前言
通常我们认为每个测试用例都是相互独立的,因此需要保证测试结果不依赖于测试顺序,以不同的顺序运行测试用例,可以得到相同的结果。
pytest默认运行用例的顺序是按模块和用例命名的 ASCII 编码顺序执行的,这就意味着每次运行用例的顺序都是一样的。
app 测试里面有个 monkey 测试,随机在页面点点点,不按常理的点点点能找到更多的不稳定性 bug。那么我们在写pytest用例的时候,既然每个用例都是相互独立的,
那就可以打乱用例的顺序随机执行,用到 pytest 的插件 pytest-random-order 可以实现此目的,github 地址https://github.com/jbasko/pytest-random-order
pytest-random-order 插件
pytest-random-order是一个pytest插件,用于随机化测试顺序。这对于检测通过的测试可能是有用的,因为该测试恰好在不相关的测试之后运行,从而使系统处于良好状态。
该插件允许用户控制他们想要引入的随机性级别,并禁止对测试子集进行重新排序。通过传递先前测试运行中报告的种子值,可以按特定顺序重新运行测试。

使用pip安装
pip install pytest-random-order
在pytest -h查看,命令行可以有三个参数选择
pytest-random-order options:
--random-order Randomise test order (by default, it is disabled) with default configuration.
--random-order-bucket={global,package,module,class,parent,grandparent,none}
Randomise test order within specified test buckets.
--random-order-seed=RANDOM_ORDER_SEED
Randomise test order using a specific seed.
从v1.0.0开始,默认情况下,此插件不再将测试随机化。要启用随机化,您必须以下列方式之一运行pytest:
pytest --random-order
pytest --random-order-bucket=<bucket_type>
pytest --random-order-seed=<seed>
如果要始终随机化测试顺序,请配置pytest。有很多方法可以做到这一点,我最喜欢的一种方法是addopts = --random-order在pytest选项(通常是[pytest]或[tool:pytest]部分)下添加特定于项目的配置文件。
# pytest.ini文件内容
[pytest]
addopts = --random-order
--random-order 随机测试
先写几个简单的用例,目录结构如下
module1/test_order1.py内容
# module1/test_order1.py
# 作者-上海悠悠 QQ交流群:717225969
# blog地址 https://www.cnblogs.com/yoyoketang/
class TestRandom():
def test_01(self):
print("用例1")
def test_02(self):
print("用例2")
def test_03(self):
print("用例3")
module2/test_order2.py内容
# module2/test_order2.py
# 作者-上海悠悠 QQ交流群:717225969
# blog地址 https://www.cnblogs.com/yoyoketang/
class TestDemo():
def test_04(self):
print("用例4")
def test_05(self):
print("用例5")
def test_06(self):
print("用例6")
带上--random-order参数运行用例
>pytest --random-order -v
================================================= test session starts =================================================
Using --random-order-bucket=module
Using --random-order-seed=357703
collected 6 items
module2/test_order2.py::TestDemo::test_04 PASSED [ 16%]
module2/test_order2.py::TestDemo::test_05 PASSED [ 33%]
module2/test_order2.py::TestDemo::test_06 PASSED [ 50%]
module1/test_order1.py::TestRandom::test_03 PASSED [ 66%]
module1/test_order1.py::TestRandom::test_02 PASSED [ 83%]
module1/test_order1.py::TestRandom::test_01 PASSED [100%]
================================================== 6 passed in 0.05s ==================================================
从运行的结果可以看出,默认使用--random-order-bucket=module,模块下的用例会被打乱随机执行,每次运行会重新生成--random-order-seed=357703,seed值不一样,用例的顺序也会不一样
--random-order-bucket 随机范围
要更改重新排序与范围,运行pytest --random-order-bucket=
插件组在存储桶中进行测试,在存储桶中进行混洗,然后对存储桶进行混洗,设计原理如图

