情况描述:当使用JOIN查询,如果SQL查询出来的记录不是按id列排序的,则生成的List结果会有问题
案例:
1) 数据库模型
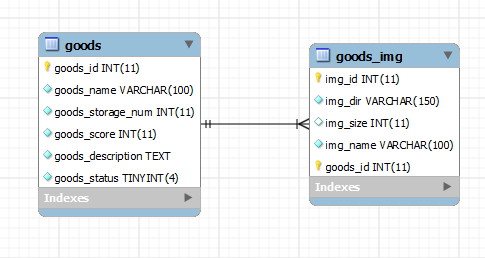
简而言之一个Goods包含多个Goods_Img
2) Java Bean
Goods.java
public class Goods { private Integer goodsId; private String goodsName; private Integer goodsStorageNum; private Integer goodsScore; private GoodsStatus goodsStatus; private String goodsDescription; private List<GoodsImg> goodsImgList; ... getter and setter ... }
GoodImg.java
public class GoodsImg { private Integer imgId; private Integer goodsId; private String imgDir; private Integer imgSize; private String imgName; ... getter and setter ... }
3) Mapper
<!-- Result Map --> <!-- goods resultmap --> <resultMap id="goodsResultMap" type="com.qunar.scoresystem.bean.Goods"> <id property="goodsId" column="goods_id" /> <result property="goodsName" column="goods_name" /> <result property="goodsStorageNum" column="goods_storage_num" /> <result property="goodsScore" column="goods_score" /> <result property="goodsDescription" column="goods_description" /> <result property="goodsStatus" column="goods_status" /> <collection property="goodsImgList" resultMap="goodsImgResult" /> </resultMap> <!-- goodsimage resultmap --> <resultMap id="goodsImgResult" type="com.qunar.scoresystem.bean.GoodsImg"> <id property="imgId" column="img_id" /> <result property="goodsId" column="goods_id" /> <result property="imgDir" column="img_dir" /> <result property="imgSize" column="img_size" /> <result property="imgName" column="img_name" /> </resultMap>
4) 执行的 SQL
select goods.goods_id as goods_id, goods.goods_name as goods_name, goods.goods_storage_num as goods_storage_num, goods.goods_score as goods_score, goods.goods_description as goods_description, goods.goods_status as goods_status , goods_img.img_name as img_name , goods_img.img_dir as img_dir , goods_img.img_size as img_size from goods join goods_img on goods.goods_id=goods_img.goods_id
5) 结果集
a. 当SQL查询的结果为

注意上图中的goods_id顺序为乱序
则MyBatis返回的List结果为
Goods{goodsId=1, goodsName='good1', goodsStorageNum=1, goodsScore=1, goodsStatus=[1 | 下架], goodsDescription='1', goodsImgList=[GoodsImg{imgId=null, goodsId=1, imgDir='d1', imgSize=1, imgName='img1'}, GoodsImg{imgId=null, goodsId=1, imgDir='d2', imgSize=2, imgName='img2'}, GoodsImg{imgId=null, goodsId=1, imgDir='d4', imgSize=4, imgName='img4'}, GoodsImg{imgId=null, goodsId=1, imgDir='d6', imgSize=6, imgName='img6'}]}
