
简要介绍
玩过node的人应该都知道ejs,jade。 mustache和他们一样都是模板渲染引擎,我个人喜欢mustache,因为他非常简洁,代码量才600多行。
mustache既可以在前端使用,也可以在后端使用。对于文档里面有的内容,这里就不摘抄了,没什么意思,记录一下文档里面讲解不清楚的地方。
使用模板
mustache有一点不是太好,他的模板无法通过指定模板的位置来加载渲染,必须读取出模板内容之后才能进行渲染。这都无所谓的,如果在后端需要从文件读取模板的话,稍稍写一下
就可以了。下面给出测试代码。
- 主文件
//Created by yyrdl on 2015/10/2.
var Mustache=require("mustache");
var tool=require("./readFile");
var view={
names:[{
"name":'zj'
},{
"name":"yyrdl"
}]
};
var tems=["./templates/base.mustache","./templates/user.mustache"];
var tasks=tems.map(function(path){
return new Promise(function(resolve,reject){
tool.readFile(path,function(err,res){
if(err){
reject(err);
}else{
resolve(res);
}
});
})
});
Promise.all(tasks).then(function(results){
var out=Mustache.render(results[0],view,{
user:results[1]
});
console.log(out);
});
- base.mustache
<h2>Names</h2>
{{#names}}
{{> user}}
{{/names}}
- user.mustache
<strong>{{name}}</strong>
-
项目结构
-
输出结果
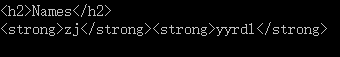
基本的mustache语法还请看mustache官网的介绍。在base.mustache里我们使用 {{>user}}引用了外部模板user,user的内容在
Mustache.render()的第三个参数里有指明.
条件编译
在ejs里可以使用if else 语句,不过是嵌在模板里,嵌多了就感觉乱糟糟的,在mustache里面不用!
{{#repos}}<b>{{name}}</b>{{/repos}}
{{^repos}}No repos :({{/repos}}
如果在传入的数据中repos字段存在,并且 !repos!==true 则上面的第一行将会被渲染,而第二行将被忽略;反之则结果想反。比如:
var template="{{#repos}}<b>{{name}}</b>{{/repos}}"+
"{{^repos}}No repos :({{/repos}}";
var data={
"repos":[{"name":"zj"}]
}
var out=Mustache.render(template,data);
// the result is: <b>zj</b>
将第一个例子中的base.mustache这样写
<h2>Names</h2>
{{#st}}
{{#names}}
{{> user}}
{{/names}}
{{/st}}
然后将主文件中的view改为:
var view={
show:false,
names:[{
"name":"zj"
},{
"name":"yyrdl"
}],
st:function(){
return this.show;
}
};
输出的结果为:
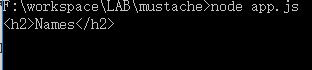
大概你已经看出,我们大可以只改变view中show的值来决定输出了,从这里可以看出mustache的灵活,也显出他的强大.
下面是将view.show=true的输出

---记录,分享