You are given a tree (an undirected connected acyclic graph) consisting of nn vertices and n−1n−1 edges. A number is written on each edge, each number is either 00 (let's call such edges 00-edges) or 11 (those are 11-edges).
Let's call an ordered pair of vertices (x,y)(x,y) (x≠yx≠y) valid if, while traversing the simple path from xx to yy, we never go through a 00-edge after going through a 11-edge. Your task is to calculate the number of valid pairs in the tree.
Input
The first line contains one integer nn (2≤n≤2000002≤n≤200000) — the number of vertices in the tree.
Then n−1n−1 lines follow, each denoting an edge of the tree. Each edge is represented by three integers xixi, yiyi and cici (1≤xi,yi≤n1≤xi,yi≤n, 0≤ci≤10≤ci≤1, xi≠yixi≠yi) — the vertices connected by this edge and the number written on it, respectively.
It is guaranteed that the given edges form a tree.
Output
Print one integer — the number of valid pairs of vertices.
题意:给定一颗树, 求满足任意两点间先0后1路径条数
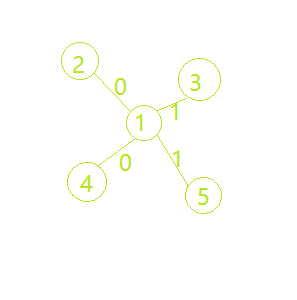
思路:如图所示
以1为当前节点
由树的性质则必有当前节点的1最大联通块为1路径条数 sa (3)
当前节点的0最大联通块为0路径条数 sb (3)
则有通过当前节点且符合题意的路径有 sa * sb - 1(减去当前节点自身的重复统计)
所以用并查集维护节点的最大联通块计算答案即可
代码:
/*
Zeolim - An AC a day keeps the bug away
*/
//#pragma GCC optimize(2)
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <cctype>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <set>
#include <sstream>
#include <map>
#include <ctime>
#include <vector>
#include <fstream>
#include <list>
#include <iomanip>
#include <numeric>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ld PI = acos(-1.0);
const ld E = exp(1.0);
const int MAXN = 1e6 + 10;
ll fa[MAXN], fb[MAXN], vla[MAXN], vlb[MAXN];
int findfa(int x)
{
return x == fa[x] ? x : fa[x] = findfa(fa[x]);
}
int findfb(int x)
{
return x == fb[x] ? x : fb[x] = findfb(fb[x]);
}
int main()
{
//ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
//cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
//freopen("D://test.in", "r", stdin);
//freopen("D://test.out", "w", stdout);
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i <= n; ++i)
{
fa[i] = fb[i] = i;
vla[i] = vlb[i] = (ll)1;
}
for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i)
{
int a, b, val;
cin >> a >> b >> val;
if(val == 1)
{
int p = findfa(a), q = findfa(b);
fa[p] = q;
vla[q] += vla[p];
}
else
{
int p = findfb(a), q = findfb(b);
fb[p] = q;
vlb[q] += vlb[p];
}
}
ll ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
{
int p = findfa(i), q = findfb(i);
ll tsum = vla[p] * vlb[q] - 1ll;
ans += (tsum);
}
cout << ans << '
';
return 0;
}