数据集拆分
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split # 分割数据集到训练集和测试集 # lb.data 特征值 # lb.target 目标值 # test_size=0.25 75%数据训练 25%数据测试 # 返回 训练特征值, 测试特征值, 训练目标值, 测试目标值 x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(lb.data, lb.target, test_size=0.25)
交叉验证
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score clf = svm.SVC(kernel='linear', C=1) # cif 估计器对象 # iris.data:特征数据 # iris.target:目标值 # cv=5 5次交叉验证 scores = cross_val_score(clf, iris.data, iris.target, cv=5) print(scores) # 结果 array([ 0.96..., 1. ..., 0.96..., 0.96..., 1. ])
网格搜索
通常情况下,有很多参数是需要手动指定的(如k-近邻算法中的K值), 这种叫超参数。但是手动过程繁杂,所以需要对模型预设几种超参数组 合。每组超参数都采用交叉验证来进行评估。最后选出最优参数组合建 立模型。


from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
param = {"n_estimators": [120, 200, 300, 500, 800, 1200], "max_depth": [5, 8, 15, 25, 30]}
# 网格搜索与交叉验证
# rf:估计器对象
# cv=2:指定几折交叉验证
gc = GridSearchCV(rf, param_grid=param, cv=2)
gc.fit(x_train, y_train)
print("准确率:", gc.score(x_test, y_test))
print("查看选择的参数模型:", gc.best_params_)
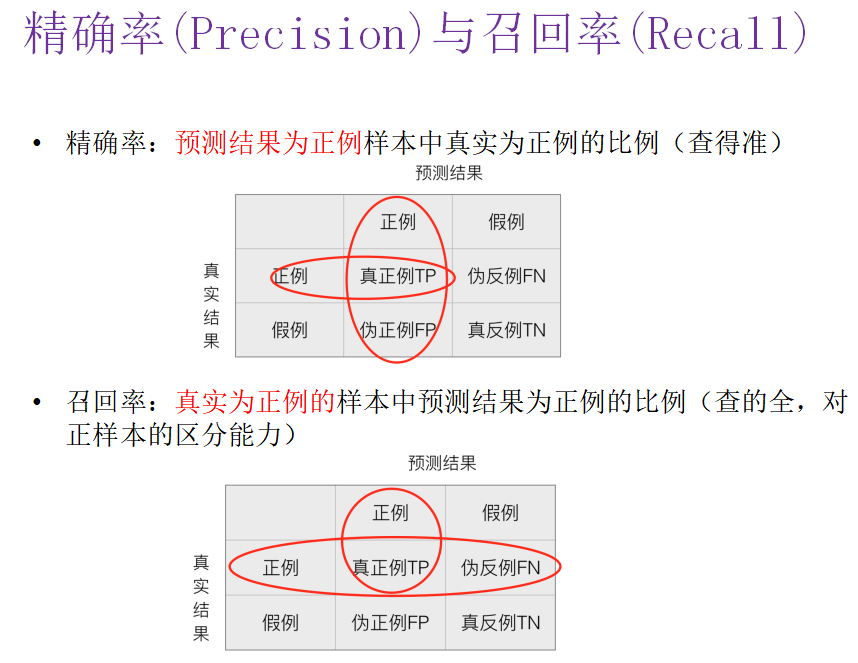
精确率(Precision)与召回率(Recall)

from sklearn.metrics import classification_report # 返回召回率 # labels:目标值 # target_names:目标值对应的名称 classification_report(y_test, y_predict, labels=[2, 4], target_names=["良性", "恶性"])