0 引子
近日,我在萧大哥的博客里闲逛,渐知μC/OS-II用途甚广,使用方便;于是就照虎画猫,写几篇博文。
1 范例
(1) ucos_ii_test.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "includes.h"
// 定义任务的栈
#define TASK_STACKSIZE 2048
OS_STK task1_stk[TASK_STACKSIZE];
OS_STK task2_stk[TASK_STACKSIZE];
OS_STK task3_stk[TASK_STACKSIZE];
OS_STK task4_stk[TASK_STACKSIZE];
// 定义任务的优先级
#define TASK1_PRIORITY 1
#define TASK2_PRIORITY 2
#define TASK3_PRIORITY 3
#define TASK4_PRIORITY 4
// 声明任务
void task1(void* pData); // 任务1:传递整型参数
void task2(void* pData); // 任务2:传递字符参数
void task3(void* pData); // 任务3:传递字符串参数
void task4(void* pData); // 任务4:传递结构体参数
// 定义结构体
typedef struct
{
int iA;
char cB;
char sC[10];
}myStruct_t;
int main()
{
//
int iA=5;
//
char cB = 't';
//
char sC[] = "test";
//
myStruct_t pStr;
pStr.iA = 5;
pStr.cB = 't';
strcpy(pStr.sC, "test");
// 任务1:传递整型参数
OSTaskCreateExt(task1,
&iA,
(void *)&task1_stk[TASK_STACKSIZE-1],
TASK1_PRIORITY,
TASK1_PRIORITY,
task1_stk,
TASK_STACKSIZE,
NULL,
0);
// 任务2:传递字符参数
OSTaskCreateExt(task2,
&cB,
(void *)&task2_stk[TASK_STACKSIZE-1],
TASK2_PRIORITY,
TASK2_PRIORITY,
task2_stk,
TASK_STACKSIZE,
NULL,
0);
// 任务3:传递字符串参数
OSTaskCreateExt(task3,
sC,
(void *)&task3_stk[TASK_STACKSIZE-1],
TASK3_PRIORITY,
TASK3_PRIORITY,
task3_stk,
TASK_STACKSIZE,
NULL,
0);
// 任务4:传到结构体参数
OSTaskCreateExt(task4,
&pStr,
(void *)&task4_stk[TASK_STACKSIZE-1],
TASK4_PRIORITY,
TASK4_PRIORITY,
task4_stk,
TASK_STACKSIZE,
NULL,
0);
OSStart();
return 0;
}
// 任务1:传递整型参数
void task1(void* pData)
{
while (1)
{
printf("task1, iA = %d\n", *((int *)pData));
OSTimeDlyHMSM(0, 0, 1, 0);
}
}
// 任务2:传递字符参数
void task2(void* pData)
{
while (1)
{
printf("task2, cB = %c\n", *((char *)pData));
OSTimeDlyHMSM(0, 0, 1, 0);
}
}
// 任务3:传递字符串参数
void task3(void* pData)
{
while (1)
{
printf("task3, sC = %s\n", (char *)pData);
OSTimeDlyHMSM(0, 0, 1, 0);
}
}
// 任务4:传递结构体参数
void task4(void* pData)
{
while (1)
{
printf("task4, iA = %i\n", ((myStruct_t *)pData)->iA);
printf("task4, cB = %c\n", ((myStruct_t *)pData)->cB);
printf("task4, sC = %s\n", ((myStruct_t *)pData)->sC);
OSTimeDlyHMSM(0, 0, 1, 0);
}
}
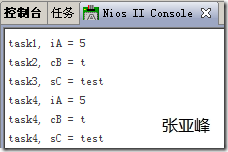
(2)运行结果
2 解析
从OSTaskCreateExt()的源代码中,可知pData就是所能传递的参数。
第48行,传递整型变量iA的地址;但是pdata却是空型指针。为了匹配存储内容,在第99行,将从&iA开始的存储区域强制转化为整型指针,故有(int *)pData;使用(*)访问内容即可,如*((int *)pData)。如表1所示。
表1 task1中所传参数的存储映射
| 表达式 | 存储地址 | 存储长度 | 存储内容 |
int iA=5; |
&iA | sizeof(int) | 5 |
void* pData |
不变 | 未知 | 未知 |
*((int *)pData) |
不变 | sizeof(int) | 5 |
任务2的字符参数与任务1的整型参数类似,如表2所示。
| 表达式 | 存储地址 | 存储长度 | 存储内容 |
char cB = 't'; |
&cB | sizeof(char) | t |
void* pData |
不变 | 未知 | 未知 |
*((char *)pData) |
不变 | sizeof(char) | t |
任务3中%s本身只需传入参数的地址即可,故使用(char *)pData将从*pData开始的存储区域强制转化为char型指针即可。
任务4中,传入的参数是结构体,另写博文浅析。
总之,以上所谓传递的四种参数类型,皆是在在传递地址,以准确映射所在地址的存储内容。
3 附录
(1)INT8U OSTaskCreateExt() 源代码
/*
*********************************************************************************************************
* CREATE A TASK (Extended Version)
*
* Description: This function is used to have uC/OS-II manage the execution of a task. Tasks can either
* be created prior to the start of multitasking or by a running task. A task cannot be
* created by an ISR. This function is similar to OSTaskCreate() except that it allows
* additional information about a task to be specified.
