这两天工作不忙,学习了下HashMap源码,记录下学习成果。
HashMap继承自AbstractMap<K,V>,且实现了MAP<K,V>接口,是非线程安全的。HashMap的底层存储结构是Entry<K,V>数组+链表的形式,其中链表是为了解决哈希碰撞而实现的,哈希碰撞,意为不相等的key,其hashCode()可能相同,这样找到HashMap中数组的索引位置相同,针对这些hash值相等的键值对就通过链表的方式存储,一个链表中的键值对,其hash值都是相等的,通过保存下一个节点,实现连接,新增的时候,都是从链表的头部插入的,即最先插入的节点在最下面,整体结构如下:(图片引用自https://home.cnblogs.com/u/chengxiao/)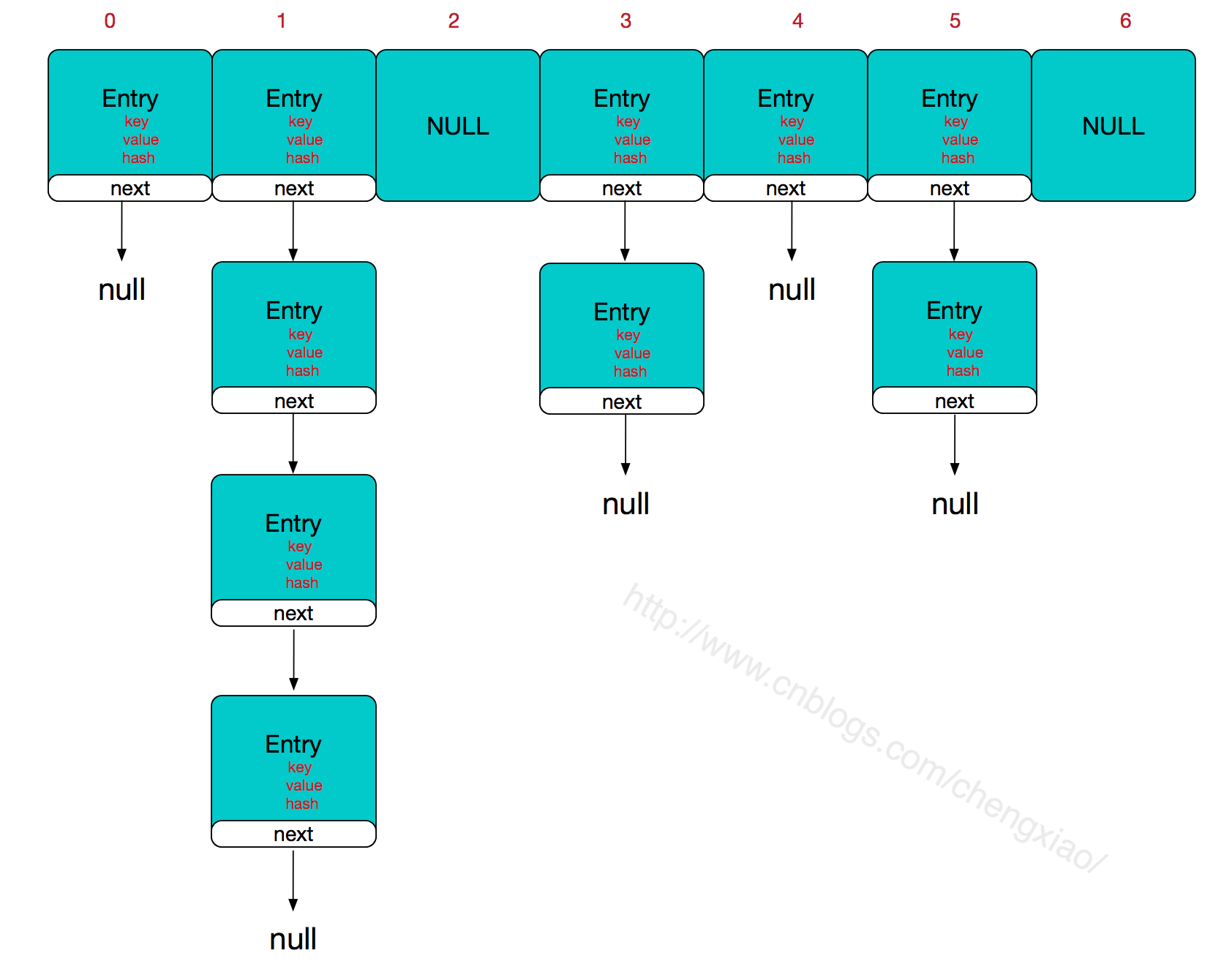
下面依据JDK1.7的源码作详细的介绍:
1、几个重要的类变量
//数组最初是空的
static final Entry<?,?>[] EMPTY_TABLE = {};
//HashMap本质就是在这个数组中存放键值对,最初该数组为空{}
transient Entry<K,V>[] table = (Entry<K,V>[]) EMPTY_TABLE;
//数组默认的最初的长度16,(<<的意思是将1向左移动4位,移动过的位置上以0填充-二进制)
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4;
//默认数组最大的长度2^30
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
//负载因子:HashMap中建立的这个数组并非全部装满的,而是有一定比例的,负载因子就代表了该数组中允许的存放量与数组长度的比值,默认是0.75f
final float loadFactor;
//数组中实际存放的键值对数量
transient int size;
//阈值:当前数组的长度*负载因子
int threshold;
//用于记录Hashmap被修改的次数
transient int modCount;
2、构造方法
第一种:参数为数组长度+负载因子
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)//如果传入的数组长度<0,则抛出异常
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)//如果传入的数组长度>默认最大长度,取默认最大长度
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))//如果负载因子<=0,则抛出异常
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
threshold = initialCapacity;//一开始的时候阈值==数组长度
init();//没有实现逻辑
}
第二种:参数为数组长度
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);//负载因子取默认值
}
第三种:无参
public HashMap() {//取默认的数组长度和负载因子
this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
第四种:入参为一个Map对象,较复杂,先不说
public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
this(Math.max((int) (m.size() / DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR) + 1,
DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY), DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);//创建一个新的Map
inflateTable(threshold);
putAllForCreate(m);
}
3、put()方法
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {//如果数组为空,则创建数组
inflateTable(threshold);
}
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key);//取key的hashCode
