是这样的,我自己写了一个block,这个block的内容如下
# 为了更加集成,给定两个角度,生成compact的倾斜图片
class Compact_Homo(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, device):
super(Compact_Homo, self).__init__()
# 假设内参数K为单位矩阵
self.d = 5 # 表示物体到光心的距离
self.device = device
def forward(self, alpha, beta, size, d):
# alpha: N, beta: N, size: N*C*W*H
# pdb.set_trace()
if d is not None:
self.d = d
B = alpha.shape[0]
# 表示图像的尺寸
if size is None:
size = (B, 3, 1024, 1024)
N, C, H, W = size
N = B
Rotx = torch.zeros(B, 3, 3).to(self.device).clone()
ones = torch.ones(B,).to(self.device).clone()
# pdb.set_trace()
Rotx[:, 0, 0] = ones
Rotx[:,1, 1] = torch.cos(beta).squeeze(1)
Rotx[:,1, 2] = -torch.sin(beta).squeeze(1)
Rotx[:,2, 1] = torch.sin(beta).squeeze(1)
Rotx[:,2, 2] = torch.cos(beta).squeeze(1)
Roty = torch.zeros(B, 3, 3).to(self.device).clone()
ones = torch.ones(B,).to(self.device).clone()
Roty[:,1,1] = ones.clone()
Roty[:,0,0] = torch.cos(alpha).squeeze(1)
Roty[:,0,2] = torch.sin(alpha).squeeze(1)
Roty[:,2,0] = -torch.sin(alpha).squeeze(1)
Roty[:,2,2] = torch.cos(alpha).squeeze(1)
# 以下过程构造homo
R = torch.bmm(Rotx, Roty)
R_1 = torch.inverse(R).clone() # 版本不一样,需要的shape也不一样
t = torch.zeros(B,3).to(self.device)
# pdb.set_trace()
t[:,2] = d.squeeze(1).clone() # 平移向量
R_1[:,:,2] = t.clone() # 将第三列赋值
temp_homo = R_1.clone()
homo = torch.inverse(R_1).clone()
# -------------------
# 以下过程构造单位圆,求解其center以及其scale
C = torch.zeros(B, 3, 3).to(self.device).clone()
C[:,0,0] = torch.tensor(1.)
C[:,1,1] = torch.tensor(1.)
C[:,2,2] = torch.tensor(-1.)
C2 = torch.bmm(torch.inverse(torch.transpose(temp_homo,1,2)), C)
C2_ = torch.bmm(C2, torch.inverse(temp_homo))
C3 = torch.inverse(C2_) # 对偶形式
a = C3[:,0,0]
b = C3[:,0,2]+C3[:,2,0]
c = C3[:,2,2]
right_x = (-b-torch.sqrt(b.mul(b)-4*a.mul(c)))/(2*a)
left_x = (-b+torch.sqrt(b.mul(b)-4*a.mul(c)))/(2*a)
right_x = -1./right_x
left_x = -1./left_x
width = right_x-left_x
center_x = (right_x+left_x)/2
a_ = C3[:,1,1]
b_ = C3[:,1,2]+C3[:,2,1]
c_ = C3[:,2,2]
bottom_y = (-b_-torch.sqrt(b_.mul(b_)-4*a_.mul(c_)))/(2*a_)
top_y = (-b_+torch.sqrt(b_.mul(b_)-4*a_.mul(c_)))/(2*a_)
bottom_y = -1./bottom_y
top_y = -1./top_y
height = bottom_y-top_y
center_y = (top_y+bottom_y)/2
scale = torch.max(width, height)
#---------------------
# 根据求解得到的homo,中心点以及产生compact的grid
# size = (1, 3, 1024, 1024)
N, C, H, W = size
N=B
base_grid = torch.zeros(N, H, W, 2).to(self.device)
linear_points = torch.linspace(-1, 1, W).to(self.device) if W > 1 else torch.Tensor([-1]).to(self.device)
base_grid[:, :, :, 0] = torch.ger(torch.ones(H).to(self.device), linear_points).expand_as(base_grid[:, :, :, 0])
linear_points = torch.linspace(-1, 1, H).to(self.device) if H > 1 else torch.Tensor([-1]).to(self.device)
base_grid[:, :, :, 1] = torch.ger(linear_points, torch.ones(W).to(self.device)).expand_as(base_grid[:, :, :, 1])
base_grid = base_grid.view(N, H * W, 2)
# 对center和scale进行变换
center_x = center_x.unsqueeze(1)
center_y = center_y.unsqueeze(1)
center = torch.cat((center_x,center_y), 1).unsqueeze(1).repeat(1,W*H,1)
