目录
1 生成图
图的表示
图表示有很多中,一般在面试中常见的如下:
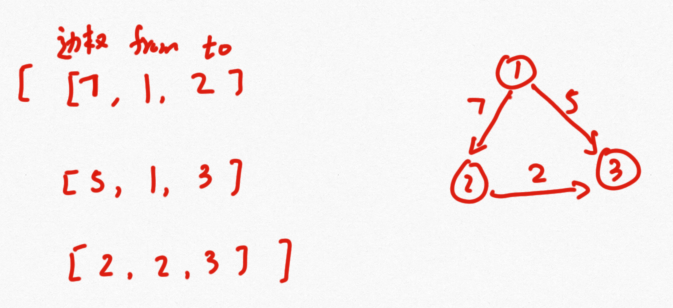
代码实现
图的节点
//图的节点的定义 public class Node { //value的类型不一定是整型可以是泛型 public int value; //节点的入度 public int in; //节点的出度 public int out; //从当前的节点出发可以到达的所有节点即当前节点的所有邻居节点 public ArrayList<Node> nexts; //从当前节点出发,发散出边的集合 public ArrayList<Edge> edges; public Node(int value) { this.value = value; in = 0; out = 0; nexts = new ArrayList<>(); edges = new ArrayList<>(); } }
图的边
//图的边的的定义 public class Edge { //边的权值是多少 public int weight; //从哪个节点出发 public Node from; //去向哪个节点 public Node to; public Edge(int weight, Node from, Node to) { this.weight = weight; this.from = from; this.to = to; } }
图的定义
//图的定义 public class Graph { //图就是所有点的集合和边的集合 public HashMap<Integer,Node> nodes; public HashSet<Edge> edges; public Graph() { nodes = new HashMap<>(); edges = new HashSet<>(); } }
生成图
public class GraphGenerator { //生成图 public static Graph createGraph(Integer[][] matrix) { Graph graph = new Graph(); //如博客中给出的示例,矩阵的行数不定但是列数为3即每一行的长度为3 for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) { Integer from = matrix[i][0]; Integer to = matrix[i][1]; Integer weight = matrix[i][2]; //如果from这个点的没有在图中定义,则建上该点 if (!graph.nodes.containsKey(from)) { graph.nodes.put(from, new Node(from)); } //如果to这个点的没有在图中定义,则建上该点 if (!graph.nodes.containsKey(to)) { graph.nodes.put(to, new Node(to)); } //拿到from点和to点 Node fromNode = graph.nodes.get(from); Node toNode = graph.nodes.get(to); //根据两个点生成一个边 Edge newEdge = new Edge(weight, fromNode, toNode); //from的邻居增加to这个点 fromNode.nexts.add(toNode); //from点出度自增 fromNode.out++; //to点入度自增 toNode.in++; //from点的边集中增加这个边 fromNode.edges.add(newEdge); //整个图的边集中增加这个边 graph.edges.add(newEdge); } return graph; } }
2 图的遍历
宽度(广度)优先遍历

依照距离起始节点的距离确定输出的先后顺序,同等距离则可能会出现不同情况,注意图的遍历顺序是不确定的
//整体与树中的BFS很类似的,不同点在于需要注意重复元素 public static void bfs(Node node) { if (node == null) { return; } //用队列实现BFS Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>(); //用来记录哪些节点已经进入了 HashSet<Node> map = new HashSet<>(); queue.add(node); map.add(node); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { Node cur = queue.poll(); System.out.println(cur.value); for (Node next : cur.nexts) { //只有没进过set集合的节点才添加,避免重复添加的问题 if (!map.contains(next)) { map.add(next); queue.add(next); } } } }
深度优先
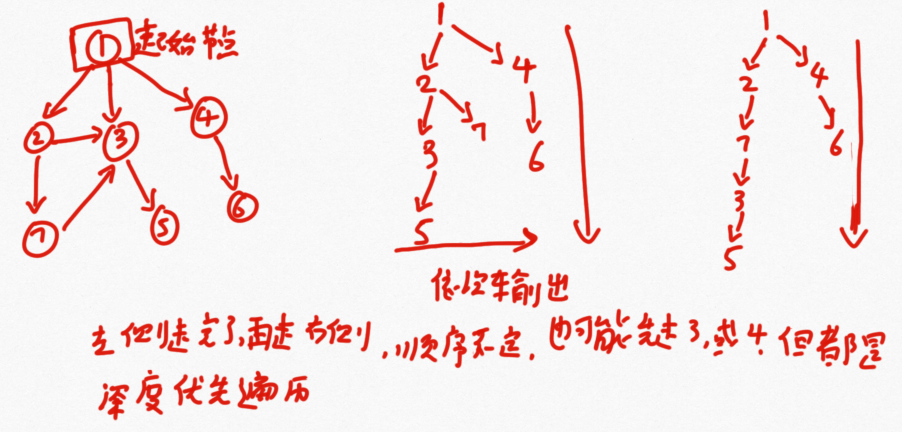
public static void dfs(Node node) { if (node == null) { return; } Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>(); HashSet<Node> set = new HashSet<>(); stack.add(node); set.add(node); System.out.println(node.value); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { Node cur = stack.pop(); for (Node next : cur.nexts) { //如果当前节点的后代不在set中,那就把当前节点和其后代都放入栈中 if (!set.contains(next)) { stack.push(cur); stack.push(next); set.add(next); System.out.println(next.value); break; } } } }