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);//根据key的hash值找到在数组中的索引
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {//找到的索引处可能存放的是一个链表,则遍历链表
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {//若链表中存在和key相等的键值对,则修改该key对应的value值为新传入的,返回老的value
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
//若当前数组中不存在和key相等的键值对,则往下走向数组中添加
modCount++;//增加修改次数
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {//若当前数组实际存放键值对个数>=阈值,则需要扩容数组
resize(2 * table.length);
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}
void resize(int newCapacity) {//扩容方法,传入的参数是当前数组长度*2
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {//如果当 前数组长度已经是最大长度,则修改阈值为最大
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];//创建一个新的数组,长度为之前的2倍
transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity));
table = newTable;
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
}
void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) {
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (Entry<K,V> e : table) {
while(null != e) {
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
if (rehash) {
e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key);
}
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);//取当前对象在新数组中的索引
e.next = newTable[i];//该方法是确保在遇到哈希碰撞的时候,将当前对象放在链表的头部
newTable[i] = e;
e = next;
}
}
}
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
}
//如果传入的key为null,则将该键值对保存在table[0]的位置
private V putForNullKey(V value) {
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(0, null, value, 0);
return null;
}
4、get()方法
public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
Entry<K,V> entry = getEntry(key);
return null == entry ? null : entry.getValue();
}
//若要取的key为null,从table[0]处取value
private V getForNullKey() {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null)
return e.value;
}
return null;
}
//key非null,则通过key.hashCode(),找到该key在数组中对应的索引,可能改索引下是一个链表,则遍历该链表,知道找到和key相等(equals())的键值对
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)];
e != null;
e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
}
return null;
}