Unit(单元)
/usr/lib/systemd/system 每个服务最主要的启动脚本设置,类似于之前的/etc/init.d目录
关键特性
1.基于socket的激活机制,socket和服务相分离
1.首先创建socket文件进行端口监听
2.当有用户访问的时候再由systemd启动相应进程
2.基于d-bus的激活机制
3.基于device的激活机制
4.基于path的激活机制 当特定目录中的文件发生变化的时候可以激活某个服务
5.自动解决启动服务的时候相互之间的依赖性(会把当前启动的服务所依赖的服务自动启动)
管理服务 service unit
注意:能兼容早期的服务脚本
命令:systemctl COMMAND name.service
启动:service name start ==> systemctl start name.service
停止:service name stop ==> systemctl stop name.service
重启:service name restart ==> systemctl restart name.service
状态:service name status ==> systemctl status name.service
chkconfig命令的对应关系:
设定某服务开机自启: chkconfig name on ==> systemctl enable name.service
设定某服务开机禁止启动: chkconfig name off ==> systemctl disable name.service
禁止自动和手动启动: systemctl mask name.service 取消禁止: systemctl unmask name.service
systemctl start service1 service2 可以一次性操作多个服务 centos6不行
服务Unit文件示例
vim /etc/systemd/system/bak.service
[Unit]
Description=backup /etc
Requires=atd.service
[Service]
Type=simple
ExecStart=/bin/bash -c "echo /testdir/bak.sh|at now"
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl start bak
centos7启动之grub2配置
centos6和cenots7的启动流程在到执行第一个进程/sbin/init(systemd)之前的步骤是一样的,后续的操作就会有比较大的差别.
grub2的主要配置文件 /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
修复配置文件 grub2-mkconfig > /boot/grub2/grub.cfg (不建议手写,内容太多) 或者 grub2-mkconfig -o grub.cfg
修复grub的方法
1. BIOS环境 grub2-install /dev/sda
2. UEFI环境 grub2-install
调整默认启动内核 vim /etc/default/grub GRUB_DEFAULT=0
centos7缺少grub.conf的手动解决
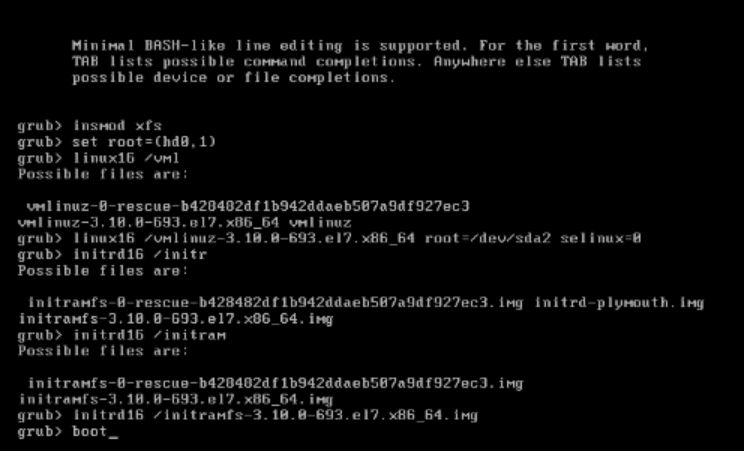
破解CentOS7的root口令
mount -o rw,remount /sysroot
按e键进入编辑模式
将光标移动linux16开始的行,改为rw init=/sysroot/bin/sh
按ctrl-x启动
chroot /sysroot
passwd root
touch /.autorelabel
exit
reboot