Goods{goodsId=1, goodsName='good1', goodsStorageNum=1, goodsScore=1, goodsStatus=[1 | 下架], goodsDescription='1', goodsImgList=[GoodsImg{imgId=null, goodsId=1, imgDir='d1', imgSize=1, imgName='img1'}, GoodsImg{imgId=null, goodsId=1, imgDir='d2', imgSize=2, imgName='img2'}, GoodsImg{imgId=null, goodsId=1, imgDir='d4', imgSize=4, imgName='img4'}, GoodsImg{imgId=null, goodsId=1, imgDir='d6', imgSize=6, imgName='img6'}]}
Goods{goodsId=1, goodsName='good1', goodsStorageNum=1, goodsScore=1, goodsStatus=[1 | 下架], goodsDescription='1', goodsImgList=[GoodsImg{imgId=null, goodsId=1, imgDir='d1', imgSize=1, imgName='img1'}, GoodsImg{imgId=null, goodsId=1, imgDir='d2', imgSize=2, imgName='img2'}, GoodsImg{imgId=null, goodsId=1, imgDir='d4', imgSize=4, imgName='img4'}, GoodsImg{imgId=null, goodsId=1, imgDir='d6', imgSize=6, imgName='img6'}]}
可见返回的结果中有 三个 一模一样的 Goods(id=1,且包含5个GoodsImg), 而我们期待的结果应该是 List{ Goods(id=1), Goods(id=2), Goods(id=3) }
b. 当使用的SQL查询结果如下

上面的查询结果为id有序结果,正则MyBatis返回的Java结果集为:
Goods{goodsId=1, goodsName='good1', goodsStorageNum=1, goodsScore=1, goodsStatus=[1 | 下架], goodsDescription='1', goodsImgList=[GoodsImg{imgId=null, goodsId=1, imgDir='d1', imgSize=1, imgName='img1'}, GoodsImg{imgId=null, goodsId=1, imgDir='d2', imgSize=2, imgName='img2'}, GoodsImg{imgId=null, goodsId=1, imgDir='d3', imgSize=3, imgName='img3'}, GoodsImg{imgId=null, goodsId=1, imgDir='d4', imgSize=4, imgName='img4'}]}
Goods{goodsId=2, goodsName='good2', goodsStorageNum=2, goodsScore=2, goodsStatus=[1 | 下架], goodsDescription='2', goodsImgList=[GoodsImg{imgId=null, goodsId=2, imgDir='d5', imgSize=5, imgName='img5'}]}
Goods{goodsId=3, goodsName='good3', goodsStorageNum=3, goodsScore=3, goodsStatus=[1 | 下架], goodsDescription='3', goodsImgList=[GoodsImg{imgId=null, goodsId=3, imgDir='d6', imgSize=6, imgName='img6'}]}
观察goodsId,我们取得了期待的结果
答案:
根据作者本人的解释, MyBatis为了降低内存开销,采用ResultHandler逐行读取的JDBC ResultSet结果集的,这就会造成MyBatis在结果行返回的时候无法判断以后的是否还会有这个id的行返回,所以它采用了一个方法来判断当前id的结果行是否已经读取完成,从而将其加入结果集List,这个方法是:
1. 读取当前行记录A,将A加入自定义Cache类,同时读取下一行记录B
2. 使用下一行记录B的id列和值为key(这个key由resultMap的<id>标签列定义)去Cache类里获取记录
3. 假如使用B的key不能够获取到记录,则说明B的id与A不同,那么A将被加入到List
4. 假如使用B的key可以获取到记录,说明A与B的id相同,则会将A与B合并(相当于将两个goodsImg合并到一个List中,而goods本身并不会增加)
5. 将B定为当前行,同时读取下一行C,重复1-5,直到没有下一行记录
6. 当没有下一行记录的时候,将最后一个合并的resultMap对应的java对象加入到List(最后一个被合并goodsImg的Goods)
所以
a. 当结果行是乱序的,例如BBAB这样的顺序,在记录行A遇到一个id不同的曾经出现过的记录行B时, A将不会被加入到List里(因为Cache里已经存在B的id为key的cahce了)
b. 当结果是顺序时,则结果集不会有任何问题,因为 记录行 A 不可能 遇到一个曾经出现过的 记录行B, 所以记录行A不会被忽略,每次遇到新行B时,都不可能使用B的key去Cache里取到值,所以A必然可以被加入到List
在MyBatis中,实现这个逻辑的代码如下
@Override protected void handleRowValues(ResultSet rs, ResultMap resultMap, ResultHandler resultHandler, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultColumnCache resultColumnCache) throws SQLException { final DefaultResultContext resultContext = new DefaultResultContext(); skipRows(rs, rowBounds); Object rowValue = null; while (shouldProcessMoreRows(rs, resultContext, rowBounds)) { final ResultMap discriminatedResultMap = resolveDiscriminatedResultMap(rs, resultMap, null); // 下一记录行的id构成的cache key final CacheKey rowKey = createRowKey(discriminatedResultMap, rs, null, resultColumnCache); Object partialObject = objectCache.get(rowKey); // 判断下一记录行是否被记录与cache中,如果不在cache中则将该记录行的对象插入List if (partialObject == null && rowValue != null) { // issue #542 delay calling ResultHandler until object if (mappedStatement.isResultOrdered()) objectCache.clear(); // issue #577 clear memory if ordered callResultHandler(resultHandler, resultContext, rowValue); } // 当前记录行的值 rowValue = getRowValue(rs, discriminatedResultMap, rowKey, rowKey, null, resultColumnCache, partialObject); } // 插入最后一记录行的对象到List if (rowValue != null) callResultHandler(resultHandler, resultContext, rowValue); }
举例:
以
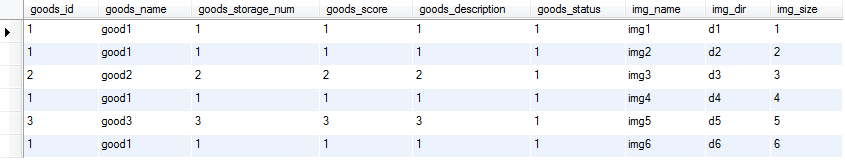
这个结果集为例,MyBatis会逐行读取记录行,我们将1~6行编号为A,B,C,D,E,F
1. 读取A行(id=1),将A行加入Cache,查看B行(id=1)的id,B行在Cache中已存在,不操作
2. 读取B行(id=1),查看C(id=2)行id,C行在Cache中不存在,将B行对应的Java对象插入List
3. 读取C(id=2)行,查看D(id=1)行ID,D行在Cache中已存在,不操作(此处漏掉一个id=2的Goods)
4. 读取D行(id=1),查看E行(id=3)ID,E行在Cache中不存在,将D行对应的java对象插入List(此处插入第一个重复的id=1的Goods)
5. 读取E行(id=3),查看F行(id=1)的ID,F行在Cache中已存在,不操作(此处漏掉一个id=3的Goods)
6. 读取F行(id=1),没有下一行,跳出循环,并插入最后一个Goods(此处插入第二个重复id=1的Goods)
所以,最后我们得到了3个一样的Goods,至于有序结果集,大家也可以按顺序去推一下,得到的结果集就是正确的
此外,源码中我们也可以看到作者原先给的注释: issue #542,讨论的就是这个问题,参见如下链接
https://github.com/mybatis/mybatis-3/pull/22
https://code.google.com/p/mybatis/issues/detail?id=542
所以,如果我们要用这种方式去查询一对多关系,恐怕只能手动排序好结果集才不会出错.
另外,我还发现一个有趣的现象,就是当MySQL在主表数据量<=3条时,Join的结果集是无序的,而当结果集的数据量>3条时,Join的结果集就变成有序了
a. 主表数据<=3条
主表:
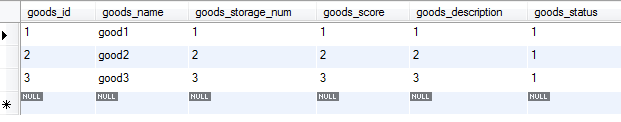
Join结果
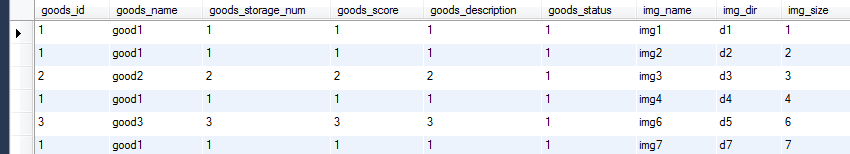
b. 主表数据>3行
主表
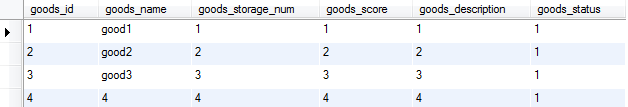
Join结果
