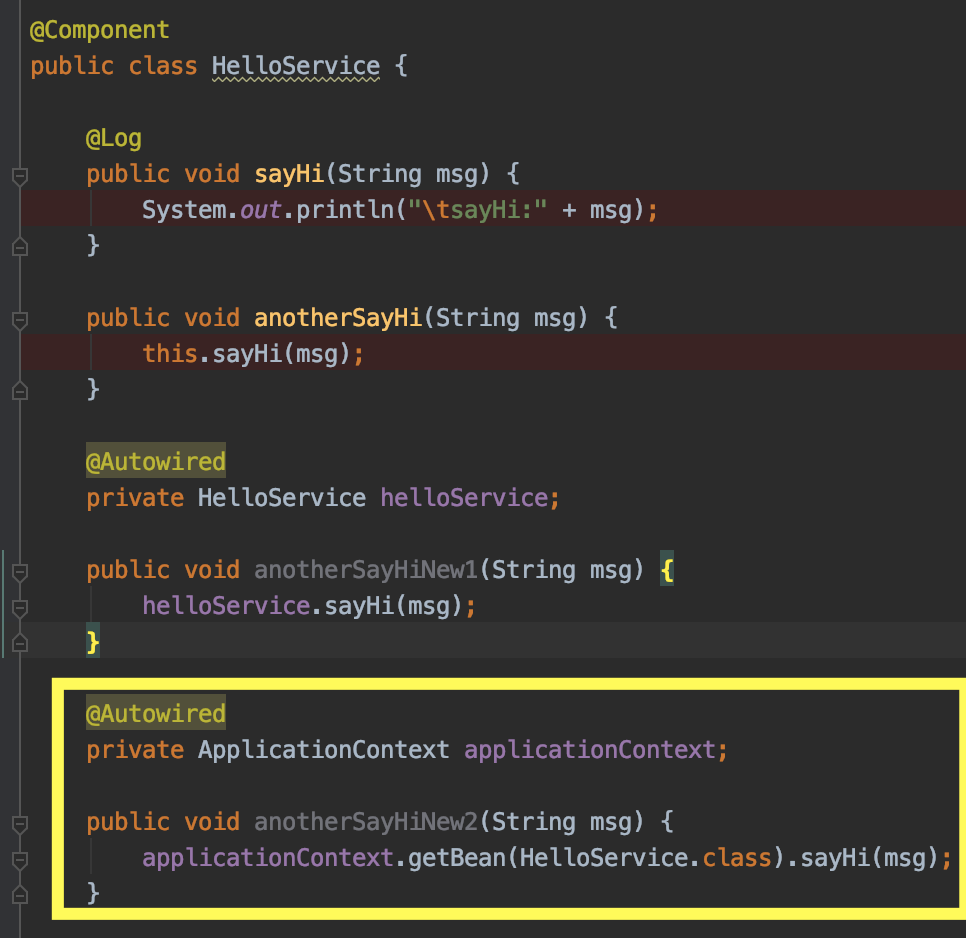
原理与方法一其实类似,不多解释。
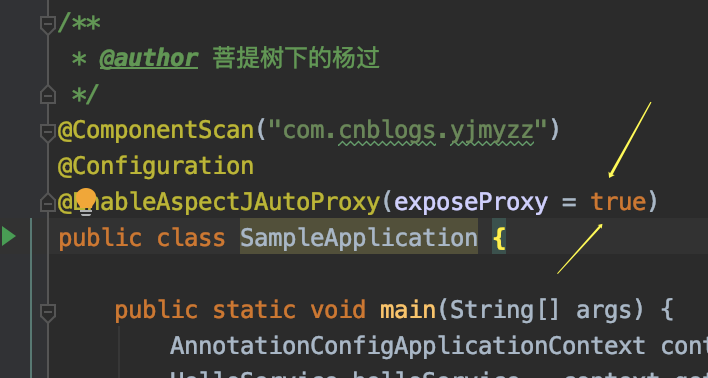
方法三: 利用AopContext