scale = scale.unsqueeze(1).repeat(1,H*W).unsqueeze(2).repeat(1,1,2)
base_grid = base_grid*scale/2
base_grid = base_grid+center
# 将homo进行扩展,方便运算
h = homo.unsqueeze(1).repeat(1, W*H, 1, 1)
temp1 = (h[:, :, 0, 0] * base_grid[:, :, 0] + h[:, :, 0, 1] * base_grid[:, :, 1] + h[:, :, 0, 2])
temp2 = (h[:, :, 2, 0] * base_grid[:, :, 0] + h[:, :, 2, 1] * base_grid[:, :, 1] + h[:, :, 2, 2])
u1 = temp1 / temp2
temp3 = (h[:, :, 1, 0] * base_grid[:, :, 0] + h[:, :, 1, 1] * base_grid[:, :, 1] + h[:, :, 1, 2])
temp4 = (h[:, :, 2, 0] * base_grid[:, :, 0] + h[:, :, 2, 1] * base_grid[:, :, 1] + h[:, :, 2, 2])
v1 = temp3 / temp4
grid1 = u1.view(N, H, W, 1)
grid2 = v1.view(N, H, W, 1)
grid = torch.cat((grid1, grid2), 3)
return grid
但是我在主程序中调用这个block的时候,计算loss,并且反传大概需要20多秒,但是前传很快。
一开始是怀疑是torch.inverse或者是torch.sqrt这些函数会拖慢反传速度,但是后来想了一下拟操作或者开方的导数并不复杂。
在pytorch forum上网上看了一个链接,他提出的问题是计算图进行了极大的扩展,而一开始我并没有往这方面想。通过逐步debug,我发现将center以及scale进行detach()之后,运算时长会极大的缩短,所以我想的是一定是不用反传所以很快,时长能从20秒降低到6秒。
继续debug
我发现将上述代码中的一段
temp1 = (h[:, :, 0, 0] * base_grid[:, :, 0] + h[:, :, 0, 1] * base_grid[:, :, 1] + h[:, :, 0, 2])
temp2 = (h[:, :, 2, 0] * base_grid[:, :, 0] + h[:, :, 2, 1] * base_grid[:, :, 1] + h[:, :, 2, 2])
u1 = temp1 / temp2
temp3 = (h[:, :, 1, 0] * base_grid[:, :, 0] + h[:, :, 1, 1] * base_grid[:, :, 1] + h[:, :, 1, 2])
temp4 = (h[:, :, 2, 0] * base_grid[:, :, 0] + h[:, :, 2, 1] * base_grid[:, :, 1] + h[:, :, 2, 2])
其中的h换成homo中的一些元素,能保留前传的梯度,如果问题出现在torch.inverse或者torch.sqrt的话,理论上应该不会影响计算速度,但是我发现当我这么操作的时候,反传时间会极大的缩短。
于是我想之所以center和scale变量进行detach()的时候,计算时长也会极大缩短,原因可能是和repeat有关,因为h也是homo的repeat很多次(W*H),所以我果断将repeat给替换掉,
h = homo
# temp1 = (h[:, :, 0, 0] * base_grid[:, :, 0] + h[:, :, 0, 1] * base_grid[:, :, 1] + h[:, :, 0, 2])
# temp2 = (h[:, :, 2, 0] * base_grid[:, :, 0] + h[:, :, 2, 1] * base_grid[:, :, 1] + h[:, :, 2, 2])
temp1 = (h[:, 0, 0] * base_grid[:, :, 0] + h[:, 0, 1] * base_grid[:, :, 1] + h[:, 0, 2])
temp2 = (h[:, 2, 0] * base_grid[:, :, 0] + h[:, 2, 1] * base_grid[:, :, 1] + h[:, 2, 2])
u1 = temp1 / temp2
# temp3 = (h[:, :, 1, 0] * base_grid[:, :, 0] + h[:, :, 1, 1] * base_grid[:, :, 1] + h[:, :, 1, 2])
# temp4 = (h[:, :, 2, 0] * base_grid[:, :, 0] + h[:, :, 2, 1] * base_grid[:, :, 1] + h[:, :, 2, 2])
temp3 = (h[:, 1, 0] * base_grid[:, :, 0] + h[:, 1, 1] * base_grid[:, :, 1] + h[:, 1, 2])
temp4 = (h[:, 2, 0] * base_grid[:, :, 0] + h[:, 2, 1] * base_grid[:, :, 1] + h[:, 2, 2])
v1 = temp3 / temp4
# 对center和scale进行变换
center_x = center_x.unsqueeze(1)
center_y = center_y.unsqueeze(1)
# center = torch.cat((center_x,center_y), 1).unsqueeze(1).repeat(1,W*H,1)
# scale = scale.unsqueeze(1).repeat(1,H*W).unsqueeze(2).repeat(1,1,2)
center = torch.cat((center_x,center_y), 1)
scale = scale
base_grid = base_grid*scale/2.
base_grid = base_grid+center
所以时长一下子由下图
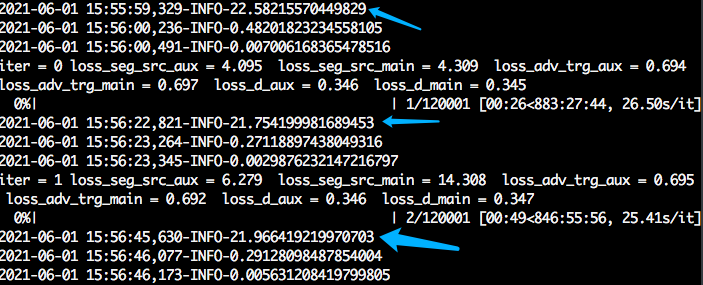
变成了
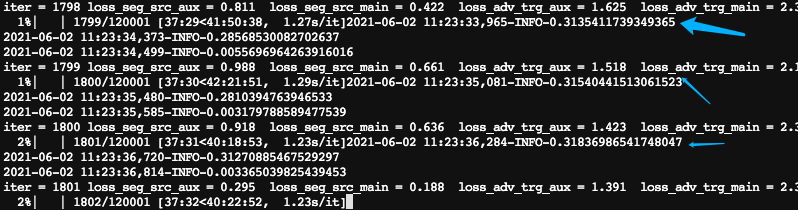
几乎不耗时
pytorch forum链接https://discuss.pytorch.org/t/why-loss-backward-is-so-slow-taking-about-20s/122956/3