对于堆排序会涉及一些完全二叉树知识。对于待排序列{10, 2, 11, 8, 7},把它看成是一颗完全二叉树,如下图所示。

堆分为大根堆和小根堆:大根堆表示每个根节点均大于其子节点(L(i) >= L(2i) && L(i) >= L(2i + 1)),小根堆表示每个根节点均小于其子节点(L(i) <= L(2i) && L(i) <= L(2i + 1))。(在完全二叉树中第i个节点的左子节点为2i,其右字节点为2i + 1)
本文将以大根堆的构建作为示例进行讲解。
堆排序的第一步——构建初始堆。如何构建初始堆呢?根据定义,关键点在于每个根节点。观察上述待排序列的完全二叉树,不难发现存在节点2和节点10有子节点,它们是需要关注的节点。
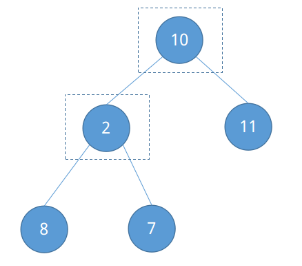
如何定位节点2呢?发现它是叶子节点,或者最后一个节点的父节点,根据完全二叉树的性质可知,除根节点外任意节点的父节点的编号为⌊n / 2⌋。已知n = 5,易知节点2的编号为⌊5 / 2⌋ = ②。比较它与左右子节点的大小并调整。
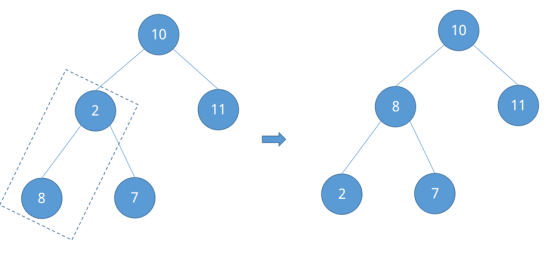
最后剩下根节点10,已知节点2的编号为②,② - 1 = ①即得到根节点10的编号。比较它与左右子节点的大小并调整。

调整完毕后发现已经构成了一个“大根堆”,示例中的待排序列较为简单,再给出一个较为复杂的待排序列,观察其构建大根堆的过程。对于待排序列{53, 17, 78, 09, 45, 65, 87, 32},将它看成一颗完全二叉树。
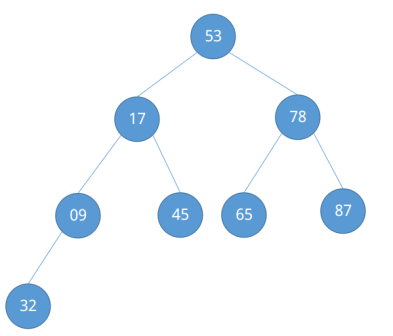
同样我们来看它所需要关注的节点有哪些。
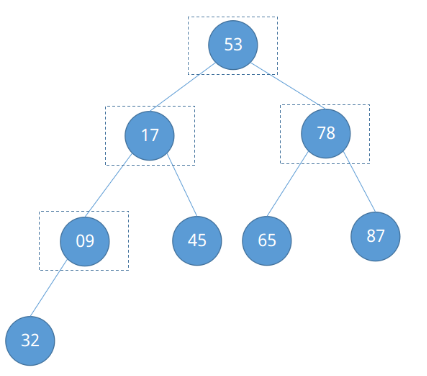
根据第一个例子,我们很容易能定位节点09的编号为⌊8 / 2⌋ = ④,节点78的编号为④ - 1 = ③……,依次类推,发现了一定的规律,即需要调整的节点位置从⌊n / 2⌋开始依次递减直到根节点①结束(⌊n / 2⌋ ~ 1)。现在开始调整。


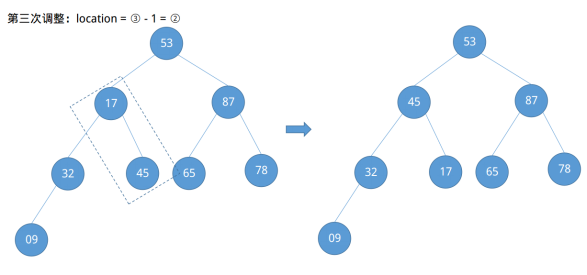
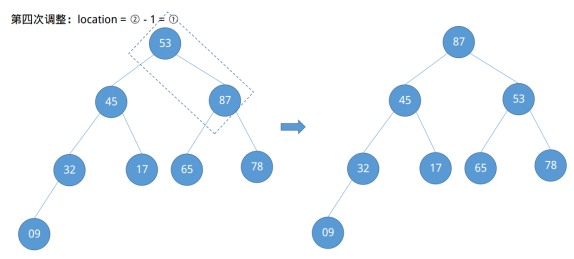
在第四次调整结束后发现节点53不满足大根堆的定义,其右子节点大于它,此时需要做进一步的向下调整。