给定上面的测试套件,以下是一些可能生成的测试顺序中的两个:
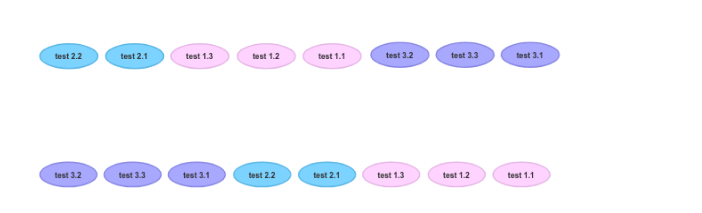
可以从以下几种类型的存储桶中进行选择:
- class 测试将在一个类中进行混洗,而各类将被混洗,但是来自一个类的测试将永远不会在其他类或模块之间运行来自其他类的测试。
- module 模块级别。如果仅使用--random-order运行pytest,同时带上参数--random-order-seed=
。 - package 程序包级别。请注意,属于package的模块(以及这些模块内的测试)x.y.z不属于package x.y,因此在对存储package桶类型进行随机分配时,它们将落入不同的存储桶中。
- parent 如果使用的是不属于任何模块的自定义测试项,则可以使用此项将测试项的重新排序限制在它们所属的父级中。对于正常测试函数,父级是声明它们的模块。
- grandparent 类似于上面的parent,但是使用测试项的父级作为bucket key。
- global 所有测试属于同一存储桶,完全随机,测试可能需要更长的时间才能运行。
- none (已弃用) 禁用混洗。自1.0.4起不推荐使用,因为此插件默认不再重做测试,因此没有禁用的功能。
如果你有测试三个桶A,B和C三个测试1和2,并3在他们每个人,那么许多潜在的排序的一个非全局随机化可以产生可能是:
c2,c1,c3,a3,a1,a2,b3,b2,b1
运行示例,带上参数--random-order-bucket=global,所有的用例都会被打乱。
>pytest --random-order -v --random-order-bucket=global
================================================= test session starts =================================================
Using --random-order-bucket=global
Using --random-order-seed=255529
collected 6 items
module1/test_order1.py::TestRandom::test_02 PASSED [ 16%]
module1/test_order1.py::TestRandom::test_01 PASSED [ 33%]
module2/test_order2.py::TestDemo::test_06 PASSED [ 50%]
module2/test_order2.py::TestDemo::test_04 PASSED [ 66%]
module2/test_order2.py::TestDemo::test_05 PASSED [ 83%]
module1/test_order1.py::TestRandom::test_03 PASSED [100%]
================================================== 6 passed in 0.05s ==================================================
最好从最小的存储桶类型开始(class或module取决于您是否有基于类的测试),并在确定测试可以处理较大的存储桶类型时切换为更大的存储桶类型。
如果您的测试依赖模块或会话范围的fixture,则测试的随机性越高,测试速度就越慢。您可能不想在编码时随机global或随机分组,package并且需要快速确认没有什么大问题。``
模块或类中禁用随机
如果我们在一个模块或类中,不想让里面的用例随机,可以设置 disabled=True 来禁用随机参数
# 写在.py文件最上面即可
pytestmark = pytest.mark.random_order(disabled=True)
def test_number_one():
assert True
def test_number_two():
assert True
也可以写在class里面
import pytest
# 作者-上海悠悠 QQ交流群:717225969
# blog地址 https://www.cnblogs.com/yoyoketang/
class TestRandom():
pytestmark = pytest.mark.random_order(disabled=True)
def test_01(self):
print("用例1")
def test_02(self):
print("用例2")
def test_03(self):
print("用例3")
这样在执行的时候,TestRandom里面的用例顺序就是test_01,test_02,test_03不会被打乱
--random-order-seed 随机种子
如果由于重新排序测试而发现测试失败,则可能希望能够以相同的失败顺序重新运行测试。为了允许重现测试订单,该插件报告其与伪随机数生成器一起使用的种子值:
============================= test session starts ==============================
..
Using --random-order-bucket=module
Using --random-order-seed=24775
...
现在,您可以使用该--random-order-seed=...位作为下一次运行的参数以产生相同的顺序:
pytest -v --random-order-seed = 24775
禁用插件
如果你觉得这个插件不好用,或者对你的其它功能会有影响,则可以将其禁用
pytest -p no:random_order
请注意,默认情况下禁用随机化。通过传递,-p no:random_order您将阻止插件的注册,因此其钩子将不会被注册,并且命令行选项也不会出现在中--help
首先运行最后失败的测试
另外 --failed-first 标志-上一次运行失败的测试将在通过测试之前运行,而不管改组存储桶类型如何。