*
* Arguments : task is a pointer to the task's code
*
* pdata is a pointer to an optional data area which can be used to pass parameters to
* the task when the task first executes. Where the task is concerned it thinks
* it was invoked and passed the argument 'pdata' as follows:
*
* void Task (void *pdata)
* {
* for (;;) {
* Task code;
* }
* }
*
* ptos is a pointer to the task's top of stack. If the configuration constant
* OS_STK_GROWTH is set to 1, the stack is assumed to grow downward (i.e. from high
* memory to low memory). 'pstk' will thus point to the highest (valid) memory
* location of the stack. If OS_STK_GROWTH is set to 0, 'pstk' will point to the
* lowest memory location of the stack and the stack will grow with increasing
* memory locations. 'pstk' MUST point to a valid 'free' data item.
*
* prio is the task's priority. A unique priority MUST be assigned to each task and the
* lower the number, the higher the priority.
*
* id is the task's ID (0..65535)
*
* pbos is a pointer to the task's bottom of stack. If the configuration constant
* OS_STK_GROWTH is set to 1, the stack is assumed to grow downward (i.e. from high
* memory to low memory). 'pbos' will thus point to the LOWEST (valid) memory
* location of the stack. If OS_STK_GROWTH is set to 0, 'pbos' will point to the
* HIGHEST memory location of the stack and the stack will grow with increasing
* memory locations. 'pbos' MUST point to a valid 'free' data item.
*
* stk_size is the size of the stack in number of elements. If OS_STK is set to INT8U,
* 'stk_size' corresponds to the number of bytes available. If OS_STK is set to
* INT16U, 'stk_size' contains the number of 16-bit entries available. Finally, if
* OS_STK is set to INT32U, 'stk_size' contains the number of 32-bit entries
* available on the stack.
*
* pext is a pointer to a user supplied memory location which is used as a TCB extension.
* For example, this user memory can hold the contents of floating-point registers
* during a context switch, the time each task takes to execute, the number of times
* the task has been switched-in, etc.
*
* opt contains additional information (or options) about the behavior of the task. The
* LOWER 8-bits are reserved by uC/OS-II while the upper 8 bits can be application
* specific. See OS_TASK_OPT_??? in uCOS-II.H.
*
* Returns : OS_NO_ERR if the function was successful.
* OS_PRIO_EXIT if the task priority already exist
* (each task MUST have a unique priority).
* OS_PRIO_INVALID if the priority you specify is higher that the maximum allowed
* (i.e. > OS_LOWEST_PRIO)
*********************************************************************************************************
*/
INT8U OSTaskCreateExt (void (*task)(void *pd),
void *pdata,
OS_STK *ptos,
INT8U prio,
INT16U id,
OS_STK *pbos,
INT32U stk_size,
void *pext,
INT16U opt)
{
#if OS_CRITICAL_METHOD == 3 /* Allocate storage for CPU status register */
OS_CPU_SR cpu_sr;
#endif
OS_STK *psp;
INT8U err;
#if OS_ARG_CHK_EN > 0
if (prio > OS_LOWEST_PRIO) { /* Make sure priority is within allowable range */
return (OS_PRIO_INVALID);
}
#endif
OS_ENTER_CRITICAL();
if (OSTCBPrioTbl[prio] == (OS_TCB *)0) { /* Make sure task doesn't already exist at this priority */
OSTCBPrioTbl[prio] = (OS_TCB *)1; /* Reserve the priority to prevent others from doing ... */
/* ... the same thing until task is created. */
OS_EXIT_CRITICAL();
if (((opt & OS_TASK_OPT_STK_CHK) != 0x0000) || /* See if stack checking has been enabled */
((opt & OS_TASK_OPT_STK_CLR) != 0x0000)) { /* See if stack needs to be cleared */
#if OS_STK_GROWTH == 1
(void)memset(pbos, 0, stk_size * sizeof(OS_STK));
#else
(void)memset(ptos, 0, stk_size * sizeof(OS_STK));
#endif
}
psp = (OS_STK *)OSTaskStkInit(task, pdata, ptos, opt); /* Initialize the task's stack */
err = OS_TCBInit(prio, psp, pbos, id, stk_size, pext, opt);
if (err == OS_NO_ERR) {
OS_ENTER_CRITICAL();
OSTaskCtr++; /* Increment the #tasks counter */
OS_EXIT_CRITICAL();
if (OSRunning == TRUE) { /* Find HPT if multitasking has started */
OS_Sched();
}
} else {
OS_ENTER_CRITICAL();
OSTCBPrioTbl[prio] = (OS_TCB *)0; /* Make this priority avail. to others */
OS_EXIT_CRITICAL();
}
return (err);
}
OS_EXIT_CRITICAL();
return (OS_PRIO_EXIST);
}
4 参考
1. 真 OO無雙.(原創) 如何傳參數到每個task? (SOC) (Nios II) (μC/OS-II) (DE2-70)
2. Micrium.Micrium-uCOS-II-V286.ZIP\Micrium\SOFTWARE\uCOS-II\Source\os_task.c