注意向下调整是每次向上调整的时候都需要做的判断是否需要向下调整,而不是在所有的向上调整结束过后再回过头来向下调整。这样大根堆就建立好了,此时待排序列数组情况已经发生了改变:{87, 45, 78, 32, 17, 65, 53, 09}。接下来是如何进行排序的问题。将大根堆的根节点与最后一个节点互换,并调整二叉树使其仍然满足大根堆。

可以看到将根节点与最后一个节点呼唤后,待排序列的最大值已经放到了数组的最后一个位置{……, 87},此时完成了第一趟排序,但这第一趟排序还没有结束,此时除节点87外,其余节点并不满足大根堆的条件,所以需要对其余节点进行调整为大根堆。排序过程不再给出,Java和Python3的代码实现如下。
Java
1 package com.algorithm.sort.heap; 2 3 import java.util.Arrays; 4 5 /** 6 * 堆排序 7 * Created by yulinfeng on 6/20/17. 8 */ 9 public class Heap { 10 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 int[] nums = {53, 17, 78, 09, 45, 65, 87, 32}; 13 nums = heapSort(nums); 14 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums)); 15 } 16 17 /** 18 * 堆排序 19 * @param nums 待排序数组序列 20 * @return 排好序的数组序列 21 */ 22 private static int[] heapSort(int[] nums) { 23 24 for (int i = nums.length / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) { 25 heapAdjust(nums, i, nums.length); 26 } 27 for (int i = nums.length - 1; i > 0; i--) { 28 int temp = nums[i]; 29 nums[i] = nums[0]; 30 nums[0] = temp; 31 heapAdjust(nums, 0, i); 32 } 33 return nums; 34 } 35 36 /** 37 * 调整堆 38 * 39 * @param nums 待排序序列 40 * @param parent 待调整根节点 41 * @param length 数组序列长度 42 */ 43 private static void heapAdjust(int[] nums, int parent, int length) { 44 int temp = nums[parent]; 45 int childIndex = 2 * parent + 1; //完全二叉树节点i从编号1开始的左子节点位置在2i,此处数组下标从0开始,即左子节点所在数组索引位置为:2i + 1 46 while (childIndex < length) { 47 if (childIndex + 1 < length && nums[childIndex] < nums[childIndex + 1]) { 48 childIndex++; //节点有右子节点,且右子节点大于左子节点,则选取右子节点 49 } 50 if (temp > nums[childIndex]) { 51 break; //如果选中节点大于其子节点,直接返回 52 } 53 nums[parent] = nums[childIndex]; 54 parent = childIndex; 55 childIndex = 2 * parent + 1; //继续向下调整 56 } 57 nums[parent] = temp; 58 } 59 }
Python3
1 #堆排序 2 def heap_sort(nums): 3 4 for i in range(int(len(nums) / 2 - 1), -1, -1): 5 heap_adjust(nums, i, len(nums)) 6 7 for i in range(len(nums) - 1, -1, -1): 8 temp = nums[i] 9 nums[i] = nums[0] 10 nums[0] = temp 11 heap_adjust(nums, 0, i) 12 13 return nums 14 15 #调整堆 16 def heap_adjust(nums, parent, length): 17 18 temp = nums[parent] 19 childIndex = 2 * parent + 1 20 while childIndex < length: 21 if childIndex + 1 < length and nums[childIndex] < nums[childIndex + 1]: 22 childIndex += 1 23 if temp > nums[childIndex]: 24 break 25 nums[parent] = nums[childIndex] 26 parent = childIndex 27 childIndex = 2 * parent + 1 28 29 nums[parent] = temp 30 31 nums = [53, 17, 78, 09, 45, 65, 87, 32]
32 nums = heap_sort(nums) 33 print(nums)