不过这个方法要注意的是,主类入口上,必须加上exporseProxy=true,参考下图:
最后来验证下这3种方法是否生效:
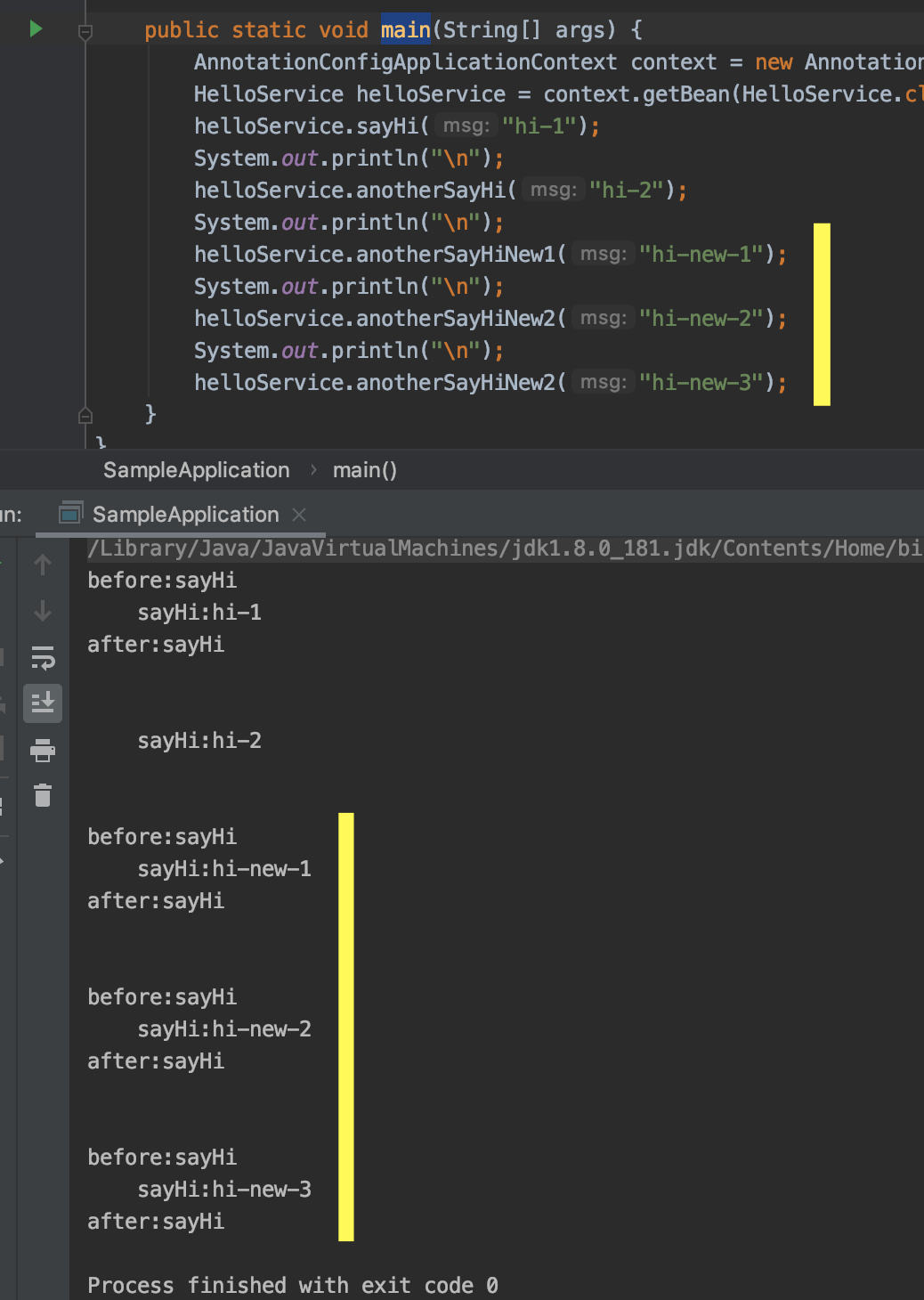
从运行结果上看,3种方法都可以解决这个问题。