为了让Node.js的文件可以相互调用,Node.js提供了一个简单的模块系统。
一个 Node.js 文件就是一个模块,这个文件可能是JavaScript 代码、JSON 或者编译过的C/C++ 扩展。
创建模块
在 Node.js 中,创建一个模块非常简单,如下我们创建一个 'hello.js' 文件,代码如下:
var hello = require('./hello'); hello.world();
以上实例中,代码 require('./hello') 引入了当前目录下的hello.js文件(./ 为当前目录,node.js默认后缀为js)。
Node.js 提供了exports 和 require 两个对象,其中 exports 是模块公开的接口,require 用于从外部获取一个模块的接口,即所获取模块的 exports 对象。
接下来我们就来创建hello.js文件,代码如下:
exports.world = function() { console.log('Hello World'); }
在以上示例中,hello.js 通过 exports 对象把 world 作为模块的访问接口,在 main.js 中通过 require('./hello') 加载这个模块,然后就可以直接访 问 hello.js 中 exports 对象的成员函数了。
有时候我们只是想把一个对象封装到模块中,格式如下:
module.exports = function() { // ... }
例如:
//hello.js function Hello() { var name; this.setName = function(thyName) { name = thyName; }; this.sayHello = function() { console.log('Hello ' + name); }; }; module.exports = Hello;
这样就可以直接获得这个对象了:
//main.js var Hello = require('./hello'); hello = new Hello(); hello.setName('BYVoid'); hello.sayHello();
服务端的模块放在哪里
Node.js中自带了一个叫做"http"的模块,我们在我们的代码中请求它并把返回值赋给一个本地变量。
这把我们的本地变量变成了一个拥有所有 http 模块所提供的公共方法的对象。
var http = require("http"); ... http.createServer(...);
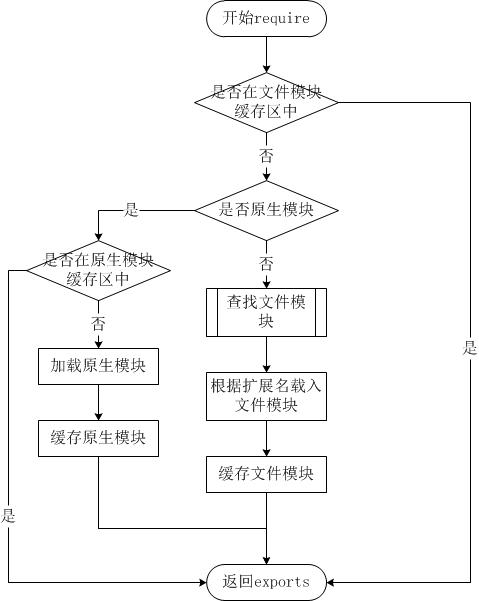
Node.js 的 require方法中的文件查找策略如下: