Java toString() 方法
toString() 方法返回此对象本身(它已经是一个字符串)
1.toString()方法 一般出现在System.out.println(类名.toString());
toString()是一种自我描述方法 本身返回的是 getClass().getName() + "@" +Integer.toHexString(hashCode());
也就是 类名 + @ +hashCode的值
重写toString() 只会对类生效,并不能字符串生效; 例如
1 public class pratise { 2 String num="aaaa"; 3 public String toString(){ 4 return num; 5 } 6 public static void main(String[] args){ 7 String s1="111"; 8 System.out.println(s1.toString()); 9 //输出111 而并非aaaa; 10 } 11 }
重写toString()对类生效
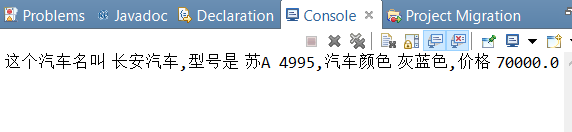
1 package com.stu; 2 3 //用toString 重写一个类 4 public class Car { 5 6 //成员变量 7 private String carNo; 8 private String carName; 9 private String color; 10 private double price; 11 12 //有参构造函数 13 Car(String carNo,String carName,String color,double price){ 14 this.carNo=carNo; 15 this.carName=carName; 16 this.color=color; 17 this.price=price; 18 } 19 20 //get set方法 21 public String getCarNo(){ 22 return carNo; 23 } 24 25 public void setCarNo(String carNo){ 26 this.carNo=carNo; 27 } 28 29 public String getCarName() { 30 return carName; 31 } 32 33 public void setCarName(String carName) { 34 this.carName = carName; 35 } 36 37 public String getColor() { 38 return color; 39 } 40 41 public void setColor(String color) { 42 this.color = color; 43 } 44 45 public double getPrice() { 46 return price; 47 } 48 49 public void setPrice(double price) { 50 this.price = price; 51 } 52 //重写toString(); 53 public String toString(){ 54 return "这个汽车名叫 "+carName+",型号是 "+carNo+",汽车颜色 "+color+",价格 "+price; 55 } 56 57 public static void main(String[] args){ 58 //创建一个Car的对象 59 Car myCar=new Car("苏A 4995","长安汽车","灰蓝色",70000.00); //类名开头字母大写 60 System.out.println(myCar.toString()); 61 } 62 }
运行结果:
2.为什么要重写toString()方法
在Object类里面定义toString()方法的时候返回的对象的哈希code码,这个hashcode码不能简单明了的表示出对象的属性。所以要重写toString()方法。
当需要将一个对象输出到显示器时,通常要调用他的toString()方法,将对象的内容转换为字符串.java中的所有类默认都有一个toString()方法。
默认情况下 System.out.println(对象名)或者System.out.println(对象名.toString())输出的是此对象的类名和此对象对应内存的首地址如果想自定义输出信息必须重写toString()方法。
注意事项:
1.必须被声明为public
2.返回类型为String
3.方法的名称必须为toString,且无参数
4.方法体中不要使用输出方法System.out.println()
重写toString() 只会对类生效,并不能字符串生效; 例如

1 public class pratise { 2 String num="aaaa"; 3 public String toString(){ 4 return num; 5 } 6 public static void main(String[] args){ 7 String s1="111"; 8 System.out.println(s1.toString()); 9 //输出111 而并非aaaa; 10 } 11 }
重写toString()对类生效
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
|
package com.stu;//用toString 重写一个类public class Car { //成员变量 private String carNo; private String carName; private String color; private double price; //有参构造函数 Car(String carNo,String carName,String color,double price){ this.carNo=carNo; this.carName=carName; this.color=color; this.price=price; } //get set方法 public String getCarNo(){ return carNo; } public void setCarNo(String carNo){ this.carNo=carNo; } public String getCarName() { return carName; } public void setCarName(String carName) { this.carName = carName; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } public double getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(double price) { this.price = price; } //重写toString(); public String toString(){ return "这个汽车名叫 "+carName+",型号是 "+carNo+",汽车颜色 "+color+",价格 "+price; } public static void main(String[] args){ //创建一个Car的对象 Car myCar=new Car("苏A 4995","长安汽车","灰蓝色",70000.00); //类名开头字母大写 System.out.println(myCar.toString()); }} |
输出结果:

假如不对toString()进行重写则 输出结果:
com.stu.Car@2542880d ==> 类名 + “@” +hashCode值