3 进阶算法
1 拓扑排序算法
适用范围:有向图,且有入度为0的节点,且没有环
使用场景:编辑一个工程A其依赖有BCDE配置文件,配置文件内部又相互依赖,决定应该先编译哪一个文件。
算法思想:

代码实现:
public static List<Node> sortedTopology(Graph graph) { //统计当前所有节点的入度 HashMap<Node, Integer> inMap = new HashMap<>(); //保存入度为0的点 Queue<Node> zeroInQueue = new LinkedList<>(); for (Node node : graph.nodes.values()) { inMap.put(node, node.in); if (node.in == 0) { zeroInQueue.add(node); } } List<Node> result = new ArrayList<>(); while (!zeroInQueue.isEmpty()) { //弹出一个入度为0的点,并在结果中保存 Node cur = zeroInQueue.poll(); result.add(cur); //把当前节点的所有后代入度自减1,实质就是消除该节点的影响 for (Node next : cur.nexts) { inMap.put(next, inMap.get(next) - 1); //如果有入度为0的点进队列 if (inMap.get(next) == 0) { zeroInQueue.add(next); } } } return result; }
最小生成树算法
适用范围:无向图
使用场景:在保证图的连通性前提下,使得图的权值最小
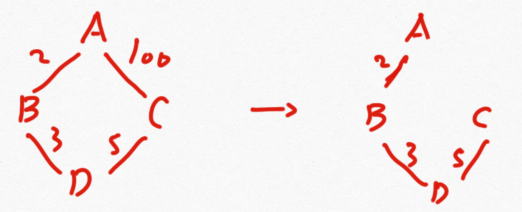
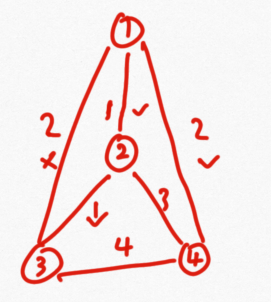
1 Kruskal 算法
算法思想:选择权值最小的边,如下图中先选择1,然后选择2,如果选择的边构成了一个回路则舍弃,当选择的边能够遍历到所有的点时算法结束。
public static Set<Edge> kruskalMST(Graph graph) { //把所有的点放入并查集中 UnionFind unionFind = new UnionFind(); unionFind.makeSets(graph.nodes.values()); //按照边的权重组成一个小根堆,堆中放的都是边 PriorityQueue<Edge> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(); for (Edge edge : graph.edges) { priorityQueue.add(edge); } //保存最后的结果 Set<Edge> result = new HashSet<>(); while (!priorityQueue.isEmpty()) { Edge edge = priorityQueue.poll(); //每次从最小堆弹出一个边,如果边的出入节点已经属于一个集合,则舍弃该边 if (!unionFind.isSameSet(edge.from, edge.to)) { //如果没有则添加该边,并把该边的出入节点合并在一起 result.add(edge); unionFind.union(edge.from, edge.to); } } return result; }
2 prim 算法
算法思想:从一个点出发(V1)找其发出边中最小的边,到达下一个新的节点,然后从这两个点的所有发出边中找到最小可以到达新的点的边,直至达到所有的点。
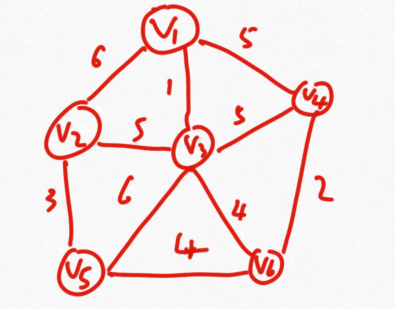
public static Set<Edge> primMST(Graph graph) { //最小堆中放边 PriorityQueue<Edge> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(); //保存已经遍历过的点 HashSet<Node> set = new HashSet<>(); //保存结果的边 Set<Edge> result = new HashSet<>(); for (Node node : graph.nodes.values()) { if (!set.contains(node)) { //如果没有遍历过该点,加入该点 set.add(node); //加入该点的所有发出边 for (Edge edge : node.edges) { priorityQueue.add(edge); } //依次弹出权值最小的边 while (!priorityQueue.isEmpty()) { Edge edge = priorityQueue.poll(); Node toNode = edge.to; //只有没遍历过的新点才加入 if (!set.contains(toNode)) { set.add(toNode); result.add(edge); //加入新的节点的所有发出边 for (Edge nextEdge : node.edges) { priorityQueue.add(nextEdge); } } } } } return result; }
0